f28b7c08f97bea9af0c9c8c82e14d268.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Lecture 5 SQL Continued INSS 651 1
Lecture 5 SQL Continued INSS 651 1
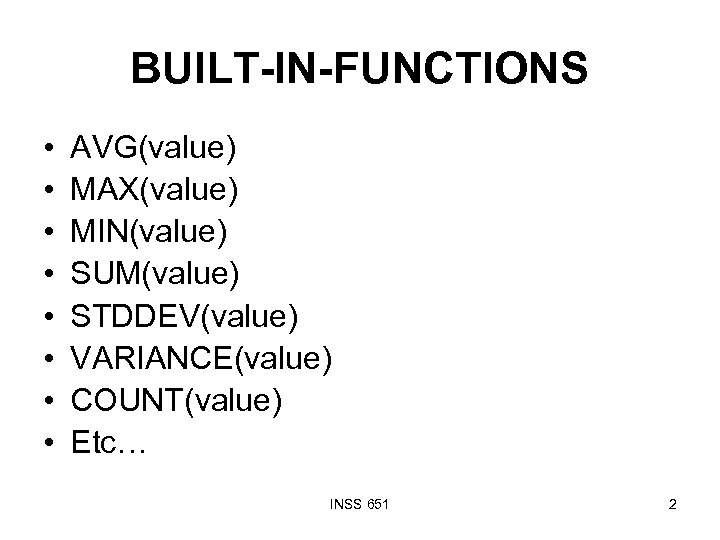 BUILT-IN-FUNCTIONS • • AVG(value) MAX(value) MIN(value) SUM(value) STDDEV(value) VARIANCE(value) COUNT(value) Etc… INSS 651 2
BUILT-IN-FUNCTIONS • • AVG(value) MAX(value) MIN(value) SUM(value) STDDEV(value) VARIANCE(value) COUNT(value) Etc… INSS 651 2
 Nested functions Select max (avg(grades)) etc. . is allowed INSS 651 3
Nested functions Select max (avg(grades)) etc. . is allowed INSS 651 3
 String functions Several strings can be concatenated Use string 1||string 2 || implies + select custname|| ‘, ’ || cust_street as address From customer; INSS 651 4
String functions Several strings can be concatenated Use string 1||string 2 || implies + select custname|| ‘, ’ || cust_street as address From customer; INSS 651 4
 Substrings Returns substrings Format: Substr(stringvalue, m, n) Where m is the starting value and n is the length of characters INSS 651 5
Substrings Returns substrings Format: Substr(stringvalue, m, n) Where m is the starting value and n is the length of characters INSS 651 5
 Assume orders have the format: ” Abc 1234 cdf 2345 etc. . Get the first and last part of the order Select substr (order_numb, 1, 3), substr (order_numb, 4, 4) From order; INSS 651 6
Assume orders have the format: ” Abc 1234 cdf 2345 etc. . Get the first and last part of the order Select substr (order_numb, 1, 3), substr (order_numb, 4, 4) From order; INSS 651 6
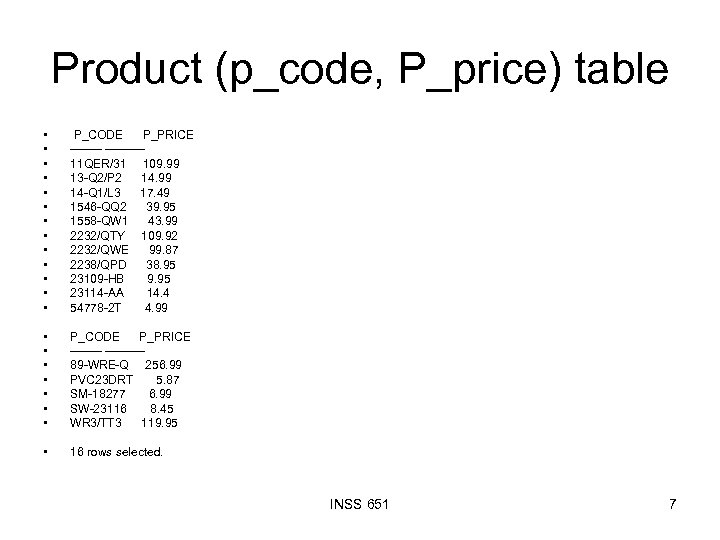 Product (p_code, P_price) table • • • • P_CODE P_PRICE ---------11 QER/31 109. 99 13 -Q 2/P 2 14. 99 14 -Q 1/L 3 17. 49 1546 -QQ 2 39. 95 1558 -QW 1 43. 99 2232/QTY 109. 92 2232/QWE 99. 87 2238/QPD 38. 95 23109 -HB 9. 95 23114 -AA 14. 4 54778 -2 T 4. 99 • • P_CODE P_PRICE ---------89 -WRE-Q 256. 99 PVC 23 DRT 5. 87 SM-18277 6. 99 SW-23116 8. 45 WR 3/TT 3 119. 95 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 7
Product (p_code, P_price) table • • • • P_CODE P_PRICE ---------11 QER/31 109. 99 13 -Q 2/P 2 14. 99 14 -Q 1/L 3 17. 49 1546 -QQ 2 39. 95 1558 -QW 1 43. 99 2232/QTY 109. 92 2232/QWE 99. 87 2238/QPD 38. 95 23109 -HB 9. 95 23114 -AA 14. 4 54778 -2 T 4. 99 • • P_CODE P_PRICE ---------89 -WRE-Q 256. 99 PVC 23 DRT 5. 87 SM-18277 6. 99 SW-23116 8. 45 WR 3/TT 3 119. 95 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 7
 Select three characters of price • SQL> select substr(p_price, 1, 3) from product; • • • • SUB --109 14. 17. 39. 43. 109 99. 38. 9. 9 14. 4. 9 • • SUB --256 5. 8 6. 9 8. 4 119 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 8
