 Lecture 3 – Automated Data Collection Distance Calculation – How? 2 dimensional using sound travel: An accurate timepiece The ability to pick up distant sound signals A map showing the coast and the locations of any soundhouses Knowledge about sound travel (750 miles/hour, or 20 Km/minute)
Lecture 3 – Automated Data Collection Distance Calculation – How? 2 dimensional using sound travel: An accurate timepiece The ability to pick up distant sound signals A map showing the coast and the locations of any soundhouses Knowledge about sound travel (750 miles/hour, or 20 Km/minute)
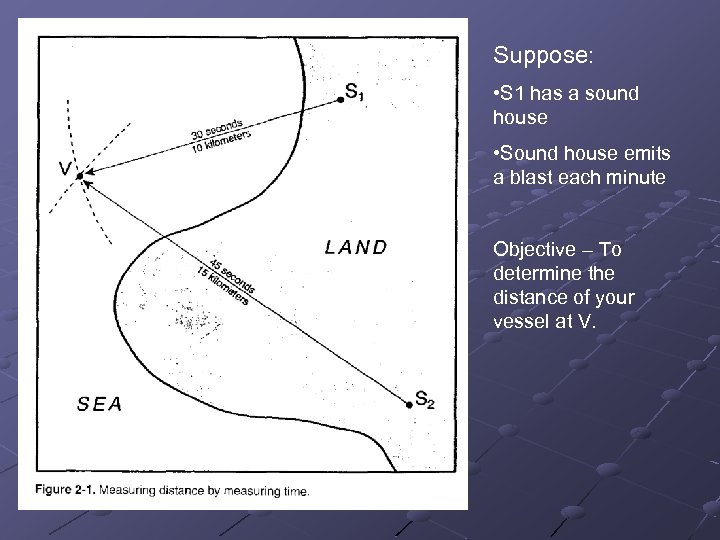 Suppose: • S 1 has a sound house • Sound house emits a blast each minute Objective – To determine the distance of your vessel at V.
Suppose: • S 1 has a sound house • Sound house emits a blast each minute Objective – To determine the distance of your vessel at V.
 How it works Measuring Distance By Measuring Time (1) Known locations of GPS satellites (2) Knowledge of signal travel speed (300000 Km/Sec) (3) Accurate clocks on GPS satellites and GPS receivers Then distances from GPS receiver to several satellites can be calculated and can be used to compute receiver’s position
How it works Measuring Distance By Measuring Time (1) Known locations of GPS satellites (2) Knowledge of signal travel speed (300000 Km/Sec) (3) Accurate clocks on GPS satellites and GPS receivers Then distances from GPS receiver to several satellites can be calculated and can be used to compute receiver’s position
 Soundhouse VS NAVSTAR 3 D VS 2 D Dynamic VS Static Radio Waves VS Sound Auto VS Manual
Soundhouse VS NAVSTAR 3 D VS 2 D Dynamic VS Static Radio Waves VS Sound Auto VS Manual
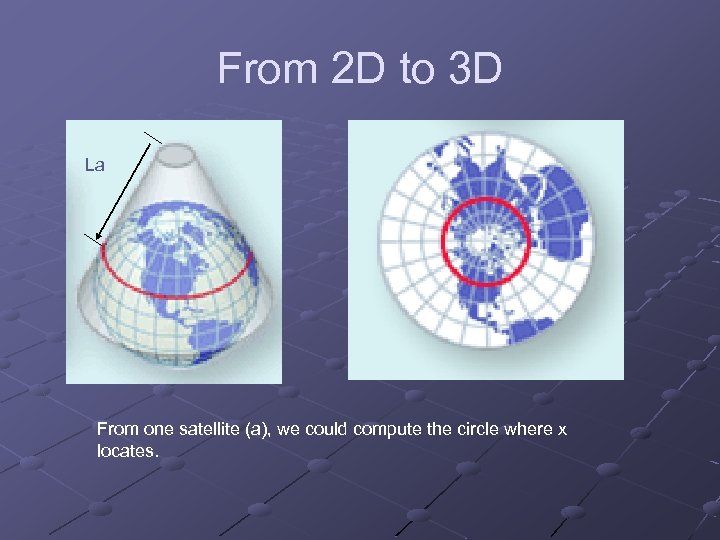 From 2 D to 3 D La From one satellite (a), we could compute the circle where x locates.
From 2 D to 3 D La From one satellite (a), we could compute the circle where x locates.
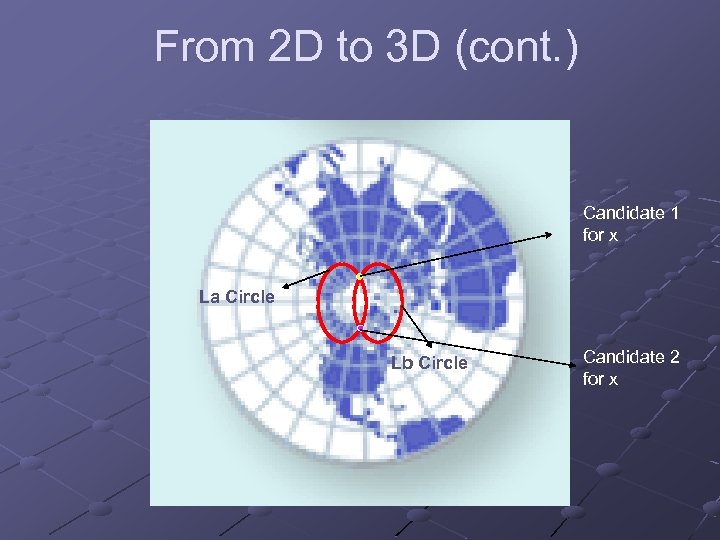 From 2 D to 3 D (cont. ) Candidate 1 for x La Circle Lb Circle Candidate 2 for x
From 2 D to 3 D (cont. ) Candidate 1 for x La Circle Lb Circle Candidate 2 for x
 Factors Affecting When and How to Collect Data Major factors that relate to the accuracy of GPS measurements are: satellite clock errors ephemeris errors receiver errors ionosphere errors troposphere errors multipath errors
Factors Affecting When and How to Collect Data Major factors that relate to the accuracy of GPS measurements are: satellite clock errors ephemeris errors receiver errors ionosphere errors troposphere errors multipath errors
 Dilution of Precision (DOP) High DOP values can magnify the other errors DOP values can be monitored during data collection and excessive DOP values can be masked out DOP values can be predicated Differential correction can not help with data collected with inappropriate DOP values
Dilution of Precision (DOP) High DOP values can magnify the other errors DOP values can be monitored during data collection and excessive DOP values can be masked out DOP values can be predicated Differential correction can not help with data collected with inappropriate DOP values
 Position Accuracy and DOP The quality (accuracy) of fix is depend on a number of factors, including the number of satellites in view, and their geometry, or arrangement, in the sky.
