96ecfe29efa4827f6dddc70e121fbb06.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 120
 Lecture 23 Human Resources Management Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 1
Lecture 23 Human Resources Management Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 1
 Chapter 9: Project Human Resource Management Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition
Chapter 9: Project Human Resource Management Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition
 What is Project Human Resource Management? § Making the most effective use of the people involved with a project. § Processes include: § Human resource planning: Identifying and documenting project roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships. § Acquiring the project team: Getting the needed personnel assigned to and working on the project. § Developing the project team: Building individual and group skills to enhance project performance. § Managing the project team: Tracking team member performance, motivating team members, providing timely feedback, resolving issues and conflicts, and coordinating changes to help enhance project performance. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 3
What is Project Human Resource Management? § Making the most effective use of the people involved with a project. § Processes include: § Human resource planning: Identifying and documenting project roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships. § Acquiring the project team: Getting the needed personnel assigned to and working on the project. § Developing the project team: Building individual and group skills to enhance project performance. § Managing the project team: Tracking team member performance, motivating team members, providing timely feedback, resolving issues and conflicts, and coordinating changes to help enhance project performance. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 3
 Keys to Managing People § Psychologists and management theorists have devoted much research and thought to the field of managing people at work. § Important areas related to project management include: § Motivation theories § Influence and power § Effectiveness Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 4
Keys to Managing People § Psychologists and management theorists have devoted much research and thought to the field of managing people at work. § Important areas related to project management include: § Motivation theories § Influence and power § Effectiveness Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 4
 Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation § Intrinsic motivation causes people to participate in an activity for their own enjoyment. § Extrinsic motivation causes people to do something for a reward or to avoid a penalty. § For example, some children take piano lessons for intrinsic motivation (they enjoy it) while others take them for extrinsic motivation (to get a reward or avoid punishment). Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 5
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation § Intrinsic motivation causes people to participate in an activity for their own enjoyment. § Extrinsic motivation causes people to do something for a reward or to avoid a penalty. § For example, some children take piano lessons for intrinsic motivation (they enjoy it) while others take them for extrinsic motivation (to get a reward or avoid punishment). Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 5
 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs § Abraham Maslow argued that human beings possess unique qualities that enable them to make independent choices, thus giving them control of their destiny. § Maslow developed a hierarchy of needs, which states that people’s behaviors are guided or motivated by a sequence of needs. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 6
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs § Abraham Maslow argued that human beings possess unique qualities that enable them to make independent choices, thus giving them control of their destiny. § Maslow developed a hierarchy of needs, which states that people’s behaviors are guided or motivated by a sequence of needs. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 6
 Figure 9 -1. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 7
Figure 9 -1. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 7
 Herzberg’s Motivational and Hygiene Factors § Frederick Herzberg wrote several famous books and articles about worker motivation. He distinguished between: § Motivational factors: Achievement, recognition, the work itself, responsibility, advancement, and growth. These factors produce job satisfaction. § Hygiene factors: Larger salaries, more supervision, and a more attractive work environment. These factors cause dissatisfaction if not present, but do not motivate workers to do more. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 8
Herzberg’s Motivational and Hygiene Factors § Frederick Herzberg wrote several famous books and articles about worker motivation. He distinguished between: § Motivational factors: Achievement, recognition, the work itself, responsibility, advancement, and growth. These factors produce job satisfaction. § Hygiene factors: Larger salaries, more supervision, and a more attractive work environment. These factors cause dissatisfaction if not present, but do not motivate workers to do more. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 8
 Mc. Clelland’s Acquired-Needs Theory § Specific needs are acquired or learned over time and are shaped by life experiences. The following are the main categories of acquired needs: § Achievement (n. Ach): People with a high need for achievement like challenging projects with attainable goals and lots of feedback. § Affiliation (n. Aff): People with high need for affiliation desire harmonious relationships and need to feel accepted by others, so managers should try to create a cooperative work environment for them. § Power (n. Pow): People with a need for power desire either personal power (not good) or institutional power (good for the organization). Provide institutional power seekers with management opportunities. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 9
Mc. Clelland’s Acquired-Needs Theory § Specific needs are acquired or learned over time and are shaped by life experiences. The following are the main categories of acquired needs: § Achievement (n. Ach): People with a high need for achievement like challenging projects with attainable goals and lots of feedback. § Affiliation (n. Aff): People with high need for affiliation desire harmonious relationships and need to feel accepted by others, so managers should try to create a cooperative work environment for them. § Power (n. Pow): People with a need for power desire either personal power (not good) or institutional power (good for the organization). Provide institutional power seekers with management opportunities. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 9
 Mc. Gregor’s Theory X and Y § Douglas Mc. Gregor popularized the human relations approach to management in the 1960 s. § Theory X: Assumes workers dislike and avoid work, so managers must use coercion, threats, and various control schemes to get workers to meet objectives. § Theory Y: Assumes individuals consider work as natural as play or rest and enjoy the satisfaction of esteem and self-actualization needs. § Theory Z: Introduced in 1981 by William Ouchi and is based on the Japanese approach to motivating workers, which emphasizes trust, quality, collective decision making, and cultural values. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 10
Mc. Gregor’s Theory X and Y § Douglas Mc. Gregor popularized the human relations approach to management in the 1960 s. § Theory X: Assumes workers dislike and avoid work, so managers must use coercion, threats, and various control schemes to get workers to meet objectives. § Theory Y: Assumes individuals consider work as natural as play or rest and enjoy the satisfaction of esteem and self-actualization needs. § Theory Z: Introduced in 1981 by William Ouchi and is based on the Japanese approach to motivating workers, which emphasizes trust, quality, collective decision making, and cultural values. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 10
 Thamhain and Wilemon’s Ways to Have Influence on Projects 1. Authority: The legitimate hierarchical right to issue orders. 2. Assignment: The project manager's perceived ability to influence a worker's later work assignments. 3. Budget: The project manager's perceived ability to authorize others' use of discretionary funds. 4. Promotion: The ability to improve a worker's position. 5. Money: The ability to increase a worker's pay and benefits. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 11
