Lecture #4 Layouts and Basic Widgets Layouts List


Lecture #4 Layouts and Basic Widgets
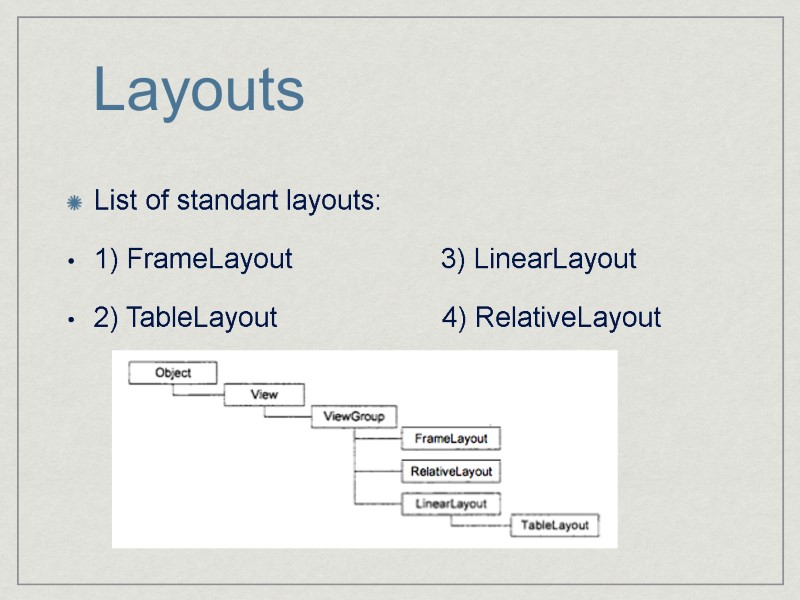
Layouts List of standart layouts: 1) FrameLayout 3) LinearLayout 2) TableLayout 4) RelativeLayout

FrameLayout Views are upper-left corner aligned(over another)

LinearLayout Aligns in either VERTICAL or HORIZONTAL direction ex: android:orientation = “horizontal” One after another in one row(height of a row = height of highest subview)
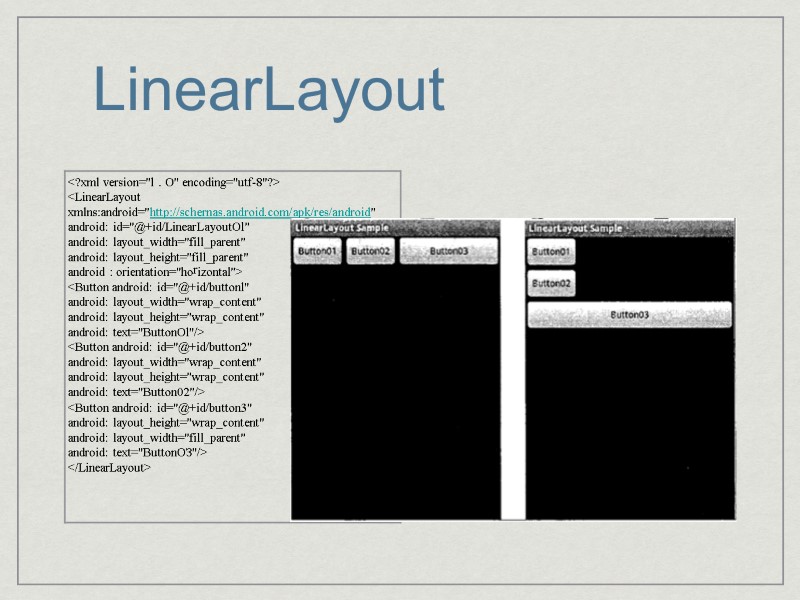
LinearLayout

