Question 22 - Lecture04.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Lecture 4_ consumer behavior Chapter CONSUMER BEHAVIOR Associate professor of Plekhanov REA marketing department Irina I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 1 Slide 5 -2

AFTER THIS LECTURE YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: • Understand Stages in the consumer decision process. • Evaluate three variations of the consumer decision process: routine, limited, and extended problem solving. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 2 Slide 5 -5

AFTER THIS LECTURE YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: • Know the psychological influences affect on consumer behavior, particularly purchase decision processes. • Explain major sociocultural influences on consumer behavior and their effects on purchase decisions. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 3 Slide 5 -6

AFTER THIS LECTURE YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: • Recognize how marketers can use knowledge of consumer behavior to better understand influence individual and family purchases. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 4 Slide 5 -7

CONSUMER PURCHASE DECISION PROCESS • Consumer Behavior • Purchase Decision Process • Problem Recognition: Perceiving a Need Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 5 Slide 5 -10

Consumer Behavior Consumer behavior is the actions a person takes in purchasing and using products and services, including the mental and social processes that come before and after these actions. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 6 Slide 5 -78
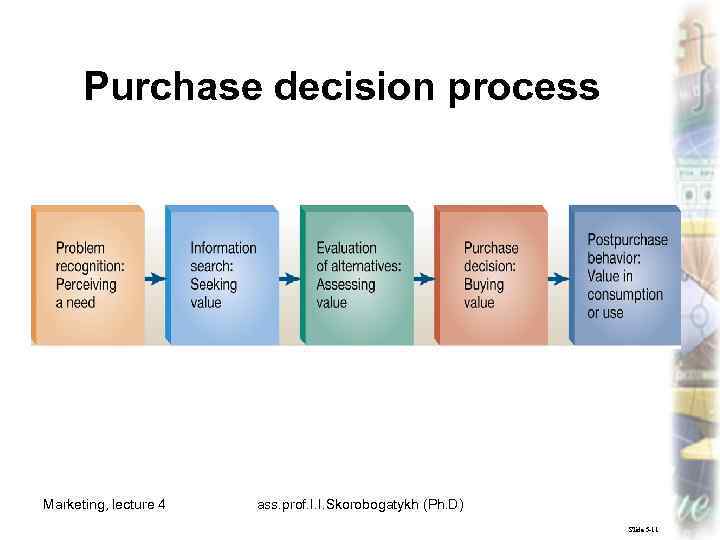
Purchase decision process Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 7 Slide 5 -11

Purchase Decision Process The stages a buyer passes through in making choices about which products and services to buy is the purchase decision process. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 8 Slide 5 -79

CONSUMER PURCHASE DECISION PROCESS • Information Search: Seeking Value § Internal Search § External Search • Personal Sources • Public Sources • Market-Dominated Sources Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 9 Slide 5 -12

CONSUMER PURCHASE DECISION PROCESS • Alternative Evaluation: Assessing Value § Evaluative Criteria § Evoked Set • Purchase Decision: Buying Value • Post-purchase Behavior: Value in Consumption or Use Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 10 Slide 5 -14
CONSUMER PURCHASE DECISION PROCESS • Involvement and Problem-Solving Variations § Involvement § Routine Problem Solving § Limited Problem Solving § Extended Problem Solving • Situational Influences (Ph. D) ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh Marketing, lecture 4 11 Slide 5 -16