Thamhain and Wilemon’s Ways to Have Influence on Projects 1. Authority: The legitimate hierarchical right to issue orders. 2. Assignment: The project manager's perceived ability to influence a worker's later work assignments. 3. Budget: The project manager's perceived ability to authorize others' use of discretionary funds. 4. Promotion: The ability to improve a worker's position. 5. Money: The ability to increase a worker's pay and benefits. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 11
 Thamhain and Wilemon’s Ways to Have Influence on Projects (cont’d) 6. Penalty: The project manager's ability to cause punishment. 7. Work challenge: The ability to assign work that capitalizes on a worker's enjoyment of doing a particular task. 8. Expertise: The project manager's perceived special knowledge that others deem important. 9. Friendship: The ability to establish friendly personal relationships between the project manager and others. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 12
Thamhain and Wilemon’s Ways to Have Influence on Projects (cont’d) 6. Penalty: The project manager's ability to cause punishment. 7. Work challenge: The ability to assign work that capitalizes on a worker's enjoyment of doing a particular task. 8. Expertise: The project manager's perceived special knowledge that others deem important. 9. Friendship: The ability to establish friendly personal relationships between the project manager and others. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 12
 Ways to Influence that Help and Hurt Projects § Projects are more likely to succeed when project managers influence people using: § Expertise § Work challenge § Projects are more likely to fail when project managers rely too heavily on: § Authority § Money § Penalty Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 13
Ways to Influence that Help and Hurt Projects § Projects are more likely to succeed when project managers influence people using: § Expertise § Work challenge § Projects are more likely to fail when project managers rely too heavily on: § Authority § Money § Penalty Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 13
 Power § Power is the potential ability to influence behavior to get people to do things they would not otherwise do. § Types of power include: § Coercive power § Legitimate power § Expert power § Reward power § Referent power Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 14
Power § Power is the potential ability to influence behavior to get people to do things they would not otherwise do. § Types of power include: § Coercive power § Legitimate power § Expert power § Reward power § Referent power Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 14
 Improving Effectiveness: Covey’s Seven Habits § Project managers can apply Covey’s seven habits to improve effectiveness on projects. § Be proactive. § Begin with the end in mind. § Put first things first. § Think win/win. § Seek first to understand, then to be understood. § Synergize. § Sharpen the saw. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 15
Improving Effectiveness: Covey’s Seven Habits § Project managers can apply Covey’s seven habits to improve effectiveness on projects. § Be proactive. § Begin with the end in mind. § Put first things first. § Think win/win. § Seek first to understand, then to be understood. § Synergize. § Sharpen the saw. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 15
 Empathic Listening and Rapport § Good project managers are empathic listeners, meaning they listen with the intent to understand. § Before you can communicate with others, you have to have rapport, which is a relation of harmony, conformity, accord, or affinity. § Mirroring is the matching of certain behaviors of the other person, and is a technique used to help establish rapport. § IT professionals need to develop empathic listening and other people skills to improve relationships with users and other stakeholders. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 16
Empathic Listening and Rapport § Good project managers are empathic listeners, meaning they listen with the intent to understand. § Before you can communicate with others, you have to have rapport, which is a relation of harmony, conformity, accord, or affinity. § Mirroring is the matching of certain behaviors of the other person, and is a technique used to help establish rapport. § IT professionals need to develop empathic listening and other people skills to improve relationships with users and other stakeholders. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 16
 Organizational Planning § Involves identifying and documenting project roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships. § Outputs include: § Project organizational charts § Staffing management plans § Responsibility assignment matrixes § Resource histograms Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 17
Organizational Planning § Involves identifying and documenting project roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships. § Outputs include: § Project organizational charts § Staffing management plans § Responsibility assignment matrixes § Resource histograms Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 17
 Team Organization § Teams are used throughout software production § Especially during implementation § Two extreme approaches to team organization § Democratic teams (Weinberg, 1971) § Chief programmer teams (Brooks, 1971; Baker, 1972) Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 18
Team Organization § Teams are used throughout software production § Especially during implementation § Two extreme approaches to team organization § Democratic teams (Weinberg, 1971) § Chief programmer teams (Brooks, 1971; Baker, 1972) Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 18
 Democratic Team Approach § Basic underlying concept—egoless programming § Egoless programming § § § § Restructure the social environment Restructure programmers’ values Encourage team members to find faults in code A fault must be considered a normal and accepted event The team as whole will develop an ethos, group identity Modules will “belong” to the team as whole A group of up to 10 egoless programmers constitutes a democratic team Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 19
Democratic Team Approach § Basic underlying concept—egoless programming § Egoless programming § § § § Restructure the social environment Restructure programmers’ values Encourage team members to find faults in code A fault must be considered a normal and accepted event The team as whole will develop an ethos, group identity Modules will “belong” to the team as whole A group of up to 10 egoless programmers constitutes a democratic team Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 19
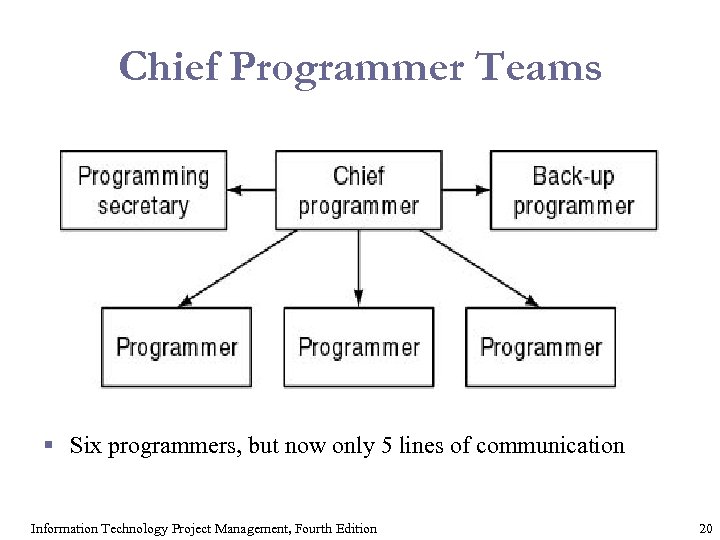 Chief Programmer Teams § Six programmers, but now only 5 lines of communication Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 20
Chief Programmer Teams § Six programmers, but now only 5 lines of communication Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 20
 Chief Programmer Teams § Two key aspects § Specialization § Hierarchy § Chief programmer is personally responsible for every line of code. § He/she must therefore be present at reviews § Chief programmer is also team manager, § He/she must therefore not be present at reviews! Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 21
Chief Programmer Teams § Two key aspects § Specialization § Hierarchy § Chief programmer is personally responsible for every line of code. § He/she must therefore be present at reviews § Chief programmer is also team manager, § He/she must therefore not be present at reviews! Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 21
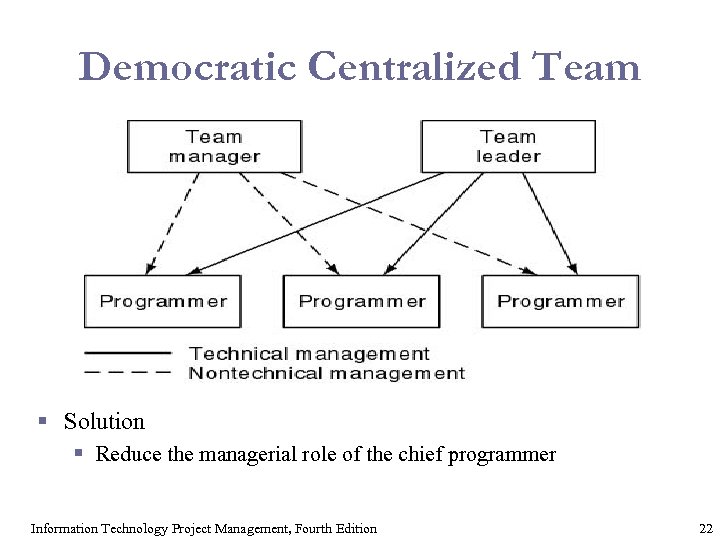 Democratic Centralized Team § Solution § Reduce the managerial role of the chief programmer Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 22
Democratic Centralized Team § Solution § Reduce the managerial role of the chief programmer Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 22
 Democratic Centralized Team § It is easier to find a team leader than a chief programmer § Each employee is responsible to exactly one manager—lines of responsibility are clearly delineated § Team leader is responsible for only technical management § Budgetary and legal issues, and performance appraisal are not handled by the team leader § Team leader participates in reviews—the team manager is not permitted to do so § Team manager participates at regular team meetings to appraise the technical skills of the team members Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 23
