3a622f07636c922acc2b3859510223f9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Lecture #9. July 13, 2001 Cell signaling: Receptor tyrosine kinases NO and NYC. Chapter 15. Axiom #9: Multitasking is essential for success
Lecture #9. July 13, 2001 Cell signaling: Receptor tyrosine kinases NO and NYC. Chapter 15. Axiom #9: Multitasking is essential for success
 The importance of G-proteins The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1994 "for their discovery of G-proteins and the role of these proteins in signal transduction in cells" Alfred G. Gilman Martin Rodbell USA University of Texas, Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX, USA National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Research Triangle Park, NC, USA 1941 - 1925 - 1998
The importance of G-proteins The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1994 "for their discovery of G-proteins and the role of these proteins in signal transduction in cells" Alfred G. Gilman Martin Rodbell USA University of Texas, Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX, USA National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Research Triangle Park, NC, USA 1941 - 1925 - 1998
 The significance of “signal transduction in the nervous system" The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2000 "signal transduction in the nervous system" Arvid Carlsson Paul Greengard Eric R Kandel Sweden USA Göteborg University Göteborg, Sweden Rockefeller University New York, NY, USA Columbia University New York, NY, USA 1923 - 1925 - 1929 -
The significance of “signal transduction in the nervous system" The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2000 "signal transduction in the nervous system" Arvid Carlsson Paul Greengard Eric R Kandel Sweden USA Göteborg University Göteborg, Sweden Rockefeller University New York, NY, USA Columbia University New York, NY, USA 1923 - 1925 - 1929 -
 Peptide signaling The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1999 "for the discovery that proteins have intrinsic signals that govern their transport and localization in the cell" Günter Blobel USA Rockefeller University New York, NY, USA and National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Research Triangle Park, NC, USA 1936 -
Peptide signaling The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1999 "for the discovery that proteins have intrinsic signals that govern their transport and localization in the cell" Günter Blobel USA Rockefeller University New York, NY, USA and National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Research Triangle Park, NC, USA 1936 -
![How do cells regulate [Ca 2+]? Sequester in ER, bind to proteins! • Calmodulin How do cells regulate [Ca 2+]? Sequester in ER, bind to proteins! • Calmodulin](https://present5.com/presentation/3a622f07636c922acc2b3859510223f9/image-5.jpg) How do cells regulate [Ca 2+]? Sequester in ER, bind to proteins! • Calmodulin binds 4 Ca 2+ ions • In most cases, CM +Ca 2+ binds to an effector • Accordingly, CM –Ca 2+ dissociates from target • CM/kinase
How do cells regulate [Ca 2+]? Sequester in ER, bind to proteins! • Calmodulin binds 4 Ca 2+ ions • In most cases, CM +Ca 2+ binds to an effector • Accordingly, CM –Ca 2+ dissociates from target • CM/kinase
 Signaling by Tyrosine Kinases
Signaling by Tyrosine Kinases
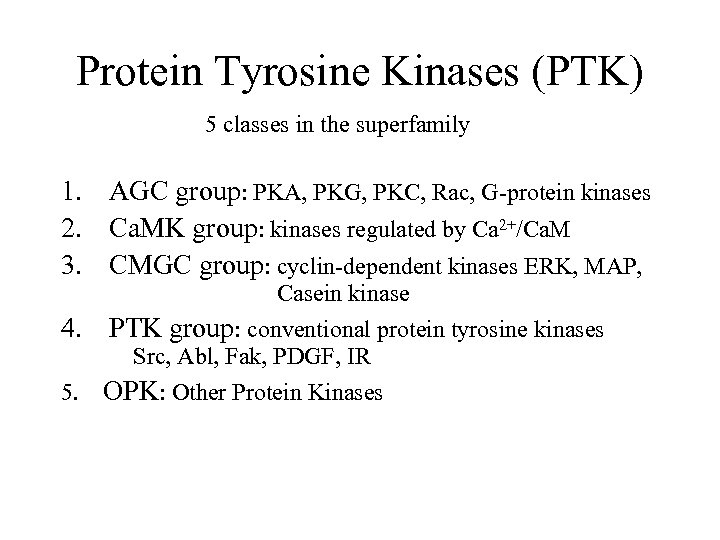 Protein Tyrosine Kinases (PTK) 5 classes in the superfamily 1. AGC group: PKA, PKG, PKC, Rac, G-protein kinases 2. Ca. MK group: kinases regulated by Ca 2+/Ca. M 3. CMGC group: cyclin-dependent kinases ERK, MAP, Casein kinase 4. PTK group: conventional protein tyrosine kinases Src, Abl, Fak, PDGF, IR 5. OPK: Other Protein Kinases
Protein Tyrosine Kinases (PTK) 5 classes in the superfamily 1. AGC group: PKA, PKG, PKC, Rac, G-protein kinases 2. Ca. MK group: kinases regulated by Ca 2+/Ca. M 3. CMGC group: cyclin-dependent kinases ERK, MAP, Casein kinase 4. PTK group: conventional protein tyrosine kinases Src, Abl, Fak, PDGF, IR 5. OPK: Other Protein Kinases
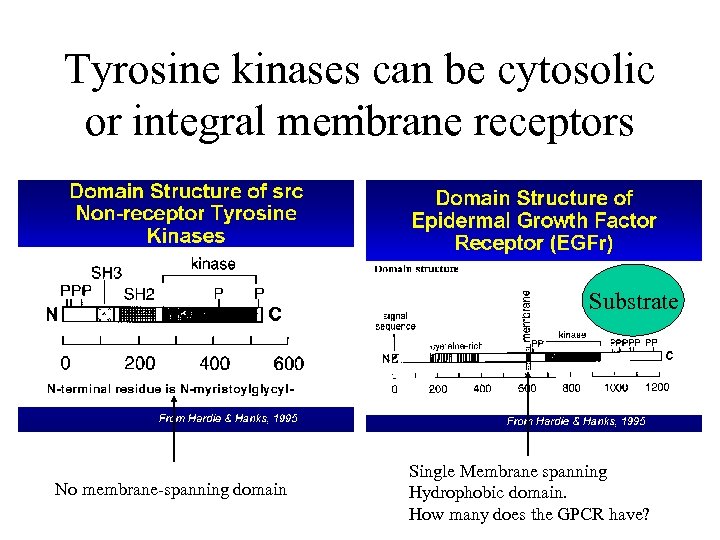 Tyrosine kinases can be cytosolic . or integral membrane receptors Substrate No membrane-spanning domain Single Membrane spanning Hydrophobic domain. How many does the GPCR have?
