Lecture #8 [Cyphering].pptx
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Lecture 8 ciphering
Lecture 8 ciphering
 Caesar ciphering is changing letter in text to letter that is in distance of n letters in alphabetical orders E. g. if n is 3 hello - plain text khoor - ciphered text
Caesar ciphering is changing letter in text to letter that is in distance of n letters in alphabetical orders E. g. if n is 3 hello - plain text khoor - ciphered text
 Secret key (symmetric) algorithm ● Traditional -- encrypt and decrypt with a single key which is kept secret ● aka "symmetric" encryption, since the key is used both for encryption and decryption ● Two results one obvious, one subtle: ● Provides: secrecy attacker intercepts the ciphertext, but cannot recover the plaintext from it ● Provides: authenticity attacker cannot "spoof" data, sent to be decrypted. If the ciphertext decrypts cleanly, it must have come from a party with the secret key ● Problem: key distribution. How do you get a copy of the key safely to the recipient?
Secret key (symmetric) algorithm ● Traditional -- encrypt and decrypt with a single key which is kept secret ● aka "symmetric" encryption, since the key is used both for encryption and decryption ● Two results one obvious, one subtle: ● Provides: secrecy attacker intercepts the ciphertext, but cannot recover the plaintext from it ● Provides: authenticity attacker cannot "spoof" data, sent to be decrypted. If the ciphertext decrypts cleanly, it must have come from a party with the secret key ● Problem: key distribution. How do you get a copy of the key safely to the recipient?
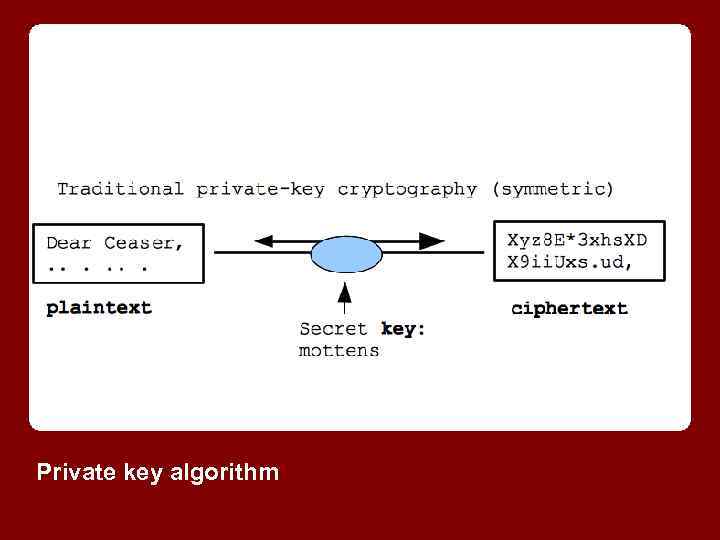 Private key algorithm
Private key algorithm
 Secret-key algorithms Caesar ciphering is an example of substitution secret-key algorithms. Where secret-key is number of shifting In a transposition cipher, the units of the plaintext are rearranged in a different and usually quite complex order, but the units themselves are left unchanged.
Secret-key algorithms Caesar ciphering is an example of substitution secret-key algorithms. Where secret-key is number of shifting In a transposition cipher, the units of the plaintext are rearranged in a different and usually quite complex order, but the units themselves are left unchanged.