Position Accuracy and DOP The quality (accuracy) of fix is depend on a number of factors, including the number of satellites in view, and their geometry, or arrangement, in the sky.
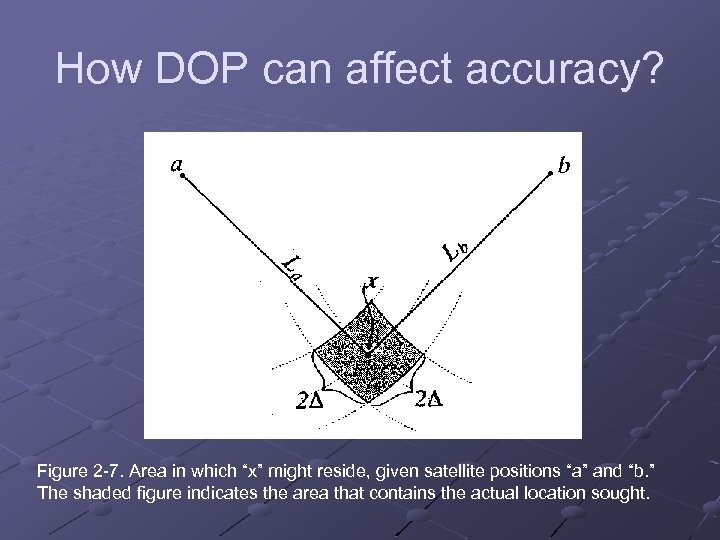 How DOP can affect accuracy? Figure 2 -7. Area in which “x” might reside, given satellite positions “a” and “b. ” The shaded figure indicates the area that contains the actual location sought.
How DOP can affect accuracy? Figure 2 -7. Area in which “x” might reside, given satellite positions “a” and “b. ” The shaded figure indicates the area that contains the actual location sought.
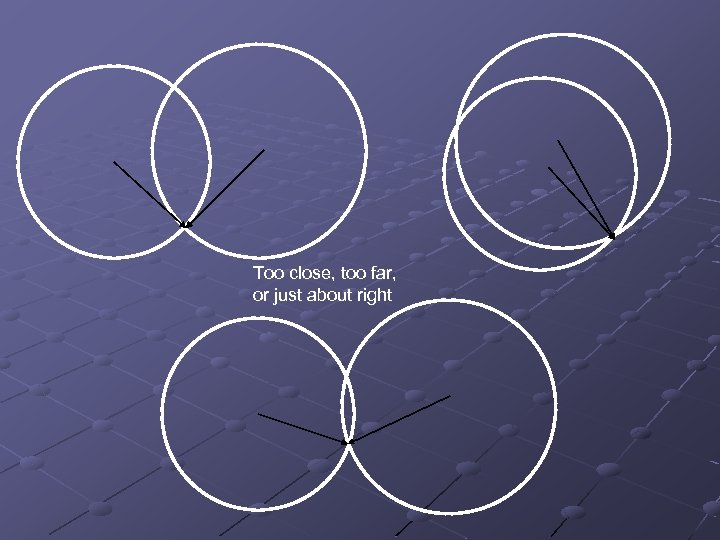 Too close, too far, or just about right
Too close, too far, or just about right
 Actually, what is DOP? DOP – sometimes referred to as GDOP (Geometric Dilution of Precision), is a number which is a measure of the quality you might expect from a position measurement of the GPS system based solely on the geometric arrangement of the satellites and the receiver being used for the measurement.
Actually, what is DOP? DOP – sometimes referred to as GDOP (Geometric Dilution of Precision), is a number which is a measure of the quality you might expect from a position measurement of the GPS system based solely on the geometric arrangement of the satellites and the receiver being used for the measurement.
 Different DOPs GDOP (Geometric Dilution Of Precision); Overall -accuracy; 3 D-coordinates and time PDOP (Positional Dilution Of Precision) ; Position accuracy; 3 D-coordinates HDOP (Horizontal Dilution Of Precision); horizontal accuracy; 2 D-coordinates VDOP (Vertical Dilution Of Precision); vertical accuracy; height TDOP (Time Dilution Of Precision); time accuracy; time
Different DOPs GDOP (Geometric Dilution Of Precision); Overall -accuracy; 3 D-coordinates and time PDOP (Positional Dilution Of Precision) ; Position accuracy; 3 D-coordinates HDOP (Horizontal Dilution Of Precision); horizontal accuracy; 2 D-coordinates VDOP (Vertical Dilution Of Precision); vertical accuracy; height TDOP (Time Dilution Of Precision); time accuracy; time