Lecture 6 .ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Lecture 6 Capital (funds). Circulation and turnover of capital. Production input(costs).
Lecture 6 Capital (funds). Circulation and turnover of capital. Production input(costs).
 Lecture outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Capital: essence, types, circulation Investment: essence, types, sources, factors Production costs: essence, types Salary and wage: essence, types, factors determine the level of wage/salary
Lecture outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Capital: essence, types, circulation Investment: essence, types, sources, factors Production costs: essence, types Salary and wage: essence, types, factors determine the level of wage/salary
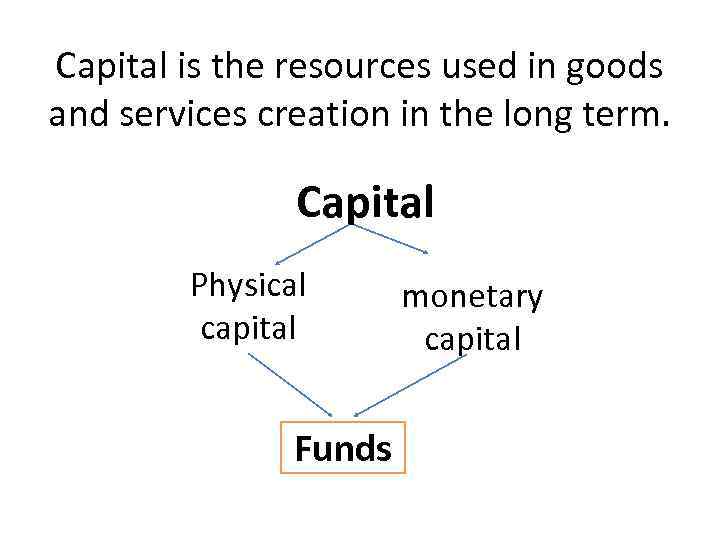 Capital is the resources used in goods and services creation in the long term. Capital Physical capital Funds monetary capital
Capital is the resources used in goods and services creation in the long term. Capital Physical capital Funds monetary capital
 Physical capital (non financial assets) • It consists of buildings, raw materials, ready goods, and other resources that are needed to produce goods and services
Physical capital (non financial assets) • It consists of buildings, raw materials, ready goods, and other resources that are needed to produce goods and services
 Monetary capital • Monetary expression of non-financial assets and money in cash
Monetary capital • Monetary expression of non-financial assets and money in cash
 • The process of the continuous circulation is called turnover of the capital and it expresses through the formula
• The process of the continuous circulation is called turnover of the capital and it expresses through the formula
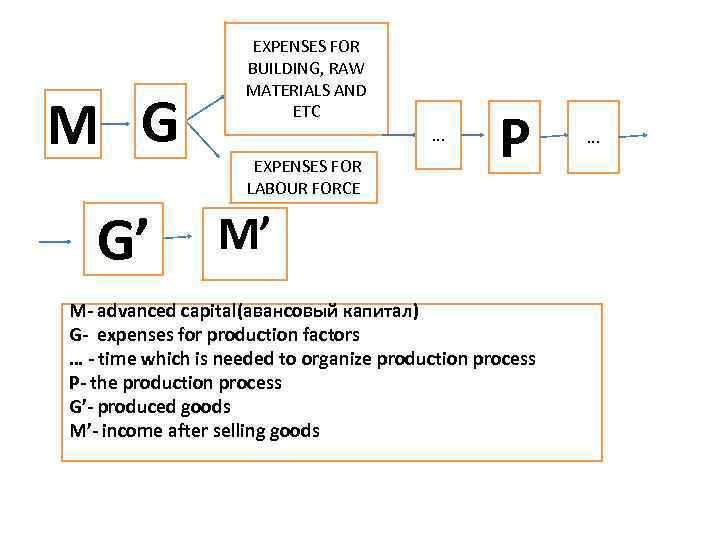 M G • G’ EXPENSES FOR BUILDING, RAW MATERIALS AND ETC. . . EXPENSES FOR LABOUR FORCE P M’ M- advanced capital(авансовый капитал) G- expenses for production factors … - time which is needed to organize production process P- the production process G’- produced goods M’- income after selling goods . . .
M G • G’ EXPENSES FOR BUILDING, RAW MATERIALS AND ETC. . . EXPENSES FOR LABOUR FORCE P M’ M- advanced capital(авансовый капитал) G- expenses for production factors … - time which is needed to organize production process P- the production process G’- produced goods M’- income after selling goods . . .
