 Lecture #3 Supporting Different Devices
Lecture #3 Supporting Different Devices
 Different Languages Just copy and paste values. Add locale information. MyProject/ res/ values/ strings.xml values-es/ strings.xml values-fr/ strings.xml
Different Languages Just copy and paste values. Add locale information. MyProject/ res/ values/ strings.xml values-es/ strings.xml values-fr/ strings.xml
 Further steps... Change locale of your device To use appropriate string from Java: String hello = getResources().getString(R.string.hello_world); TextView textView = new TextView(this); textView.setText(R.string.hello_world);
Further steps... Change locale of your device To use appropriate string from Java: String hello = getResources().getString(R.string.hello_world); TextView textView = new TextView(this); textView.setText(R.string.hello_world);
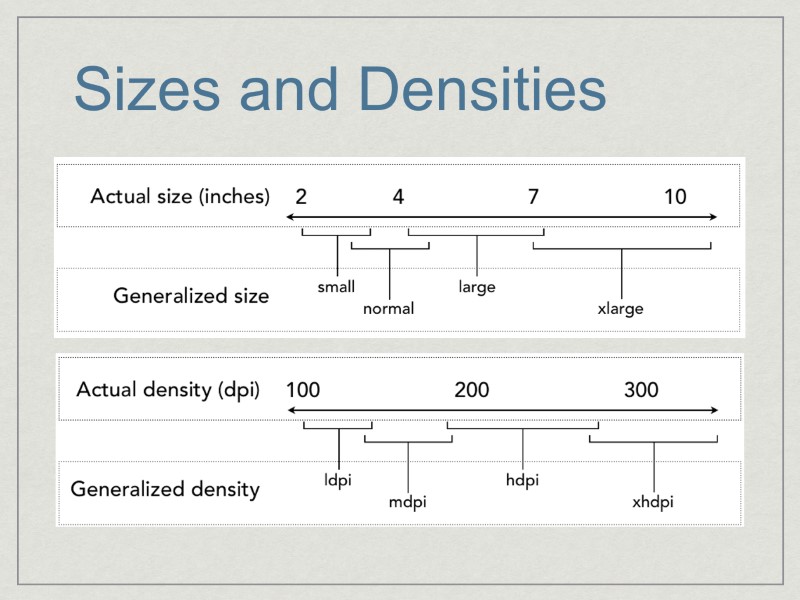
 Different Screens Screen Size The actual physical size, measured as the screen’s diagonal(small, normal, large, xlarge) Screen Density The quantity of pixels within a physical area of the screen(ldpi, mdpi, hdpi, xhdpi)
Different Screens Screen Size The actual physical size, measured as the screen’s diagonal(small, normal, large, xlarge) Screen Density The quantity of pixels within a physical area of the screen(ldpi, mdpi, hdpi, xhdpi)
 Sizes and Densities
Sizes and Densities
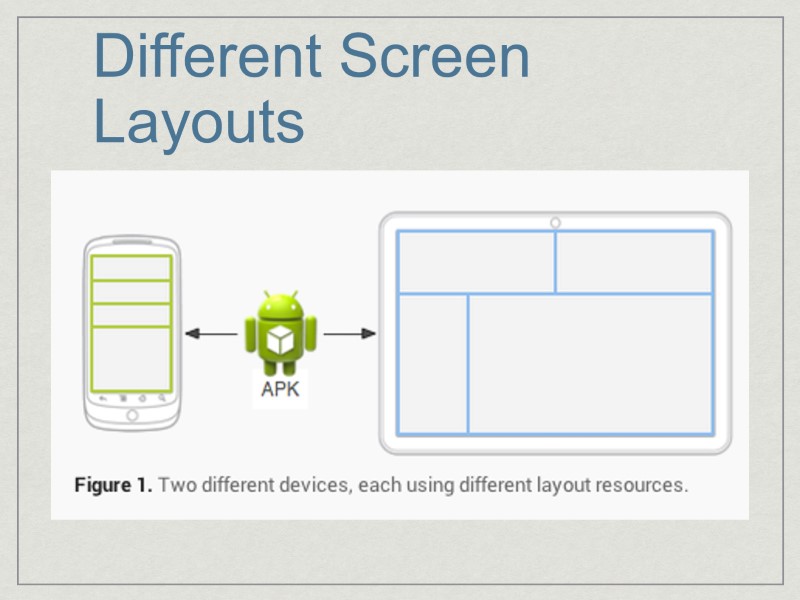 Different Screen Layouts
Different Screen Layouts
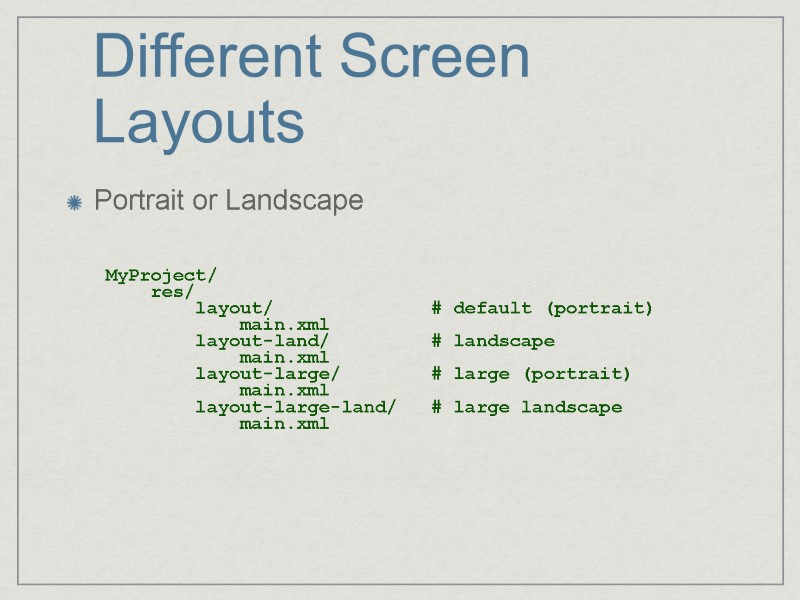 Different Screen Layouts Portrait or Landscape MyProject/ res/ layout/ # default (portrait) main.xml layout-land/ # landscape main.xml layout-large/ # large (portrait) main.xml layout-large-land/ # large landscape main.xml
Different Screen Layouts Portrait or Landscape MyProject/ res/ layout/ # default (portrait) main.xml layout-land/ # landscape main.xml layout-large/ # large (portrait) main.xml layout-large-land/ # large landscape main.xml
 Different Screen Bitmaps Screen sizes xlarge screens are at least 960dp x 720dp. large screens are at least 640dp x 480dp. normal screens are at least 470dp x 320dp. small screens are at least 426dp x 320dp.
