fead6d422a166e3301c56fc941043c94.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Lecture-2 - The Strategic Role of Information Systems Thepul Ginige 1
Lecture-2 - The Strategic Role of Information Systems Thepul Ginige 1
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Analyze roles of 6 types of information systems • Describe types of information systems • Analyze relationships between business processes 2
LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Analyze roles of 6 types of information systems • Describe types of information systems • Analyze relationships between business processes 2
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Explain how systems & networks create new efficiencies • Evaluate benefits & limitations of systems & networks 3
LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Explain how systems & networks create new efficiencies • Evaluate benefits & limitations of systems & networks 3
 MANAGEMENT CHALLENGES • Key system applications • Functional perspective of systems • Integrating functions & processes 4
MANAGEMENT CHALLENGES • Key system applications • Functional perspective of systems • Integrating functions & processes 4
 MANAGEMENT CHALLENGES 1. INTEGRATION: Different systems serve variety of functions, connecting organizational levels difficult, costly 2. ENLARGING SCOPE OF MANAGEMENT THINKING: Huge system investments, long development time must be guided by common objectives 5
MANAGEMENT CHALLENGES 1. INTEGRATION: Different systems serve variety of functions, connecting organizational levels difficult, costly 2. ENLARGING SCOPE OF MANAGEMENT THINKING: Huge system investments, long development time must be guided by common objectives 5
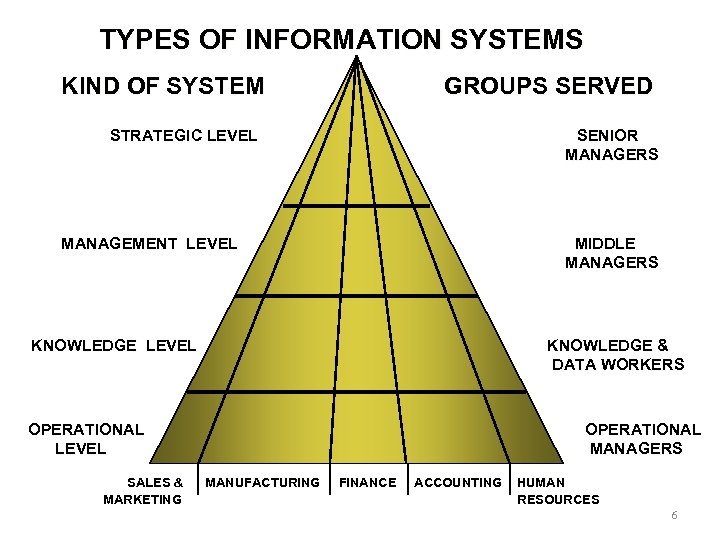 TYPES OF INFORMATION SYSTEMS KIND OF SYSTEM GROUPS SERVED STRATEGIC LEVEL SENIOR MANAGERS MANAGEMENT LEVEL MIDDLE MANAGERS KNOWLEDGE LEVEL KNOWLEDGE & DATA WORKERS OPERATIONAL LEVEL SALES & MARKETING OPERATIONAL MANAGERS MANUFACTURING FINANCE ACCOUNTING HUMAN RESOURCES 6
TYPES OF INFORMATION SYSTEMS KIND OF SYSTEM GROUPS SERVED STRATEGIC LEVEL SENIOR MANAGERS MANAGEMENT LEVEL MIDDLE MANAGERS KNOWLEDGE LEVEL KNOWLEDGE & DATA WORKERS OPERATIONAL LEVEL SALES & MARKETING OPERATIONAL MANAGERS MANUFACTURING FINANCE ACCOUNTING HUMAN RESOURCES 6
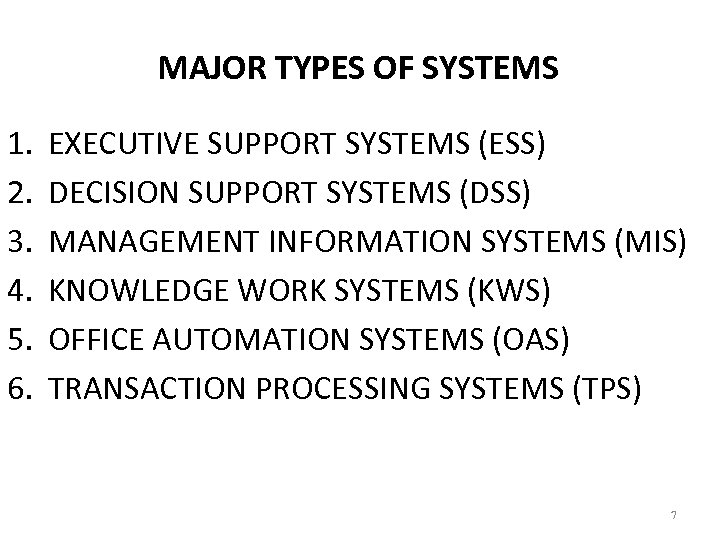 MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS (MIS) KNOWLEDGE WORK SYSTEMS (KWS) OFFICE AUTOMATION SYSTEMS (OAS) TRANSACTION PROCESSING SYSTEMS (TPS) 7
MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS (MIS) KNOWLEDGE WORK SYSTEMS (KWS) OFFICE AUTOMATION SYSTEMS (OAS) TRANSACTION PROCESSING SYSTEMS (TPS) 7
 TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Sales & Marketing Systems MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Sales management, market research, promotion, pricing, new products MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • Sales order info system, market research system, pricing system 8
TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Sales & Marketing Systems MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Sales management, market research, promotion, pricing, new products MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • Sales order info system, market research system, pricing system 8
