Lecture 5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Lecture 5. PFLT. Foreign Language learner’s strategies.
Lecture 5. PFLT. Foreign Language learner’s strategies.
 Strategies specific ‘attacks’ that we make on a given problem; moment by moment techniques that we employ to such problems posed by second language input and output.
Strategies specific ‘attacks’ that we make on a given problem; moment by moment techniques that we employ to such problems posed by second language input and output.
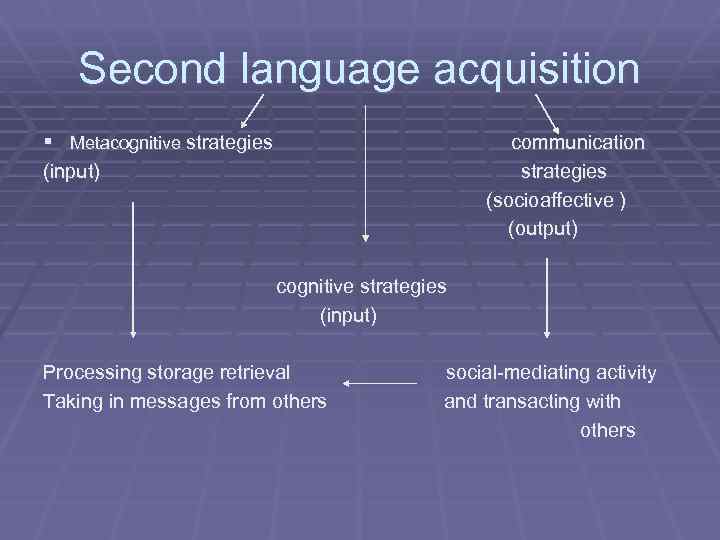 Second language acquisition § Metacognitive strategies communication strategies (socioaffective ) (output) (input) cognitive strategies (input) Processing storage retrieval Taking in messages from others social-mediating activity and transacting with others
Second language acquisition § Metacognitive strategies communication strategies (socioaffective ) (output) (input) cognitive strategies (input) Processing storage retrieval Taking in messages from others social-mediating activity and transacting with others
 a) b) c) Teaching learners how to learn is crucial! Learner strategies are the key to learner autonomy! To make learners successful means to teach them realization of successful strategies!
a) b) c) Teaching learners how to learn is crucial! Learner strategies are the key to learner autonomy! To make learners successful means to teach them realization of successful strategies!
 Learner strategy training ►I Teach them Metacognitive strategies. Centering their learning (overviewing and linking with already known: delaying ( speech production to focus on listening) Arranging and planning their learning (setting goals, identifying the purpose of the L task planning for a L task seeking practice opportunities) Evaluating their learning (selfmonitoring; selfevaluating)
Learner strategy training ►I Teach them Metacognitive strategies. Centering their learning (overviewing and linking with already known: delaying ( speech production to focus on listening) Arranging and planning their learning (setting goals, identifying the purpose of the L task planning for a L task seeking practice opportunities) Evaluating their learning (selfmonitoring; selfevaluating)
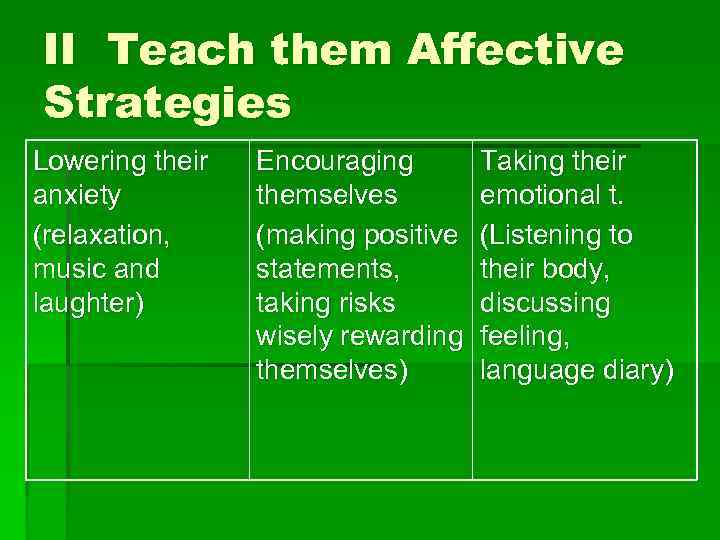 II Teach them Affective Strategies Lowering their anxiety (relaxation, music and laughter) Encouraging themselves (making positive statements, taking risks wisely rewarding themselves) Taking their emotional t. (Listening to their body, discussing feeling, language diary)
II Teach them Affective Strategies Lowering their anxiety (relaxation, music and laughter) Encouraging themselves (making positive statements, taking risks wisely rewarding themselves) Taking their emotional t. (Listening to their body, discussing feeling, language diary)
 III Teach them Social Strategies Asking questions (asking for clarification, verification, correction) Cooperating with others (with other language learners and proficient users) Empathizing with others (developing cultural understanding aware of others’ feelings and thoughts)
