 Lecture 7 America - the superpower Lecture plan 1. Cold War 2. American Political System
Lecture 7 America - the superpower Lecture plan 1. Cold War 2. American Political System
 1. Cold War America had the world's biggest air force and navy, it was the only nation armed with atomic bombs. After the US came the Soviet Union. In 1946 Britain's wartime leader, Winston Churchill, spoke of an "Iron Curtain" across Europe, separating these communist-ruled nations of the east from the countries of the west. Stalin feared that the US might drop atomic bombs on his country at any moment. The new President, Truman, suspected that Stalin's actions in Eastern Europe were the first steps in a plan to convert the world to communism.
1. Cold War America had the world's biggest air force and navy, it was the only nation armed with atomic bombs. After the US came the Soviet Union. In 1946 Britain's wartime leader, Winston Churchill, spoke of an "Iron Curtain" across Europe, separating these communist-ruled nations of the east from the countries of the west. Stalin feared that the US might drop atomic bombs on his country at any moment. The new President, Truman, suspected that Stalin's actions in Eastern Europe were the first steps in a plan to convert the world to communism.
 Truman decided to use American power and money to "contain" Soviet influence - that is, to stop it from spreading. In November 1952, American scientists tested a new weapon - they had exploded the first hydrogen, or H-bomb. In August 1963, the US and the Soviet Union signed a treaty agreeing to stop testing new nuclear weapons in the atmosphere or under water. Both the Soviet Union and the United States had continued to develop new and more deadly nuclear missiles. Attempts were made to slow down this arms race.
Truman decided to use American power and money to "contain" Soviet influence - that is, to stop it from spreading. In November 1952, American scientists tested a new weapon - they had exploded the first hydrogen, or H-bomb. In August 1963, the US and the Soviet Union signed a treaty agreeing to stop testing new nuclear weapons in the atmosphere or under water. Both the Soviet Union and the United States had continued to develop new and more deadly nuclear missiles. Attempts were made to slow down this arms race.
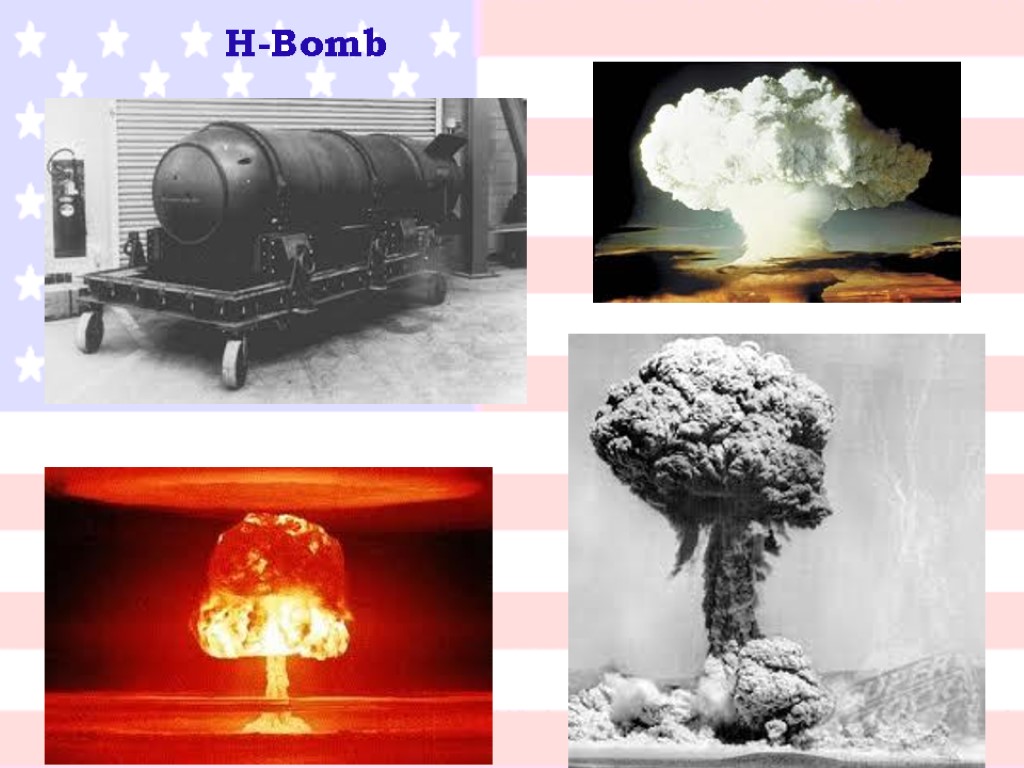 H-Bomb
H-Bomb
 American Political System The U. S. is a democracy. United States Government Legislative Branch Executive Branch Judicial Branch CONGRESS Senate House of Repre- sentatives PRESIDENT Vice President Cabinet Executive Office of the President SUPREME COURT of the US
American Political System The U. S. is a democracy. United States Government Legislative Branch Executive Branch Judicial Branch CONGRESS Senate House of Repre- sentatives PRESIDENT Vice President Cabinet Executive Office of the President SUPREME COURT of the US
 The White House
The White House
 The legislative branch is made up of elected representatives from all of the states and is the only branch that can make federal laws, levy federal taxes, declare war or put foreign treaties into effect. The chief executive of the U. S., the president, often proposes legislation to Congress. The president can also forbid any bill passed by Congress. Today the 13 departments are: State, Treasury, Defense, Justice, Interior, Agriculture, Commerce, Labor, Health and Human Services, Housing and Urban Development, Transportation, Energy and Education.
The legislative branch is made up of elected representatives from all of the states and is the only branch that can make federal laws, levy federal taxes, declare war or put foreign treaties into effect. The chief executive of the U. S., the president, often proposes legislation to Congress. The president can also forbid any bill passed by Congress. Today the 13 departments are: State, Treasury, Defense, Justice, Interior, Agriculture, Commerce, Labor, Health and Human Services, Housing and Urban Development, Transportation, Energy and Education.
 Under the Constitution, the president is responsible for foreign relations with other nations, he appoints ambassadors and other officials, represents the U. S. abroad in consultations with other heads of state. The judicial branch is headed by the Supreme Court, In addition, the Congress has established 11 federal courts of appeal and below them, 91 federal district courts. The Bill of Rights (adopted in 1791) - consists of ten very short paragraphs which guarantee freedom and individual rights and forbid interference with the lives of individuals by the government.
Under the Constitution, the president is responsible for foreign relations with other nations, he appoints ambassadors and other officials, represents the U. S. abroad in consultations with other heads of state. The judicial branch is headed by the Supreme Court, In addition, the Congress has established 11 federal courts of appeal and below them, 91 federal district courts. The Bill of Rights (adopted in 1791) - consists of ten very short paragraphs which guarantee freedom and individual rights and forbid interference with the lives of individuals by the government.
 Today, the U. S. has 2 major political parties. One is the Democratic party which evolved out of Th. Jefferson's party, formed before 1800. The other is the Republican party, which was formed in the 1850s, by people such as A. Lincoln, who wanted the government to prevent the expansion of slavery into new states.
Today, the U. S. has 2 major political parties. One is the Democratic party which evolved out of Th. Jefferson's party, formed before 1800. The other is the Republican party, which was formed in the 1850s, by people such as A. Lincoln, who wanted the government to prevent the expansion of slavery into new states.



