Select three characters of price • SQL> select substr(p_price, 1, 3) from product; • • • • SUB --109 14. 17. 39. 43. 109 99. 38. 9. 9 14. 4. 9 • • SUB --256 5. 8 6. 9 8. 4 119 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 8
 Padding characters Rpad (string, length, ’set’) Lpad (string, length, ’set’) 1* select rpad (p_code, 15, '. ') as rightpad, p_price from product • SQL> / • • • • RIGHTPAD P_PRICE --------11 QER/31. . . . 109. 99 13 -Q 2/P 2. . . . 14. 99 14 -Q 1/L 3. . . . 17. 49 1546 -QQ 2. . . . 39. 95 1558 -QW 1. . . . 43. 99 2232/QTY. . . . 109. 92 2232/QWE. . . . 99. 87 2238/QPD. . . . 38. 95 23109 -HB. . . . 9. 95 23114 -AA. . . . 14. 4 54778 -2 T. . . . 4. 99 • • RIGHTPAD P_PRICE --------89 -WRE-Q. . . . 256. 99 PVC 23 DRT. . . . 5. 87 SM-18277. . . . 6. 99 SW-23116. . . . 8. 45 WR 3/TT 3. . . . 119. 95 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 9
Padding characters Rpad (string, length, ’set’) Lpad (string, length, ’set’) 1* select rpad (p_code, 15, '. ') as rightpad, p_price from product • SQL> / • • • • RIGHTPAD P_PRICE --------11 QER/31. . . . 109. 99 13 -Q 2/P 2. . . . 14. 99 14 -Q 1/L 3. . . . 17. 49 1546 -QQ 2. . . . 39. 95 1558 -QW 1. . . . 43. 99 2232/QTY. . . . 109. 92 2232/QWE. . . . 99. 87 2238/QPD. . . . 38. 95 23109 -HB. . . . 9. 95 23114 -AA. . . . 14. 4 54778 -2 T. . . . 4. 99 • • RIGHTPAD P_PRICE --------89 -WRE-Q. . . . 256. 99 PVC 23 DRT. . . . 5. 87 SM-18277. . . . 6. 99 SW-23116. . . . 8. 45 WR 3/TT 3. . . . 119. 95 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 9
 Length of string format length (string) Returns length of the string INSS 651 10
Length of string format length (string) Returns length of the string INSS 651 10
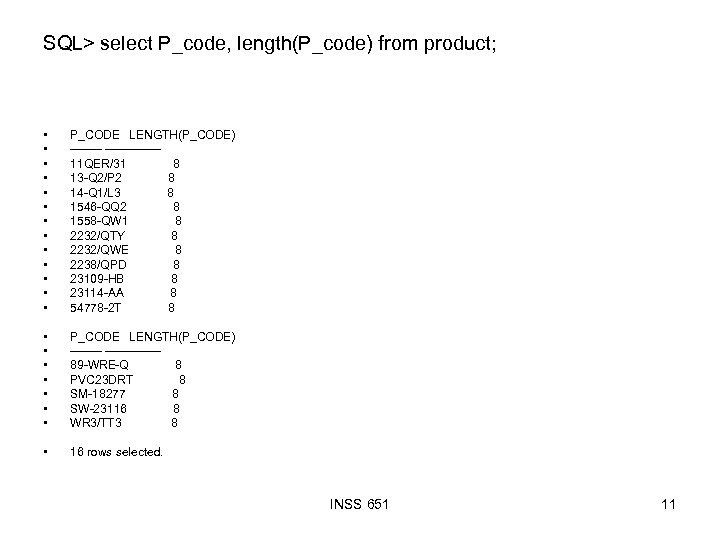 SQL> select P_code, length(P_code) from product; • • • • P_CODE LENGTH(P_CODE) -------------11 QER/31 8 13 -Q 2/P 2 8 14 -Q 1/L 3 8 1546 -QQ 2 8 1558 -QW 1 8 2232/QTY 8 2232/QWE 8 2238/QPD 8 23109 -HB 8 23114 -AA 8 54778 -2 T 8 • • P_CODE LENGTH(P_CODE) -------------89 -WRE-Q 8 PVC 23 DRT 8 SM-18277 8 SW-23116 8 WR 3/TT 3 8 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 11
SQL> select P_code, length(P_code) from product; • • • • P_CODE LENGTH(P_CODE) -------------11 QER/31 8 13 -Q 2/P 2 8 14 -Q 1/L 3 8 1546 -QQ 2 8 1558 -QW 1 8 2232/QTY 8 2232/QWE 8 2238/QPD 8 23109 -HB 8 23114 -AA 8 54778 -2 T 8 • • P_CODE LENGTH(P_CODE) -------------89 -WRE-Q 8 PVC 23 DRT 8 SM-18277 8 SW-23116 8 WR 3/TT 3 8 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 11
 Trimming data LTrim, Rtrim. . remove unwanted characters Format: RTRIM (string, ‘set’) Ltrim (string, ‘set’) Set is the collection of characters you want to trim INSS 651 12
Trimming data LTrim, Rtrim. . remove unwanted characters Format: RTRIM (string, ‘set’) Ltrim (string, ‘set’) Set is the collection of characters you want to trim INSS 651 12