III Teach them Social Strategies Asking questions (asking for clarification, verification, correction) Cooperating with others (with other language learners and proficient users) Empathizing with others (developing cultural understanding aware of others’ feelings and thoughts)
 IV Teach them memory strategies Creating mental linkages (grouping, associating) Applying images and sounds (imagery, sem. mapping, keywords) Employing action (using physical response, mechanical techniques)
IV Teach them memory strategies Creating mental linkages (grouping, associating) Applying images and sounds (imagery, sem. mapping, keywords) Employing action (using physical response, mechanical techniques)
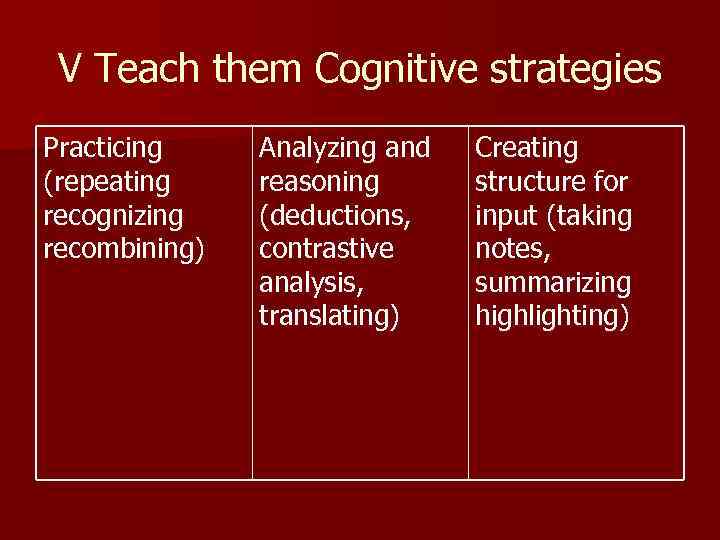 V Teach them Cognitive strategies Practicing (repeating recognizing recombining) Analyzing and reasoning (deductions, contrastive analysis, translating) Creating structure for input (taking notes, summarizing highlighting)
V Teach them Cognitive strategies Practicing (repeating recognizing recombining) Analyzing and reasoning (deductions, contrastive analysis, translating) Creating structure for input (taking notes, summarizing highlighting)
 VI Teach them compensation strategies Guessing intelligently (using linguistic and other clues) Overcoming limitations in speaking and writing (switching to mother tongue, getting help, using mime or gesture, avoiding communicating partially or totally, using synonym, selecting a topic)
VI Teach them compensation strategies Guessing intelligently (using linguistic and other clues) Overcoming limitations in speaking and writing (switching to mother tongue, getting help, using mime or gesture, avoiding communicating partially or totally, using synonym, selecting a topic)
 Characteristics of a good language learner. o o o o find their own way, taking charge of their learning. organize information about language are creative, developing a ‘feel’ for the language by experimenting with its grammar and words. make their own opportunities for practice in using the language inside and outside the classroom learn to live with uncertainty by not getting flustered and by continuing to talk or listen without understanding every word use mnemonics and other memory strategies to recall what has been learned make errors work for them and not against them use linguistic knowledge, including knowledge of their first language, in learning a second language use contextual cues to help them in comprehension learn to make intelligent guesses learn chunks of language as wholes and formalized routines to help them perform ‘beyond their competence’ learn certain tricks that help to keep conversations going learn certain production strategies to fill in gaps in their own competence learn different styles of speech and writing and learn to vary their language according to the formality of the situation.
