Int business Integration Lecture 3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Lecture 3 INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Globalization & internationalization: from theories to facts; analyzing the global environment and markets

Table of contents 1. Globalization • • • What is it? Effects of globalization for the IB Drivers toward globalization 2. Internationalization • • • What is it? Internationalization theories in use Internationalization development stages Internationalization motives International companies’ mentalities 3. Internationalization strategy • • 5 -stages model Different analyses used at each stage
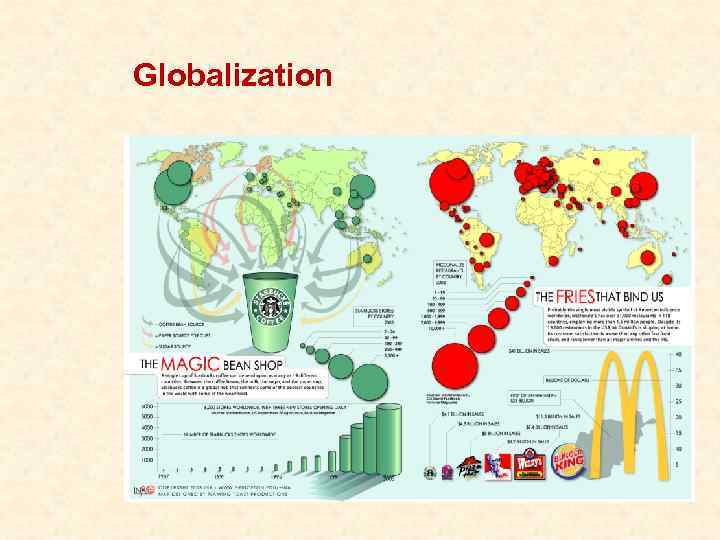
Globalization

Definition and effects • Globalization is a complex economical, cultural and social phenomena, which requires global adjustment, integration and close connection of business activities in a totally new manner, leading to a new standardized quality and enabling individuals, corporations, and nation-states to reach around the world farther, faster, deeper and cheaper than ever before. • Global markets are defined as those markets in which buyer preferences are similar across countries. • FACTORS of globalization: • Growing stake of IB within FDI • Faster growth of international trade share within GDP • Higher importance of FDI, economies of scale, knowledge transfer • The appearance of integrated financial markets GLOBAL MIGRATION OF PEOPLE AND INVESTMENTS: • • • 1980: working better – reengineering 1990: working cheaper – outsourcing 2000: working elsewhere – offshoring