LinearLayout: weight

TableLayout Represents view in terms of ROWS & COLUMNS TableRow object is used to define a single row Single row can contain several or no cells. Any object of ViewGroup can be putted in a cell
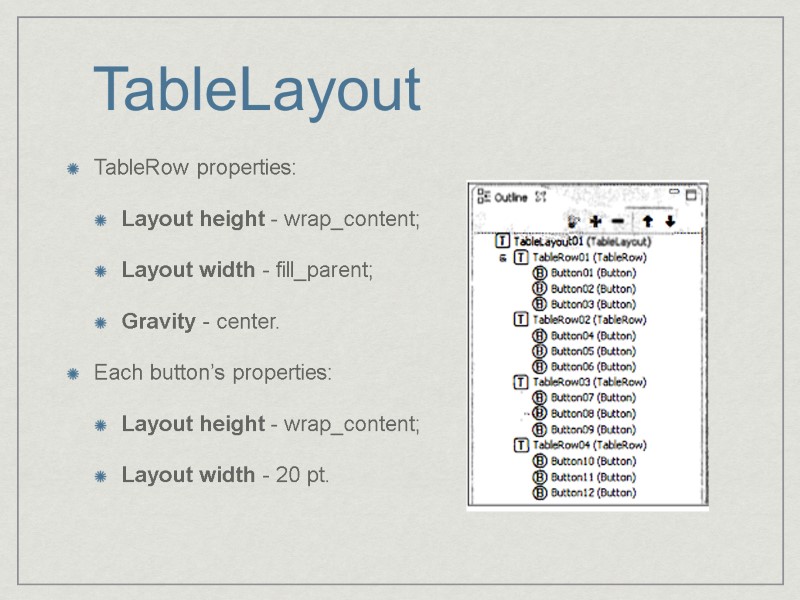
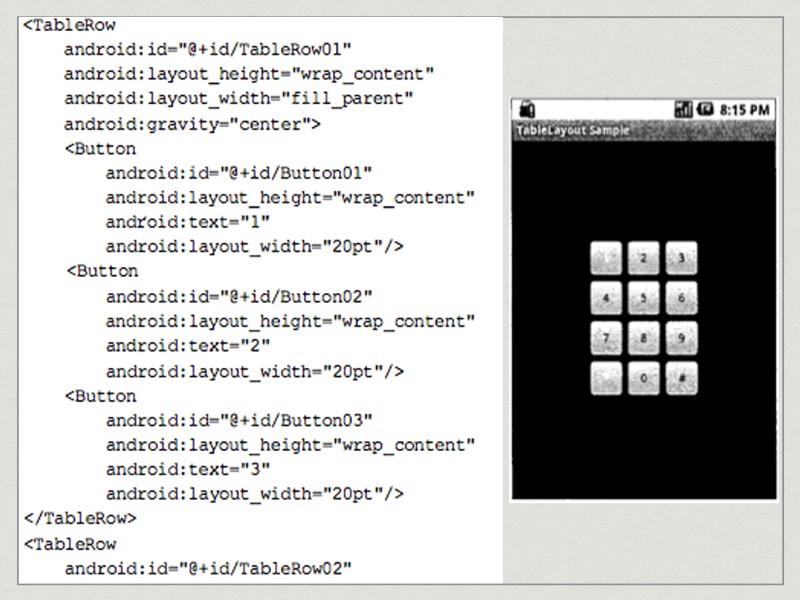
TableLayout TableRow properties: Layout height - wrap_content; Layout width - fill_parent; Gravity - center. Each button’s properties: Layout height - wrap_content; Layout width - 20 pt.

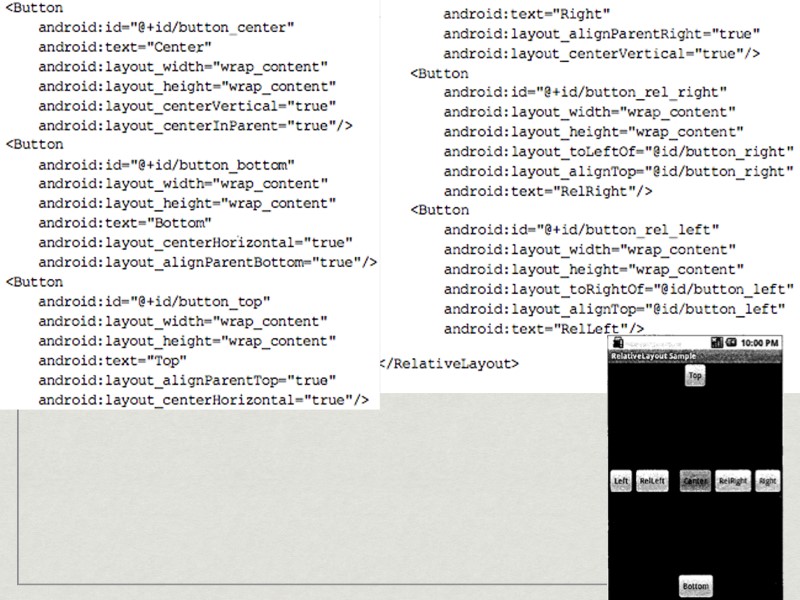
RelativeLayout Aligns with respect to parent view or its neighbors

