be36b1f3c0d67ff39c8373c95d6e343b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Lecture 3: The American republic and Constitution

Origins of Republicanism in the US Republicanism = Idea that the people (through their representatives) can rule themselves

I. Models from Antiquity • The rise of Greek city-states (800 -500 BC) - Athens--small, turbulent, and “democratic” • The Roman Republic - creation of the “Senate”--indirectly representative govt. - large, powerful, lasted 100 s of years - as American ideal--politics, art, architecture, legend

Washington in a toga

II. Experience of Self-rule • A history of administering their own affairs for almost 150 years Virginia House of Burgesses

Creation of a Republican national govt • An “experiment” in republican govt--many expected to fail • Americans’ sense of state identity, and fear of centralization • First try: The Articles of Confederation (drafted in 1777)

Article I. The Stile of this Confederacy shall be "The United States of America. " Article II. Each state retains its sovereignty, freedom, and independence. . .

Features/Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation • No U. S. judiciary to settle disputes between states • No real executive power to carry out or enforce federal (national) laws • 9 of 13 states needed to approve legislation • No power to collect taxes directly • No power to raise an army directly
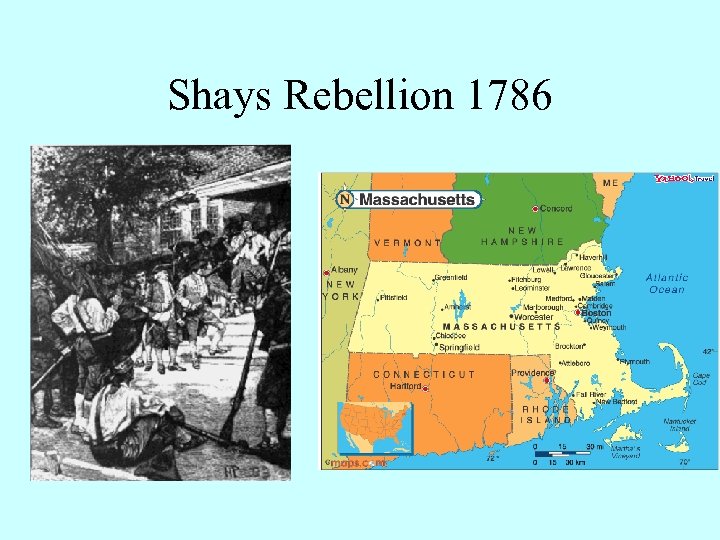
Shays Rebellion 1786

Another attempt at a federal (national) govt • 1787 States agree to send reps to Philadelphia to amend Articles • Debates and compromises: - Virginia Plan vs New Jersey Plan - Senate and House apportioned differently - Slavery and direct taxation/representation - “the 3/5 compromise” - Federalists vs Anti-federalists - Bill of Rights added

signing the Constitution

Madison and the Principles of the Constitution • 1: Republicanism--not quite democracy “democracy is the most vile form of government. . . democracies have ever been spectacles of turbulence and contention: have ever been found incompatible with personal security or the rights of property” • 2: Federalist Papers 10 & 51 • “ambition to counteract ambition” in checks and balances • “cross-cutting cleavages” of a large republic

Review of U. S. Constitution (1789) • Preamble - “People” not “States” • Article 1 (Article, Section, Clause) • Congress - Sec 2 --House of Representatives • Pg 3 • 3/5 rule

Article I, cont’d - Sec 3 --Senate • Pg 1 • --representing state, elected by state legislature - Sec 8 --Powers of Congress • raise taxes, raise army, regulate commerce among states, necessary and proper - Sec 9 --Restraints on Congress • banning slave trade, suspend habeas corpus, create nobility

Review of U. S. Constitution • Article 2 --Presidency and electoral college • Article 3 --Federal Judiciary • Article 4 --Full faith and credit, fugitive slave • Article 5 --amendment formulas • Article 6, Pg 2 --”Supremacy Clause” • Article 7 --Ratification

Bill of Rights • • Amend 1 --religion and speech Amend 2 --guns Amend 4 --search and seizure Amend 5 --double jeopardy, self-incrim, due process • Amend 6, 7 --trial procedure--jury trial, counsel • Amend 8 --Cruel and unusual, excessive bail • Amend 9, 10 --non-specified rights remain with the states and people
be36b1f3c0d67ff39c8373c95d6e343b.ppt