Trends in international business Abundance of products New technologies

Trends in international business New customer segments Movement of production

THE GLOBAL COMPONENTS OF A BIG MAC IN UKRAINE

Big mac index
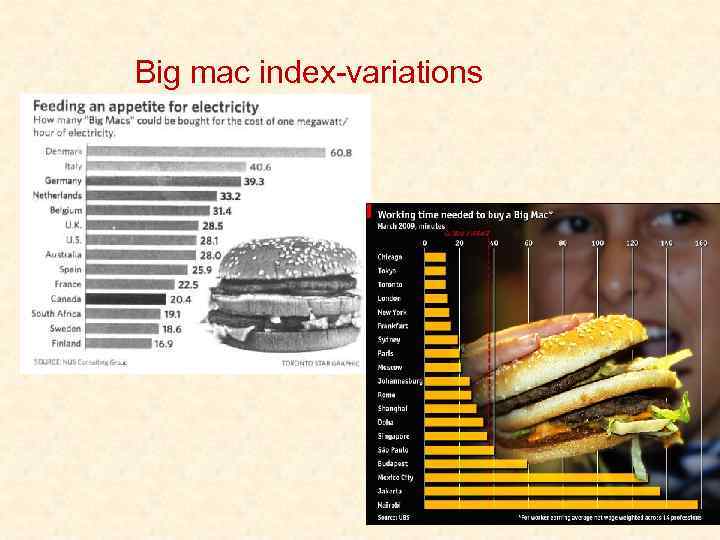
Big mac index-variations

Drivers toward globalization 1. MARKET DRIVERS 2. COMPETITIVE DRIVERS 3. COST DRIVERS 4. TECHNOLOGY DRIVERS 5. ENVIRONMENTAL DRIVERS 6. GOVERNMENT DRIVERS
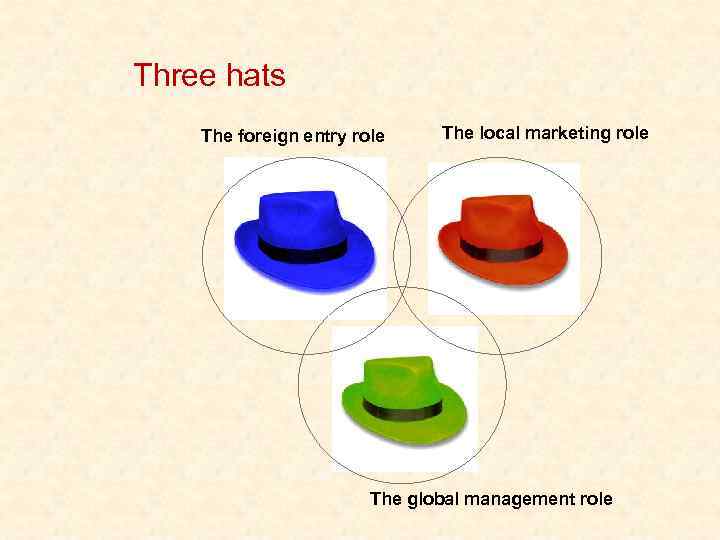
Three hats The foreign entry role The local marketing role The global management role

INTERNATIONALIZATION

What is internationalization? And what is the opposite of the internationalization? ? ?

Broader definition of internationalization Internationalization is defined as an expansion of economic activity among more countries and is related to all forms of international economic cooperation.
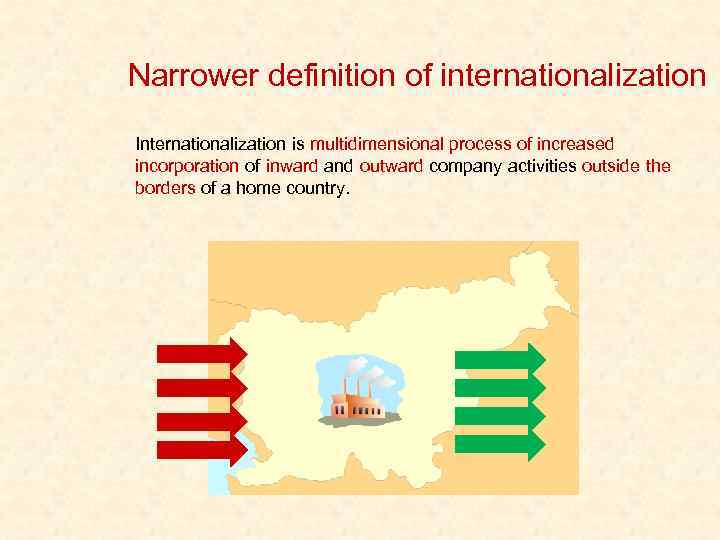
Narrower definition of internationalization Internationalization is multidimensional process of increased incorporation of inward and outward company activities outside the borders of a home country.
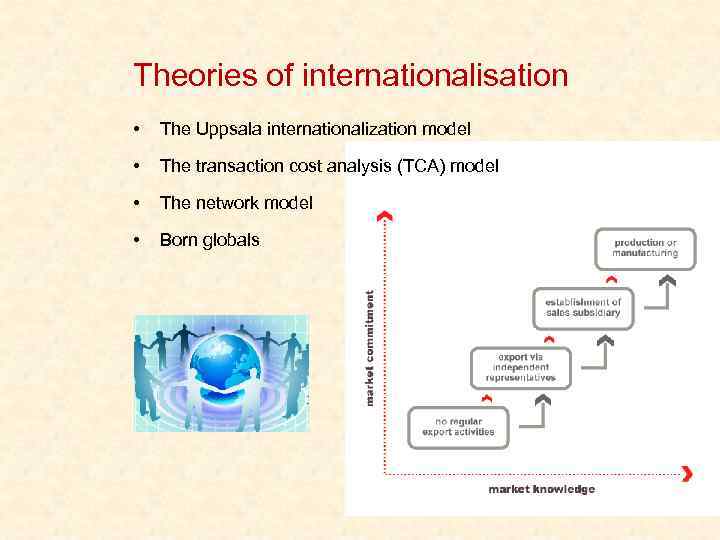
Theories of internationalisation • The Uppsala internationalization model • The transaction cost analysis (TCA) model • The network model • Born globals