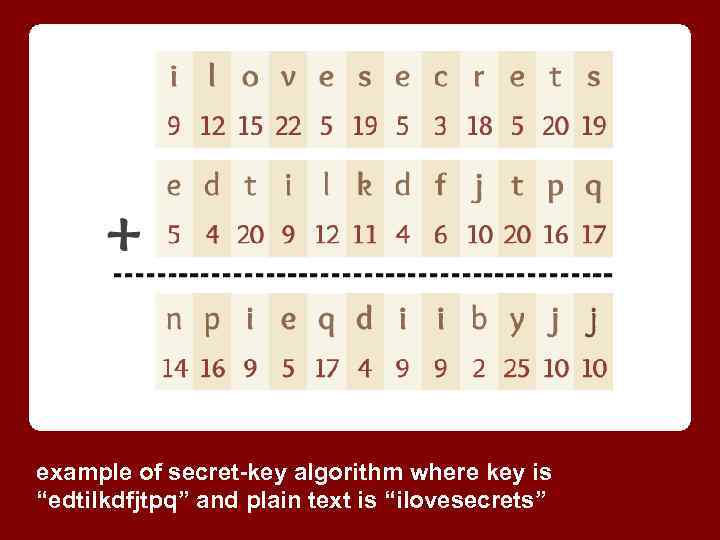 example of secret-key algorithm where key is “edtilkdfjtpq” and plain text is “ilovesecrets”
example of secret-key algorithm where key is “edtilkdfjtpq” and plain text is “ilovesecrets”
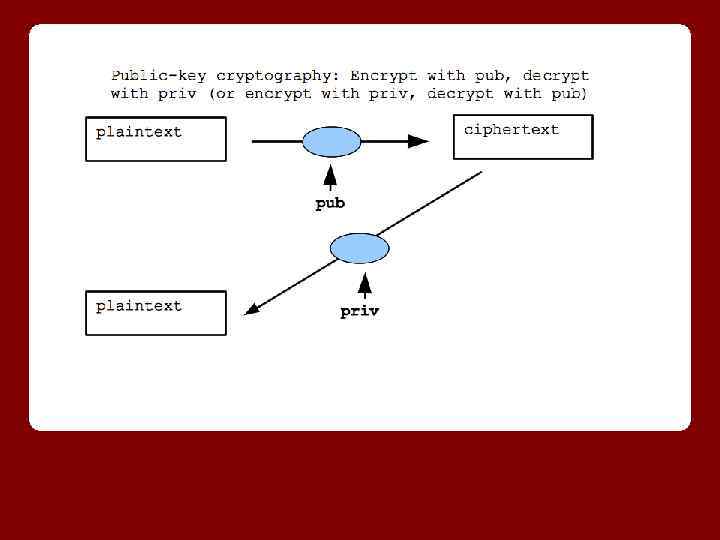
 Public-key cryptography ● Instead of a simple key, the key is created with two parts: public and private ● Your computer can just make up a pub/priv key pair out of thin air based on random numbers Key features: o The pub/priv keys work as encryption opposites of each other: encrypt with pub, decrypt with priv, Or encrypt with priv and decrypt with pub. o If someone knows pub, they cannot easily compute priv from it. This is an impressive feature, given how closely pub/priv must be related to work as opposites.
Public-key cryptography ● Instead of a simple key, the key is created with two parts: public and private ● Your computer can just make up a pub/priv key pair out of thin air based on random numbers Key features: o The pub/priv keys work as encryption opposites of each other: encrypt with pub, decrypt with priv, Or encrypt with priv and decrypt with pub. o If someone knows pub, they cannot easily compute priv from it. This is an impressive feature, given how closely pub/priv must be related to work as opposites.
 Public key application 1. Suppose www. example. com wants to accept packets from anyone, but so they are secret from eavesdropping 2. example. com makes up a pub/priv pair 3. example. com publishes the pub part of the pair so everyone can see and downlaod it. Priv is kept inside example. com. 4. This is a typical structure -- the pub key is published in what is called a "certificate", and priv is kept secret. 5. Someone who wants to send a packet to example. com first encrypts it with pub 6. At www. example. com the encrypted packet is decrypted with priv 7. Provides: no key exchange problem! 8. Does not provide authenticity. Anybody can compose an encrypted packet, but only www. example. com can decrypt them (asymmetric)
Public key application 1. Suppose www. example. com wants to accept packets from anyone, but so they are secret from eavesdropping 2. example. com makes up a pub/priv pair 3. example. com publishes the pub part of the pair so everyone can see and downlaod it. Priv is kept inside example. com. 4. This is a typical structure -- the pub key is published in what is called a "certificate", and priv is kept secret. 5. Someone who wants to send a packet to example. com first encrypts it with pub 6. At www. example. com the encrypted packet is decrypted with priv 7. Provides: no key exchange problem! 8. Does not provide authenticity. Anybody can compose an encrypted packet, but only www. example. com can decrypt them (asymmetric)
 Public key algorithm: signature ● How do you write something online and prove it's from you? ● These are called "digital signatures" ● Suppose you have a document you want to sign ● Generate a pub/priv key pair, publish the pub part publicly, declaring that it goes with, say, your email addr (this is essentially what a "certificate" is) ● Encrypt the document with your priv key, attach the encrypted form to the end of the document ● Provides: anyone with the doc can do the decryption with your pub key, see that the result matches. ● They conclude: only the holder of the priv key could have made this ● Provides: an attacker cannot forge the sig (they do not have the priv key. Indeed, the priv key never needs to leave your machine)
Public key algorithm: signature ● How do you write something online and prove it's from you? ● These are called "digital signatures" ● Suppose you have a document you want to sign ● Generate a pub/priv key pair, publish the pub part publicly, declaring that it goes with, say, your email addr (this is essentially what a "certificate" is) ● Encrypt the document with your priv key, attach the encrypted form to the end of the document ● Provides: anyone with the doc can do the decryption with your pub key, see that the result matches. ● They conclude: only the holder of the priv key could have made this ● Provides: an attacker cannot forge the sig (they do not have the priv key. Indeed, the priv key never needs to leave your machine)
 If you are interested in public-key algorithms (do not need for quiz) RSA was the first public-key encryption system that worked in the real world. Invented more than 30 years ago, it coincided with the introduction of the more powerful computers that were needed to run the big numbers. RSA is still the most popular public-key encryption system in the world. The basic premise of RSA is that factoring large numbers is difficult. Let’s choose two prime numbers: 61 and 53. I’m using the numbers from Wikipedia’s article on “RSA” in case you want more details. Multiply these two numbers and you get 3233: 61 × 53 = 3233 The security of RSA comes from the difficulty of getting back to 61 and 53 if you only know 3233. There’s no good way to get the factors of 3233 (i. e. the numbers that multiply to make the result) without just looking for all of them. To think of this another way, the weight of our backpack is 3233 kilos, and inside are 61 weights weighing 53 kilos each. If you make the resulting number large enough, then finding the numbers that produced it would be very difficult.