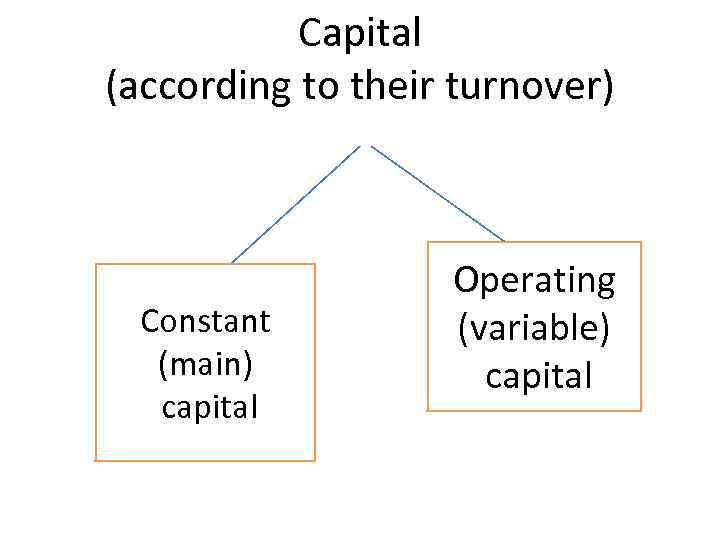 Capital (according to their turnover) Constant (main) capital Operating (variable) capital
Capital (according to their turnover) Constant (main) capital Operating (variable) capital
 Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. • In economics, investment is the accumulation of newly produced physical entities, such as factories, machinery, houses, and goods inventories.
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. • In economics, investment is the accumulation of newly produced physical entities, such as factories, machinery, houses, and goods inventories.
 • In finance, investment is putting money into an asset with the expectation of capital appreciation, dividends, and/or interest earnings.
• In finance, investment is putting money into an asset with the expectation of capital appreciation, dividends, and/or interest earnings.
 Investment types 1. Financial and real investment 2. Direct and portfolio investment
Investment types 1. Financial and real investment 2. Direct and portfolio investment
 Financial investment • Financial investment is money of government, private companies or person which is directed to buy stocks (акции), bonds (oблигации) and other securities
Financial investment • Financial investment is money of government, private companies or person which is directed to buy stocks (акции), bonds (oблигации) and other securities
 Real investment (нақты инвестиция) • Real investment is money which is used to increase real production funds.
Real investment (нақты инвестиция) • Real investment is money which is used to increase real production funds.
 Direct investment (тікелей инвестиция) • Direct investment is the money of foreigners that is used in national economy.
Direct investment (тікелей инвестиция) • Direct investment is the money of foreigners that is used in national economy.
 Portfolio investment • Portfolio investment is the money which is directed to buy foreign companies’ stocks, bonds and other securities.
Portfolio investment • Portfolio investment is the money which is directed to buy foreign companies’ stocks, bonds and other securities.
 Investment sources(инвестиция көздері) Investment sources are: • free money of people • profit of individual enterprises • profit of joint enterprises • profit of public enterprises.
Investment sources(инвестиция көздері) Investment sources are: • free money of people • profit of individual enterprises • profit of joint enterprises • profit of public enterprises.
 Why does level of investment change? • The level of investment depends on the following factors: level of profit, interest rate, tax rate, and political, economical stabilities in the society.
Why does level of investment change? • The level of investment depends on the following factors: level of profit, interest rate, tax rate, and political, economical stabilities in the society.
 Production costs • Costs are the money and other material expenditures used in producing and selling of goods during certain period of time.
Production costs • Costs are the money and other material expenditures used in producing and selling of goods during certain period of time.
 Types of costs 1. Fixed costs (FC) 2. Variable costs (VC) 3. Total costs (TC) 4. Average costs (AC) 5. Marginal costs (MC)
Types of costs 1. Fixed costs (FC) 2. Variable costs (VC) 3. Total costs (TC) 4. Average costs (AC) 5. Marginal costs (MC)
 Fixed/constant costs (FC) • Fixed costs (FC) are the costs that do not vary with output levels. E. g. rent expenses, depreciation payment, repay a debt, capital expenditures on equipment and others. These costs exist even if output is zero.
Fixed/constant costs (FC) • Fixed costs (FC) are the costs that do not vary with output levels. E. g. rent expenses, depreciation payment, repay a debt, capital expenditures on equipment and others. These costs exist even if output is zero.
 Variable costs (VC) өзгермелі шығындар • Variable costs (VC) are costs that change as output changes. E. g. expenses for labour force wage, raw materials, packing expenses, stationary expenses, storage expenses, transportation expenses and others.
Variable costs (VC) өзгермелі шығындар • Variable costs (VC) are costs that change as output changes. E. g. expenses for labour force wage, raw materials, packing expenses, stationary expenses, storage expenses, transportation expenses and others.
 Total costs (TC) жалпы шығындар TC is whole sum of money that is used in producing goods/services TC=FC+VC
Total costs (TC) жалпы шығындар TC is whole sum of money that is used in producing goods/services TC=FC+VC
 Average costs (AC) • AC- is amount of money that is used in producing one unit of product • AC- piece costs • AC-unit costs
Average costs (AC) • AC- is amount of money that is used in producing one unit of product • AC- piece costs • AC-unit costs
 How to calculate AC? AC=TC: Q e. g. TC=100 000 tenge, number of produced goods (Q)=5 000. AC=100 000: 5000=20
How to calculate AC? AC=TC: Q e. g. TC=100 000 tenge, number of produced goods (Q)=5 000. AC=100 000: 5000=20
 Why is AC important for a businessman? • AC is foundation of price formation • AC helps to define price of a product. P= AC+ extra charge • P= 20 tenge+5 tenge=25 tenge • Extra charges are profit sources. A profit maximizing firm must produce its output at minimum cost.