Tyrosine kinases can be cytosolic . or integral membrane receptors Substrate No membrane-spanning domain Single Membrane spanning Hydrophobic domain. How many does the GPCR have?
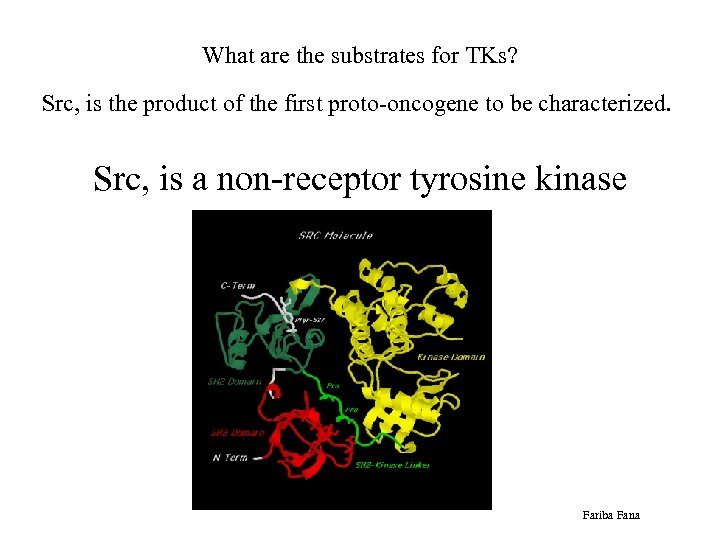 What are the substrates for TKs? Src, is the product of the first proto-oncogene to be characterized. Src, is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase Fariba Fana
What are the substrates for TKs? Src, is the product of the first proto-oncogene to be characterized. Src, is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase Fariba Fana
 Even though Src is a cytoplasmic Tyrosine Kinase, Src and other proteins that have Src-homology domains can bind to RTKs! Src homology domains: (SH)
Even though Src is a cytoplasmic Tyrosine Kinase, Src and other proteins that have Src-homology domains can bind to RTKs! Src homology domains: (SH)
 Other proteins have homologies to Src domains SH Src-homology regions • SH 1 domain: Catalytic domain of the protein: kinase activity • SH 2 and SH 3 domains: mediate protein-protein interactions in cellular signaling cascades: very common in proteins outside the Src family. • SH 2: binds peptides with consensus: (PTyr-Met/Val-X-Met) • SH 3: b-barrel. Interacts with proline-rich peptide targets • SH 4 domain: myristylation and membrane-localization signal
Other proteins have homologies to Src domains SH Src-homology regions • SH 1 domain: Catalytic domain of the protein: kinase activity • SH 2 and SH 3 domains: mediate protein-protein interactions in cellular signaling cascades: very common in proteins outside the Src family. • SH 2: binds peptides with consensus: (PTyr-Met/Val-X-Met) • SH 3: b-barrel. Interacts with proline-rich peptide targets • SH 4 domain: myristylation and membrane-localization signal
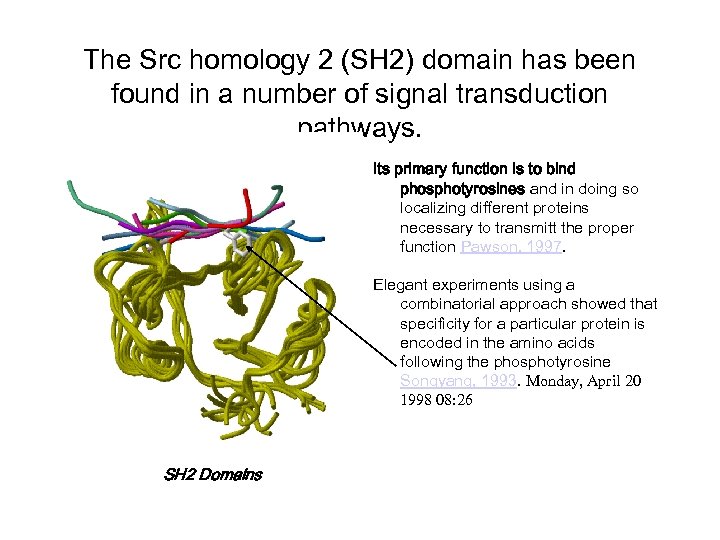 The Src homology 2 (SH 2) domain has been found in a number of signal transduction pathways. Its primary function is to bind phosphotyrosines and in doing so localizing different proteins necessary to transmitt the proper function Pawson, 1997. Elegant experiments using a combinatorial approach showed that specificity for a particular protein is encoded in the amino acids following the phosphotyrosine Songyang, 1993. Monday, April 20 1998 08: 26 SH 2 Domains