Involvement The level of involvement a consumer has in a particular purchase depends on the personal, social, and economic consequences of that purchase to the consumer. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 12 Slide 5 -80
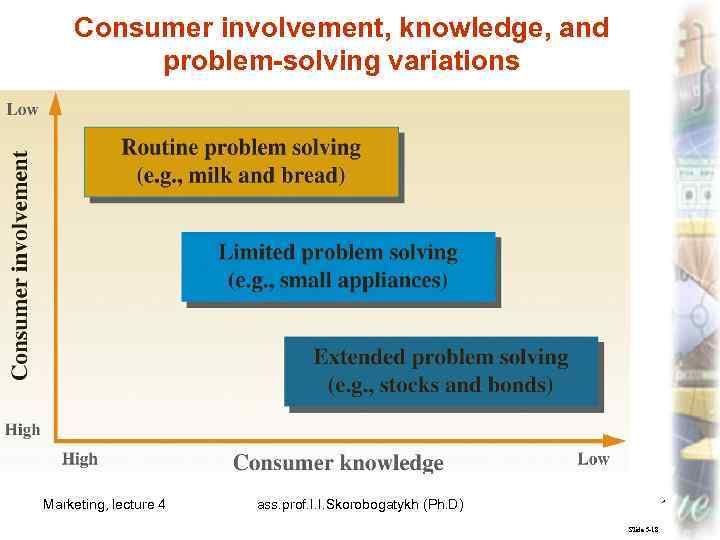
Consumer involvement, knowledge, and problem-solving variations Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 13 Slide 5 -18
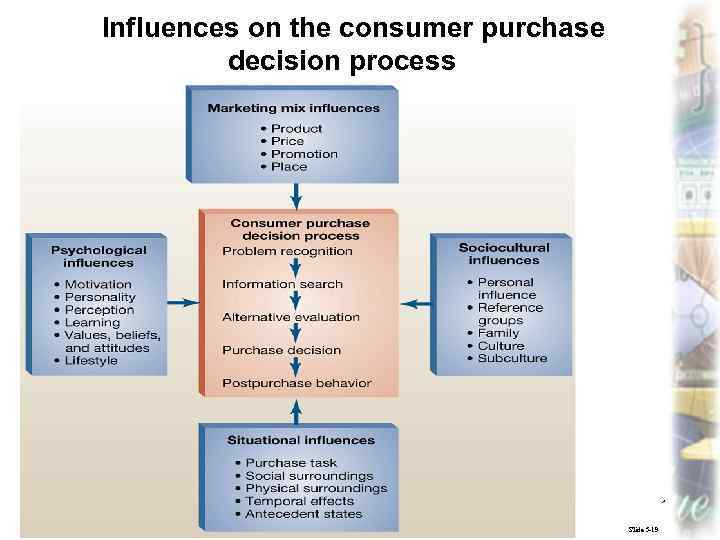
Influences on the consumer purchase decision process Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 14 Slide 5 -19

PSYCHOLOGICAL INFLUENCES ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR • Motivation and Personality § Motivation § Personality • Physiological Needs • Self-Concept • Safety Needs • Social Needs • Personal Needs • Self-Actualization Needs Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 15 Slide 5 -22

Motivation is the energizing force that stimulates behavior to satisfy a need. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 16 Slide 5 -81
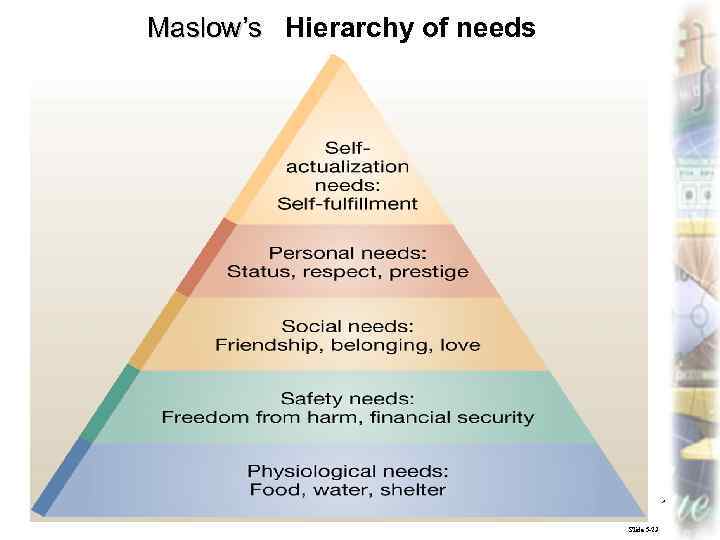
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 17 Slide 5 -23

PSYCHOLOGICAL INFLUENCES ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR • Perception § Selective Perception • Selective Exposure • Selective Comprehension • Selective Retention § Perceived Risk ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) Marketing, lecture 4 18 Slide 5 -24

Perception is the process by which an individual selects, organizes, and interprets information to create a meaningful picture of the world. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 19 Slide 5 -83
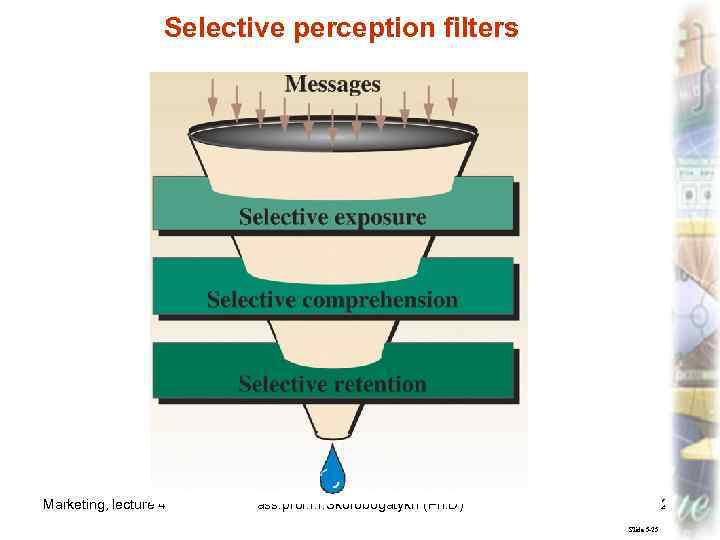
Selective perception filters Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 20 Slide 5 -25