Basics Widgets TextView EditText ScrollView HorizontalScrollView ImageView Button CheckBox ToggleButton RadioButton ImageButton TabHost TabWidget ProgressBar RatingBar SeekBar AnalogClock DigitalClock Chronometer

TextView From XML layout: android:text="Hello, Android! From Java Code: TextView text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.t2) ; text.setText("Hello, Android!"); Multilingual: android: text="@string/text_hello" TextView text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.t2) ; text.setText(R.string.text_hello); );

android:textSize px - pixels dp - (density-independent pixels) sp - (scale-independent pixels) in - inches pt - 1/72 inch mm - millimeters android:textStyle normal, bold, italic android:textColor #RGB, #RRGGBB, #ARGB, #AARRGGBB A-alpha(opacity)

EditText Is designed to input/retrieve text information Methods: - getText() - returns text from EditText field - selectAll() - selects whole text in a window - setSelection(int start, int stop) - selects an area from start to stop - setSelection(int index) - put carriage(cursor) at index Most methods are overridden from TextView class
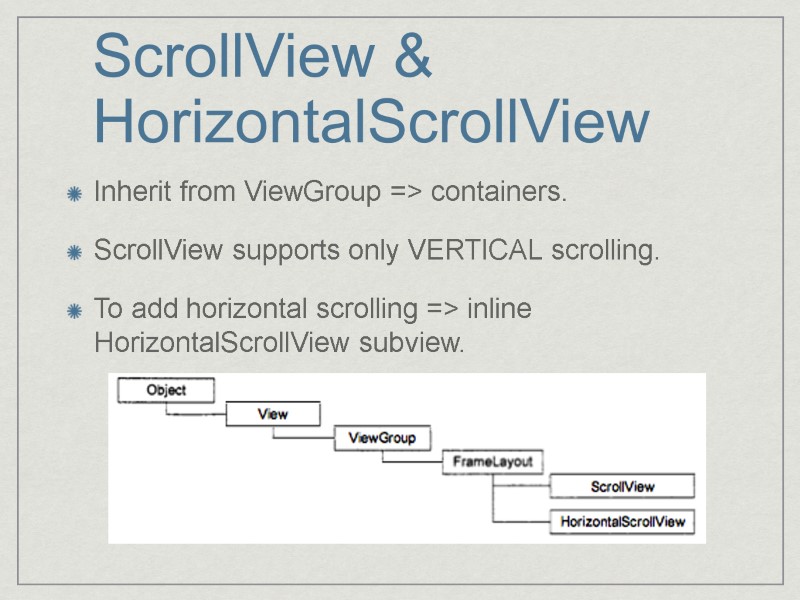
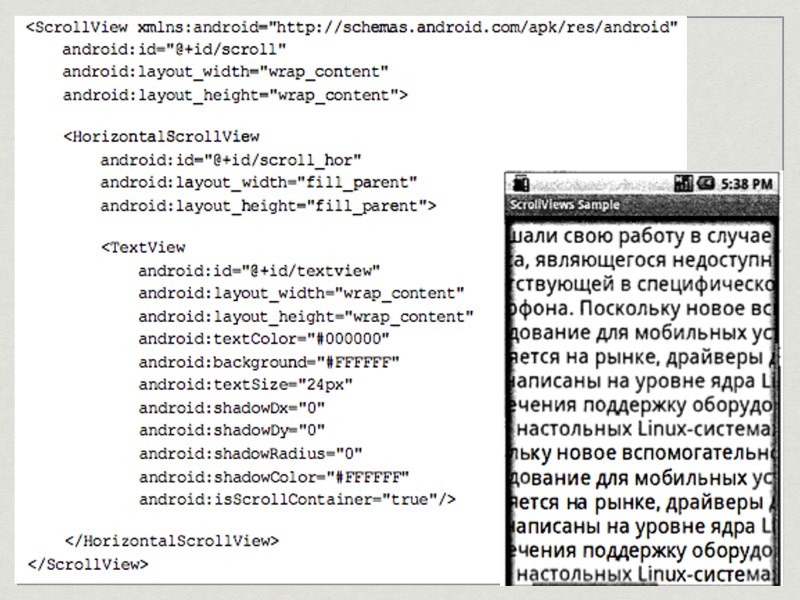
ScrollView & HorizontalScrollView Inherit from ViewGroup => containers. ScrollView supports only VERTICAL scrolling. To add horizontal scrolling => inline HorizontalScrollView subview.

