fe8e12b6dd8b8c8bade5885d3fadb11a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Lecture 22 Intonation and Discourse CS 4705
Lecture 22 Intonation and Discourse CS 4705
 What does prosody convey? • In general, information about: – What the speaker is trying to convey • Is this a statement or a question? – The speaker state • Is the speaker getting angry, frustrated? • In dialogue, information about: – The structure of the dialogue • Is the user or the system trying to start a new topic? • Is the speaker talking about given or new information? – The state of the interaction: • Is the user having trouble being understood? • Is the user having trouble understanding the system?
What does prosody convey? • In general, information about: – What the speaker is trying to convey • Is this a statement or a question? – The speaker state • Is the speaker getting angry, frustrated? • In dialogue, information about: – The structure of the dialogue • Is the user or the system trying to start a new topic? • Is the speaker talking about given or new information? – The state of the interaction: • Is the user having trouble being understood? • Is the user having trouble understanding the system?
 Current Trends • New description schemes (e. g. To. BI) • Corpus-based research and machine learning • Emphasis on evaluation of algorithms and systems (NLE ‘ 00 special issue) • Investigation of spontaneous speech phenomena and variation in speaking style • Applications to CTS, ASR and SDS
Current Trends • New description schemes (e. g. To. BI) • Corpus-based research and machine learning • Emphasis on evaluation of algorithms and systems (NLE ‘ 00 special issue) • Investigation of spontaneous speech phenomena and variation in speaking style • Applications to CTS, ASR and SDS
 Corpora • Public and semi-public databases – ATIS, Switch. Board, Call Home, Meetings (NIST/DARPA/LDC) – TRAINS/TRIPS (U. Rochester), FM Radio (BU), BDC (Harvard, AT&T) • Private collections – Acquired for speech or dialogue research (August, KTH; Voicemail, AT&T, IBM) – Meetings, call centers, operator services, focus group collections • The Web – Newscasts, radio
Corpora • Public and semi-public databases – ATIS, Switch. Board, Call Home, Meetings (NIST/DARPA/LDC) – TRAINS/TRIPS (U. Rochester), FM Radio (BU), BDC (Harvard, AT&T) • Private collections – Acquired for speech or dialogue research (August, KTH; Voicemail, AT&T, IBM) – Meetings, call centers, operator services, focus group collections • The Web – Newscasts, radio
 To(nes and)B(reak)I(ndices) • Developed by prosody researchers in four meetings over 1991 -94 • Goals: – devise common labeling scheme for Standard American English that is robust and reliable – promote collection of large, prosodically labeled, shareable corpora • To. BI standards also proposed for Japanese, German, Italian, Spanish, British and Australian English, . .
To(nes and)B(reak)I(ndices) • Developed by prosody researchers in four meetings over 1991 -94 • Goals: – devise common labeling scheme for Standard American English that is robust and reliable – promote collection of large, prosodically labeled, shareable corpora • To. BI standards also proposed for Japanese, German, Italian, Spanish, British and Australian English, . .
 • Minimal To. BI transcription: – recording of speech – f 0 contour – To. BI tiers: • orthographic tier: words • break-index tier: degrees of junction (Price et al ‘ 89) • tonal tier: pitch accents, phrase accents, boundary tones (Pierrehumbert ‘ 80) • miscellaneous tier: disfluencies, non-speech sounds, etc.
• Minimal To. BI transcription: – recording of speech – f 0 contour – To. BI tiers: • orthographic tier: words • break-index tier: degrees of junction (Price et al ‘ 89) • tonal tier: pitch accents, phrase accents, boundary tones (Pierrehumbert ‘ 80) • miscellaneous tier: disfluencies, non-speech sounds, etc.