 SQL> select P_code, length(rtrim (P_code, ' ')) from product; • • • • P_CODE LENGTH(RTRIM(P_CODE, '')) ----------------11 QER/31 8 13 -Q 2/P 2 8 14 -Q 1/L 3 8 1546 -QQ 2 8 1558 -QW 1 8 2232/QTY 8 2232/QWE 8 2238/QPD 8 23109 -HB 8 23114 -AA 8 54778 -2 T 8 • • P_CODE LENGTH(RTRIM(P_CODE, '')) ----------------89 -WRE-Q 8 PVC 23 DRT 8 SM-18277 8 SW-23116 8 WR 3/TT 3 7 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 13
SQL> select P_code, length(rtrim (P_code, ' ')) from product; • • • • P_CODE LENGTH(RTRIM(P_CODE, '')) ----------------11 QER/31 8 13 -Q 2/P 2 8 14 -Q 1/L 3 8 1546 -QQ 2 8 1558 -QW 1 8 2232/QTY 8 2232/QWE 8 2238/QPD 8 23109 -HB 8 23114 -AA 8 54778 -2 T 8 • • P_CODE LENGTH(RTRIM(P_CODE, '')) ----------------89 -WRE-Q 8 PVC 23 DRT 8 SM-18277 8 SW-23116 8 WR 3/TT 3 7 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 13
 Remove. From price • SQL> select ltrim(p_price, '. '), p_code from product; • • • • LTRIM(P_PRICE, '. ') P_CODE --------------------109. 99 11 QER/31 14. 99 13 -Q 2/P 2 17. 49 14 -Q 1/L 3 39. 95 1546 -QQ 2 43. 99 1558 -QW 1 109. 92 2232/QTY 99. 87 2232/QWE 38. 95 2238/QPD 9. 95 23109 -HB 14. 4 23114 -AA 4. 99 54778 -2 T • • LTRIM(P_PRICE, '. ') P_CODE --------------------256. 99 89 -WRE-Q 5. 87 PVC 23 DRT 6. 99 SM-18277 8. 45 SW-23116 119. 95 WR 3/TT 3 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 14
Remove. From price • SQL> select ltrim(p_price, '. '), p_code from product; • • • • LTRIM(P_PRICE, '. ') P_CODE --------------------109. 99 11 QER/31 14. 99 13 -Q 2/P 2 17. 49 14 -Q 1/L 3 39. 95 1546 -QQ 2 43. 99 1558 -QW 1 109. 92 2232/QTY 99. 87 2232/QWE 38. 95 2238/QPD 9. 95 23109 -HB 14. 4 23114 -AA 4. 99 54778 -2 T • • LTRIM(P_PRICE, '. ') P_CODE --------------------256. 99 89 -WRE-Q 5. 87 PVC 23 DRT 6. 99 SM-18277 8. 45 SW-23116 119. 95 WR 3/TT 3 • 16 rows selected. INSS 651 14
 INSTR function Allows searching for a string of characters, gives the position of the string but does Not cut off anything Format: Instr(string, start, occurrence) Start is the start of the string Occurrence is the position of occurrence that you want to search INSS 651 15
INSTR function Allows searching for a string of characters, gives the position of the string but does Not cut off anything Format: Instr(string, start, occurrence) Start is the start of the string Occurrence is the position of occurrence that you want to search INSS 651 15
 Search for first “/” in p_code SQL> select p_code, instr(p_code, '/') from product ; • • • • P_CODE INSTR(P_CODE, '/') ------------11 QER/31 6 13 -Q 2/P 2 6 14 -Q 1/L 3 6 1546 -QQ 2 0 1558 -QW 1 0 2232/QTY 5 2232/QWE 5 2238/QPD 5 23109 -HB 0 23114 -AA 0 54778 -2 T 0 • • P_CODE INSTR(P_CODE, '/') ------------89 -WRE-Q 0 PVC 23 DRT 0 SM-18277 0 SW-23116 0 WR 3/TT 3 4 • ; 16 rows selected. INSS 651 16