Democratic Centralized Team § It is easier to find a team leader than a chief programmer § Each employee is responsible to exactly one manager—lines of responsibility are clearly delineated § Team leader is responsible for only technical management § Budgetary and legal issues, and performance appraisal are not handled by the team leader § Team leader participates in reviews—the team manager is not permitted to do so § Team manager participates at regular team meetings to appraise the technical skills of the team members Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 23
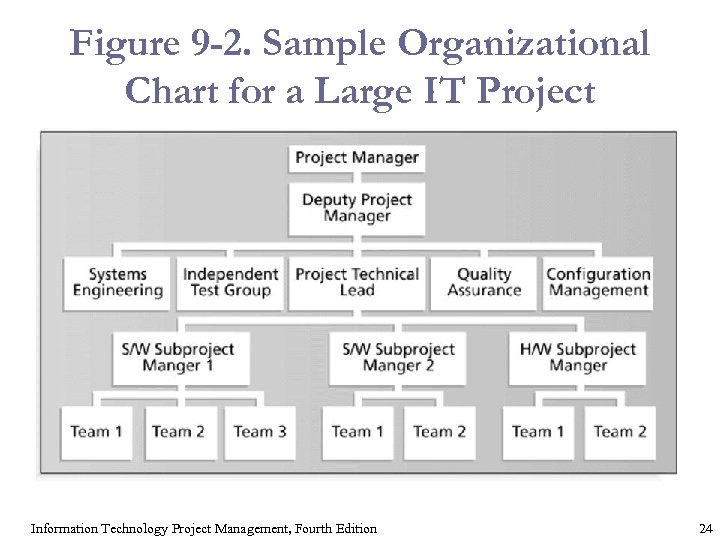 Figure 9 -2. Sample Organizational Chart for a Large IT Project Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 24
Figure 9 -2. Sample Organizational Chart for a Large IT Project Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 24
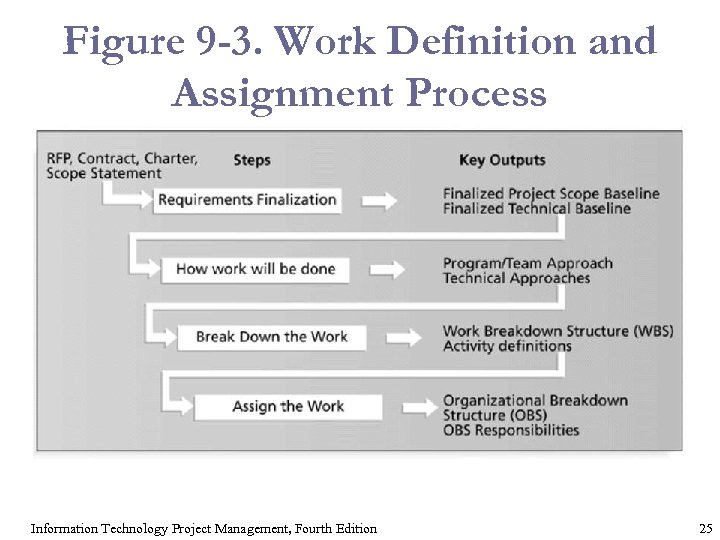 Figure 9 -3. Work Definition and Assignment Process Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 25
Figure 9 -3. Work Definition and Assignment Process Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 25
 Responsibility Assignment Matrixes § A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) is a matrix that maps the work of the project, as described in the WBS, to the people responsible for performing the work, as described in the OBS. § Can be created in different ways to meet unique project needs. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 26
Responsibility Assignment Matrixes § A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) is a matrix that maps the work of the project, as described in the WBS, to the people responsible for performing the work, as described in the OBS. § Can be created in different ways to meet unique project needs. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 26
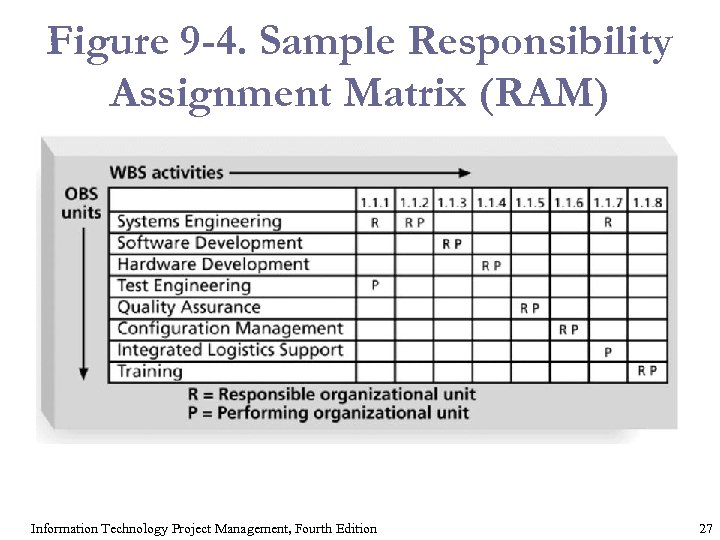 Figure 9 -4. Sample Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 27
Figure 9 -4. Sample Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 27
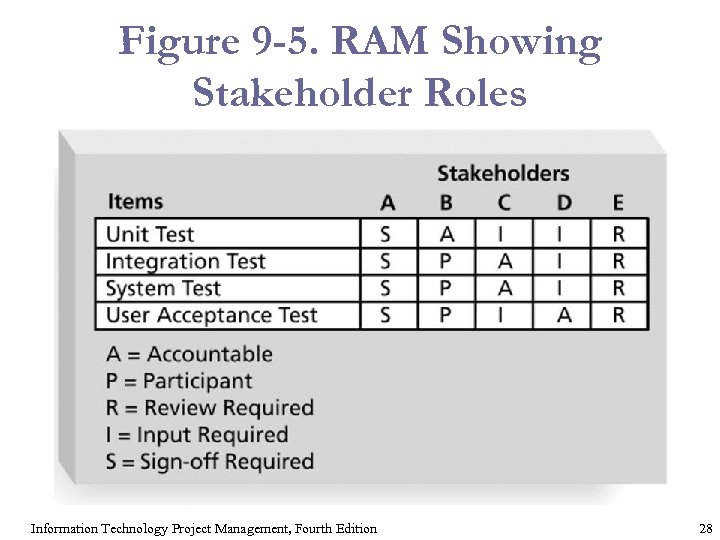 Figure 9 -5. RAM Showing Stakeholder Roles Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 28
Figure 9 -5. RAM Showing Stakeholder Roles Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 28
 Staffing Management Plans and Resource Histograms § A staffing management plan describes when and how people will be added to and taken off the project team. § A resource histogram is a column chart that shows the number of resources assigned to a project over time. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 29
Staffing Management Plans and Resource Histograms § A staffing management plan describes when and how people will be added to and taken off the project team. § A resource histogram is a column chart that shows the number of resources assigned to a project over time. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 29
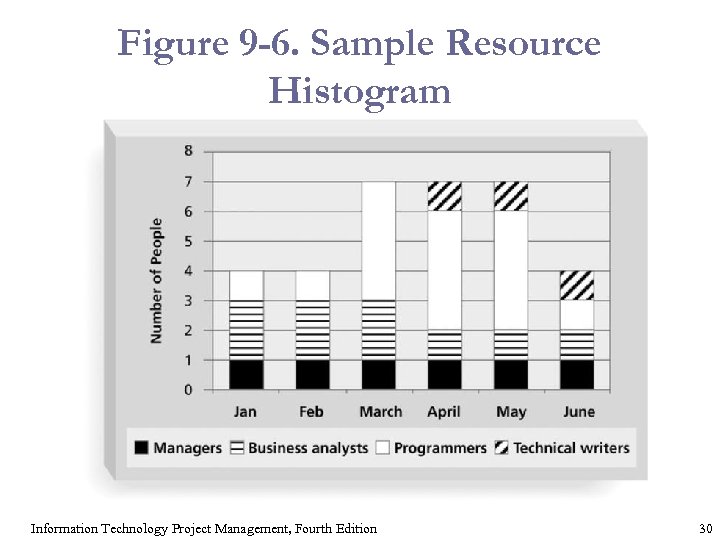 Figure 9 -6. Sample Resource Histogram Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 30
Figure 9 -6. Sample Resource Histogram Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 30
 Acquiring the Project Team § Acquiring qualified people for teams is crucial. § The project manager who is the smartest person on the team has done a poor job of recruiting! § Staffing plans and good hiring procedures are important, as are incentives for recruiting and retention. § Some companies give their employees one dollar for every hour that a new person who they helped hire works. § Some organizations allow people to work from home as an incentive. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 31
Acquiring the Project Team § Acquiring qualified people for teams is crucial. § The project manager who is the smartest person on the team has done a poor job of recruiting! § Staffing plans and good hiring procedures are important, as are incentives for recruiting and retention. § Some companies give their employees one dollar for every hour that a new person who they helped hire works. § Some organizations allow people to work from home as an incentive. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 31
 Why People Leave Their Jobs § They feel they do not make a difference. § They do not get proper recognition. § They are not learning anything new or growing as a person. § They do not like their coworkers. § They want to earn more money. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 32
Why People Leave Their Jobs § They feel they do not make a difference. § They do not get proper recognition. § They are not learning anything new or growing as a person. § They do not like their coworkers. § They want to earn more money. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 32
 Developing the Project Team § The main goal of team development is to help people work together more effectively to improve project performance. § It takes teamwork to successfully complete most projects. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 33
Developing the Project Team § The main goal of team development is to help people work together more effectively to improve project performance. § It takes teamwork to successfully complete most projects. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 33
 Managing the Project Team § Project managers must lead their teams in performing various project activities. § After assessing team performance and related information, the project manager must decide: § If changes should be requested to the project. § If corrective or preventive actions should be recommended. § If updates are needed to the project management plan or organizational process assets. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 34
Managing the Project Team § Project managers must lead their teams in performing various project activities. § After assessing team performance and related information, the project manager must decide: § If changes should be requested to the project. § If corrective or preventive actions should be recommended. § If updates are needed to the project management plan or organizational process assets. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 34
 Tools and Techniques for Managing Project Teams § Observation and conversation § Project performance appraisals § Conflict management § Issue logs Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 35
Tools and Techniques for Managing Project Teams § Observation and conversation § Project performance appraisals § Conflict management § Issue logs Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 35
 General Advice on Teams § Be patient and kind with your team. § Fix the problem instead of blaming people. § Establish regular, effective meetings. § Allow time for teams to go through the basic teambuilding stages. § Limit the size of work teams to three to seven members. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 36
General Advice on Teams § Be patient and kind with your team. § Fix the problem instead of blaming people. § Establish regular, effective meetings. § Allow time for teams to go through the basic teambuilding stages. § Limit the size of work teams to three to seven members. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 36
 General Advice on Teams (cont’d) § Plan some social activities to help project team members and other stakeholders get to know each other better. § Stress team identity. § Nurture team members and encourage them to help each other. § Take additional actions to work with virtual team members. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 37
General Advice on Teams (cont’d) § Plan some social activities to help project team members and other stakeholders get to know each other better. § Stress team identity. § Nurture team members and encourage them to help each other. § Take additional actions to work with virtual team members. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 37
 Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management
 Human Resources Management
Human Resources Management
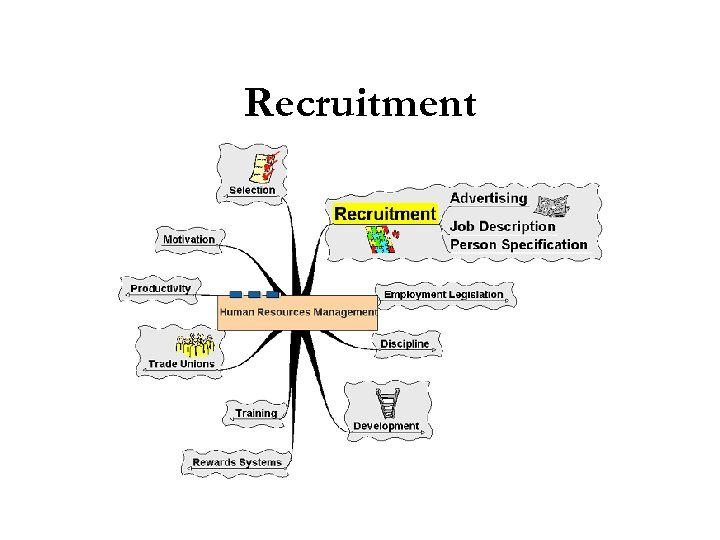 Recruitment
Recruitment
 Recruitment § The process by which a job vacancy is identified and potential employees are notified. § The nature of the recruitment process is regulated and subject to employment law. § Main forms of recruitment through advertising in newspapers, magazines, trade papers and internal vacancy lists.
Recruitment § The process by which a job vacancy is identified and potential employees are notified. § The nature of the recruitment process is regulated and subject to employment law. § Main forms of recruitment through advertising in newspapers, magazines, trade papers and internal vacancy lists.