Internationalization development stages Internationalization steps of a company (COMPANY VIEW): Development stages of export operations (MARKET VIEW): 1. STAGE ~ Individual export tasks 2. STAGE ~ Establishing a subsidiary in the most promising markets 3. STAGE ~ Licensing and strategic alliances 4. STAGE ~ Establishing own production facility in the foreign market 1. STAGE ~ Export of excess products • company does not have resources to perform continuous export 2. STAGE ~ Export marketing • company is already trying alone to win sales in foreign markets • company is prepared to adapt marketing in limited terms 3. STAGE ~ Development of foreign markets • company adapts its products and marketing to foreign markets needs 4. STAGE ~ Technological development • company develops new products for existing or new markets
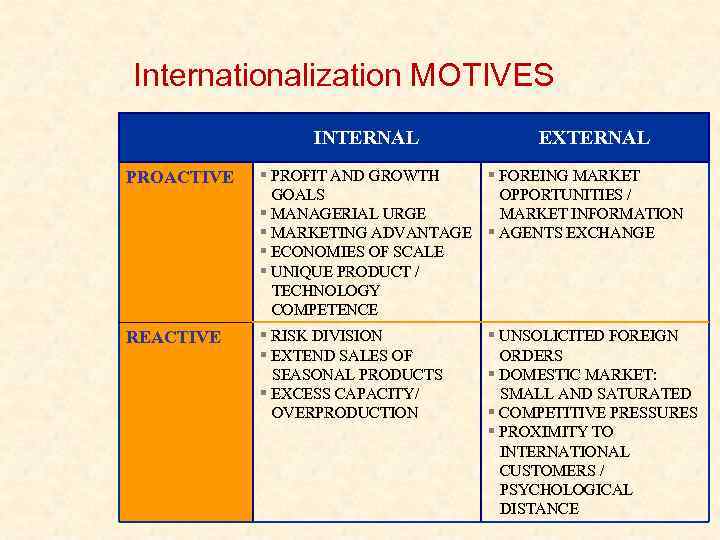
Internationalization MOTIVES INTERNAL EXTERNAL PROACTIVE PROFIT AND GROWTH FOREING MARKET GOALS OPPORTUNITIES / MANAGERIAL URGE MARKET INFORMATION MARKETING ADVANTAGE AGENTS EXCHANGE ECONOMIES OF SCALE UNIQUE PRODUCT / TECHNOLOGY COMPETENCE REACTIVE RISK DIVISION EXTEND SALES OF SEASONAL PRODUCTS EXCESS CAPACITY/ OVERPRODUCTION UNSOLICITED FOREIGN ORDERS DOMESTIC MARKET: SMALL AND SATURATED COMPETITIVE PRESSURES PROXIMITY TO INTERNATIONAL CUSTOMERS / PSYCHOLOGICAL DISTANCE

What do the following companies have in common?