The Src homology 2 (SH 2) domain has been found in a number of signal transduction pathways. Its primary function is to bind phosphotyrosines and in doing so localizing different proteins necessary to transmitt the proper function Pawson, 1997. Elegant experiments using a combinatorial approach showed that specificity for a particular protein is encoded in the amino acids following the phosphotyrosine Songyang, 1993. Monday, April 20 1998 08: 26 SH 2 Domains
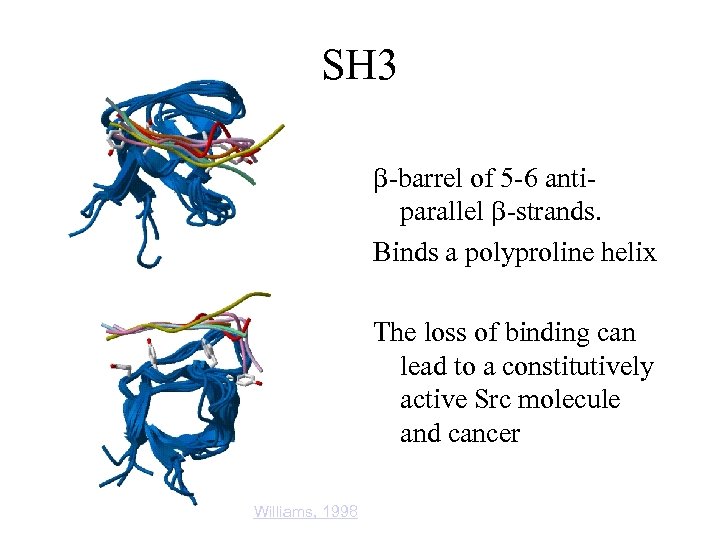 SH 3 b-barrel of 5 -6 antiparallel b-strands. Binds a polyproline helix The loss of binding can lead to a constitutively active Src molecule and cancer Williams, 1998
SH 3 b-barrel of 5 -6 antiparallel b-strands. Binds a polyproline helix The loss of binding can lead to a constitutively active Src molecule and cancer Williams, 1998
 Receptor tyrosine kinases All are single membrane-spanning proteins General Relevance • Tyrosine phosphorylation is frequently an EARLY event in signaling. • Amplification by downstream signaling elements greatly amplifies the effects of low levels of tyrosine phosphorylation that are most directly induced by extracellular triggers. Example: PLC and PI 3 K • Activation of multiple kinases (kinase cascades) including ser/thr as well as tyrosine kinases, is a frequent consequence of these early events. Example: MAP Kinase • There is often cross-talk between tyrosine kinase-induced pathways and other, e. g. G protein, signaling pathways.
Receptor tyrosine kinases All are single membrane-spanning proteins General Relevance • Tyrosine phosphorylation is frequently an EARLY event in signaling. • Amplification by downstream signaling elements greatly amplifies the effects of low levels of tyrosine phosphorylation that are most directly induced by extracellular triggers. Example: PLC and PI 3 K • Activation of multiple kinases (kinase cascades) including ser/thr as well as tyrosine kinases, is a frequent consequence of these early events. Example: MAP Kinase • There is often cross-talk between tyrosine kinase-induced pathways and other, e. g. G protein, signaling pathways.