 Recruitment § Job description – outline of the role of the job holder § Person specification – outline of the skills and qualities required of the post holder § Applicants may demonstrate their suitability through application form, letter or curriculum vitae (CV)
Recruitment § Job description – outline of the role of the job holder § Person specification – outline of the skills and qualities required of the post holder § Applicants may demonstrate their suitability through application form, letter or curriculum vitae (CV)
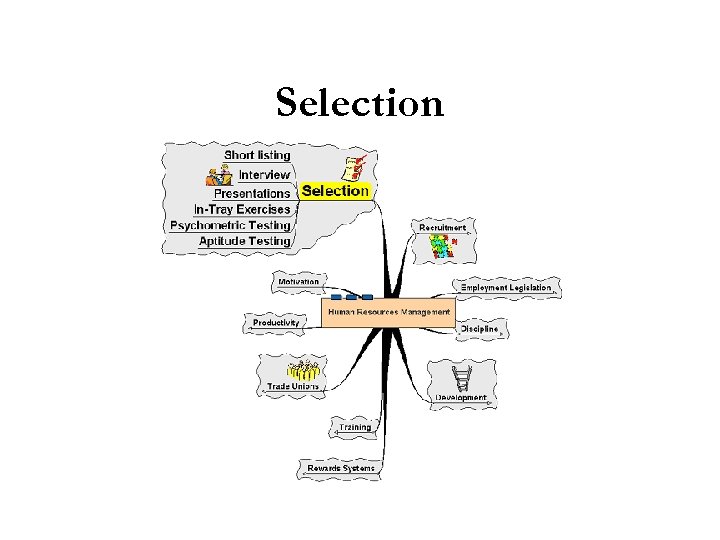 Selection
Selection
 Selection § The process of assessing candidates and appointing a post holder § Applicants short listed – most suitable candidates selected § Selection process – varies according to organisation:
Selection § The process of assessing candidates and appointing a post holder § Applicants short listed – most suitable candidates selected § Selection process – varies according to organisation:
 Selection § Interview – most common method § Psychometric testing – assessing the personality of the applicants – will they fit in? § Aptitude testing – assessing the skills of applicants § In-tray exercise – activity based around what the applicant will be doing, e. g. writing a letter to a disgruntled customer § Presentation – looking for different skills as well as the ideas of the candidate
Selection § Interview – most common method § Psychometric testing – assessing the personality of the applicants – will they fit in? § Aptitude testing – assessing the skills of applicants § In-tray exercise – activity based around what the applicant will be doing, e. g. writing a letter to a disgruntled customer § Presentation – looking for different skills as well as the ideas of the candidate
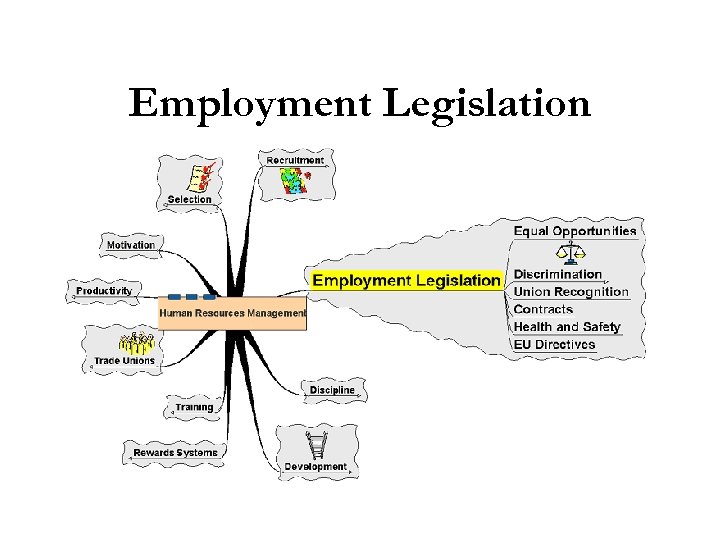 Employment Legislation
Employment Legislation
 Employment Legislation § Increasingly important aspect of the HRM role § Wide range of areas for attention § Adds to the cost of the business Even in a small business, the legislation relating to employees is important – chemicals used in a hairdressing salon for example have to be carefully stored and handled to protect employees.
Employment Legislation § Increasingly important aspect of the HRM role § Wide range of areas for attention § Adds to the cost of the business Even in a small business, the legislation relating to employees is important – chemicals used in a hairdressing salon for example have to be carefully stored and handled to protect employees.
 Discrimination § Crucial aspects of employment legislation: § Race § Gender § Disability is no longer an issue for employers to ignore, they must take reasonable steps to accommodate and recruit disabled workers. Copyright: Mela, http: //www. sxc. hu
Discrimination § Crucial aspects of employment legislation: § Race § Gender § Disability is no longer an issue for employers to ignore, they must take reasonable steps to accommodate and recruit disabled workers. Copyright: Mela, http: //www. sxc. hu
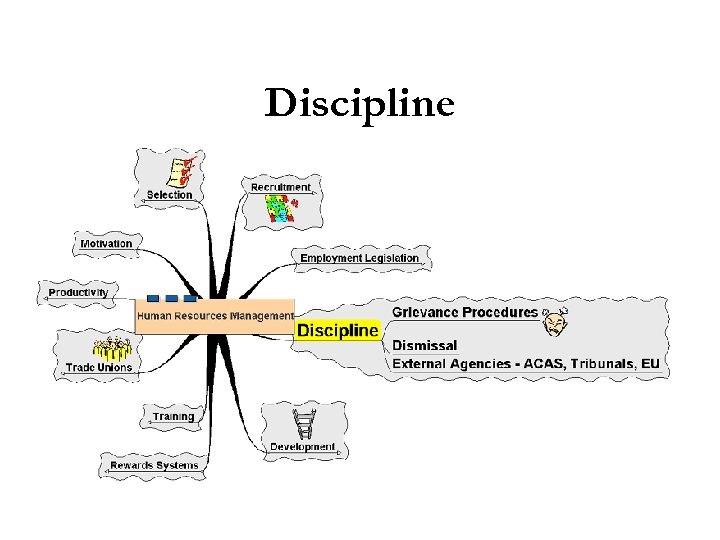 Discipline
Discipline
 Discipline § Firms cannot just ‘sack’ workers § Wide range of procedures and steps in dealing with workplace conflict § § § Informal meetings Formal meetings Verbal warnings Written warnings Grievance procedures Working with external agencies
Discipline § Firms cannot just ‘sack’ workers § Wide range of procedures and steps in dealing with workplace conflict § § § Informal meetings Formal meetings Verbal warnings Written warnings Grievance procedures Working with external agencies
 Development
Development
 Development § Developing the employee can be regarded as investing in a valuable asset § A source of motivation § A source of helping the employee fulfil potential
Development § Developing the employee can be regarded as investing in a valuable asset § A source of motivation § A source of helping the employee fulfil potential
 Training
Training
 Training § Similar to development: § Provides new skills for the employee § Keeps the employee up to date with changes in the field § Aims to improve efficiency § Can be external or ‘in-house’
Training § Similar to development: § Provides new skills for the employee § Keeps the employee up to date with changes in the field § Aims to improve efficiency § Can be external or ‘in-house’
 Rewards Systems
Rewards Systems
 Rewards Systems § The system of pay and benefits used by the firm to reward workers § Money not the only method § Fringe benefits § Flexibility at work § Holidays, etc.
Rewards Systems § The system of pay and benefits used by the firm to reward workers § Money not the only method § Fringe benefits § Flexibility at work § Holidays, etc.
 Trade Unions
Trade Unions
 Trade Unions § Importance of building relationships with employee representatives § Role of Trade Unions has changed § Importance of consultation and negotiation and working with trade unions § Contributes to smooth change management and leadership
Trade Unions § Importance of building relationships with employee representatives § Role of Trade Unions has changed § Importance of consultation and negotiation and working with trade unions § Contributes to smooth change management and leadership
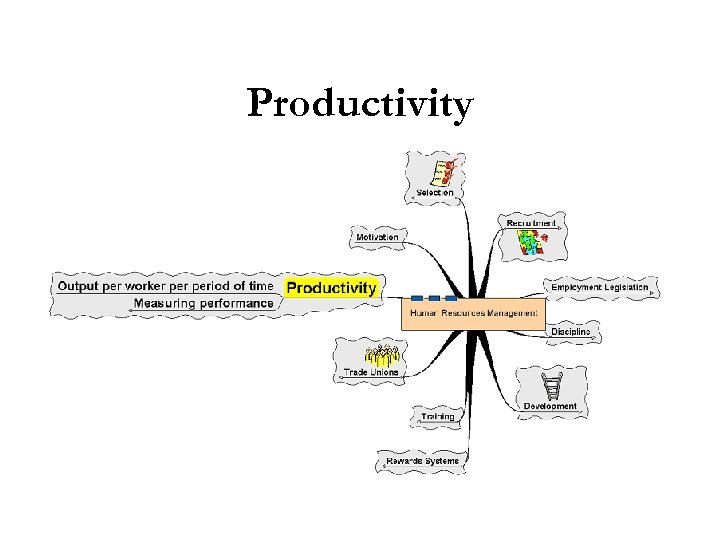 Productivity
Productivity
 Productivity § Measuring performance: § How to value the workers contribution § Difficulty in measuring some types of output – especially in the service industry § Appraisal § Meant to be non-judgmental § Involves the worker and a nominated appraiser § Agreeing strengths, weaknesses and ways forward to help both employee and organisation
Productivity § Measuring performance: § How to value the workers contribution § Difficulty in measuring some types of output – especially in the service industry § Appraisal § Meant to be non-judgmental § Involves the worker and a nominated appraiser § Agreeing strengths, weaknesses and ways forward to help both employee and organisation
 Human Resource Management Strategy HR Management MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
Human Resource Management Strategy HR Management MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 Human Resource Management Strategy The Meaning of “Strategy” § A critical factor that affects Firm Performance § A factor that contributes to Competitive Advantage in markets § Having a long-term focus § Plans that involve the top executives and/or board of directors of the firm § A general framework that provides a perspective for selecting specific policies and procedures MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
Human Resource Management Strategy The Meaning of “Strategy” § A critical factor that affects Firm Performance § A factor that contributes to Competitive Advantage in markets § Having a long-term focus § Plans that involve the top executives and/or board of directors of the firm § A general framework that provides a perspective for selecting specific policies and procedures MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 Human Resource Management Strategy Why is HR critical to firm performance? § 85% of all firms in the US are service firms. § Service is delivered by people. § Low quality HR leads to low quality customer service. § In the 21 st century effective knowledge management translates into competitive advantage and profits. § Knowledge comes from a firm’s people. MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
Human Resource Management Strategy Why is HR critical to firm performance? § 85% of all firms in the US are service firms. § Service is delivered by people. § Low quality HR leads to low quality customer service. § In the 21 st century effective knowledge management translates into competitive advantage and profits. § Knowledge comes from a firm’s people. MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 Human Resource Management Strategy What is unique about Human Resource Management? § HR is multidisciplinary: It applies the disciplines of Economics (wages, markets, resources), Psychology (motivation, satisfaction), Sociology (organization structure, culture) and Law (min. wage, labor contracts, EEOC) § HR is embedded within the work of all managers, and most individual contributors due to the need of managing people (subordinates, peers and superiors) as well as teams to get things done. MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
Human Resource Management Strategy What is unique about Human Resource Management? § HR is multidisciplinary: It applies the disciplines of Economics (wages, markets, resources), Psychology (motivation, satisfaction), Sociology (organization structure, culture) and Law (min. wage, labor contracts, EEOC) § HR is embedded within the work of all managers, and most individual contributors due to the need of managing people (subordinates, peers and superiors) as well as teams to get things done. MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
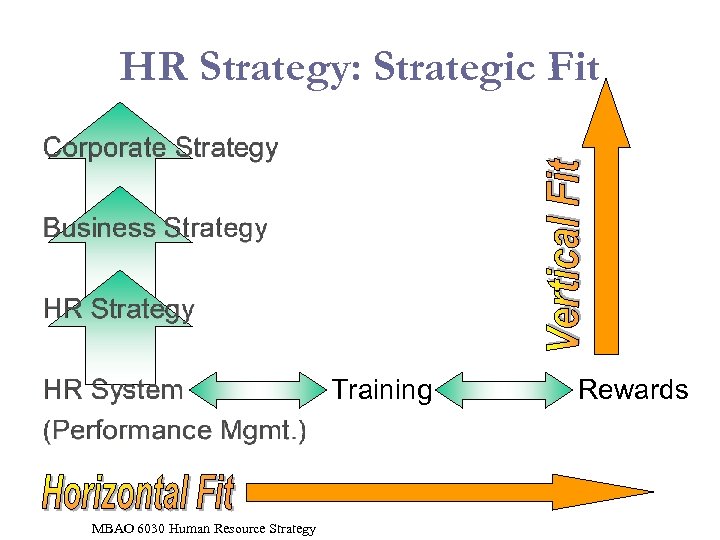 HR Strategy: Strategic Fit Training MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy Rewards
HR Strategy: Strategic Fit Training MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy Rewards