If you are interested in public-key algorithms (do not need for quiz) RSA was the first public-key encryption system that worked in the real world. Invented more than 30 years ago, it coincided with the introduction of the more powerful computers that were needed to run the big numbers. RSA is still the most popular public-key encryption system in the world. The basic premise of RSA is that factoring large numbers is difficult. Let’s choose two prime numbers: 61 and 53. I’m using the numbers from Wikipedia’s article on “RSA” in case you want more details. Multiply these two numbers and you get 3233: 61 × 53 = 3233 The security of RSA comes from the difficulty of getting back to 61 and 53 if you only know 3233. There’s no good way to get the factors of 3233 (i. e. the numbers that multiply to make the result) without just looking for all of them. To think of this another way, the weight of our backpack is 3233 kilos, and inside are 61 weights weighing 53 kilos each. If you make the resulting number large enough, then finding the numbers that produced it would be very difficult.
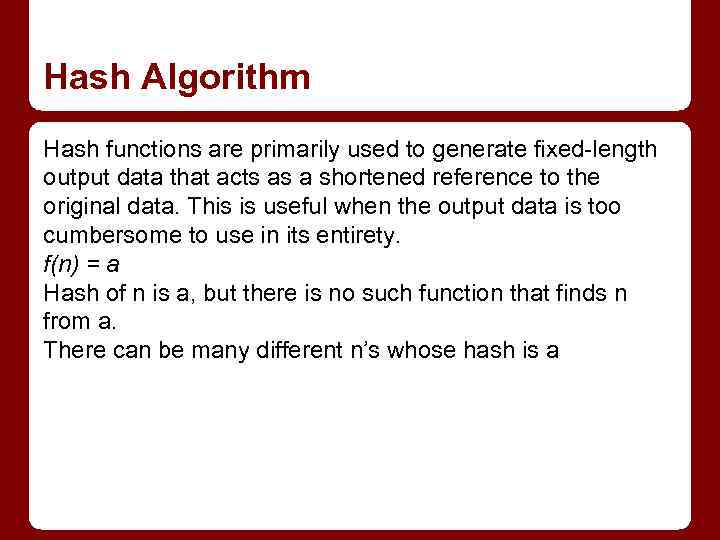 Hash Algorithm Hash functions are primarily used to generate fixed-length output data that acts as a shortened reference to the original data. This is useful when the output data is too cumbersome to use in its entirety. f(n) = a Hash of n is a, but there is no such function that finds n from a. There can be many different n’s whose hash is a
Hash Algorithm Hash functions are primarily used to generate fixed-length output data that acts as a shortened reference to the original data. This is useful when the output data is too cumbersome to use in its entirety. f(n) = a Hash of n is a, but there is no such function that finds n from a. There can be many different n’s whose hash is a
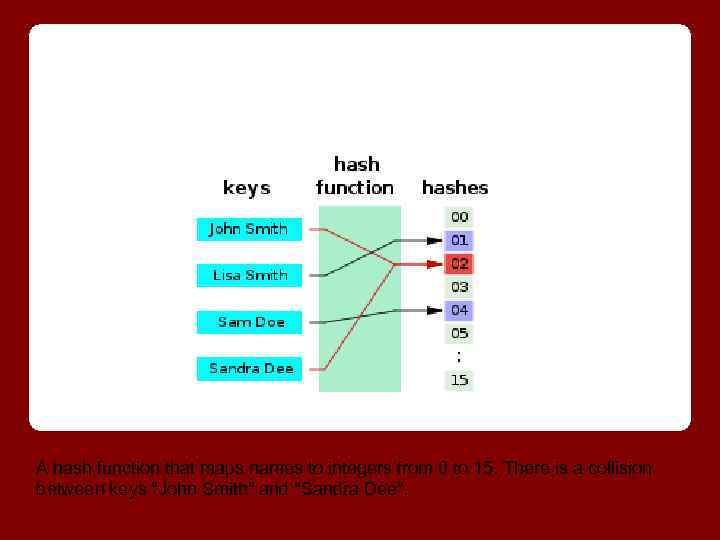 A hash function that maps names to integers from 0 to 15. There is a collision between keys "John Smith" and "Sandra Dee".
