Theme 2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Lecture 3. The Correlation of International and National Law
Lecture 3. The Correlation of International and National Law
 Questions to discuss: § Dualist and monist theories. § The attitude of international law to municipal law. § The attitude of national legal systems to international law. § Public international law and private international law.
Questions to discuss: § Dualist and monist theories. § The attitude of international law to municipal law. § The attitude of national legal systems to international law. § Public international law and private international law.
 Is there a conflict between the national and international law?
Is there a conflict between the national and international law?
 It is generally accepted that international law may influence domestic courts The South African Constitution explicitly states in Section 233 on the Application of International Law: "When interpreting any legislation, every court must prefer any reasonable interpretation of the legislation that is consistent with international law over any alternative interpretation that is inconsistent with international law. "
It is generally accepted that international law may influence domestic courts The South African Constitution explicitly states in Section 233 on the Application of International Law: "When interpreting any legislation, every court must prefer any reasonable interpretation of the legislation that is consistent with international law over any alternative interpretation that is inconsistent with international law. "
 It is generally accepted that international law may influence domestic courts Section 9 of the Nepal Treaty Act (1991) provides that any treaty to which Nepal is a States party is enforceable as national law. In case of disparity between a domestic law and a treaty, the latter will be given effect.
It is generally accepted that international law may influence domestic courts Section 9 of the Nepal Treaty Act (1991) provides that any treaty to which Nepal is a States party is enforceable as national law. In case of disparity between a domestic law and a treaty, the latter will be given effect.
 Співвідношення національного та міжнародного права Cт. 9 Конституції України 1996 року: «Чинні міжнародні договори, згода на обов’язковість яких надана Верховною Радою України, є частиною національного законодавства України.
Співвідношення національного та міжнародного права Cт. 9 Конституції України 1996 року: «Чинні міжнародні договори, згода на обов’язковість яких надана Верховною Радою України, є частиною національного законодавства України.
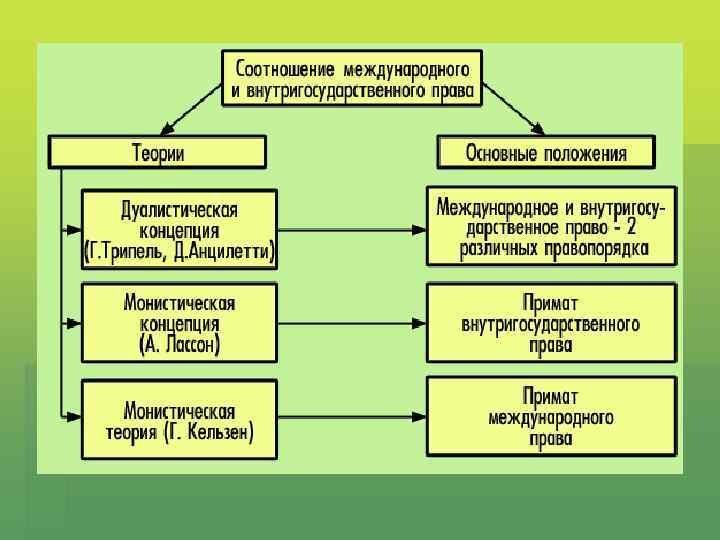
 Dualist and monist theories
Dualist and monist theories
 Dualist theory International law and National Law are two separate legal systems which exist independently of each other
Dualist theory International law and National Law are two separate legal systems which exist independently of each other

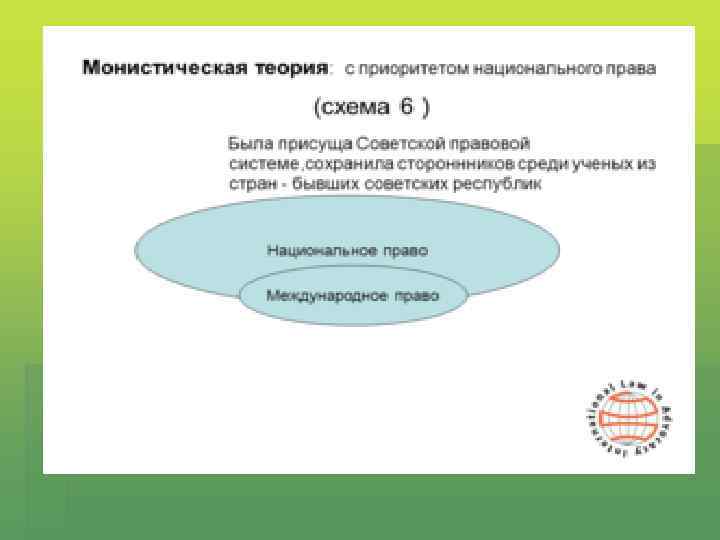
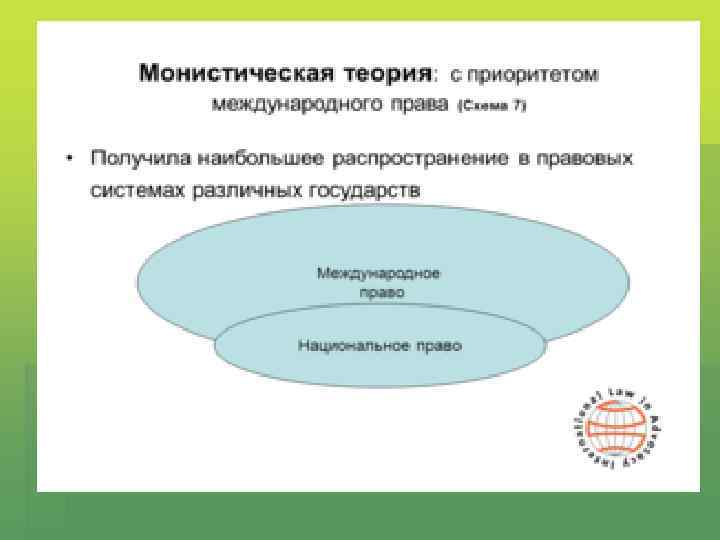
 Monist theories § International and National law are the forming part of one and the same legal order
Monist theories § International and National law are the forming part of one and the same legal order
 Kelsen’s theory § All rules of international law were supreme over municipal law § Municipal law inconsistent with international law. It is automatically null and void. § The rules of international law were directly applicable in the domestic sphere of states.