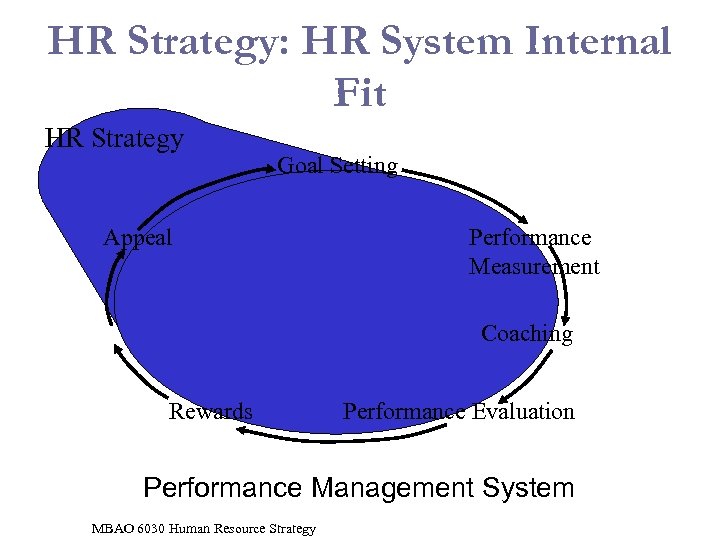 HR Strategy: HR System Internal Fit HR Strategy Goal Setting Appeal Performance Measurement Coaching Rewards Performance Evaluation Performance Management System MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: HR System Internal Fit HR Strategy Goal Setting Appeal Performance Measurement Coaching Rewards Performance Evaluation Performance Management System MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Context of HR System 1. The “Five Factors” Influencing the HR System § External Environment § Social: social values, roles, trends, etc. § Political: political forces, changes. Ex. Bush presidency and its agenda for Social Security. § Legal: laws, court decisions, regulatory rules. § Economic: product, labor, capital, factor markets. MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Context of HR System 1. The “Five Factors” Influencing the HR System § External Environment § Social: social values, roles, trends, etc. § Political: political forces, changes. Ex. Bush presidency and its agenda for Social Security. § Legal: laws, court decisions, regulatory rules. § Economic: product, labor, capital, factor markets. MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Context of HR System 2. The Workforce § Demographics MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Context of HR System 2. The Workforce § Demographics MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Context of HR System 3. Organization Culture § § Weak vs. Strong culture “Type” of culture MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Context of HR System 3. Organization Culture § § Weak vs. Strong culture “Type” of culture MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Context of HR System 4. Organization Strategy What are a firm’s distinctive competencies? § What is the basis that competitive strategy be sustained? § What are a firm’s strategic objectives? § Compare corporate and Business strategies. § MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Context of HR System 4. Organization Strategy What are a firm’s distinctive competencies? § What is the basis that competitive strategy be sustained? § What are a firm’s strategic objectives? § Compare corporate and Business strategies. § MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Context of HR System 5. Technology of Production & Organization of Work § § § Physical layout/employee proximity Required employee skills Ease of monitoring employees’ input MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Context of HR System 5. Technology of Production & Organization of Work § § § Physical layout/employee proximity Required employee skills Ease of monitoring employees’ input MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Context of HR System Critical Thinking Questions: 1. Should a company monitor the HR environment and imitate “Best Practices” of HR from successful firms? What caveats would you want to applying Best HR Practices? 2. Give an example of a type of Organizational Culture that would reinforce strategy: What type of HR practices would fit with this culture? 3. What type of HR practices would fit with jobs with tasks that are highly ambiguous, uncertain and creative? What about predictable, routine and certain tasks? MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Context of HR System Critical Thinking Questions: 1. Should a company monitor the HR environment and imitate “Best Practices” of HR from successful firms? What caveats would you want to applying Best HR Practices? 2. Give an example of a type of Organizational Culture that would reinforce strategy: What type of HR practices would fit with this culture? 3. What type of HR practices would fit with jobs with tasks that are highly ambiguous, uncertain and creative? What about predictable, routine and certain tasks? MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Strategic Roles Distribution of Task Outcomes: 3 Possibilities 1. “Foot soldier”: low upside, low downside of performance variance 2. “Guardian”: low upside, high downside of performance variance 3. “Star”: high upside, low downside of performance variance MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Strategic Roles Distribution of Task Outcomes: 3 Possibilities 1. “Foot soldier”: low upside, low downside of performance variance 2. “Guardian”: low upside, high downside of performance variance 3. “Star”: high upside, low downside of performance variance MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Strategic Roles Critical Thinking Questions: 1. Which Roles are Strategic? Foot soldier, guardian or star? 2. What are the advantages of focusing on foot soldiers with the company HR policies? 3. What are the liabilities of stars? When is it advantageous to cultivate and sustain stars? MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Strategic Roles Critical Thinking Questions: 1. Which Roles are Strategic? Foot soldier, guardian or star? 2. What are the advantages of focusing on foot soldiers with the company HR policies? 3. What are the liabilities of stars? When is it advantageous to cultivate and sustain stars? MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Consistency is an important quality related to the implementation of HR policies. Employees should receive a clear, undiluted message of what behaviors are important and desirable. When there is a fit between HR systems, employees are likely to receive consistent feedback. The 3 types of consistency are… 1. Single-employee consistency 2. Among-employee consistency 3. Temporal consistency MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Consistency is an important quality related to the implementation of HR policies. Employees should receive a clear, undiluted message of what behaviors are important and desirable. When there is a fit between HR systems, employees are likely to receive consistent feedback. The 3 types of consistency are… 1. Single-employee consistency 2. Among-employee consistency 3. Temporal consistency MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 HR Strategy: Consistency Critical Thinking Questions 1. Are there circumstances when it is effective to have inconsistent HR policies? Give an example. 2. Does an emphasis on temporal consistency create a barrier for change when change is necessary? 3. What impact (if any) would consistency have on the organization culture? MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
HR Strategy: Consistency Critical Thinking Questions 1. Are there circumstances when it is effective to have inconsistent HR policies? Give an example. 2. Does an emphasis on temporal consistency create a barrier for change when change is necessary? 3. What impact (if any) would consistency have on the organization culture? MBAO 6030 Human Resource Strategy
 Changing Nature of Human Resource Management Jack Welch- Winning “Elevate HR to a position of power and primacy in the organization, and make sure HR people have the special qualities to help managers build leaders and careers. In fact, the best HR types are pastors and parents in the same package. ” “The head of human resources at any company should be at least as important as the CFO. ” Chapter 1
Changing Nature of Human Resource Management Jack Welch- Winning “Elevate HR to a position of power and primacy in the organization, and make sure HR people have the special qualities to help managers build leaders and careers. In fact, the best HR types are pastors and parents in the same package. ” “The head of human resources at any company should be at least as important as the CFO. ” Chapter 1
 HR versus Management
HR versus Management
 Leaders are Readers § Peter Drucker § The Essential Drucker (2008) § “Business management must always, in every decision and action, put economic performance first. ”
Leaders are Readers § Peter Drucker § The Essential Drucker (2008) § “Business management must always, in every decision and action, put economic performance first. ”
 Leaders are Readers § Good to Great § Jim Collins (2001) § “Good is the enemy of great. ”
Leaders are Readers § Good to Great § Jim Collins (2001) § “Good is the enemy of great. ”
 Learning Objectives § After you have read this chapter, you should be able to: § Define HR management and identify the seven categories of HR activities. § Discuss three challenges facing HR today. § Describe how the major roles of HR management are being transformed. § Identify the purposes and uses of HR technology. § Discuss why ethical issues affect HR management. § Explain the key competencies needed by HR professionals and why certification is important.
Learning Objectives § After you have read this chapter, you should be able to: § Define HR management and identify the seven categories of HR activities. § Discuss three challenges facing HR today. § Describe how the major roles of HR management are being transformed. § Identify the purposes and uses of HR technology. § Discuss why ethical issues affect HR management. § Explain the key competencies needed by HR professionals and why certification is important.
 Today § In what kind of environment are we doing HR today? § HR Activities- what do HR people do? § HR Management Challenges- what external and internal factors influence what HR people do? § HR Roles- how do HR people do their jobs?
Today § In what kind of environment are we doing HR today? § HR Activities- what do HR people do? § HR Management Challenges- what external and internal factors influence what HR people do? § HR Roles- how do HR people do their jobs?
 Nature of Human Resource Management § Human Resource (HR) Management § The design of formal systems in an organization to ensure effective and efficient use of human talent to accomplish organizational goals.
Nature of Human Resource Management § Human Resource (HR) Management § The design of formal systems in an organization to ensure effective and efficient use of human talent to accomplish organizational goals.