What is a MNC? • MNCs as a contemporary economic structures and socio-cultural contexts – “The multinational corporation has become the dominant organizational form of modern capitalism. It now commands tremendous influence and power over the economic, social, political, and cultural lives of many nations and people” – “lead agents of the globalization process” – “ultimate carriers of progress and development opportunities, or seen as the extreme expression of predatory behavior, based on the systematic appropriation of rents”

Definition of a MNC • One of the most widely used definitions of the MNC today is that of the OECD and UNCTC, which define it as “an enterprise that engages in foreign direct investments (FDIs) and owns or controls value-adding activities in more than one country”. • Underlying this view are two crucial parts, one pertaining to a (1) long-term investment of resources in other countries (FDIs) and the other to the (2) control of value-adding activities in foreign environments.
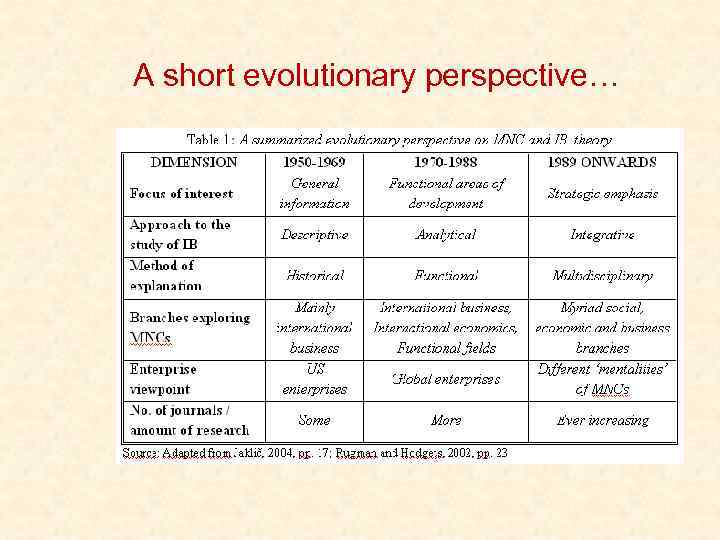
A short evolutionary perspective…

Bartlett & Ghoshal: 4 mentalities • • 1989: Bartlett & Ghoshal Managing across borders: the transnational solution (one of the 100 most influential economic and business books of the 20 th century) Any internationally active company must fulfill 3 important strategic goals: – GLOBAL EFFICIENCY in existing activities – INTERNATIONAL FLEXIBILITY and LOCAL RESPONSIVENESS (appropriate management of risks and opportunities) – WORLD-WIDE LEARNING thought its exposure to local contexts • 4 company mentalities: – – INTERNATIONAL COMPANY MULTINATIONAL COMPANY GLOBAL COMPANY TRANSNATIONAL COMPANY (a revolutionary new form; NEW MANAGEMENTALITY!)
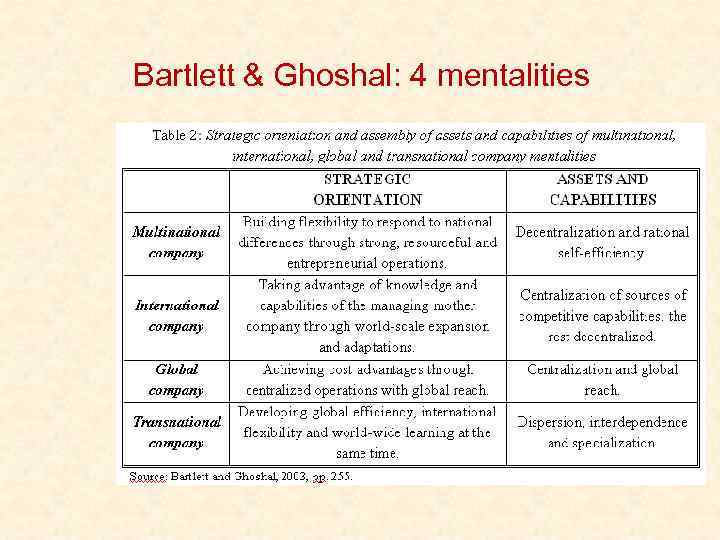
Bartlett & Ghoshal: 4 mentalities

Who else is participating in international business? SMEs {small and medium enterprises} • SMEs are defined as independent companies that employ less than 250 people (OECD, 2009). OECD estimates say that SMEs perform 95 % of all world business and employ 60 – 70 % of all active population. • SMEs have appeared as a direct result of internationalization, as they started to take over functions, which were given by multinationals to external service providers (outsourcing). • Technological advancement and integration processes are considered to be main factors to barrier decrease for SMEs to enter international business. • SMEs contribution to global economy: development of new employment, flexibility in the process of goods creation, increase of market competitiveness, capability of creating innovative environment and development of entrepreneurship, etc.