Kelsen’s theory § All rules of international law were supreme over municipal law § Municipal law inconsistent with international law. It is automatically null and void. § The rules of international law were directly applicable in the domestic sphere of states.

 The attitude of international law to municipal law § International law does not entirely ignore municipal law. § Municipal law may be used as evidence of international custom or of general principles of law.
The attitude of international law to municipal law § International law does not entirely ignore municipal law. § Municipal law may be used as evidence of international custom or of general principles of law.
 Free Zones case § “It is certain that France cannot rely on her own legislation to limit the scope of her international obligations”
Free Zones case § “It is certain that France cannot rely on her own legislation to limit the scope of her international obligations”
 Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties 1969 Article 27. INTERNAL LAW AND OBSERVANCE OF TREATIES A party may not invoke the provisions of its internal law as justification for its failure to perform a treaty.
Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties 1969 Article 27. INTERNAL LAW AND OBSERVANCE OF TREATIES A party may not invoke the provisions of its internal law as justification for its failure to perform a treaty.
 The attitude of national legal systems to international law § A treaty is not part of English law unless and until it has been incorporated into the law by leguslation § The legislature participates in the process of ratification.
The attitude of national legal systems to international law § A treaty is not part of English law unless and until it has been incorporated into the law by leguslation § The legislature participates in the process of ratification.
 Álvarez-Machaín case of abduction (викрадення) § A U. S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) special agent was kidnapped and murdered by a Mexican drug cartel in 1985. After an investigation, the DEA concluded that Humberto Álvarez. Machaín had participated in the murder. A warrant for his arrest was issued by a federal district court. The DEA, however, was unable to convince Mexico to extradite Álvarez-Machaín, so they hired several Mexican nationals to capture him and bring him back to the United States. His subsequent trial was appealed all the way to the Supreme Court, which found that the government could try a person who had been forcibly abducted, but that the abduction itself might violate international law and provide grounds for a civil suit. When the case went back to the district court for trial, Álvarez-Machaín was found not guilty for lack of evidence.
Álvarez-Machaín case of abduction (викрадення) § A U. S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) special agent was kidnapped and murdered by a Mexican drug cartel in 1985. After an investigation, the DEA concluded that Humberto Álvarez. Machaín had participated in the murder. A warrant for his arrest was issued by a federal district court. The DEA, however, was unable to convince Mexico to extradite Álvarez-Machaín, so they hired several Mexican nationals to capture him and bring him back to the United States. His subsequent trial was appealed all the way to the Supreme Court, which found that the government could try a person who had been forcibly abducted, but that the abduction itself might violate international law and provide grounds for a civil suit. When the case went back to the district court for trial, Álvarez-Machaín was found not guilty for lack of evidence.
 Public international law and private international law § Public international law is law regulating the relations between states and private persons. Examples are the wide of the national sea, who "owns" the moon and the South Polar region. § Do airplanes need permission to pass over a country etc. Conventions and treaties can be part of international public law.
Public international law and private international law § Public international law is law regulating the relations between states and private persons. Examples are the wide of the national sea, who "owns" the moon and the South Polar region. § Do airplanes need permission to pass over a country etc. Conventions and treaties can be part of international public law.
 Public international law and private international law § Private international law is the regulation of the relation between two private parties that have international aspects. § What if two persons from different countries want to divorce: What law should be used and which judge should do the case (jurisdiction)? § What if two persons have a car accident abroad. Nowadays much is ruled by conventions but still also by common law.
Public international law and private international law § Private international law is the regulation of the relation between two private parties that have international aspects. § What if two persons from different countries want to divorce: What law should be used and which judge should do the case (jurisdiction)? § What if two persons have a car accident abroad. Nowadays much is ruled by conventions but still also by common law.


