a42734afc9c649b628b0ac266c15bbe8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Lecture 4 a: Communication and Networking CSCI 102 - Introduction to Information Technology B ITCS 905 - Fundamentals of Information Technology
Lecture 4 a: Communication and Networking CSCI 102 - Introduction to Information Technology B ITCS 905 - Fundamentals of Information Technology
 Overview Network standards and standardization bodies The ISO 7 -layer reference model in general and its instantiation in TCP/IP Circuit switching and packet switching Streams and datagrams
Overview Network standards and standardization bodies The ISO 7 -layer reference model in general and its instantiation in TCP/IP Circuit switching and packet switching Streams and datagrams
 Overview Physical layer networking concepts Theoretical basis Transmission media Standards Data link layer concepts Framing Error control Flow control
Overview Physical layer networking concepts Theoretical basis Transmission media Standards Data link layer concepts Framing Error control Flow control
 Standards and Organisations. International: ITU-T: International Telecommunications Union - Telecommunications Standardization Sector Telephone and data communications Formerly the CCITT ITU-R: Radiocommunications Sector Radio Frequencies Formerly the CCIR
Standards and Organisations. International: ITU-T: International Telecommunications Union - Telecommunications Standardization Sector Telephone and data communications Formerly the CCITT ITU-R: Radiocommunications Sector Radio Frequencies Formerly the CCIR
 Standards and Organisations. International: ISO - International Standards Organisation for all communication types IETF – Internet Engineering Task Force
Standards and Organisations. International: ISO - International Standards Organisation for all communication types IETF – Internet Engineering Task Force
