6d11a2fbe039ac4e3b108927b2847e18.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Lecture 6 Marketing Communication Dr. Lucy Ting Lucy. Ting@manchester. ac. uk
Lecture 6 Marketing Communication Dr. Lucy Ting Lucy. Ting@manchester. ac. uk
 Agenda • Marketing Communications – Consumer Perspective • Integrated Marketing Communications – Definitions – Characteristics – Levels of Integration • Drivers and Barriers • Communication Mix Tools – Mass Market Appeal – Personal Appeal – Buzz Appeal
Agenda • Marketing Communications – Consumer Perspective • Integrated Marketing Communications – Definitions – Characteristics – Levels of Integration • Drivers and Barriers • Communication Mix Tools – Mass Market Appeal – Personal Appeal – Buzz Appeal
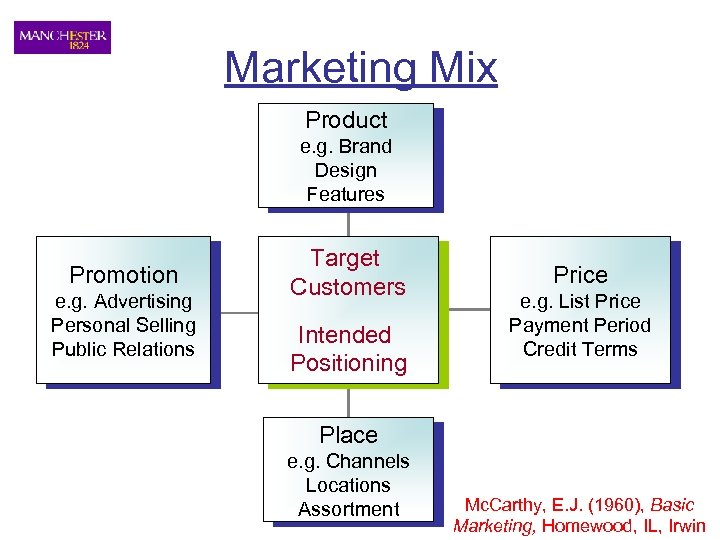 Marketing Mix Product e. g. Brand Design Features Promotion e. g. Advertising Personal Selling Public Relations Target Customers Intended Positioning Price e. g. List Price Payment Period Credit Terms Place e. g. Channels Locations Assortment Mc. Carthy, E. J. (1960), Basic Marketing, Homewood, IL, Irwin
Marketing Mix Product e. g. Brand Design Features Promotion e. g. Advertising Personal Selling Public Relations Target Customers Intended Positioning Price e. g. List Price Payment Period Credit Terms Place e. g. Channels Locations Assortment Mc. Carthy, E. J. (1960), Basic Marketing, Homewood, IL, Irwin
 Marketing Communications (Mar. Com) • • • Advertising Sales promotions Sponsorship Public relations Point-of-purchase communications Exhibitions and trade fairs Direct marketing communications Personal selling E-communications
Marketing Communications (Mar. Com) • • • Advertising Sales promotions Sponsorship Public relations Point-of-purchase communications Exhibitions and trade fairs Direct marketing communications Personal selling E-communications
 Customer Perspective • Consumers may be more sensitive to commonalities and discrepancies among message than to the specific Mar. Coms used to transmit them • Added value is created in terms of a faster and better comprehension of the communication and integration occurs at the consumer or perceiver level. Englis and Solomon (1996), ‘Using Consumption Constellations to Develop Integrated Communiication Strategies’, Journal of Business Research, 37, 183 -191
Customer Perspective • Consumers may be more sensitive to commonalities and discrepancies among message than to the specific Mar. Coms used to transmit them • Added value is created in terms of a faster and better comprehension of the communication and integration occurs at the consumer or perceiver level. Englis and Solomon (1996), ‘Using Consumption Constellations to Develop Integrated Communiication Strategies’, Journal of Business Research, 37, 183 -191