 Nature of Human Resource Management cont § Who Is an HR Manager? § In the course carrying out their duties, every operating manager is, in essence, an HR manager. § HR specialists design processes and systems that operating managers help implement. .
Nature of Human Resource Management cont § Who Is an HR Manager? § In the course carrying out their duties, every operating manager is, in essence, an HR manager. § HR specialists design processes and systems that operating managers help implement. .
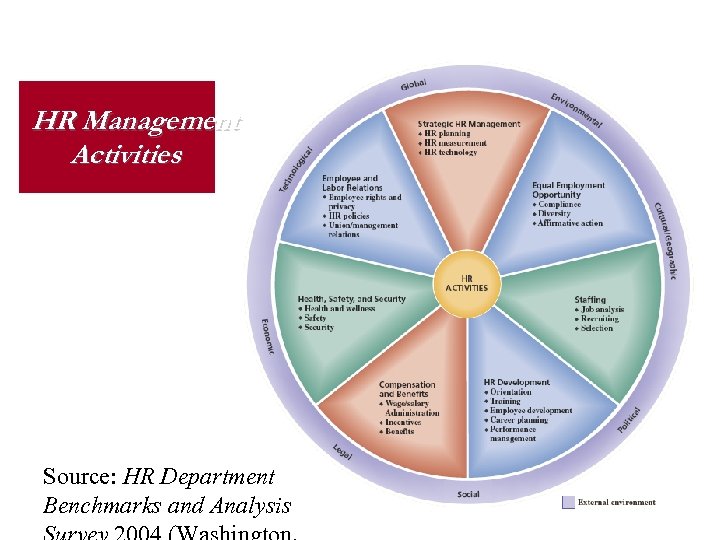 HR Management Activities Source: HR Department Benchmarks and Analysis
HR Management Activities Source: HR Department Benchmarks and Analysis
 HR Activities Strategic HR Management What is “Strategic”? Metrics Environmental Scanning/Anticipation High Performance Work Practices Leveraging Core Competencies
HR Activities Strategic HR Management What is “Strategic”? Metrics Environmental Scanning/Anticipation High Performance Work Practices Leveraging Core Competencies
 HR Activities Continued Equal Employment Opportunity Compliance Multicultural Organizations Diversity Affirmative Action Global Impacts: Resources, Markets, Employees EEOC and the OFCCP
HR Activities Continued Equal Employment Opportunity Compliance Multicultural Organizations Diversity Affirmative Action Global Impacts: Resources, Markets, Employees EEOC and the OFCCP
 HR Activities Continued Staffing Attraction Selection Attrition Model Job Description Job Analysis Qualifications Recruiting, Interviewing HR Development Orientation Socialization Job Training Leadership Development Performance Management
HR Activities Continued Staffing Attraction Selection Attrition Model Job Description Job Analysis Qualifications Recruiting, Interviewing HR Development Orientation Socialization Job Training Leadership Development Performance Management
 HR Activities Continued § Compensation and Benefits § § § § Base Pay Merit Pay/Incentives Gainsharing Employee Ownership Management of Health and Dental Costs Cafeteria Plans Employee Rewards
HR Activities Continued § Compensation and Benefits § § § § Base Pay Merit Pay/Incentives Gainsharing Employee Ownership Management of Health and Dental Costs Cafeteria Plans Employee Rewards
 HR Activities Continued Health, Safety, and Security OSHA (1970)…who has the responsibility for healthy employees? Safety in the workplace Security post 9 -11 EAPs Health Promotion Employee and Labor Relations Unionization Policies and Procedures Communication (Justice Theory)
HR Activities Continued Health, Safety, and Security OSHA (1970)…who has the responsibility for healthy employees? Safety in the workplace Security post 9 -11 EAPs Health Promotion Employee and Labor Relations Unionization Policies and Procedures Communication (Justice Theory)
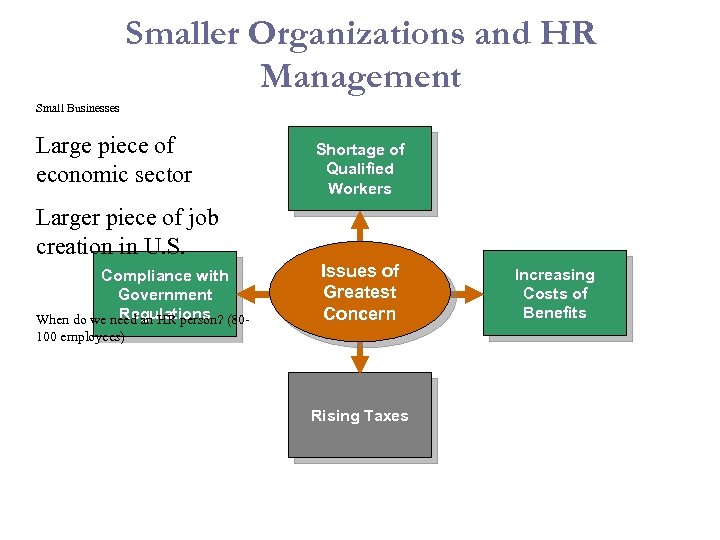 Smaller Organizations and HR Management Small Businesses Large piece of economic sector Shortage of Qualified Workers Larger piece of job creation in U. S. Compliance with Government Regulations When do we need an HR person? (80 - Issues of Greatest Concern 100 employees) Rising Taxes Increasing Costs of Benefits
Smaller Organizations and HR Management Small Businesses Large piece of economic sector Shortage of Qualified Workers Larger piece of job creation in U. S. Compliance with Government Regulations When do we need an HR person? (80 - Issues of Greatest Concern 100 employees) Rising Taxes Increasing Costs of Benefits
 Management of Human Capital In Organizations § Physical, Financial, Intangible and § Human Capital § The collective value of the capabilities, knowledge, skills, life experiences, and motivation of an organizational workforce. § Also known as intellectual capital. § How to measure the strategic value of human assets? § Core Competency § A unique capability that creates high value and differentiates an organization from its competition. § HR competencies: a source of competitive advantage.
Management of Human Capital In Organizations § Physical, Financial, Intangible and § Human Capital § The collective value of the capabilities, knowledge, skills, life experiences, and motivation of an organizational workforce. § Also known as intellectual capital. § How to measure the strategic value of human assets? § Core Competency § A unique capability that creates high value and differentiates an organization from its competition. § HR competencies: a source of competitive advantage.
 Human Capital in Organizations Human Capital Core Competency The collective value of the capabilities, knowledge, skills, life experiences, and motivation of an organizational workforce. A unique capability that creates high value and differentiates an organization from its competition. 1– 93
Human Capital in Organizations Human Capital Core Competency The collective value of the capabilities, knowledge, skills, life experiences, and motivation of an organizational workforce. A unique capability that creates high value and differentiates an organization from its competition. 1– 93
 HR Management Challenges § Globalization of Business § Outsourcing and increased competition § Stockholder, employee, manager concerns? § Is this socially responsible? § Should the U. S. pass legislation protecting these jobs? Why/Why not? § What about the perspective that this is good for the long run as it lowers the costs of goods and services? Do you agree? Why/Why not?
HR Management Challenges § Globalization of Business § Outsourcing and increased competition § Stockholder, employee, manager concerns? § Is this socially responsible? § Should the U. S. pass legislation protecting these jobs? Why/Why not? § What about the perspective that this is good for the long run as it lowers the costs of goods and services? Do you agree? Why/Why not?
 HR Management Challenges § Globalization of Business § The threat of terrorism- How does this impact what we do? OSHA? § Economic and Technological Changes § Occupational shifts from manufacturing and agriculture to service industries and telecommunications. § Pressures of global competition causing firms to adapt by lowering costs and increasing productivity. § Technological Shifts and the Internet § Growth of information technology.
HR Management Challenges § Globalization of Business § The threat of terrorism- How does this impact what we do? OSHA? § Economic and Technological Changes § Occupational shifts from manufacturing and agriculture to service industries and telecommunications. § Pressures of global competition causing firms to adapt by lowering costs and increasing productivity. § Technological Shifts and the Internet § Growth of information technology.