 You know that I’m going to ask you why you should care about receptor tyrosine kinases! Activation of receptor tyrosine kinases ultimately leads to cell division or differentiation, for example, during embryonic development. Other functions • Growth control Are these processes important? What happens if a check point looses function? • Cell-cell recognition • Cell cycle control • Immune responses • Development • Differentiation
You know that I’m going to ask you why you should care about receptor tyrosine kinases! Activation of receptor tyrosine kinases ultimately leads to cell division or differentiation, for example, during embryonic development. Other functions • Growth control Are these processes important? What happens if a check point looses function? • Cell-cell recognition • Cell cycle control • Immune responses • Development • Differentiation
 Tyrosine Kinases and associated genes and proteins are implicated in developmental defects and cancer. • Excessive activation of receptor tyrosine kinases can lead to uncontrolled growth and malignant transformation. • Many defective or viral forms of tyrosine kinases and associated proteins are oncogenic: • v-src • abl • erb. B
Tyrosine Kinases and associated genes and proteins are implicated in developmental defects and cancer. • Excessive activation of receptor tyrosine kinases can lead to uncontrolled growth and malignant transformation. • Many defective or viral forms of tyrosine kinases and associated proteins are oncogenic: • v-src • abl • erb. B
 Classes of Receptor Tyrosine kinases 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. EGFreceptor, NEU/HER 2, HER 3 Insulin receptor PDGF FGF VEGF Eph
Classes of Receptor Tyrosine kinases 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. EGFreceptor, NEU/HER 2, HER 3 Insulin receptor PDGF FGF VEGF Eph
 What makes a RTK active? a) Conformational change: Insulin Receptor Kinase (IRK) Binds insulin Autophosphorylates Activates substrates including IRS-1 (insulin receptor substrate 1) by tyrosine phosphorylation b) Dimerization: 1. PDGF Receptor: Binds platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) Monomeric integral membrane protein Autophosphorylates Activates enzymes including PI 3 kinase, Phospholipase Cg and GAP (GTPase activating protein) by tyrosine phosphorylation 2. EGF Receptor 3. Eph Receptor family: Erythropoietin producing hepatocellular Monomeric integral membrane protein carcinoma cell line Binds to Ephrins (ligand) Role in neurogenesis (neuronal pathfinding)
What makes a RTK active? a) Conformational change: Insulin Receptor Kinase (IRK) Binds insulin Autophosphorylates Activates substrates including IRS-1 (insulin receptor substrate 1) by tyrosine phosphorylation b) Dimerization: 1. PDGF Receptor: Binds platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) Monomeric integral membrane protein Autophosphorylates Activates enzymes including PI 3 kinase, Phospholipase Cg and GAP (GTPase activating protein) by tyrosine phosphorylation 2. EGF Receptor 3. Eph Receptor family: Erythropoietin producing hepatocellular Monomeric integral membrane protein carcinoma cell line Binds to Ephrins (ligand) Role in neurogenesis (neuronal pathfinding)