 Marketing Communication • Factors influence Marketing Communications 1. Changing Consumers • The availability of information and increased resistance in mass-market broadcasting 2. Changing Marketing Strategies • Fragmented market and more personalised marketing strategies 3. Changes in Technology • e. g. Internet, Mobile, Ipod, Satellite & Cable Armstrong and Kotler (2009) Chpt 12
Marketing Communication • Factors influence Marketing Communications 1. Changing Consumers • The availability of information and increased resistance in mass-market broadcasting 2. Changing Marketing Strategies • Fragmented market and more personalised marketing strategies 3. Changes in Technology • e. g. Internet, Mobile, Ipod, Satellite & Cable Armstrong and Kotler (2009) Chpt 12
 IMC: Mix and Match • Integrated Marketing Communication – A planning process designed to assure that all brand contacts received by a customer or prospect for a product, service, or organisation are relevant to that person and consistent over time American Marketing Association
IMC: Mix and Match • Integrated Marketing Communication – A planning process designed to assure that all brand contacts received by a customer or prospect for a product, service, or organisation are relevant to that person and consistent over time American Marketing Association
 IMC: Mix and Match • Basic Concepts 1. The whole is greater than the sum. 2. Affects brand awareness, by which it creates, maintains, or strengthens favourable and unique brand associations. 3. Aims to build strong customer relationships
IMC: Mix and Match • Basic Concepts 1. The whole is greater than the sum. 2. Affects brand awareness, by which it creates, maintains, or strengthens favourable and unique brand associations. 3. Aims to build strong customer relationships
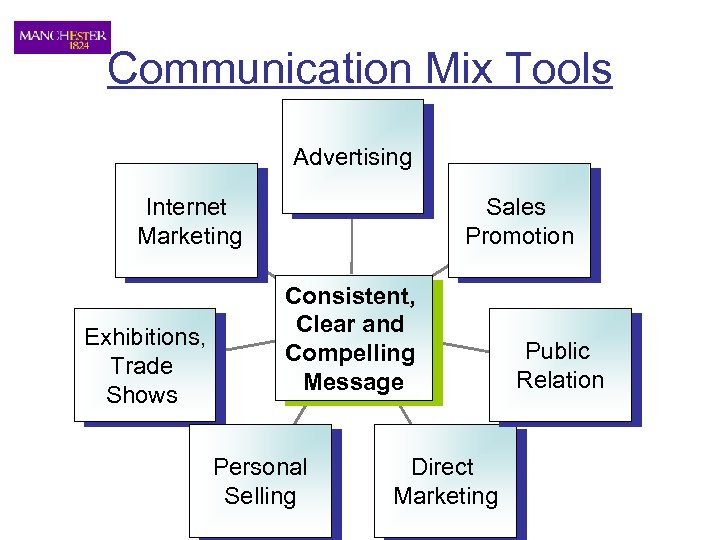 Communication Mix Tools Advertising Internet Marketing Exhibitions, Trade Shows Sales Promotion Consistent, Clear and Compelling Message Personal Selling Direct Marketing Public Relation
Communication Mix Tools Advertising Internet Marketing Exhibitions, Trade Shows Sales Promotion Consistent, Clear and Compelling Message Personal Selling Direct Marketing Public Relation
 Creating Synergies • Sales team has easier job when brand is well-known through advertising or sponsorship. • A promotional campaign that is supported by advertising is more successful. • Public relations, sponsorship and advertising can have synergetic effects on company and brand image. • Websites have to be supported by off-line campaigns.
Creating Synergies • Sales team has easier job when brand is well-known through advertising or sponsorship. • A promotional campaign that is supported by advertising is more successful. • Public relations, sponsorship and advertising can have synergetic effects on company and brand image. • Websites have to be supported by off-line campaigns.