Examples Elektronček Akrapovič

Internationalization strategy Figure 1: The internationalization model Source: Adapted from Hollensen, 2004; Czinkota, Ronkainen, Moffett, 2005; Kotler, 2005; and own modification.
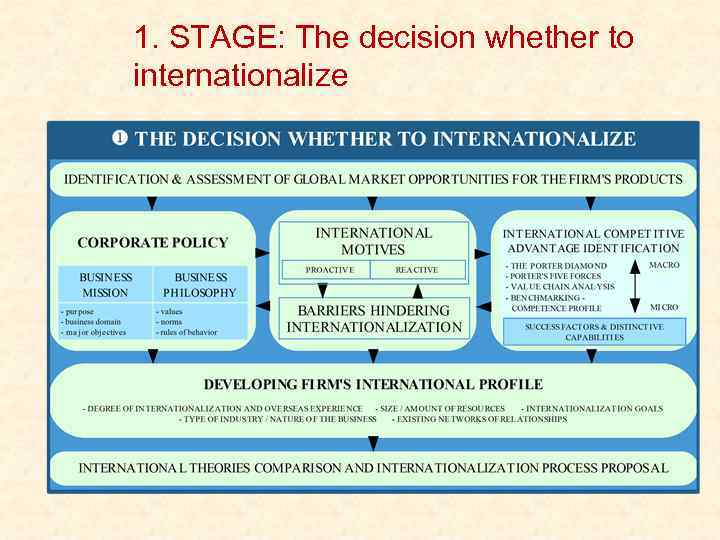
1. STAGE: The decision whether to internationalize
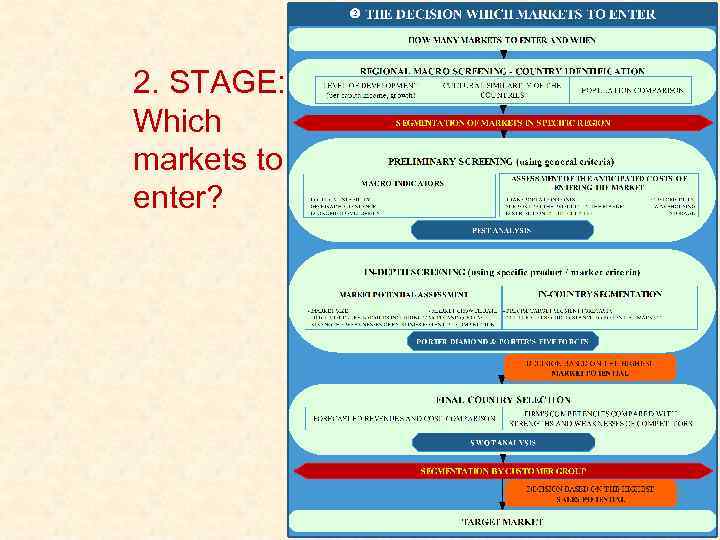
2. STAGE: Which markets to enter?
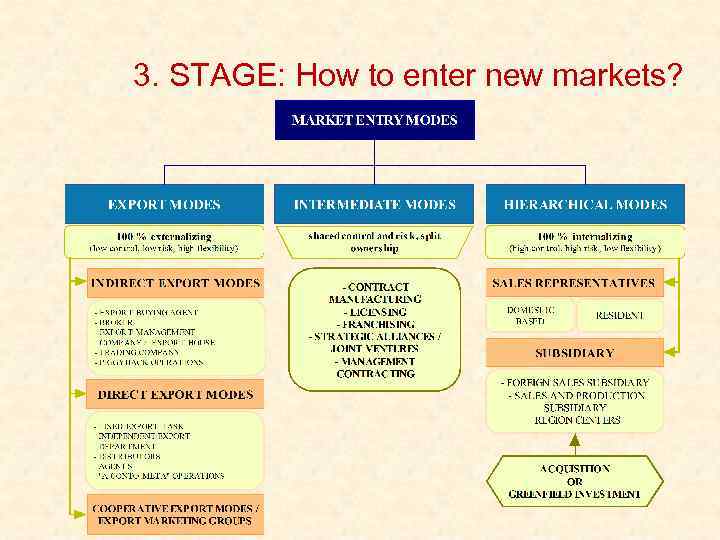
3. STAGE: How to enter new markets?
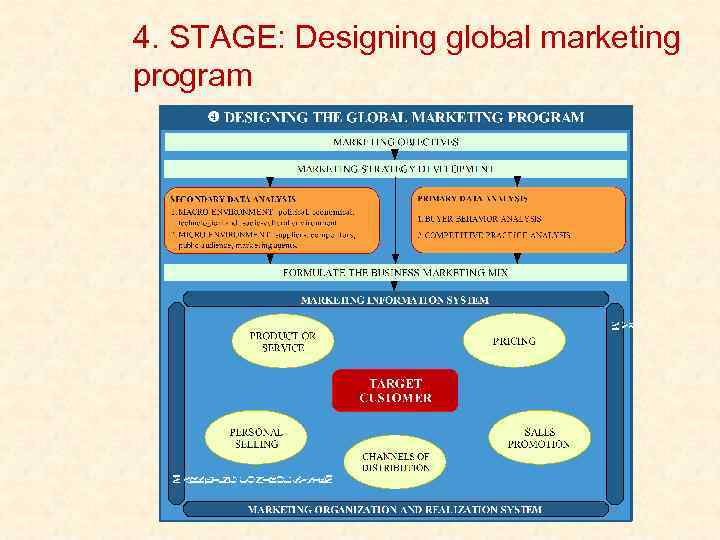