Different Screen Bitmaps Screen sizes xlarge screens are at least 960dp x 720dp. large screens are at least 640dp x 480dp. normal screens are at least 470dp x 320dp. small screens are at least 426dp x 320dp.
 Different Screen Bitmaps To generate images, use the following scaling: xhdpi: 2.0 hdpi: 1.5 mdpi: 1.0 (baseline) ldpi: 0.75 This means that if you generate a 200x200 image for xhdpi devices, you should generate the same resource in 150x150 for hdpi, 100x100 for mdpi, and 75x75 for ldpi devices
Different Screen Bitmaps To generate images, use the following scaling: xhdpi: 2.0 hdpi: 1.5 mdpi: 1.0 (baseline) ldpi: 0.75 This means that if you generate a 200x200 image for xhdpi devices, you should generate the same resource in 150x150 for hdpi, 100x100 for mdpi, and 75x75 for ldpi devices
 Examples A QVGA screen is 320x240 ldpi. Converting to mdpi (a 4/3 scaling factor) gives us 426dp x 320dp; The Xoom is a typical 10” tablet with a 1280x800 mdpi screen The Dell Streak is a 800x480 mdpi screen A typical 7” tablet has a 1024x600 mdpi screen
Examples A QVGA screen is 320x240 ldpi. Converting to mdpi (a 4/3 scaling factor) gives us 426dp x 320dp; The Xoom is a typical 10” tablet with a 1280x800 mdpi screen The Dell Streak is a 800x480 mdpi screen A typical 7” tablet has a 1024x600 mdpi screen
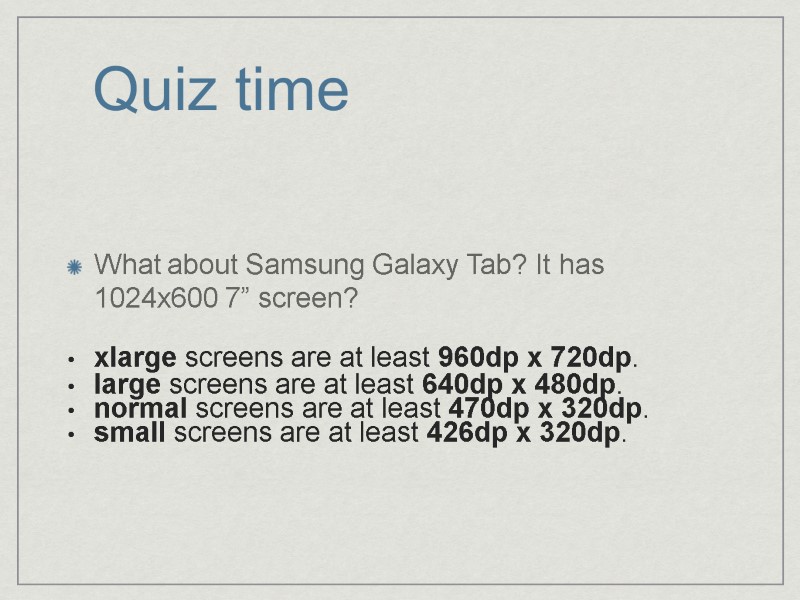 Quiz time What about Samsung Galaxy Tab? It has 1024x600 7” screen? xlarge screens are at least 960dp x 720dp. large screens are at least 640dp x 480dp. normal screens are at least 470dp x 320dp. small screens are at least 426dp x 320dp.
Quiz time What about Samsung Galaxy Tab? It has 1024x600 7” screen? xlarge screens are at least 960dp x 720dp. large screens are at least 640dp x 480dp. normal screens are at least 470dp x 320dp. small screens are at least 426dp x 320dp.
 Quiz time: The Samsung Galaxy Tab is an interesting case. Physically it is a 1024x600 7” screen and thus classified as “large”(hdpi) After applying ⅔ scaling factor the screen is 682dp x 400dp. The Tab actually reports that it is “large” but in fact it is “normal”
Quiz time: The Samsung Galaxy Tab is an interesting case. Physically it is a 1024x600 7” screen and thus classified as “large”(hdpi) After applying ⅔ scaling factor the screen is 682dp x 400dp. The Tab actually reports that it is “large” but in fact it is “normal”
 The end
The end



