 Marketing Mix and IMC Hutton, J. H. (1996), ‘Integrated Marketing Communication and the Evolution of Marketing Thought’, Journal of Business Research, 37, 155– 62
Marketing Mix and IMC Hutton, J. H. (1996), ‘Integrated Marketing Communication and the Evolution of Marketing Thought’, Journal of Business Research, 37, 155– 62
 Integrated Marketing Communications
Integrated Marketing Communications
 Definitions Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC) – IMC is a concept of marketing communications planning that recognises the added value of a comprehensive plan that evaluates the strategic roles of a variety of communication disciplines and combine these disciplines to provide clarity, consistency, and maximum communications impact American Association of Advertising Agencies; Reported in Schultz (1993) “Integrated Marketing Communications: Maybe Definition is in the Point of View, ” Marketing News, 18 January
Definitions Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC) – IMC is a concept of marketing communications planning that recognises the added value of a comprehensive plan that evaluates the strategic roles of a variety of communication disciplines and combine these disciplines to provide clarity, consistency, and maximum communications impact American Association of Advertising Agencies; Reported in Schultz (1993) “Integrated Marketing Communications: Maybe Definition is in the Point of View, ” Marketing News, 18 January
 Definitions – IMC is the strategic choice of elements of marketing communications which will effectively and economically influence transactions between an organisation and its existing and potential customers, clients and consumers. Betts et al. (1995), Marketing Communications Strategy, 2 nd Edition BPP Publishing
Definitions – IMC is the strategic choice of elements of marketing communications which will effectively and economically influence transactions between an organisation and its existing and potential customers, clients and consumers. Betts et al. (1995), Marketing Communications Strategy, 2 nd Edition BPP Publishing
 Definitions – IMC is the concept under which a company carefully integrates and coordinates its many communications channels to deliver a clear, consistent and compelling message about the organisation and its products Kotler et al. (1999), Principles of Marketing 2 nd European Edition, Prentice Hall
Definitions – IMC is the concept under which a company carefully integrates and coordinates its many communications channels to deliver a clear, consistent and compelling message about the organisation and its products Kotler et al. (1999), Principles of Marketing 2 nd European Edition, Prentice Hall
 Definitions – IMC is an organisation’s unified, coordinated effort to promote a brand concept through the use of multiple communications tools that “speak with a single voice. ” Shimp (2000), Advertising, Promotion, and Supplemental Aspects of Integrated Marketing Communications, 5 th Edition, Dryden Press