 Standards and Organisations American ANSI: American National Standards Institute for data communications EIA: Electrical Industries Association for interfaces, connectors, facsimile, media IEEE: Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers specifically for 802 LAN standards NIST: National Institute of Standards and Technology the all American equivalent to the ISO (of course!!)
Standards and Organisations American ANSI: American National Standards Institute for data communications EIA: Electrical Industries Association for interfaces, connectors, facsimile, media IEEE: Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers specifically for 802 LAN standards NIST: National Institute of Standards and Technology the all American equivalent to the ISO (of course!!)
 The OSI Stack Proposed by the International Standards Organisation (ISO) and other standards bodies Its a layered approach to network protocols involving encapsulation of packets at each level of the stack and the sub-layers
The OSI Stack Proposed by the International Standards Organisation (ISO) and other standards bodies Its a layered approach to network protocols involving encapsulation of packets at each level of the stack and the sub-layers
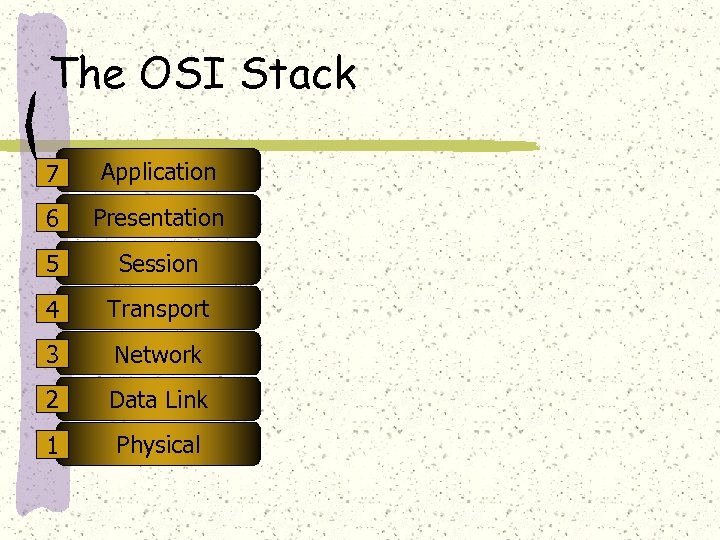 The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical
The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical
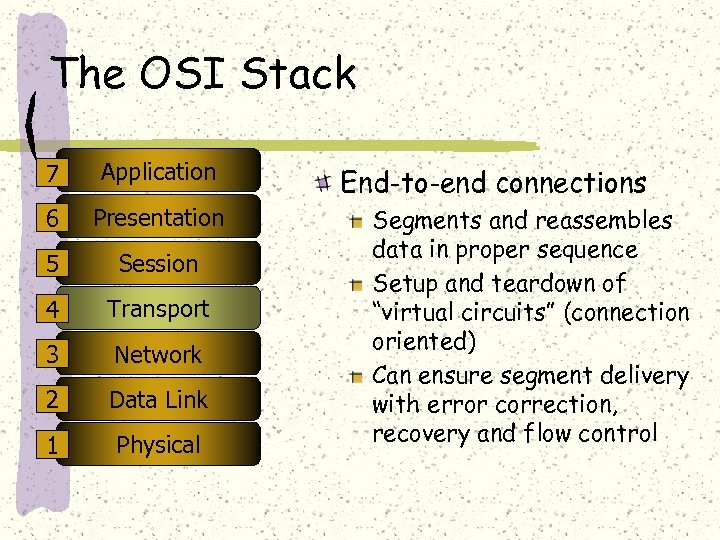 The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical End-to-end connections Segments and reassembles data in proper sequence Setup and teardown of “virtual circuits” (connection oriented) Can ensure segment delivery with error correction, recovery and flow control
The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical End-to-end connections Segments and reassembles data in proper sequence Setup and teardown of “virtual circuits” (connection oriented) Can ensure segment delivery with error correction, recovery and flow control
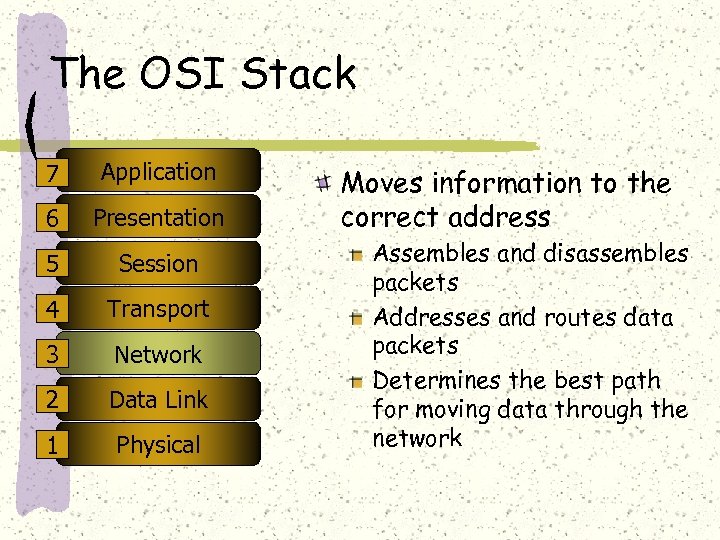 The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical Moves information to the correct address Assembles and disassembles packets Addresses and routes data packets Determines the best path for moving data through the network