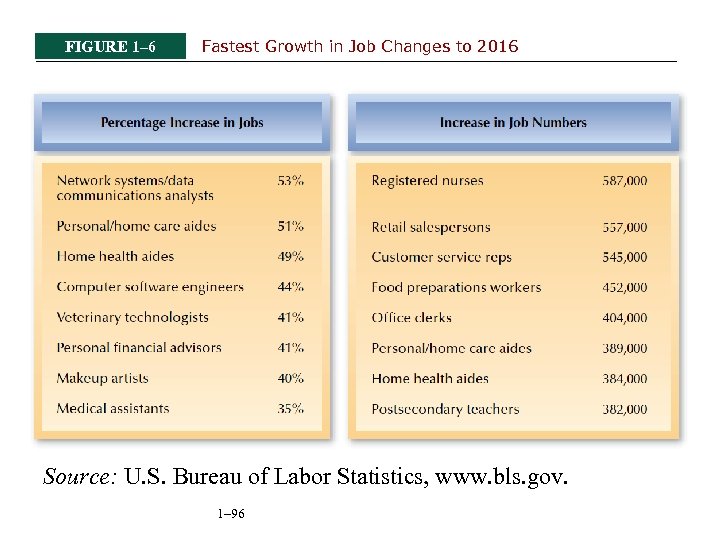 FIGURE 1– 6 Fastest Growth in Job Changes to 2016 Source: U. S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, www. bls. gov. 1– 96
FIGURE 1– 6 Fastest Growth in Job Changes to 2016 Source: U. S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, www. bls. gov. 1– 96
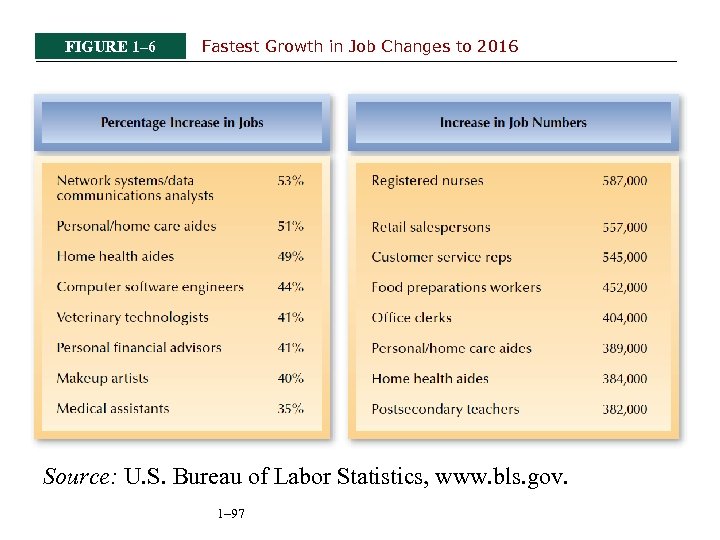 FIGURE 1– 6 Fastest Growth in Job Changes to 2016 Source: U. S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, www. bls. gov. 1– 97
FIGURE 1– 6 Fastest Growth in Job Changes to 2016 Source: U. S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, www. bls. gov. 1– 97
 HR Management Challenges Workforce Availability and Quality Concerns Inadequate supply of workers with needed skills for “knowledge jobs” 80% of manufacturing jobs report shortage of qualified workers Education of workers in basic skills Not enough specific skills, not enough technology skills Growth in Contingent Workforce Represents 20% of the workforce Increases in temporary workers, independent contractors, leased employees, and part-timers caused by: Need for flexibility in staffing levels Increased difficulty in firing regular employees. Reduced legal liability from contract employees Boeing Strategy- manage employment cycles in suppliers and partners
HR Management Challenges Workforce Availability and Quality Concerns Inadequate supply of workers with needed skills for “knowledge jobs” 80% of manufacturing jobs report shortage of qualified workers Education of workers in basic skills Not enough specific skills, not enough technology skills Growth in Contingent Workforce Represents 20% of the workforce Increases in temporary workers, independent contractors, leased employees, and part-timers caused by: Need for flexibility in staffing levels Increased difficulty in firing regular employees. Reduced legal liability from contract employees Boeing Strategy- manage employment cycles in suppliers and partners
 HR Management Challenges Workforce Demographics and Diversity Increasing Racial/Ethnic Diversity From the Melting Pot to the Salad Bowl More Women in the Workforce Single-parent households Dual-career couples Domestic partners Working mothers and family/childcare Significantly Aging Workforce Age discrimination
HR Management Challenges Workforce Demographics and Diversity Increasing Racial/Ethnic Diversity From the Melting Pot to the Salad Bowl More Women in the Workforce Single-parent households Dual-career couples Domestic partners Working mothers and family/childcare Significantly Aging Workforce Age discrimination
 HR Management Challenges § Organizational Cost Pressures and Restructuring § Mergers and Acquisitions § “Right-sizing”—eliminating of layers of management, closing facilities, merging with other organizations, and outplacing workers § Intended results are flatter organizations, increases in productivity, quality, service and lower costs. § Costs are “survivor mentality”, loss of employee loyalty, and turnover of valuable employees. § HR managers must work toward ensuring cultural compatibility in mergers.
HR Management Challenges § Organizational Cost Pressures and Restructuring § Mergers and Acquisitions § “Right-sizing”—eliminating of layers of management, closing facilities, merging with other organizations, and outplacing workers § Intended results are flatter organizations, increases in productivity, quality, service and lower costs. § Costs are “survivor mentality”, loss of employee loyalty, and turnover of valuable employees. § HR managers must work toward ensuring cultural compatibility in mergers.
 HR Management Roles § Administrative Role § Clerical and administrative support operations (e. g. , payroll and benefits work) § Technology is transforming how HR services are delivered. § Outsourcing HR services to reduce HR staffing costs § Operational and Employee Advocate Role § “Champion” for employee concerns § Employee crisis management § Responding to employee complaints
HR Management Roles § Administrative Role § Clerical and administrative support operations (e. g. , payroll and benefits work) § Technology is transforming how HR services are delivered. § Outsourcing HR services to reduce HR staffing costs § Operational and Employee Advocate Role § “Champion” for employee concerns § Employee crisis management § Responding to employee complaints
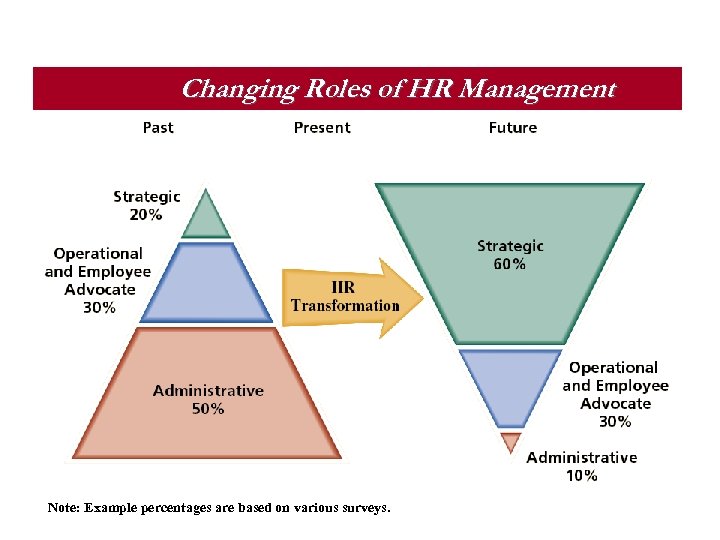 Changing Roles of HR Management Note: Example percentages are based on various surveys.
Changing Roles of HR Management Note: Example percentages are based on various surveys.
 Strategic Role for HR § § Administrative Role Operational Role Employee Advocate Role Strategic Role § “Contributing at the Table” to organizational results § HR becomes a strategic business partner by: § Focusing on developing HR programs that enhance organizational performance. § Involving HR in strategic planning at the onset. § Participating in decision making on mergers, acquisitions, and downsizing. § Redesigning organizations and work processes § Accounting and documenting the financial results of HR activities. § Some HR people get this, some don’t…CEOs want those that do and oust those that don’t
Strategic Role for HR § § Administrative Role Operational Role Employee Advocate Role Strategic Role § “Contributing at the Table” to organizational results § HR becomes a strategic business partner by: § Focusing on developing HR programs that enhance organizational performance. § Involving HR in strategic planning at the onset. § Participating in decision making on mergers, acquisitions, and downsizing. § Redesigning organizations and work processes § Accounting and documenting the financial results of HR activities. § Some HR people get this, some don’t…CEOs want those that do and oust those that don’t
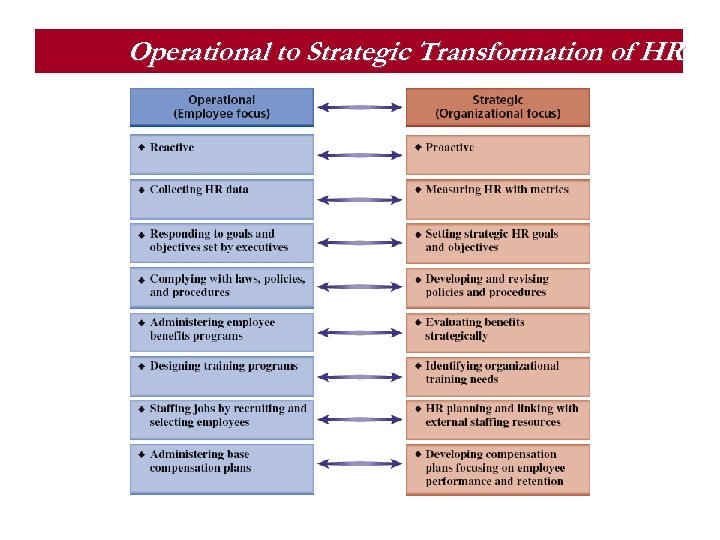 Operational to Strategic Transformation of HR
Operational to Strategic Transformation of HR
 HR Technology Human Resource Management System (HRMS) An integrated system providing information used by HR management in decision making. Purposes (Benefits) of HRMS Administrative and operational efficiency in compiling HR data Availability of data for effective HR strategic planning Uses of HRMS Automation of payroll and benefit activities EEO/affirmative action tracking HR Workflow: increased access to HR information Employee self-service reduces HR costs.
HR Technology Human Resource Management System (HRMS) An integrated system providing information used by HR management in decision making. Purposes (Benefits) of HRMS Administrative and operational efficiency in compiling HR data Availability of data for effective HR strategic planning Uses of HRMS Automation of payroll and benefit activities EEO/affirmative action tracking HR Workflow: increased access to HR information Employee self-service reduces HR costs.
 Uses of an HRMS Bulletin boards What information will be available and what is information needed? Data access To what uses will the information be put? Employee self-service Who will be allowed to access to what information? Web-based services and access Extended linkage When, where, and how often will the information be needed?
Uses of an HRMS Bulletin boards What information will be available and what is information needed? Data access To what uses will the information be put? Employee self-service Who will be allowed to access to what information? Web-based services and access Extended linkage When, where, and how often will the information be needed?
 Ethics and HR Management Firms with High Ethical Standards Are more likely to reach strategic goals. Are viewed more positively by stakeholders Are better able to attract and retain human resources. Ethics and Global Differences Different legal, political, and cultural factors in other countries can lead to ethical conflicts for global managers. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) Prohibits U. S. firms from engaging in bribery and other practices in other countries.
Ethics and HR Management Firms with High Ethical Standards Are more likely to reach strategic goals. Are viewed more positively by stakeholders Are better able to attract and retain human resources. Ethics and Global Differences Different legal, political, and cultural factors in other countries can lead to ethical conflicts for global managers. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) Prohibits U. S. firms from engaging in bribery and other practices in other countries.