Definitions – IMC is an organisation’s unified, coordinated effort to promote a brand concept through the use of multiple communications tools that “speak with a single voice. ” Shimp (2000), Advertising, Promotion, and Supplemental Aspects of Integrated Marketing Communications, 5 th Edition, Dryden Press
 Definitions – IMC is a process of managing the customer relationships that drive brand value. More specifically, it is a cross-functional process for creating and nourishing profitable relationships with customers and stakeholders by strategically controlling or influencing all messages sent to these groups and encouraging data-driven, purposeful dialogue with them Duncan (2002), IMC: Using Advertising and Promotion to Build Brands, International Edition, The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies
Definitions – IMC is a process of managing the customer relationships that drive brand value. More specifically, it is a cross-functional process for creating and nourishing profitable relationships with customers and stakeholders by strategically controlling or influencing all messages sent to these groups and encouraging data-driven, purposeful dialogue with them Duncan (2002), IMC: Using Advertising and Promotion to Build Brands, International Edition, The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies
 Definitions Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC) – A planning process designed to assure that all brand contacts received by a customer or prospect for a product, service, or organization are relevant to that person and consistent over time American Marketing Association
Definitions Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC) – A planning process designed to assure that all brand contacts received by a customer or prospect for a product, service, or organization are relevant to that person and consistent over time American Marketing Association
 Characteristics • Five Essential Elements of IMC 1. The aim to affect behaviour through direct communication 2. The IMC process should start from customer or prospects and then work backwards to brand communicators 3. IMC should use all forms of communication and all sources of brand or company contacts as prospective message delivery channels 4. The need for synergy, with coordination helping to achieve a strong brand image 5. The need to build and strength brand relationships Shimp (2000), Advertising, Promotion, and Supplemental Aspects of Integrated Marketing Communications, 5 th Edition, Dryden Press
Characteristics • Five Essential Elements of IMC 1. The aim to affect behaviour through direct communication 2. The IMC process should start from customer or prospects and then work backwards to brand communicators 3. IMC should use all forms of communication and all sources of brand or company contacts as prospective message delivery channels 4. The need for synergy, with coordination helping to achieve a strong brand image 5. The need to build and strength brand relationships Shimp (2000), Advertising, Promotion, and Supplemental Aspects of Integrated Marketing Communications, 5 th Edition, Dryden Press