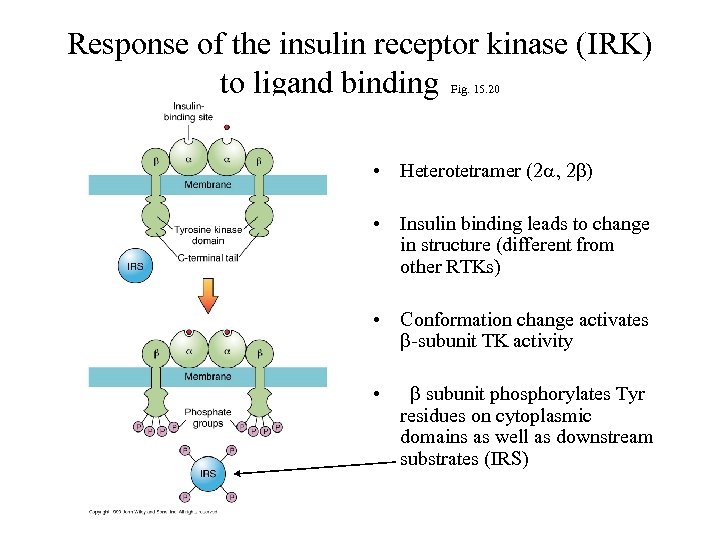 Response of the insulin receptor kinase (IRK) to ligand binding Fig. 15. 20 • Heterotetramer (2 a, 2 b) • Insulin binding leads to change in structure (different from other RTKs) • Conformation change activates b-subunit TK activity • b subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS)
Response of the insulin receptor kinase (IRK) to ligand binding Fig. 15. 20 • Heterotetramer (2 a, 2 b) • Insulin binding leads to change in structure (different from other RTKs) • Conformation change activates b-subunit TK activity • b subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS)
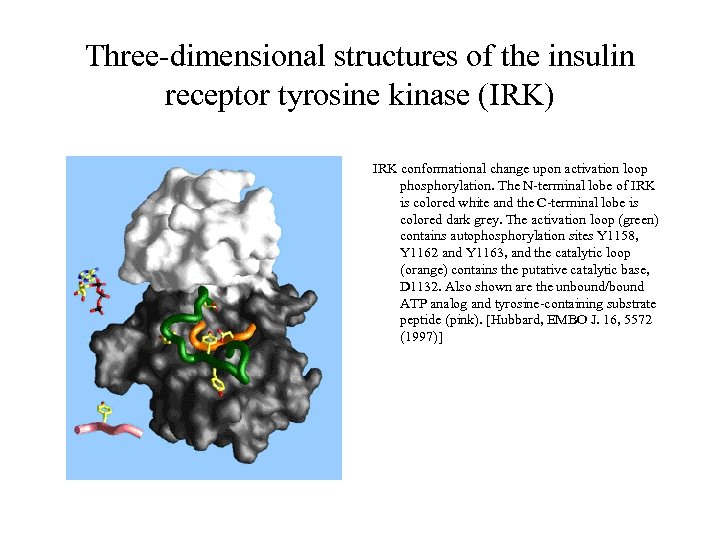 Three-dimensional structures of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase (IRK) IRK conformational change upon activation loop phosphorylation. The N-terminal lobe of IRK is colored white and the C-terminal lobe is colored dark grey. The activation loop (green) contains autophosphorylation sites Y 1158, Y 1162 and Y 1163, and the catalytic loop (orange) contains the putative catalytic base, D 1132. Also shown are the unbound/bound ATP analog and tyrosine-containing substrate peptide (pink). [Hubbard, EMBO J. 16, 5572 (1997)]
Three-dimensional structures of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase (IRK) IRK conformational change upon activation loop phosphorylation. The N-terminal lobe of IRK is colored white and the C-terminal lobe is colored dark grey. The activation loop (green) contains autophosphorylation sites Y 1158, Y 1162 and Y 1163, and the catalytic loop (orange) contains the putative catalytic base, D 1132. Also shown are the unbound/bound ATP analog and tyrosine-containing substrate peptide (pink). [Hubbard, EMBO J. 16, 5572 (1997)]
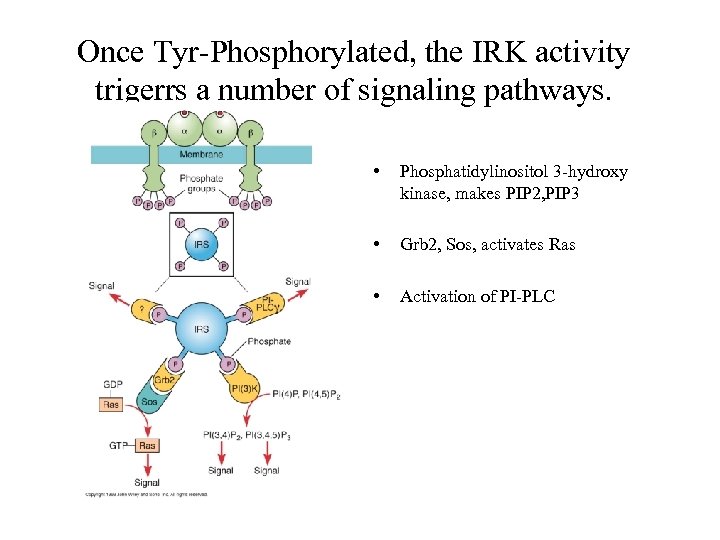 Once Tyr-Phosphorylated, the IRK activity trigerrs a number of signaling pathways. • Phosphatidylinositol 3 -hydroxy kinase, makes PIP 2, PIP 3 • Grb 2, Sos, activates Ras • Activation of PI-PLC
Once Tyr-Phosphorylated, the IRK activity trigerrs a number of signaling pathways. • Phosphatidylinositol 3 -hydroxy kinase, makes PIP 2, PIP 3 • Grb 2, Sos, activates Ras • Activation of PI-PLC
 Unlike IRK, most RTKs are present as a monomer in the resting cell membrane
Unlike IRK, most RTKs are present as a monomer in the resting cell membrane
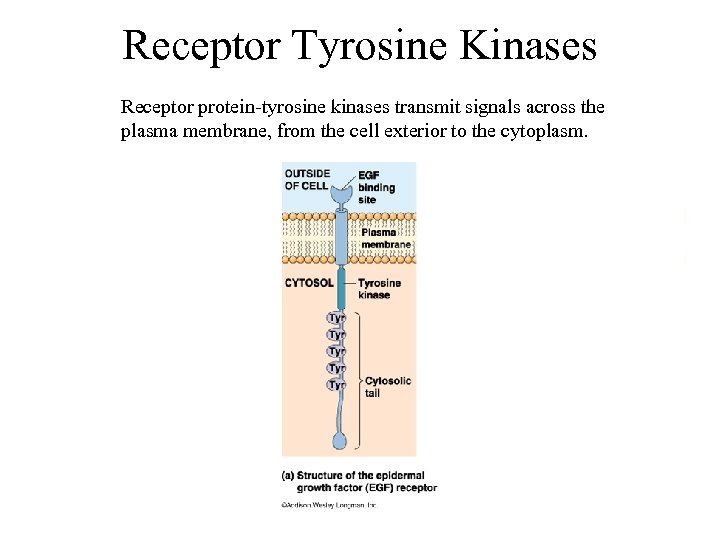 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Receptor protein-tyrosine kinases transmit signals across the plasma membrane, from the cell exterior to the cytoplasm.
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Receptor protein-tyrosine kinases transmit signals across the plasma membrane, from the cell exterior to the cytoplasm.