PSYCHOLOGICAL INFLUENCES ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR • Values, Beliefs, and Attitudes § Attitude Formation • Attitude • Beliefs § Attitude Change Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 21 Slide 5 -31

PSYCHOLOGICAL INFLUENCES ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR • Lifestyle § Psychographics § VALS™ Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 22 Slide 5 -34
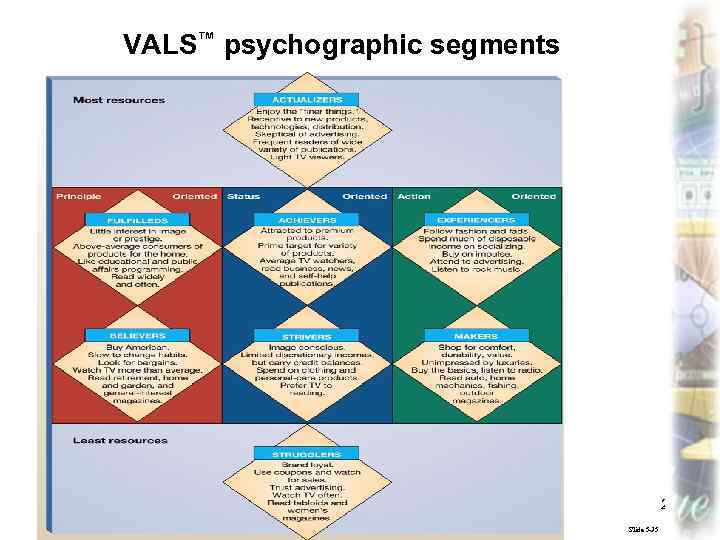
VALS™ psychographic segments Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 23 Slide 5 -35

SOCIOCULTURAL INFLUENCES ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR • Personal Influence § Opinion Leaders § Word of Mouth • Reference Groups § Membership Group § Aspiration Group § Dissociative Group Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 24 Slide 5 -39

Opinion Leaders Opinion leaders individuals who have social influence over others. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 25 Slide 5 -89

Word of Mouth People influencing each other during conversations is called word of mouth. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 26 Slide 5 -90

Reference Groups Reference groups are people to whom an individual looks as a basis for self-appraisal or as a source of personal standards. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 27 Slide 5 -91
SOCIOCULTURAL INFLUENCES ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR • Family Influence § Consumer Socialization § Family Life Cycle § Family Decision Making Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 28 Slide 5 -43
Family Life Cycle The family life cycle concept describes the distinct phases that a family progresses through from formation to retirement, each phase bringing with it identifiable purchasing behaviors. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 29 Slide 5 -92

SOCIOCULTURAL INFLUENCES ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR • Culture and Subculture § Subcultures § African-American Buying Patterns § Hispanic Buying Patterns § Asian-American Buying Patterns § What subcultures in RF do you know? Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 30 Slide 5 -46

Subcultures Subgroups within the larger, or national, culture with unique values, ideas, and attitudes are referred to as subcultures. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 31 Slide 5 -93

Personality refers to a person’s consistent behaviors or responses to recurring situations. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 32 Slide 5 -82

Perceived Risk Perceived risk represents the anxieties felt because the consumer cannot anticipate the outcomes of a purchase but believes that there may be negative consequences. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 33 Slide 5 -84

Learning refers to those behaviors that result from (1) repeated experience and (2) reasoning. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 34 Slide 5 -85

Brand Loyalty Brand loyalty is a favorable attitude toward and consistent purchase of a single brand over time. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 35 Slide 5 -86

Attitude An attitude is a “learned predisposition to respond to an object or class of objects in a consistently favorable or unfavorable way. ” Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 36 Slide 5 -87

Beliefs are one’s perception of how a product or brand performs on different attributes. Marketing, lecture 4 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D) 37 Slide 5 -88
Question 22 - Lecture04.ppt