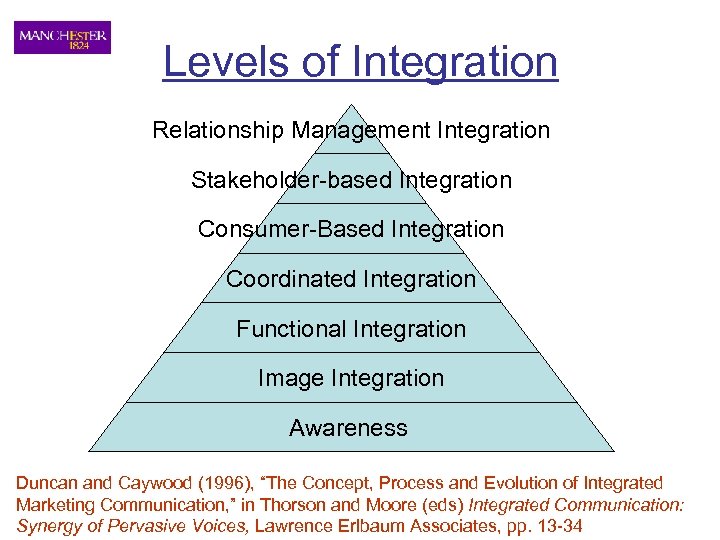 Levels of Integration Relationship Management Integration Stakeholder-based Integration Consumer-Based Integration Coordinated Integration Functional Integration Image Integration Awareness Duncan and Caywood (1996), “The Concept, Process and Evolution of Integrated Marketing Communication, ” in Thorson and Moore (eds) Integrated Communication: Synergy of Pervasive Voices, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, pp. 13 -34
Levels of Integration Relationship Management Integration Stakeholder-based Integration Consumer-Based Integration Coordinated Integration Functional Integration Image Integration Awareness Duncan and Caywood (1996), “The Concept, Process and Evolution of Integrated Marketing Communication, ” in Thorson and Moore (eds) Integrated Communication: Synergy of Pervasive Voices, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, pp. 13 -34
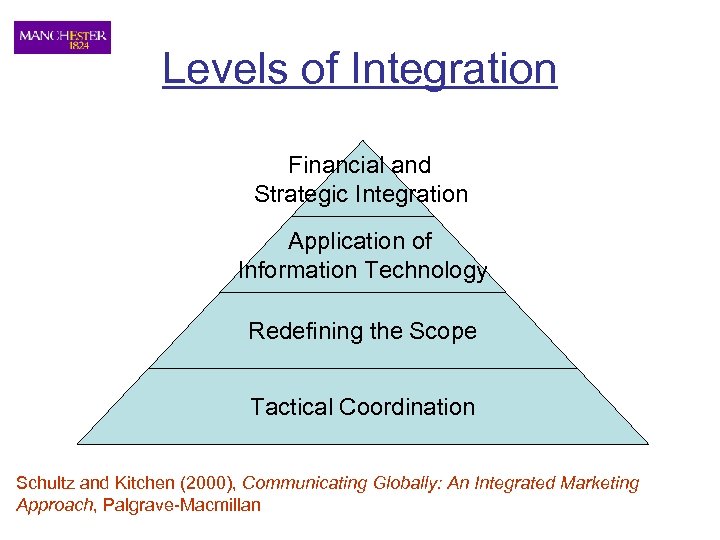 Levels of Integration Financial and Strategic Integration Application of Information Technology Redefining the Scope Tactical Coordination Schultz and Kitchen (2000), Communicating Globally: An Integrated Marketing Approach, Palgrave-Macmillan
Levels of Integration Financial and Strategic Integration Application of Information Technology Redefining the Scope Tactical Coordination Schultz and Kitchen (2000), Communicating Globally: An Integrated Marketing Approach, Palgrave-Macmillan
 Key Drivers of Integration De Pelsmaker and den Bergh (2007)
Key Drivers of Integration De Pelsmaker and den Bergh (2007)
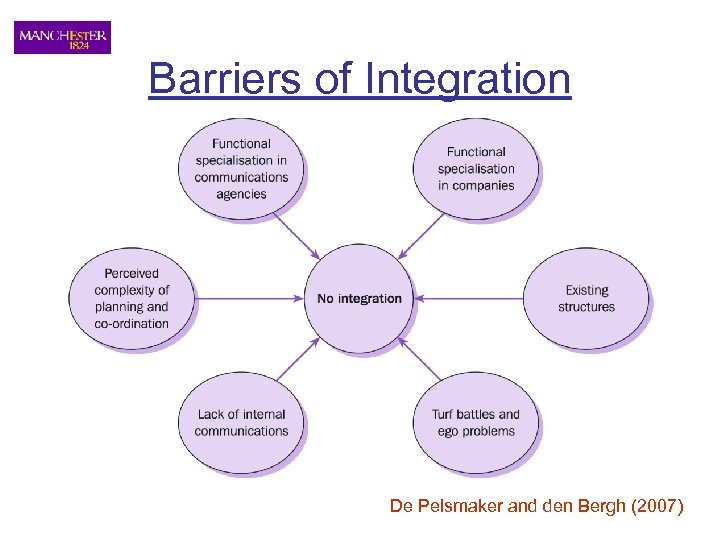 Barriers of Integration De Pelsmaker and den Bergh (2007)
Barriers of Integration De Pelsmaker and den Bergh (2007)
 Communication Tools
Communication Tools
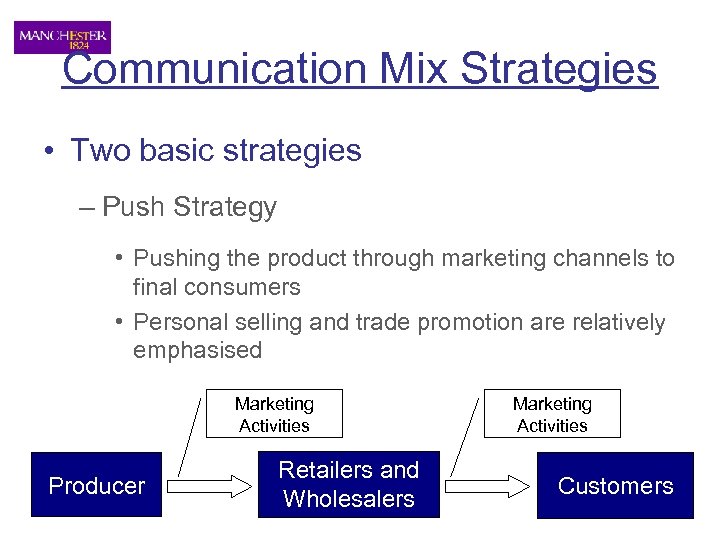 Communication Mix Strategies • Two basic strategies – Push Strategy • Pushing the product through marketing channels to final consumers • Personal selling and trade promotion are relatively emphasised Marketing Activities Producer Retailers and Wholesalers Marketing Activities Customers
Communication Mix Strategies • Two basic strategies – Push Strategy • Pushing the product through marketing channels to final consumers • Personal selling and trade promotion are relatively emphasised Marketing Activities Producer Retailers and Wholesalers Marketing Activities Customers
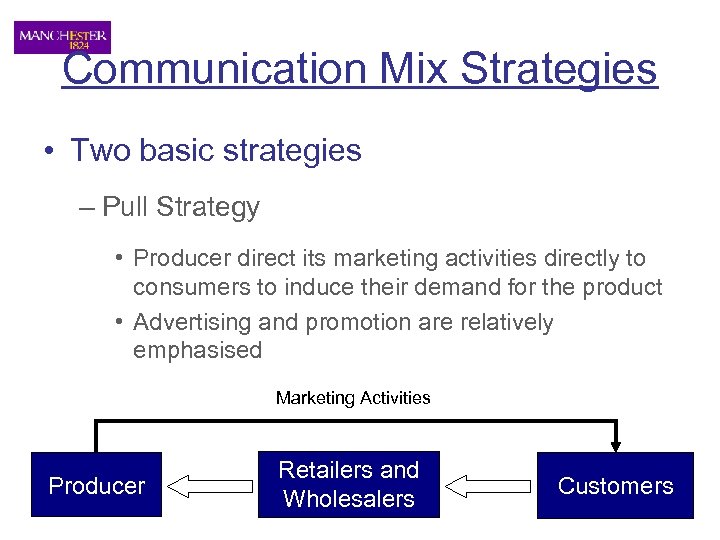 Communication Mix Strategies • Two basic strategies – Pull Strategy • Producer direct its marketing activities directly to consumers to induce their demand for the product • Advertising and promotion are relatively emphasised Marketing Activities Producer Retailers and Wholesalers Customers
Communication Mix Strategies • Two basic strategies – Pull Strategy • Producer direct its marketing activities directly to consumers to induce their demand for the product • Advertising and promotion are relatively emphasised Marketing Activities Producer Retailers and Wholesalers Customers