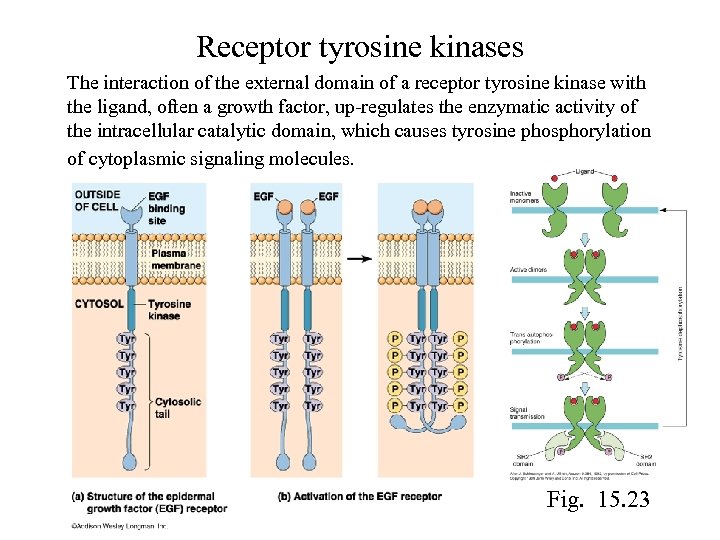 Receptor tyrosine kinases The interaction of the external domain of a receptor tyrosine kinase with the ligand, often a growth factor, up-regulates the enzymatic activity of the intracellular catalytic domain, which causes tyrosine phosphorylation of cytoplasmic signaling molecules. Fig. 15. 23
Receptor tyrosine kinases The interaction of the external domain of a receptor tyrosine kinase with the ligand, often a growth factor, up-regulates the enzymatic activity of the intracellular catalytic domain, which causes tyrosine phosphorylation of cytoplasmic signaling molecules. Fig. 15. 23
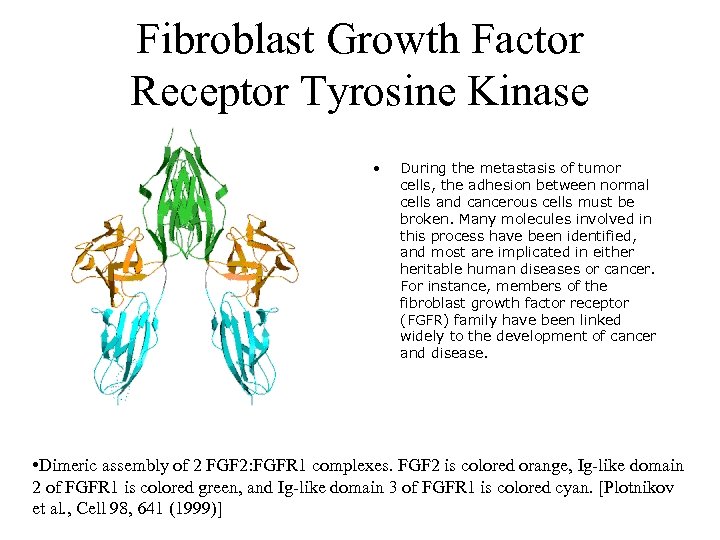 Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase • During the metastasis of tumor cells, the adhesion between normal cells and cancerous cells must be broken. Many molecules involved in this process have been identified, and most are implicated in either heritable human diseases or cancer. For instance, members of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family have been linked widely to the development of cancer and disease. • Dimeric assembly of 2 FGF 2: FGFR 1 complexes. FGF 2 is colored orange, Ig-like domain 2 of FGFR 1 is colored green, and Ig-like domain 3 of FGFR 1 is colored cyan. [Plotnikov et al. , Cell 98, 641 (1999)]
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase • During the metastasis of tumor cells, the adhesion between normal cells and cancerous cells must be broken. Many molecules involved in this process have been identified, and most are implicated in either heritable human diseases or cancer. For instance, members of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family have been linked widely to the development of cancer and disease. • Dimeric assembly of 2 FGF 2: FGFR 1 complexes. FGF 2 is colored orange, Ig-like domain 2 of FGFR 1 is colored green, and Ig-like domain 3 of FGFR 1 is colored cyan. [Plotnikov et al. , Cell 98, 641 (1999)]
 • N-CAM modulates tumor-cell adhesion to matrix by inducing FGF-receptor signaling UGO CAVALLARO, JOACHIM NIEDERMEYER, MARTIN FUXA, Nature Cell Biology 3, 650 -657 (July 2001)
• N-CAM modulates tumor-cell adhesion to matrix by inducing FGF-receptor signaling UGO CAVALLARO, JOACHIM NIEDERMEYER, MARTIN FUXA, Nature Cell Biology 3, 650 -657 (July 2001)
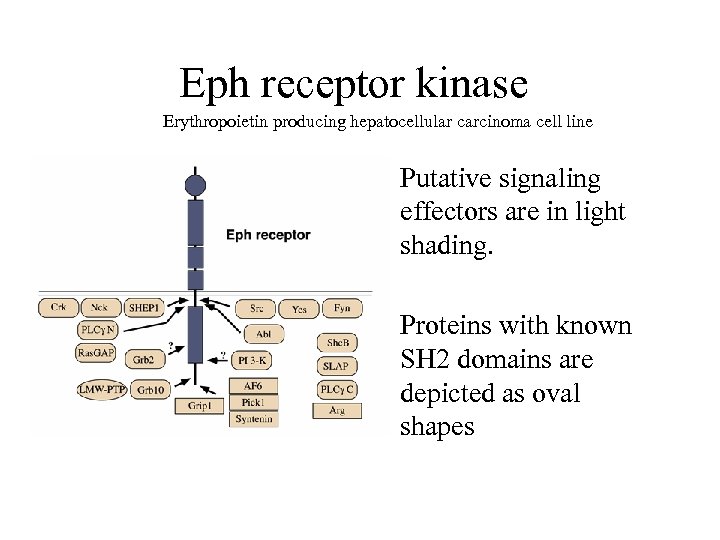 Eph receptor kinase Erythropoietin producing hepatocellular carcinoma cell line • Putative signaling effectors are in light shading. • Proteins with known SH 2 domains are depicted as oval shapes
Eph receptor kinase Erythropoietin producing hepatocellular carcinoma cell line • Putative signaling effectors are in light shading. • Proteins with known SH 2 domains are depicted as oval shapes
 RTKs can activate the Ras pathway of cellular signaling • Ras is a small G-protein (monomeric 21 -k. D) • Mutant Ras proteins are unable to dissociate GTP, so they are stuck in the ON or proliferative state: ras (gene) mutations found in 30% of human cancers. • Do you think mutations in Ras-GAPs can lead to disease? Oui!