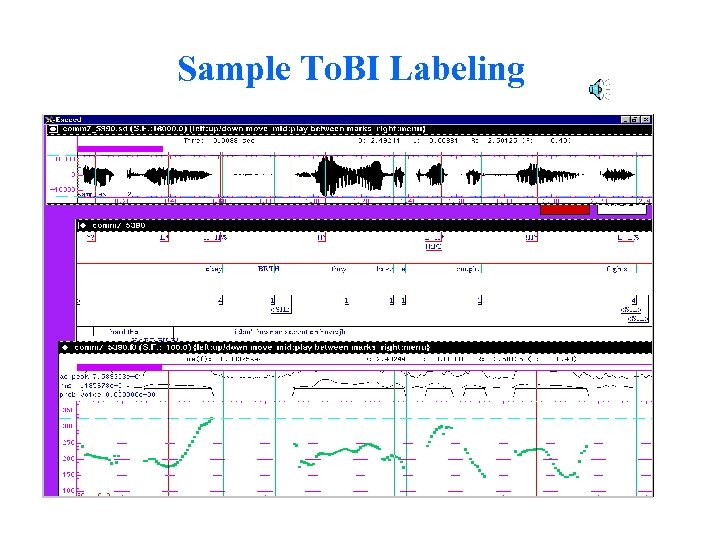 Sample To. BI Labeling
Sample To. BI Labeling
 • Online training material, available at: – http: //www. ling. ohio-state. edu/phonetics/To. BI/ • Evaluation – Good inter-labeler reliability for expert and naive labelers: 88% agreement on presence/absence of tonal category, 81% agreement on category label, 91% agreement on break indices to within 1 level (Silverman et al. ‘ 92, Pitrelli et al ‘ 94)
• Online training material, available at: – http: //www. ling. ohio-state. edu/phonetics/To. BI/ • Evaluation – Good inter-labeler reliability for expert and naive labelers: 88% agreement on presence/absence of tonal category, 81% agreement on category label, 91% agreement on break indices to within 1 level (Silverman et al. ‘ 92, Pitrelli et al ‘ 94)
 Pitch Accent/Prominence in To. BI • Which items are made intonationally prominent and how? • Accent type: – – H* L* L*+H L+H* simple high (declarative) simple low (ynq) scooped, late rise (uncertainty/ incredulity) early rise to stress (contrastive focus) – H+!H* fall onto stress (implied familiarity)
Pitch Accent/Prominence in To. BI • Which items are made intonationally prominent and how? • Accent type: – – H* L* L*+H L+H* simple high (declarative) simple low (ynq) scooped, late rise (uncertainty/ incredulity) early rise to stress (contrastive focus) – H+!H* fall onto stress (implied familiarity)
 • Downstepped accents: • !H*, L+!H*, L*+!H • Degree of prominence: §within a phrase: Hi. F 0 §across phrases
• Downstepped accents: • !H*, L+!H*, L*+!H • Degree of prominence: §within a phrase: Hi. F 0 §across phrases
 Functions of Pitch Accent • Given/new information – S: Do you need a return ticket? – U: No, thanks, I don’t need a return. • Contrast (narrow focus) – U: No, thanks, I don’t need a RETURN…. (I need a time schedule, receipt, …) • Disambiguation of discourse markers – S: Now let me get you the train information. – U: Okay (thanks) vs. Okay…. (but I really want…)
Functions of Pitch Accent • Given/new information – S: Do you need a return ticket? – U: No, thanks, I don’t need a return. • Contrast (narrow focus) – U: No, thanks, I don’t need a RETURN…. (I need a time schedule, receipt, …) • Disambiguation of discourse markers – S: Now let me get you the train information. – U: Okay (thanks) vs. Okay…. (but I really want…)
 Predicting Accent: Is it accented or not? • Applications: TTS and CTS • Corpora: read and spontaneous speech • Features: pos window of 3, sentence position, position within NP, # of syllables, position in complex nominal, inferred given/new status, inferred focus, mutual information • Results: 75 -85% correct, depending on genre
Predicting Accent: Is it accented or not? • Applications: TTS and CTS • Corpora: read and spontaneous speech • Features: pos window of 3, sentence position, position within NP, # of syllables, position in complex nominal, inferred given/new status, inferred focus, mutual information • Results: 75 -85% correct, depending on genre
 Prosodic Phrasing in To. BI • ‘Levels’ of phrasing: – intermediate phrase: one or more pitch accents plus a phrase accent (Hor L- ) – intonational phrase: 1 or more intermediate phrases + boundary tone (H% or L% ) • To. BI break-index tier – 0 no word boundary – 1 word boundary – 2 strong juncture with no tonal markings – 3 intermediate phrase boundary – 4 intonational phrase boundary
Prosodic Phrasing in To. BI • ‘Levels’ of phrasing: – intermediate phrase: one or more pitch accents plus a phrase accent (Hor L- ) – intonational phrase: 1 or more intermediate phrases + boundary tone (H% or L% ) • To. BI break-index tier – 0 no word boundary – 1 word boundary – 2 strong juncture with no tonal markings – 3 intermediate phrase boundary – 4 intonational phrase boundary
 Functions of Phrasing • Disambiguates syntactic constructions, e. g. PP attachment, restrictive/non relative clause: – S: You should buy the ticket with the discount coupon. – S: The itinerary which I faxed includes deluxe accommodations • Disambiguates scope ambiguities, e. g. Negation: – S: You aren’t booked through Rome because of the fare. • Or modifier scope: – S: This fare is restricted to retired politicians and civil servants.