 Communication Tools • Mass Appeal – Tools which aim to reach many prospective customers at the same time 1. Advertising 2. Sales Promotion 3. Public Relations Solomon et al. (2008)
Communication Tools • Mass Appeal – Tools which aim to reach many prospective customers at the same time 1. Advertising 2. Sales Promotion 3. Public Relations Solomon et al. (2008)
 Communication Tools 1. Advertising – It can offers reasons to buy and reach masses of geographically dispersed buyers with repeated exposures. Pros • Marketers have control over what the message will say, when it will appear and who is likely to see it Cons • Often expensive to produce and distribute • May have low credibility and/or be ignored by audience
Communication Tools 1. Advertising – It can offers reasons to buy and reach masses of geographically dispersed buyers with repeated exposures. Pros • Marketers have control over what the message will say, when it will appear and who is likely to see it Cons • Often expensive to produce and distribute • May have low credibility and/or be ignored by audience
 Communication Tool • Advertising Objectives – Informative Advertising • To communicate customer value and is used heavily when introducing a new product – Persuasive Advertising • To build brand value and sometimes compare with competing brands – Reminder Advertising • Maintain customer relationships and keep customers thinking about the product
Communication Tool • Advertising Objectives – Informative Advertising • To communicate customer value and is used heavily when introducing a new product – Persuasive Advertising • To build brand value and sometimes compare with competing brands – Reminder Advertising • Maintain customer relationships and keep customers thinking about the product
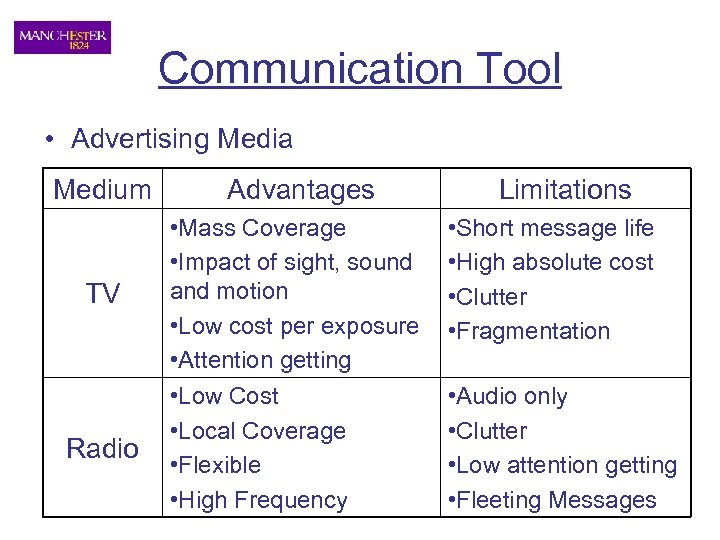 Communication Tool • Advertising Media Medium TV Radio Advantages • Mass Coverage • Impact of sight, sound and motion • Low cost per exposure • Attention getting • Low Cost • Local Coverage • Flexible • High Frequency Limitations • Short message life • High absolute cost • Clutter • Fragmentation • Audio only • Clutter • Low attention getting • Fleeting Messages
Communication Tool • Advertising Media Medium TV Radio Advantages • Mass Coverage • Impact of sight, sound and motion • Low cost per exposure • Attention getting • Low Cost • Local Coverage • Flexible • High Frequency Limitations • Short message life • High absolute cost • Clutter • Fragmentation • Audio only • Clutter • Low attention getting • Fleeting Messages
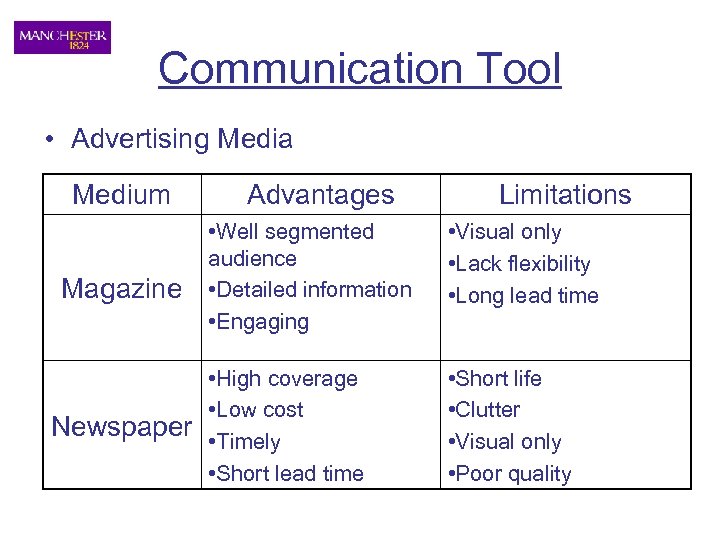 Communication Tool • Advertising Media Medium Magazine Newspaper Advantages Limitations • Well segmented audience • Detailed information • Engaging • Visual only • Lack flexibility • Long lead time • High coverage • Low cost • Timely • Short lead time • Short life • Clutter • Visual only • Poor quality