ImageView Graphics, icons, UI, ... android:src = “@drawable/sdu” Methods: - setImageResource(int resId) => from resources - setImageURI(Uri uri) => Uniform Resource Ident.. - setImageBitmap(Bitmap bitmap) => raster graphics or bitmap loader - setMaxHeight(), setMaxWidth(), getScaleType(), ..
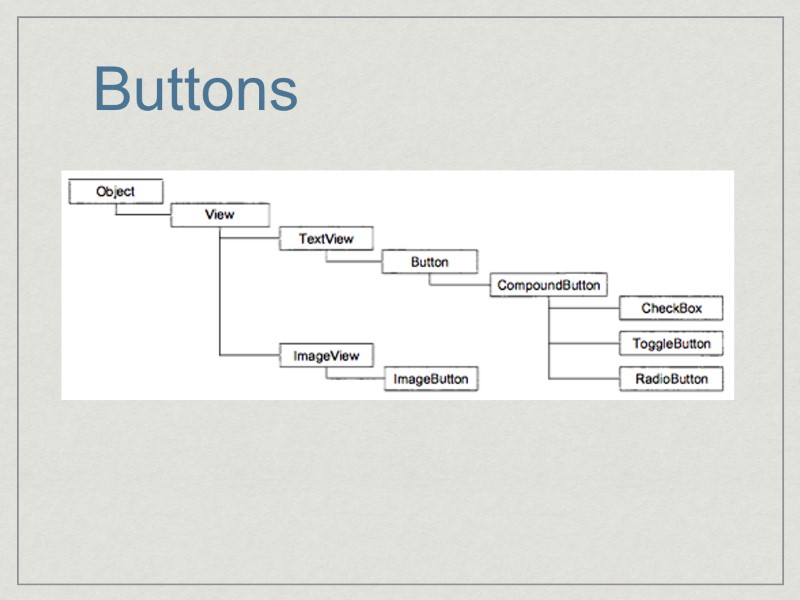
Buttons