4. STAGE: Designing global marketing program
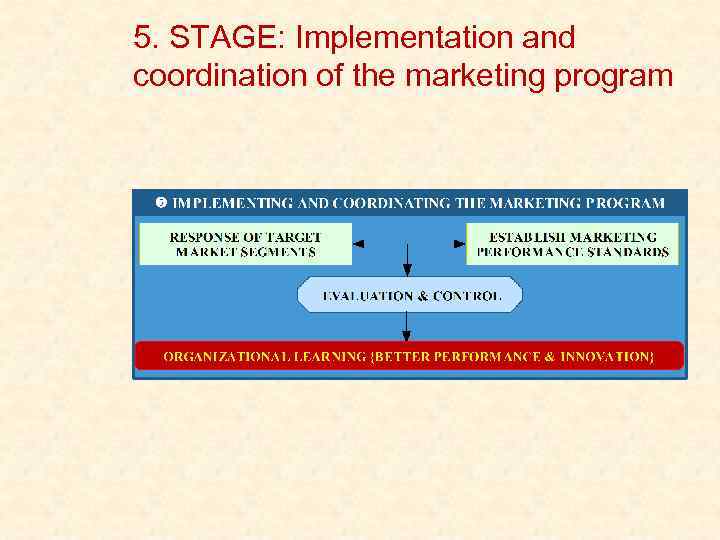
5. STAGE: Implementation and coordination of the marketing program

Task • Make a research – Positive and Negative sides of globalization. • Write a paper - ~5 p stating the “+”s and “-”s of globalization. State your opinion • Be ready to present and defend your opinion. • The paper should be sent by email by Sep. 22 • Email: tetyana. chernykh@gmail. com
Int business Integration Lecture 3.ppt