Communication Tool • Advertising Media Medium Magazine Newspaper Advantages Limitations • Well segmented audience • Detailed information • Engaging • Visual only • Lack flexibility • Long lead time • High coverage • Low cost • Timely • Short lead time • Short life • Clutter • Visual only • Poor quality
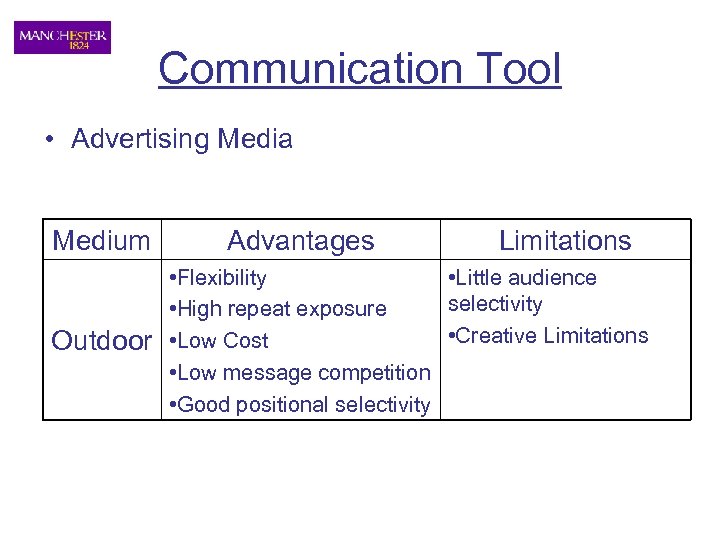 Communication Tool • Advertising Media Medium Outdoor Advantages Limitations • Flexibility • Little audience selectivity • High repeat exposure • Creative Limitations • Low Cost • Low message competition • Good positional selectivity
Communication Tool • Advertising Media Medium Outdoor Advantages Limitations • Flexibility • Little audience selectivity • High repeat exposure • Creative Limitations • Low Cost • Low message competition • Good positional selectivity
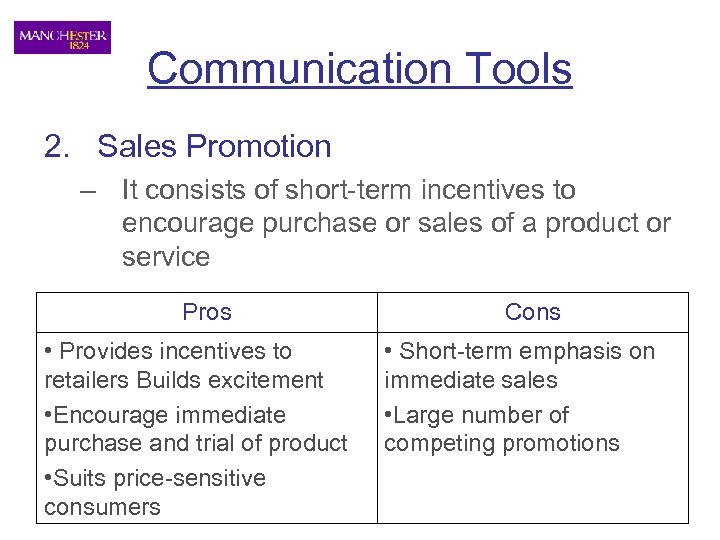 Communication Tools 2. Sales Promotion – It consists of short-term incentives to encourage purchase or sales of a product or service Pros • Provides incentives to retailers Builds excitement • Encourage immediate purchase and trial of product • Suits price-sensitive consumers Cons • Short-term emphasis on immediate sales • Large number of competing promotions
Communication Tools 2. Sales Promotion – It consists of short-term incentives to encourage purchase or sales of a product or service Pros • Provides incentives to retailers Builds excitement • Encourage immediate purchase and trial of product • Suits price-sensitive consumers Cons • Short-term emphasis on immediate sales • Large number of competing promotions
 Communication Tool • Sales Promotion Objectives – Consumer Promotion • • Short-term customer buying Temporary brand switching Reinforce positioning strategy Build long-term customer relationship – Trade Promotion • More sales force support for products • Getting salespeople to sign up new accounts
Communication Tool • Sales Promotion Objectives – Consumer Promotion • • Short-term customer buying Temporary brand switching Reinforce positioning strategy Build long-term customer relationship – Trade Promotion • More sales force support for products • Getting salespeople to sign up new accounts
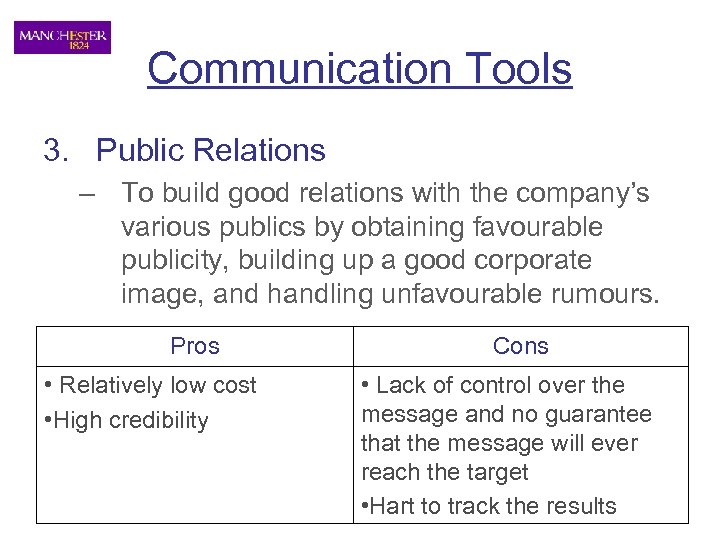 Communication Tools 3. Public Relations – To build good relations with the company’s various publics by obtaining favourable publicity, building up a good corporate image, and handling unfavourable rumours. Pros • Relatively low cost • High credibility Cons • Lack of control over the message and no guarantee that the message will ever reach the target • Hart to track the results
Communication Tools 3. Public Relations – To build good relations with the company’s various publics by obtaining favourable publicity, building up a good corporate image, and handling unfavourable rumours. Pros • Relatively low cost • High credibility Cons • Lack of control over the message and no guarantee that the message will ever reach the target • Hart to track the results