A hash function that maps names to integers from 0 to 15. There is a collision between keys "John Smith" and "Sandra Dee".
 Hash Algorithm where to use? For data that have many rows, to find needed row by comparing hash In database when storing password, store hash of password, not itself In torrents compare hash of received file and hash given on site, to verify that file was received correctly
Hash Algorithm where to use? For data that have many rows, to find needed row by comparing hash In database when storing password, store hash of password, not itself In torrents compare hash of received file and hash given on site, to verify that file was received correctly
 Brute-force attack Checks for all possible variants of key. If we have password that has maximum length of 4 lowercase letters, how many variants will we have to look? 26*26*26*26 = 456976
Brute-force attack Checks for all possible variants of key. If we have password that has maximum length of 4 lowercase letters, how many variants will we have to look? 26*26*26*26 = 456976
 how many combinations?
how many combinations?
 Dictionary attack ● Try to log in again and again ● Works if the password is common, e. g. "password" "password 123" ● Also known as "dictionary attack", try all the words in a dictionary ● This fails mostly, but success here and there with an account with a poor password is good enough for the bad guys ● Therefore: avoid having an obvious or commonly used password o a word in a dictionary o a pun that someone else might also use
Dictionary attack ● Try to log in again and again ● Works if the password is common, e. g. "password" "password 123" ● Also known as "dictionary attack", try all the words in a dictionary ● This fails mostly, but success here and there with an account with a poor password is good enough for the bad guys ● Therefore: avoid having an obvious or commonly used password o a word in a dictionary o a pun that someone else might also use
 Bad passwords ● ● ● Do not need to be super elaborate (some sites go crazy with this) List of common passwords - do not use these! -Common passwordspassword 1 1234567890 abc 123 computer tigger 1234 qwerty You must avoid a password that thousands of others out there have also chosen -- these will certainly be used by dictionary attacks The attack proceeds from outside the target site, just guessing 1 password per second all the time
Bad passwords ● ● ● Do not need to be super elaborate (some sites go crazy with this) List of common passwords - do not use these! -Common passwordspassword 1 1234567890 abc 123 computer tigger 1234 qwerty You must avoid a password that thousands of others out there have also chosen -- these will certainly be used by dictionary attacks The attack proceeds from outside the target site, just guessing 1 password per second all the time
 Good passwords ● ● ● What I do for secure passwords, e. g a bank site or email Note that email is your most important, since it is used for password resets Start with a word, add misspelling, then add some random letters Could add some digits and/or punctuation and maybe some upper case letters Say I start with the word "mittens" mottens, erx -- fine Mottens, 9 erx -- better Moten. X, 97 erx -- probably more complex than necessary Important that the "erx" is truly nonsense, not like "xyz" that someone else on earth might tend to pick. Other problem: what if the site itself is compromised, so the bad-guy possibly gets your password that way? Therefore, do not re-use your passwords across important sites like banks. Consider writing down important passwords on a slip of paper at home. Otherwise it's hard to keep it all straight in your head.
Good passwords ● ● ● What I do for secure passwords, e. g a bank site or email Note that email is your most important, since it is used for password resets Start with a word, add misspelling, then add some random letters Could add some digits and/or punctuation and maybe some upper case letters Say I start with the word "mittens" mottens, erx -- fine Mottens, 9 erx -- better Moten. X, 97 erx -- probably more complex than necessary Important that the "erx" is truly nonsense, not like "xyz" that someone else on earth might tend to pick. Other problem: what if the site itself is compromised, so the bad-guy possibly gets your password that way? Therefore, do not re-use your passwords across important sites like banks. Consider writing down important passwords on a slip of paper at home. Otherwise it's hard to keep it all straight in your head.