Search for first “/” in p_code SQL> select p_code, instr(p_code, '/') from product ; • • • • P_CODE INSTR(P_CODE, '/') ------------11 QER/31 6 13 -Q 2/P 2 6 14 -Q 1/L 3 6 1546 -QQ 2 0 1558 -QW 1 0 2232/QTY 5 2232/QWE 5 2238/QPD 5 23109 -HB 0 23114 -AA 0 54778 -2 T 0 • • P_CODE INSTR(P_CODE, '/') ------------89 -WRE-Q 0 PVC 23 DRT 0 SM-18277 0 SW-23116 0 WR 3/TT 3 4 • ; 16 rows selected. INSS 651 16
 Separate P_code in two parts: before _ and after _ for names that contain SQL> select p_code, substr(P_code, 1, instr(p_code, '/')) part 1 from product where p_code like '%/%'; • 2 3 • P_CODE PART 1 • ------- • 11 QER/31 11 QER/ • 13 -Q 2/P 2 13 -Q 2/ • 14 -Q 1/L 3 14 -Q 1/ • 2232/QTY 2232/ • 2232/QWE 2232/ • 2238/QPD 2238/ • WR 3/TT 3 WR 3/ • 7 rows selected. INSS 651 17
Separate P_code in two parts: before _ and after _ for names that contain SQL> select p_code, substr(P_code, 1, instr(p_code, '/')) part 1 from product where p_code like '%/%'; • 2 3 • P_CODE PART 1 • ------- • 11 QER/31 11 QER/ • 13 -Q 2/P 2 13 -Q 2/ • 14 -Q 1/L 3 14 -Q 1/ • 2232/QTY 2232/ • 2232/QWE 2232/ • 2238/QPD 2238/ • WR 3/TT 3 WR 3/ • 7 rows selected. INSS 651 17
 SQL> select p_code, substr(P_code, 1, instr(p_code, '/')-1) part 1 from product where p_code like '%/%'; 2 3 • P_CODE PART 1 • ------- • 11 QER/31 11 QER • 13 -Q 2/P 2 13 -Q 2 • 14 -Q 1/L 3 14 -Q 1 • 2232/QTY 2232 • 2232/QWE 2232 • 2238/QPD 2238 • WR 3/TT 3 WR 3 • 7 rows selected. INSS 651 18
SQL> select p_code, substr(P_code, 1, instr(p_code, '/')-1) part 1 from product where p_code like '%/%'; 2 3 • P_CODE PART 1 • ------- • 11 QER/31 11 QER • 13 -Q 2/P 2 13 -Q 2 • 14 -Q 1/L 3 14 -Q 1 • 2232/QTY 2232 • 2232/QWE 2232 • 2238/QPD 2238 • WR 3/TT 3 WR 3 • 7 rows selected. INSS 651 18
 Get the right part INSS 651 19
Get the right part INSS 651 19
 Remove the period from price INSS 651 20
Remove the period from price INSS 651 20
 GROUP BY (think of grouping as categorizing) Group by …. Having condition INSS 651 21
GROUP BY (think of grouping as categorizing) Group by …. Having condition INSS 651 21
 SUBQUERIES. Queries inside query There are times when you need information from a table to answer query related to the same table or another table INSS 651 22
SUBQUERIES. Queries inside query There are times when you need information from a table to answer query related to the same table or another table INSS 651 22
 Format: SQL>SELECT …. FROM WHERE colname 1 condition(SELECT col 2. . (SELECT. . )) INSS 651 23
Format: SQL>SELECT …. FROM WHERE colname 1 condition(SELECT col 2. . (SELECT. . )) INSS 651 23