Functions of Phrasing • Disambiguates syntactic constructions, e. g. PP attachment, restrictive/non relative clause: – S: You should buy the ticket with the discount coupon. – S: The itinerary which I faxed includes deluxe accommodations • Disambiguates scope ambiguities, e. g. Negation: – S: You aren’t booked through Rome because of the fare. • Or modifier scope: – S: This fare is restricted to retired politicians and civil servants.
 Predicting Phrase Boundaries • Applications: TTS, CTS, ASR • Corpora: AP news, Penn Treebank, ATIS • Features: sentence position, sentence length, pos window of 4, location of previous predicted boundary, mutual information, constituent information, dependency structure • Results: 96% correct
Predicting Phrase Boundaries • Applications: TTS, CTS, ASR • Corpora: AP news, Penn Treebank, ATIS • Features: sentence position, sentence length, pos window of 4, location of previous predicted boundary, mutual information, constituent information, dependency structure • Results: 96% correct
 Contours: Accent + Phrasing • What do intonational contours ‘mean’ (Ladd ‘ 80, Bolinger ‘ 89)? – Speech acts (statements, questions, requests) S: That’ll be credit card? (L* H- H%) – Propositional attitude (uncertainty, incredulity) S: You’d like an evening flight. (L*+H L- H%) – Speaker affect (anger, happiness, love) U: I said four SEVEN one! (L+H* L- L%) – “Personality” S: Welcome to the Sunshine Travel System.
Contours: Accent + Phrasing • What do intonational contours ‘mean’ (Ladd ‘ 80, Bolinger ‘ 89)? – Speech acts (statements, questions, requests) S: That’ll be credit card? (L* H- H%) – Propositional attitude (uncertainty, incredulity) S: You’d like an evening flight. (L*+H L- H%) – Speaker affect (anger, happiness, love) U: I said four SEVEN one! (L+H* L- L%) – “Personality” S: Welcome to the Sunshine Travel System.
 Pitch Range and Timing • Level of speaker engagement – S: Welcome to Info. Travel. How may I help you? • Contour interpretation – S: You can take the L*+H bus from Malpensa to Rome L-H%. – U: Take the bus. vs. Take the bus! • Discourse/topic structure – Topic beginnings have higher pitch range, faster, preceded by longer pauses – Endings the opposite
Pitch Range and Timing • Level of speaker engagement – S: Welcome to Info. Travel. How may I help you? • Contour interpretation – S: You can take the L*+H bus from Malpensa to Rome L-H%. – U: Take the bus. vs. Take the bus! • Discourse/topic structure – Topic beginnings have higher pitch range, faster, preceded by longer pauses – Endings the opposite
 Prosody and Speaker Emotion • What makes an utterance sound angry? Sad? – How much comes from the lexical information? – How much from the acoustic/prosodic? – Does all anger, e. g. , sound the same? • Cahn ‘ 88 (examples)
Prosody and Speaker Emotion • What makes an utterance sound angry? Sad? – How much comes from the lexical information? – How much from the acoustic/prosodic? – Does all anger, e. g. , sound the same? • Cahn ‘ 88 (examples)
 Applications • Text-to-Speech and Concept-to-Speech generation: improve naturalness • Speech Recognition: identify suprasegmental meaning • Spoken Dialogue Systems: understand when people are confused, angry • Audio Browsing: format corpora for browsing and search
Applications • Text-to-Speech and Concept-to-Speech generation: improve naturalness • Speech Recognition: identify suprasegmental meaning • Spoken Dialogue Systems: understand when people are confused, angry • Audio Browsing: format corpora for browsing and search
 Challenges • We don’t really know what most contours ‘mean’ • Our accent prediction needs more sensitivity to better model of given/new, focus, grammatical function • Our phrasing prediction needs better information about e. g. attachment • We don’t know much about emotional speech or ‘personality’ -- critical to applications
Challenges • We don’t really know what most contours ‘mean’ • Our accent prediction needs more sensitivity to better model of given/new, focus, grammatical function • Our phrasing prediction needs better information about e. g. attachment • We don’t know much about emotional speech or ‘personality’ -- critical to applications