RTKs can activate the Ras pathway of cellular signaling • Ras is a small G-protein (monomeric 21 -k. D) • Mutant Ras proteins are unable to dissociate GTP, so they are stuck in the ON or proliferative state: ras (gene) mutations found in 30% of human cancers. • Do you think mutations in Ras-GAPs can lead to disease? Oui!
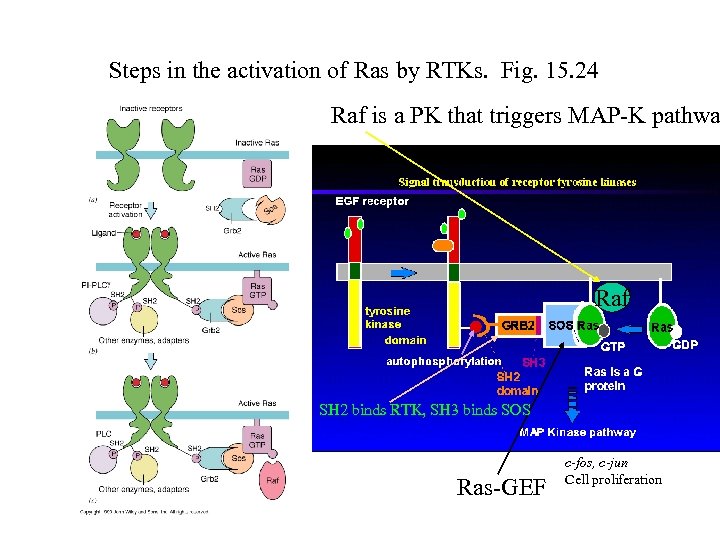 Steps in the activation of Ras by RTKs. Fig. 15. 24 Raf is a PK that triggers MAP-K pathwa Raf SH 2 binds RTK, SH 3 binds SOS Ras-GEF c-fos, c-jun Cell proliferation
Steps in the activation of Ras by RTKs. Fig. 15. 24 Raf is a PK that triggers MAP-K pathwa Raf SH 2 binds RTK, SH 3 binds SOS Ras-GEF c-fos, c-jun Cell proliferation
 NO signaling The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1998 "for their discoveries concerning nitric oxide as a signalling molecule in the cardiovascular system" Robert F. Furchgott Louis J. Ignarro Ferid Murad USA SUNY Health Science Center Brooklyn, NY, USA UCLA School of Medicine Los Angeles, CA, USA University of Texas, Health Science Center Dallas, TX, USA 1916 - 1941 - 1936 -
NO signaling The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1998 "for their discoveries concerning nitric oxide as a signalling molecule in the cardiovascular system" Robert F. Furchgott Louis J. Ignarro Ferid Murad USA SUNY Health Science Center Brooklyn, NY, USA UCLA School of Medicine Los Angeles, CA, USA University of Texas, Health Science Center Dallas, TX, USA 1916 - 1941 - 1936 -
 Nitric oxide is a free radical • It contains an unpaired electron • . N=O • Role in macrophage killing of pathogens • NO also acts as a second messenger that causes relaxation of smooth muscle
Nitric oxide is a free radical • It contains an unpaired electron • . N=O • Role in macrophage killing of pathogens • NO also acts as a second messenger that causes relaxation of smooth muscle
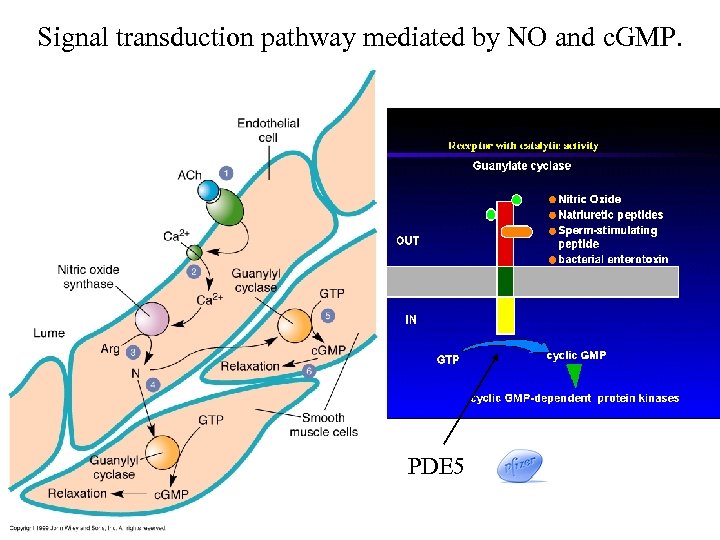 Signal transduction pathway mediated by NO and c. GMP. PDE 5 136252
Signal transduction pathway mediated by NO and c. GMP. PDE 5 136252
 Nitric oxide (NO) is a small membranepermeating free radical. It is synthesized as needed, since it cannot be stored in vesicles. Consequently, regulation of its synthesis is crucial. Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) converts arginine to NO and citrulline • NOS is activated by Ca 2+/calmodulin • NOS is inactivated by phosphorylation • NOS is located only in neurons in CNS (2% of all cells)