The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical Moves information to the correct address Assembles and disassembles packets Addresses and routes data packets Determines the best path for moving data through the network
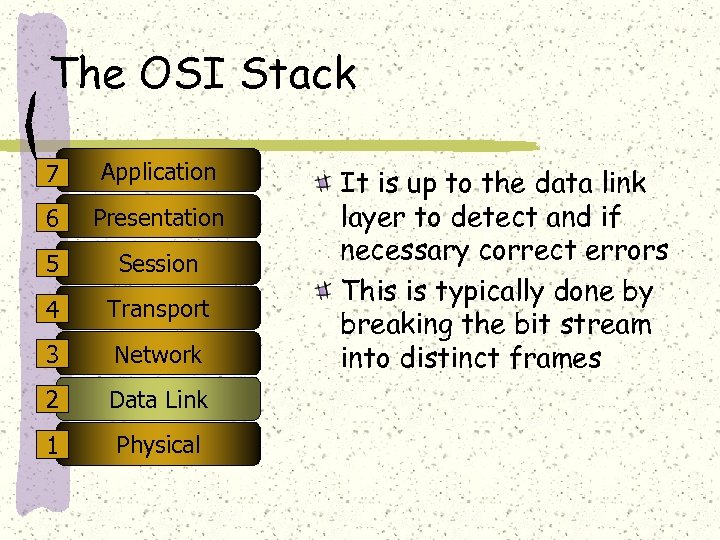 The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical It is up to the data link layer to detect and if necessary correct errors This is typically done by breaking the bit stream into distinct frames
The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical It is up to the data link layer to detect and if necessary correct errors This is typically done by breaking the bit stream into distinct frames
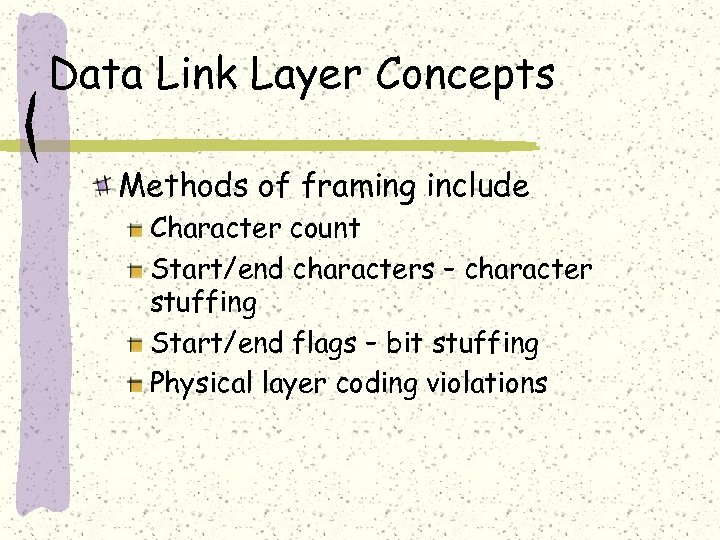 Data Link Layer Concepts Methods of framing include Character count Start/end characters – character stuffing Start/end flags – bit stuffing Physical layer coding violations
Data Link Layer Concepts Methods of framing include Character count Start/end characters – character stuffing Start/end flags – bit stuffing Physical layer coding violations
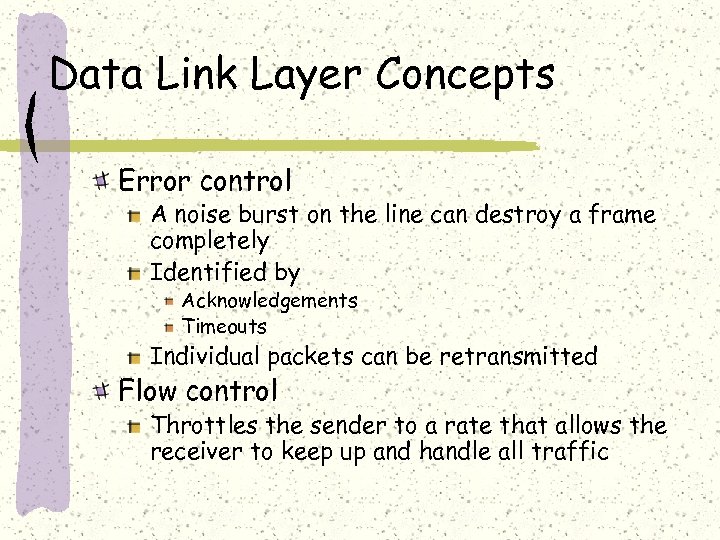 Data Link Layer Concepts Error control A noise burst on the line can destroy a frame completely Identified by Acknowledgements Timeouts Individual packets can be retransmitted Flow control Throttles the sender to a rate that allows the receiver to keep up and handle all traffic
Data Link Layer Concepts Error control A noise burst on the line can destroy a frame completely Identified by Acknowledgements Timeouts Individual packets can be retransmitted Flow control Throttles the sender to a rate that allows the receiver to keep up and handle all traffic
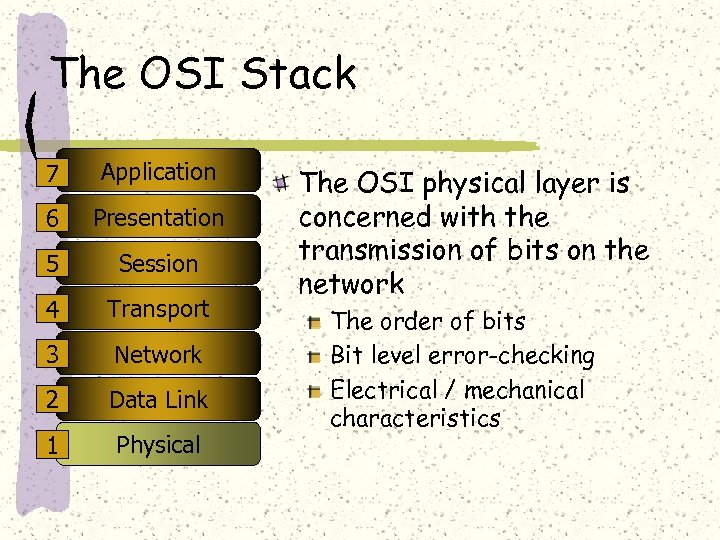 The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical The OSI physical layer is concerned with the transmission of bits on the network The order of bits Bit level error-checking Electrical / mechanical characteristics