 Leaders are Readers § The Smartest Guys in the Room (2004) § Mc. Lean and Elkind § “The tale of Enron is a story of human weakness, of hubris and greed and rampant self-delusion; of ambition run amok; of a grand experiment in the deregulated world; of a business model that didn’t’ work; and of smart people who believed their next gamble could cover up their last disaster—and who couldn’t admit they were wrong”.
Leaders are Readers § The Smartest Guys in the Room (2004) § Mc. Lean and Elkind § “The tale of Enron is a story of human weakness, of hubris and greed and rampant self-delusion; of ambition run amok; of a grand experiment in the deregulated world; of a business model that didn’t’ work; and of smart people who believed their next gamble could cover up their last disaster—and who couldn’t admit they were wrong”.
 FIGURE 1– 4 © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May Business Ethics and HR Management Consequences 1– 109
FIGURE 1– 4 © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May Business Ethics and HR Management Consequences 1– 109
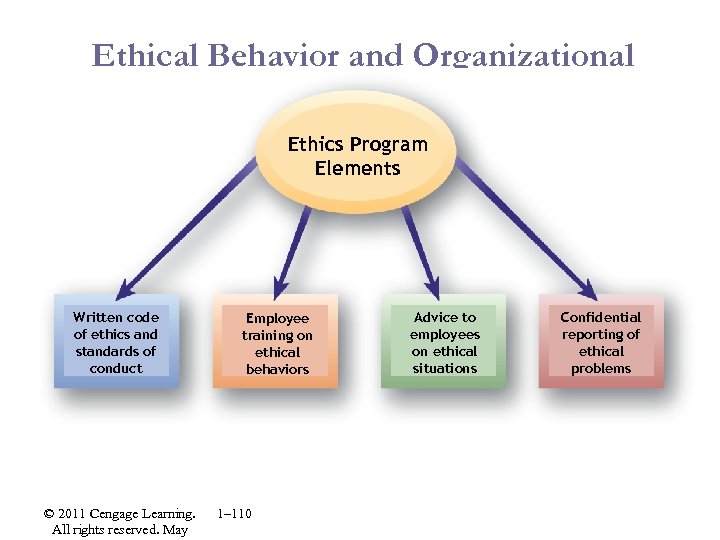 Ethical Behavior and Organizational Culture Ethics Program Elements Written code of ethics and standards of conduct © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May Employee training on ethical behaviors 1– 110 Advice to employees on ethical situations Confidential reporting of ethical problems
Ethical Behavior and Organizational Culture Ethics Program Elements Written code of ethics and standards of conduct © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May Employee training on ethical behaviors 1– 110 Advice to employees on ethical situations Confidential reporting of ethical problems
 HR’s Role in Organizational Ethics Legal Question Ethical Question • Does the behavior or result meet all applicable laws, regulations, and government codes? • Does the behavior or result meet both organizational standards and professional standards of ethical behavior? © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May 1– 111
HR’s Role in Organizational Ethics Legal Question Ethical Question • Does the behavior or result meet all applicable laws, regulations, and government codes? • Does the behavior or result meet both organizational standards and professional standards of ethical behavior? © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May 1– 111
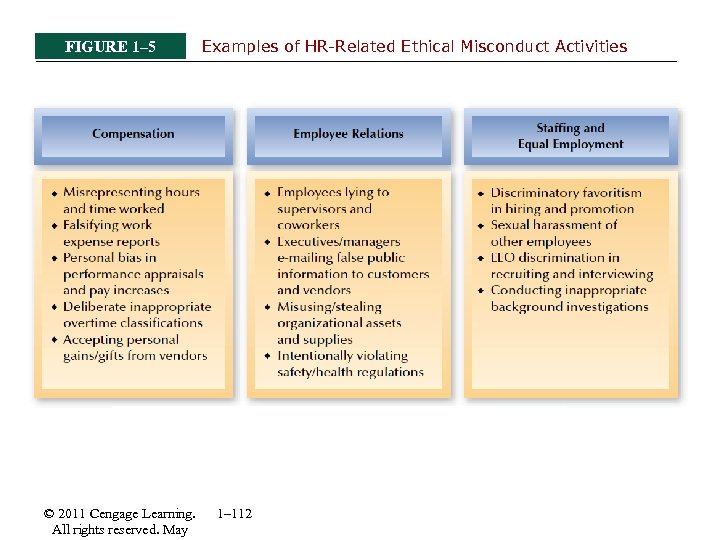 FIGURE 1– 5 © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May Examples of HR-Related Ethical Misconduct Activities 1– 112
FIGURE 1– 5 © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. May Examples of HR-Related Ethical Misconduct Activities 1– 112
 HR Ethics and Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) § Reduce the likelihood of illegal and unethical behaviors by: § Having a written code of ethics and conduct standards § Providing ethical behavior training and advice § Establishing confidential reporting systems for ethical misconduct § Providing whistle-blower protection § Supporting HR’s role as “keeper and voice” of organizational ethics 1– 113
HR Ethics and Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) § Reduce the likelihood of illegal and unethical behaviors by: § Having a written code of ethics and conduct standards § Providing ethical behavior training and advice § Establishing confidential reporting systems for ethical misconduct § Providing whistle-blower protection § Supporting HR’s role as “keeper and voice” of organizational ethics 1– 113
 Ethical Behavior and Organizational Culture § Classic Management Article § “The perpetuation of unethical practices in organizations” § Socialization § Attrition § Justification from small to large
Ethical Behavior and Organizational Culture § Classic Management Article § “The perpetuation of unethical practices in organizations” § Socialization § Attrition § Justification from small to large
 HR Management Competencies and Careers § Important HR Competencies § Strategic contribution to organizational success § Business knowledge of organization and its strategies § Effective and effective delivery of HR services § Familiarity with HRMS technology § Personal credibility § SPEAK THE LANGUAGE OF THE BUSINESS
HR Management Competencies and Careers § Important HR Competencies § Strategic contribution to organizational success § Business knowledge of organization and its strategies § Effective and effective delivery of HR services § Familiarity with HRMS technology § Personal credibility § SPEAK THE LANGUAGE OF THE BUSINESS
 HR Management as a Career Field § HR Generalist § A person with responsibility for performing a variety of HR activities. § HR Specialist § A person with in-depth knowledge and expertise in a limited area of HR. § HR Manager § A person who is a line manager for HR Generalists and Specialists
HR Management as a Career Field § HR Generalist § A person with responsibility for performing a variety of HR activities. § HR Specialist § A person with in-depth knowledge and expertise in a limited area of HR. § HR Manager § A person who is a line manager for HR Generalists and Specialists
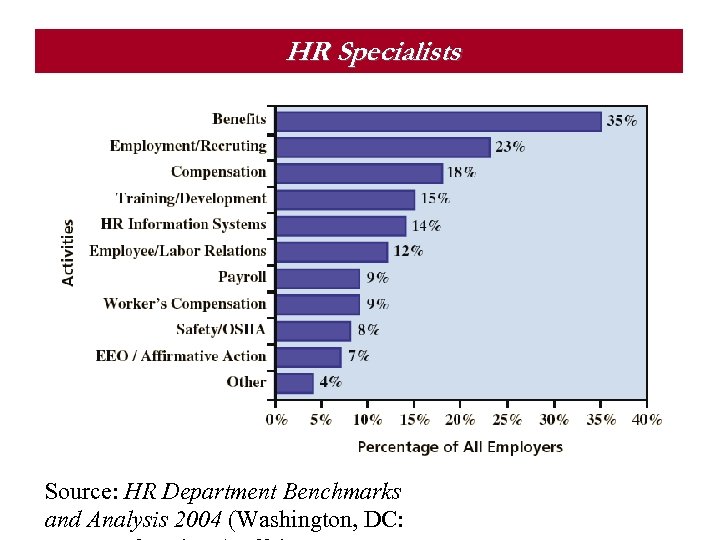 HR Specialists Source: HR Department Benchmarks and Analysis 2004 (Washington, DC:
HR Specialists Source: HR Department Benchmarks and Analysis 2004 (Washington, DC:
 HR Certification The Human Resource Certification Institute offers three types of professional certifications for HR generalists. Details on these certifications are available from the Human Resources Certification Institute, www. hrci. org.
HR Certification The Human Resource Certification Institute offers three types of professional certifications for HR generalists. Details on these certifications are available from the Human Resources Certification Institute, www. hrci. org.
 Other HR Certifications Certified Compensation Professional (CCP), sponsored by the World at Work Association Certified Employee Benefits Specialist (CEBS), sponsored by the International Foundation of Employee Benefits Plans Certified Benefits Professional (CBP), sponsored by the Worldat. Work Association Certified Performance Technologist (CPT), co- sponsored by the American Society for Training & Development and the International Society for Performance Improvement Certified Safety Professional (CSP), sponsored by the Board of Certified Safety Professionals Occupational Health and Safety Technologist (OHST), given by the American Board of Industrial Hygiene and the Board of Certified Safety Professionals Certified Professional Outsourcing, provided by New York University and the Human Resource Outsourcing Association
Other HR Certifications Certified Compensation Professional (CCP), sponsored by the World at Work Association Certified Employee Benefits Specialist (CEBS), sponsored by the International Foundation of Employee Benefits Plans Certified Benefits Professional (CBP), sponsored by the Worldat. Work Association Certified Performance Technologist (CPT), co- sponsored by the American Society for Training & Development and the International Society for Performance Improvement Certified Safety Professional (CSP), sponsored by the Board of Certified Safety Professionals Occupational Health and Safety Technologist (OHST), given by the American Board of Industrial Hygiene and the Board of Certified Safety Professionals Certified Professional Outsourcing, provided by New York University and the Human Resource Outsourcing Association
 PFEFFER'S HR CLASSIC
PFEFFER'S HR CLASSIC