Nitric oxide (NO) is a small membranepermeating free radical. It is synthesized as needed, since it cannot be stored in vesicles. Consequently, regulation of its synthesis is crucial. Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) converts arginine to NO and citrulline • NOS is activated by Ca 2+/calmodulin • NOS is inactivated by phosphorylation • NOS is located only in neurons in CNS (2% of all cells)
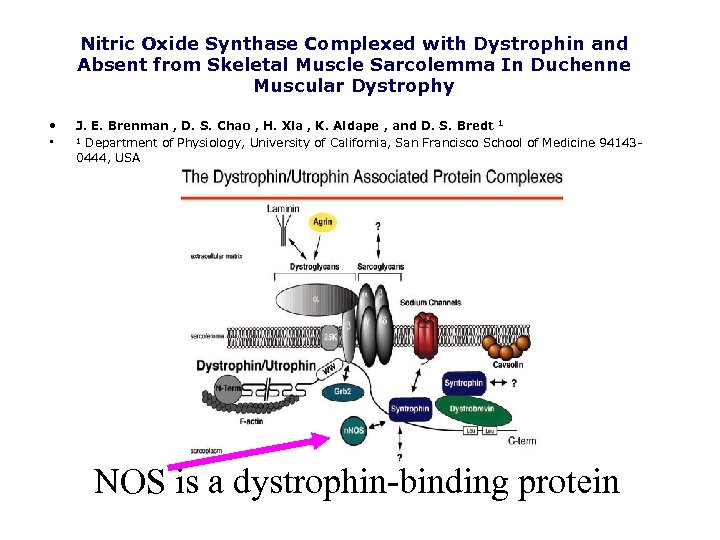 Nitric Oxide Synthase Complexed with Dystrophin and Absent from Skeletal Muscle Sarcolemma In Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy • • J. E. Brenman , D. S. Chao , H. Xia , K. Aldape , and D. S. Bredt 1 1 Department of Physiology, University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine 941430444, USA NOS is a dystrophin-binding protein
Nitric Oxide Synthase Complexed with Dystrophin and Absent from Skeletal Muscle Sarcolemma In Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy • • J. E. Brenman , D. S. Chao , H. Xia , K. Aldape , and D. S. Bredt 1 1 Department of Physiology, University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine 941430444, USA NOS is a dystrophin-binding protein
 Pfizer web site • VIAGRA enables many men with erectile dysfunction to respond to sexual stimulation. When a man is sexually excited, VIAGRA helps the penis fill with enough blood to cause an erection. After sex is over, the erection goes away.
Pfizer web site • VIAGRA enables many men with erectile dysfunction to respond to sexual stimulation. When a man is sexually excited, VIAGRA helps the penis fill with enough blood to cause an erection. After sex is over, the erection goes away.
 How does Viagra work? • Enlivens the male “wunder horn” with fresh sound? • Sildenafil inhibits PDE 5 (phosphodiesterase 5) • c. GMP build up in the cell • Enhances the effects of NO • Not for patients using nitrates (nitroglycerine)
How does Viagra work? • Enlivens the male “wunder horn” with fresh sound? • Sildenafil inhibits PDE 5 (phosphodiesterase 5) • c. GMP build up in the cell • Enhances the effects of NO • Not for patients using nitrates (nitroglycerine)
 Summary Be able to outline pathways for: • GPCR (Fig. 15. 13) • IRK activation and downstream effectors • RTK and activation of Ras • Compare and contrast activation events mediated by Ca 2+, c. AMP and NO.
Summary Be able to outline pathways for: • GPCR (Fig. 15. 13) • IRK activation and downstream effectors • RTK and activation of Ras • Compare and contrast activation events mediated by Ca 2+, c. AMP and NO.
 Finito • For Monday • Read Chapter 16, the Biology of Cancer
Finito • For Monday • Read Chapter 16, the Biology of Cancer