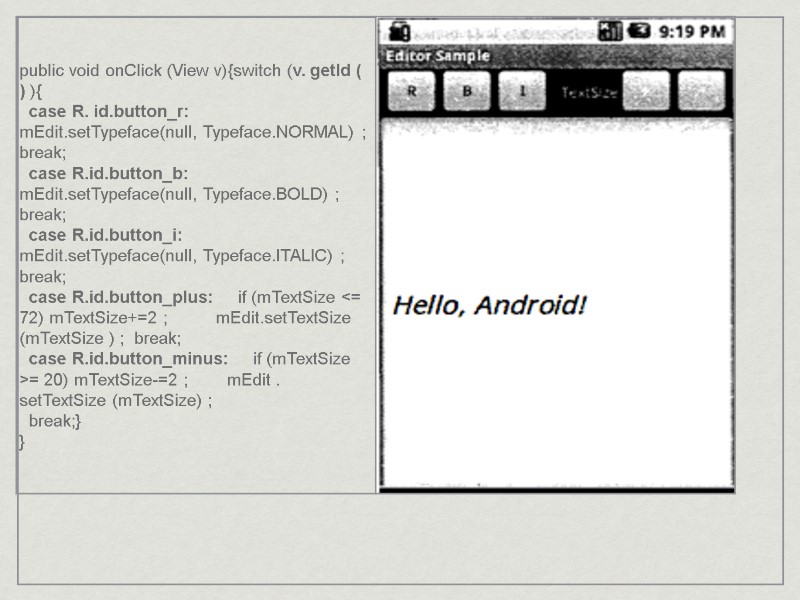
Button generally onClick event handling is used. final Button b =(Button) findViewById (R. id.but) ;
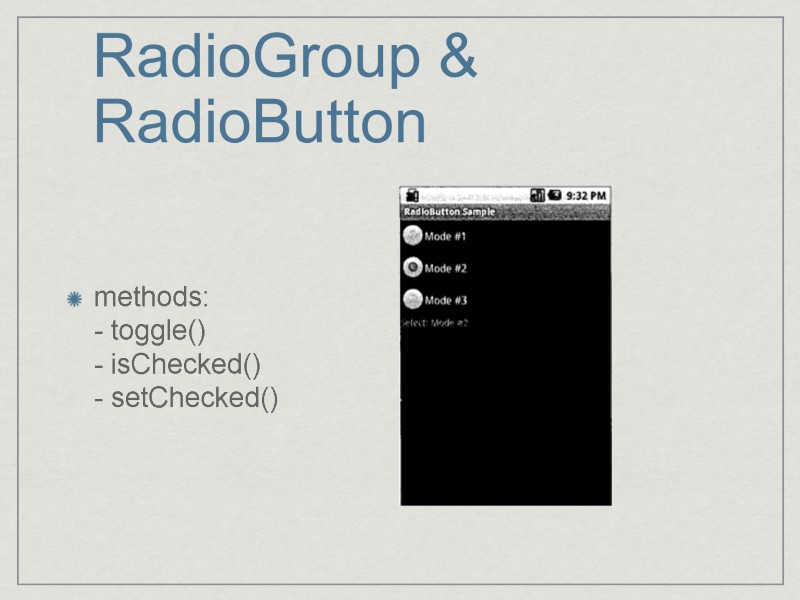
RadioGroup & RadioButton methods: - toggle() - isChecked() - setChecked()
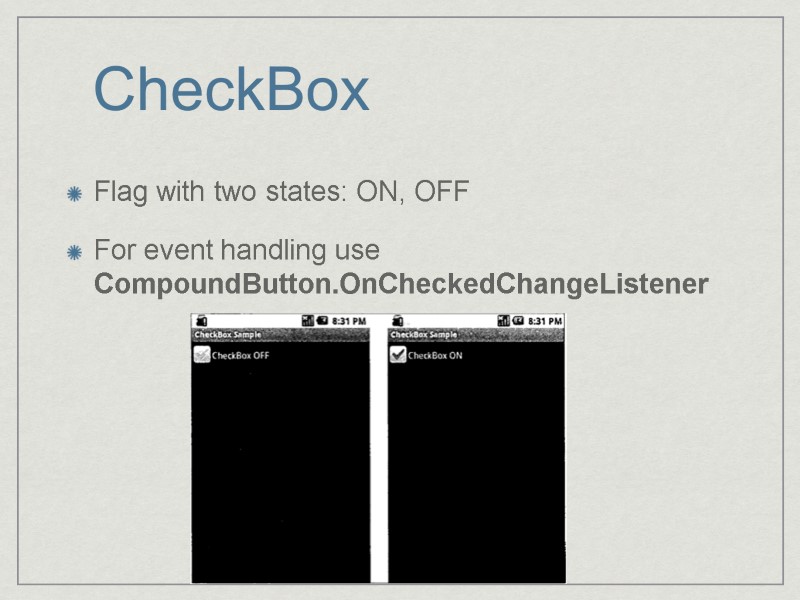
CheckBox Flag with two states: ON, OFF For event handling use CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener

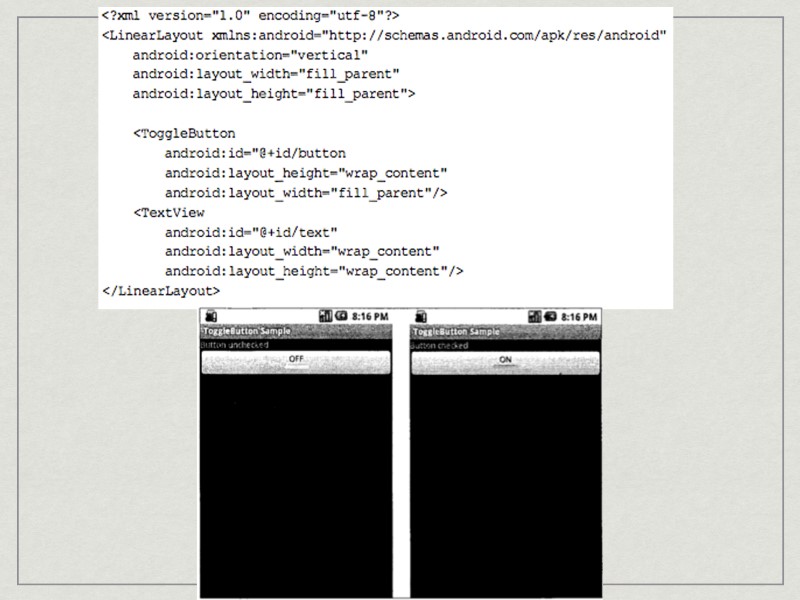
ToggleButton Button with two conditions: ON/OFF Usual LED indicator, when ON -> Green Light Main properties: android:textOff -> setTextOff() android:textOn -> setTextOn() setChecked(boolean checked) main action -> onCheckedChanged()
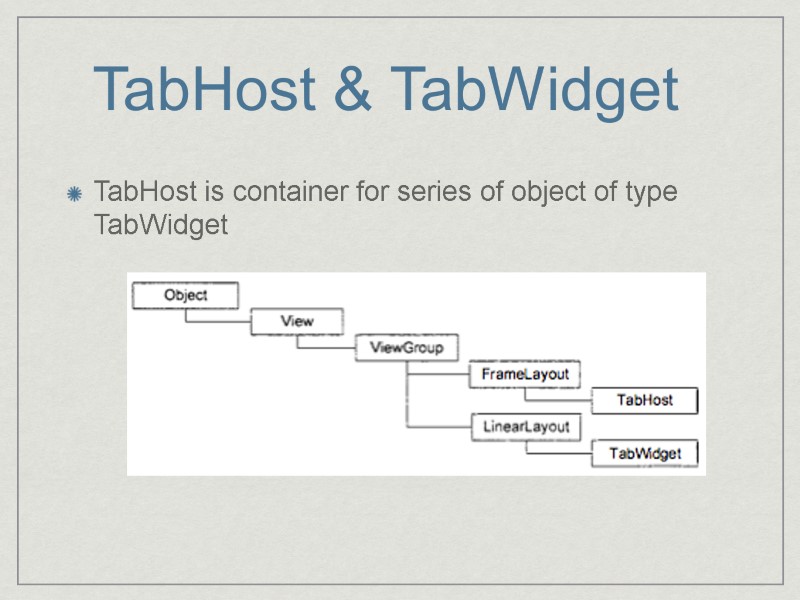
TabHost & TabWidget TabHost is container for series of object of type TabWidget

TabHost - setup() - initializes tab container(before findVieById()) - addTab() - add new tab - setCurrentTab() - front view for a tab Tabs have tabulation, information filling. Has to be defined in TabSpec: TabHost .TabSpec spec = tabs.newТabSpec ("tagl"); spec.setContent(R.id.tabPage1) ; spec.setIndicator("Document 1") ; tabs.addTab(spec) ;

Read the rest at home Book name: “Голощапов А. Л. - Google Android программирование для мобильных устройств - 2011” Available at: vk.com/sduandroid Chapter 5 and 6
16816-lecture_4_widgets.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