Characteristics of a good language learner. o o o o find their own way, taking charge of their learning. organize information about language are creative, developing a ‘feel’ for the language by experimenting with its grammar and words. make their own opportunities for practice in using the language inside and outside the classroom learn to live with uncertainty by not getting flustered and by continuing to talk or listen without understanding every word use mnemonics and other memory strategies to recall what has been learned make errors work for them and not against them use linguistic knowledge, including knowledge of their first language, in learning a second language use contextual cues to help them in comprehension learn to make intelligent guesses learn chunks of language as wholes and formalized routines to help them perform ‘beyond their competence’ learn certain tricks that help to keep conversations going learn certain production strategies to fill in gaps in their own competence learn different styles of speech and writing and learn to vary their language according to the formality of the situation.
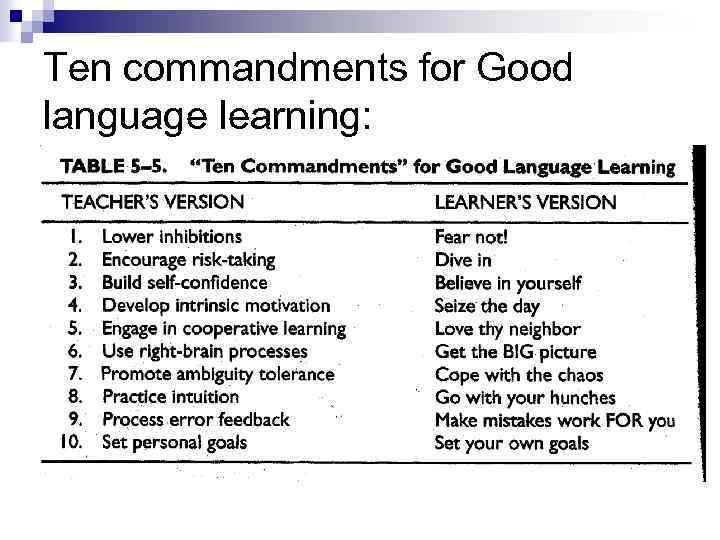 Ten commandments for Good language learning:
Ten commandments for Good language learning:
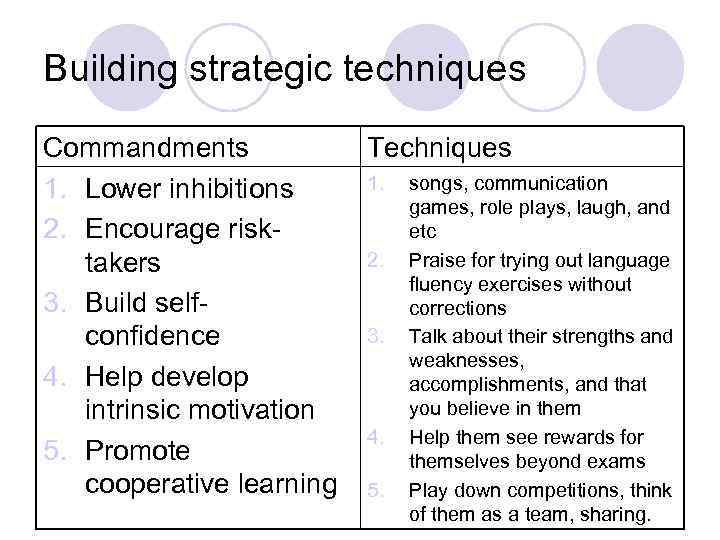 Building strategic techniques Commandments 1. Lower inhibitions 2. Encourage risktakers 3. Build selfconfidence 4. Help develop intrinsic motivation 5. Promote cooperative learning Techniques 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. songs, communication games, role plays, laugh, and etc Praise for trying out language fluency exercises without corrections Talk about their strengths and weaknesses, accomplishments, and that you believe in them Help them see rewards for themselves beyond exams Play down competitions, think of them as a team, sharing.