 List customers whose balance is greater than the average balance of all customers Logic: • To answer this query we need to know average balance of all customers • We will have to put this in a sub query INSS 651 24
List customers whose balance is greater than the average balance of all customers Logic: • To answer this query we need to know average balance of all customers • We will have to put this in a sub query INSS 651 24
 List customers whose balance are greater than the average balance of all customers SQL> select * from customer where cust_balance > (Select avg(cust_balance) From customer); INSS 651 25
List customers whose balance are greater than the average balance of all customers SQL> select * from customer where cust_balance > (Select avg(cust_balance) From customer); INSS 651 25
 give the customer balance of customer whose order is 123 Logic: Before we can find balance of customer whose order is 123 we need to find the cust_numb first INSS 651 26
give the customer balance of customer whose order is 123 Logic: Before we can find balance of customer whose order is 123 we need to find the cust_numb first INSS 651 26
 JOINING TABLES when information needed is in more than one table, we need to join tables; WHERE clause in the select SQL statement creates a join. Note some queries can also be answered using sub query INSS 651 27
JOINING TABLES when information needed is in more than one table, we need to join tables; WHERE clause in the select SQL statement creates a join. Note some queries can also be answered using sub query INSS 651 27
 Rules FOR joining WHERE attribute 1 condition attribute 2 Ex: where employee. ssn=student. ssn Value(s) from one table are matched value(s) from other tables all matching values are attached allows joining of tables based on common attribute domains without the WHERE clause it will produce a Cartesian product also INSS 651 28
Rules FOR joining WHERE attribute 1 condition attribute 2 Ex: where employee. ssn=student. ssn Value(s) from one table are matched value(s) from other tables all matching values are attached allows joining of tables based on common attribute domains without the WHERE clause it will produce a Cartesian product also INSS 651 28
 Give the names of salesperson and their customers in maryland SQL>Select cust_name, Sales_name from Customer C, salesperson S where c. sales_numb= s. sales_numb’ And Upper(c. cust_st) =‘MD’; C & S are aliases for tables Customer and Salesperson respectively INSS 651 29
Give the names of salesperson and their customers in maryland SQL>Select cust_name, Sales_name from Customer C, salesperson S where c. sales_numb= s. sales_numb’ And Upper(c. cust_st) =‘MD’; C & S are aliases for tables Customer and Salesperson respectively INSS 651 29