The OSI Stack 7 Application 6 Presentation 5 Session 4 Transport 3 Network 2 Data Link 1 Physical The OSI physical layer is concerned with the transmission of bits on the network The order of bits Bit level error-checking Electrical / mechanical characteristics
 Network Transmission Media To be propagated (sent) from one location to another, a signal must travel along a physical path The physical path that is used to carry a signal between a signal transmitter and a signal receiver is called the "transmission medium"
Network Transmission Media To be propagated (sent) from one location to another, a signal must travel along a physical path The physical path that is used to carry a signal between a signal transmitter and a signal receiver is called the "transmission medium"
 Network Transmission Media There are two types of transmission media Guided media Unguided media
Network Transmission Media There are two types of transmission media Guided media Unguided media
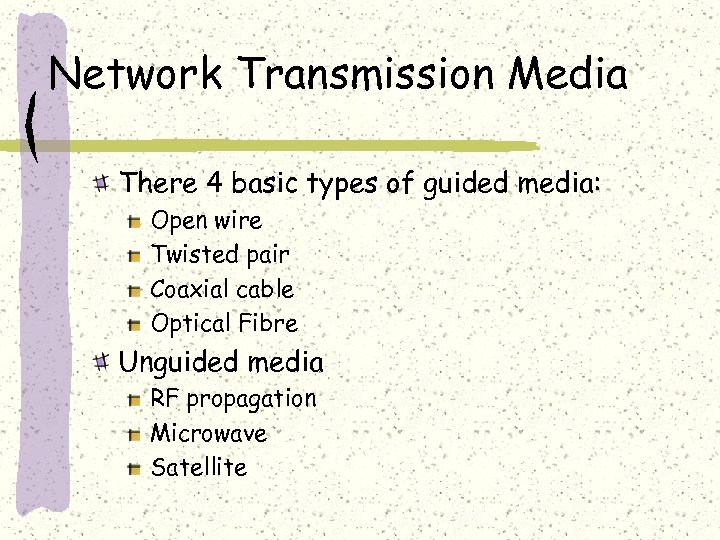 Network Transmission Media There 4 basic types of guided media: Open wire Twisted pair Coaxial cable Optical Fibre Unguided media RF propagation Microwave Satellite
Network Transmission Media There 4 basic types of guided media: Open wire Twisted pair Coaxial cable Optical Fibre Unguided media RF propagation Microwave Satellite
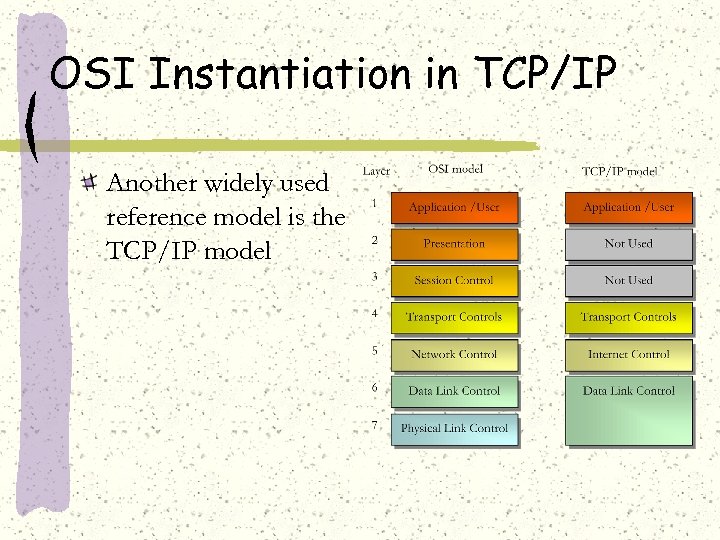 OSI Instantiation in TCP/IP Another widely used reference model is the TCP/IP model
OSI Instantiation in TCP/IP Another widely used reference model is the TCP/IP model
 Principles Used to Determine Layers Level of conception Accurately defined duty Internationally standardised protocols Minimal information flow across layer boundaries Number of layers
Principles Used to Determine Layers Level of conception Accurately defined duty Internationally standardised protocols Minimal information flow across layer boundaries Number of layers