Building strategic techniques Commandments 1. Lower inhibitions 2. Encourage risktakers 3. Build selfconfidence 4. Help develop intrinsic motivation 5. Promote cooperative learning Techniques 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. songs, communication games, role plays, laugh, and etc Praise for trying out language fluency exercises without corrections Talk about their strengths and weaknesses, accomplishments, and that you believe in them Help them see rewards for themselves beyond exams Play down competitions, think of them as a team, sharing.
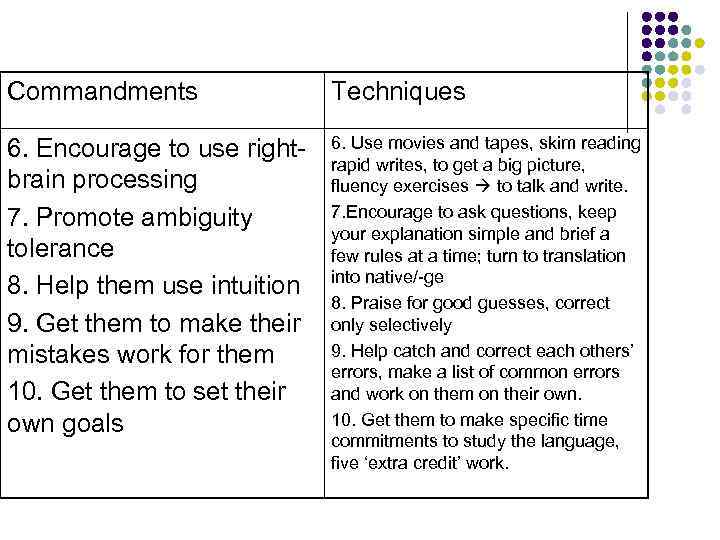 Commandments Techniques 6. Encourage to use rightbrain processing 7. Promote ambiguity tolerance 8. Help them use intuition 9. Get them to make their mistakes work for them 10. Get them to set their own goals 6. Use movies and tapes, skim reading rapid writes, to get a big picture, fluency exercises to talk and write. 7. Encourage to ask questions, keep your explanation simple and brief a few rules at a time; turn to translation into native/-ge 8. Praise for good guesses, correct only selectively 9. Help catch and correct each others’ errors, make a list of common errors and work on them on their own. 10. Get them to make specific time commitments to study the language, five ‘extra credit’ work.
Commandments Techniques 6. Encourage to use rightbrain processing 7. Promote ambiguity tolerance 8. Help them use intuition 9. Get them to make their mistakes work for them 10. Get them to set their own goals 6. Use movies and tapes, skim reading rapid writes, to get a big picture, fluency exercises to talk and write. 7. Encourage to ask questions, keep your explanation simple and brief a few rules at a time; turn to translation into native/-ge 8. Praise for good guesses, correct only selectively 9. Help catch and correct each others’ errors, make a list of common errors and work on them on their own. 10. Get them to make specific time commitments to study the language, five ‘extra credit’ work.
 Seminar questions. I 1. What is a FL Learner strategy and which types of strategies are distinguished in the field of SLA? 2. Describe a ‘good’ language learner in terms of personal characteristics, styles, and strategies. 3. What is the most important goal of language training? 4. Is it worth opening up students’ minds to the possibility that they may not be engaging in strategies that could make them successful? How we can do this? 5. What is highlighted in a) metacognitive b) affective c) social d) memory e) cognitive f) compensation strategies? 6. Which ten rules are the principles hints about successful learning and communications strategies ? 7. Illustrate each commandment with strategic techniques helpful for both teachers and learners
Seminar questions. I 1. What is a FL Learner strategy and which types of strategies are distinguished in the field of SLA? 2. Describe a ‘good’ language learner in terms of personal characteristics, styles, and strategies. 3. What is the most important goal of language training? 4. Is it worth opening up students’ minds to the possibility that they may not be engaging in strategies that could make them successful? How we can do this? 5. What is highlighted in a) metacognitive b) affective c) social d) memory e) cognitive f) compensation strategies? 6. Which ten rules are the principles hints about successful learning and communications strategies ? 7. Illustrate each commandment with strategic techniques helpful for both teachers and learners