 Communication Tools • Personal Appeal – Tools which aim to communicate with consumers on a personal, one-to-one level. 1. Personal Selling 2. Direct Marketing Solomon et al. (2008)
Communication Tools • Personal Appeal – Tools which aim to communicate with consumers on a personal, one-to-one level. 1. Personal Selling 2. Direct Marketing Solomon et al. (2008)
 Communication Tools 1. Personal Selling – Personal presentation by the firm’s sales force for the purpose of making sales and building customer relationships Pros Cons • Direct contact with the customer gives the salesperson the opportunity to be flexible and modify the sales message to coincide with the customer’s needs • The salesperson can get immediate feedback from the customer • High cost per contact with customer • Difficult to ensure consistency of message when delivered by different salespersons • The credibility of sales people often depends on the quality of the company’s image
Communication Tools 1. Personal Selling – Personal presentation by the firm’s sales force for the purpose of making sales and building customer relationships Pros Cons • Direct contact with the customer gives the salesperson the opportunity to be flexible and modify the sales message to coincide with the customer’s needs • The salesperson can get immediate feedback from the customer • High cost per contact with customer • Difficult to ensure consistency of message when delivered by different salespersons • The credibility of sales people often depends on the quality of the company’s image
 Communication Tools 2. Direct Marketing • Direct connections with carefully targeted individual consumers to both obtain and immediate response and cultivate lasting customer relationships Pros Cons • Can target specific groups with different offers • Results can be easily measured • Can provide extensive product information and multiple offers within a single appeal • Provides a means for collecting information • Consumers may have a negative opinion of some types of direct marketing • Costs more per contact than mass appeals
Communication Tools 2. Direct Marketing • Direct connections with carefully targeted individual consumers to both obtain and immediate response and cultivate lasting customer relationships Pros Cons • Can target specific groups with different offers • Results can be easily measured • Can provide extensive product information and multiple offers within a single appeal • Provides a means for collecting information • Consumers may have a negative opinion of some types of direct marketing • Costs more per contact than mass appeals
 Communication Tools • Buzz Appeal – The new out-of-box tools which aim to communicate especially with the young consumers who tend to be cynical about corporations. 1. Direct Marketing (Digital) Solomon et al. (2008)
Communication Tools • Buzz Appeal – The new out-of-box tools which aim to communicate especially with the young consumers who tend to be cynical about corporations. 1. Direct Marketing (Digital) Solomon et al. (2008)