Why is AC important for a businessman? • AC is foundation of price formation • AC helps to define price of a product. P= AC+ extra charge • P= 20 tenge+5 tenge=25 tenge • Extra charges are profit sources. A profit maximizing firm must produce its output at minimum cost.
 Income types • • Salary/Wage Rent Interest Dividend
Income types • • Salary/Wage Rent Interest Dividend
 Wage Payment for labor or services to a worker, especially remuneration on an hourly, daily, or weekly basis or by the piece.
Wage Payment for labor or services to a worker, especially remuneration on an hourly, daily, or weekly basis or by the piece.
 Salary • A salary is a form of periodic payment from an employer to an employee, which may be specified in an employment contract. Salary types: • nominal salary • real salary.
Salary • A salary is a form of periodic payment from an employer to an employee, which may be specified in an employment contract. Salary types: • nominal salary • real salary.
 • The difference between wage and salary is that wage is used to refer to the amount paid to an employee depending on the amount of hours worked, whereas salary refers to a fixed monthly remuneration an employee receives not considering of hours worked. Employment agreement is used to determine the type payments an employer pays the employees.
• The difference between wage and salary is that wage is used to refer to the amount paid to an employee depending on the amount of hours worked, whereas salary refers to a fixed monthly remuneration an employee receives not considering of hours worked. Employment agreement is used to determine the type payments an employer pays the employees.
 Nominal salary is the whole money which you get during certain period of time according to the contract or agreement. Salary measured in terms of money paid, not in terms of purchasing power. Real salary is nominal wage after paying taxes. Real salary=nominal salary-taxes
Nominal salary is the whole money which you get during certain period of time according to the contract or agreement. Salary measured in terms of money paid, not in terms of purchasing power. Real salary is nominal wage after paying taxes. Real salary=nominal salary-taxes
 Wage level depends on the following factors: • Changes in demand for and supply of labour • Labour hours • Trade unions activities • Inflation rate
Wage level depends on the following factors: • Changes in demand for and supply of labour • Labour hours • Trade unions activities • Inflation rate
 Interest / interest rate • Interest is an income that is received by capital owner, e. g. deposits, investments, bonds. Types of interest rate: 1. Nominal 2. Real
Interest / interest rate • Interest is an income that is received by capital owner, e. g. deposits, investments, bonds. Types of interest rate: 1. Nominal 2. Real
 The nominal interest rate • The nominal interest rate tells us how many actual tenge will be earned in interest by lending 1 tenge for one year. At a nominal interest rate of 10 per cent, 100 tenge lent today will accumulate to 110 tenge by next year. But we will be interested in how many goods that 110 tenge will then buy.
The nominal interest rate • The nominal interest rate tells us how many actual tenge will be earned in interest by lending 1 tenge for one year. At a nominal interest rate of 10 per cent, 100 tenge lent today will accumulate to 110 tenge by next year. But we will be interested in how many goods that 110 tenge will then buy.
 The real interest rate measures the return on a loan as the increase in goods that can be purchased rather than as the increase in the nominal or the money value of the loan fund. • Real interest rate=nominal interest rateinflation rate
The real interest rate measures the return on a loan as the increase in goods that can be purchased rather than as the increase in the nominal or the money value of the loan fund. • Real interest rate=nominal interest rateinflation rate
 Rent • Rent is the payment for land services(renting assets/real estate and land). The land plays different role in the life of the people. Land as a place of enterprise to produce goods or land a place for growing plants (agricultural earth). Land is an asset in fixed supply.
Rent • Rent is the payment for land services(renting assets/real estate and land). The land plays different role in the life of the people. Land as a place of enterprise to produce goods or land a place for growing plants (agricultural earth). Land is an asset in fixed supply.
 Types of land /ground rents • The income which is got by landowner is called ground rent. Types of land rents 1. economic/differential rent I 2. economic/differential rent II.
Types of land /ground rents • The income which is got by landowner is called ground rent. Types of land rents 1. economic/differential rent I 2. economic/differential rent II.
 Economic/ differential • Economic/ differential rent I is the income which is got by land owners from rich soil (плородная почва) and from the land is not situated far from the road.
Economic/ differential • Economic/ differential rent I is the income which is got by land owners from rich soil (плородная почва) and from the land is not situated far from the road.
 Economic / differential rent II • Economic rent II is the money which is got by land owners after investing some money to the land, e. g. applying some chemical things/ manuring (удобрение), transportation costs and others.
Economic / differential rent II • Economic rent II is the money which is got by land owners after investing some money to the land, e. g. applying some chemical things/ manuring (удобрение), transportation costs and others.
 • The land’s price depends on land rental rate. If the land rental rate is high the land’s also is high and vice versa.
• The land’s price depends on land rental rate. If the land rental rate is high the land’s also is high and vice versa.