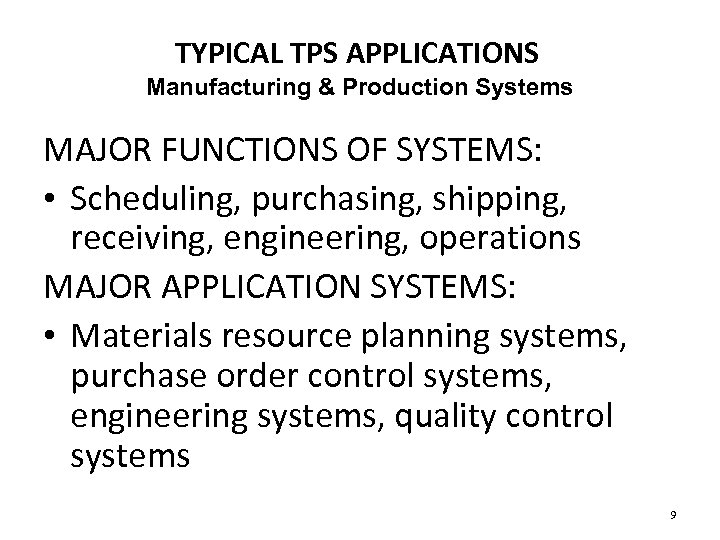 TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Manufacturing & Production Systems MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Scheduling, purchasing, shipping, receiving, engineering, operations MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • Materials resource planning systems, purchase order control systems, engineering systems, quality control systems 9
TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Manufacturing & Production Systems MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Scheduling, purchasing, shipping, receiving, engineering, operations MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • Materials resource planning systems, purchase order control systems, engineering systems, quality control systems 9
 TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Finance & Accounting Systems MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Budgeting, general ledger, billing, cost accounting MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • General ledger, accounts receivable, accounts payable, budgeting, funds management systems 10
TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Finance & Accounting Systems MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Budgeting, general ledger, billing, cost accounting MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • General ledger, accounts receivable, accounts payable, budgeting, funds management systems 10
 TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Human Resources Systems MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Personnel records, benefits, compensation, labor relations, training MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • Payroll, employee records, benefit systems, career path systems, personnel training systems 11
TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Human Resources Systems MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Personnel records, benefits, compensation, labor relations, training MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • Payroll, employee records, benefit systems, career path systems, personnel training systems 11
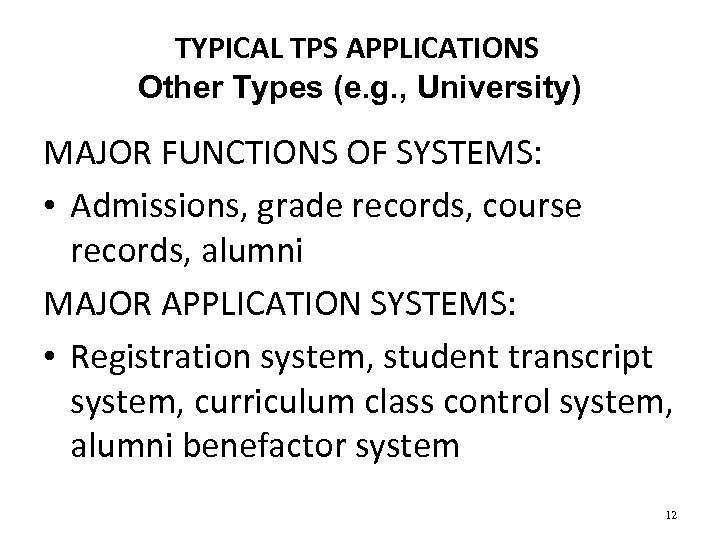 TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Other Types (e. g. , University) MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Admissions, grade records, course records, alumni MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • Registration system, student transcript system, curriculum class control system, alumni benefactor system 12
TYPICAL TPS APPLICATIONS Other Types (e. g. , University) MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS: • Admissions, grade records, course records, alumni MAJOR APPLICATION SYSTEMS: • Registration system, student transcript system, curriculum class control system, alumni benefactor system 12
 OFFICE AUTOMATION SYSTEMS (OAS) • Toward a “paperless” office • Redesign of work flow • Integrated software • Ergonomic design • Bright, cheerful work space EXAMPLE: PRESENTATION GRAPHICS 13
OFFICE AUTOMATION SYSTEMS (OAS) • Toward a “paperless” office • Redesign of work flow • Integrated software • Ergonomic design • Bright, cheerful work space EXAMPLE: PRESENTATION GRAPHICS 13
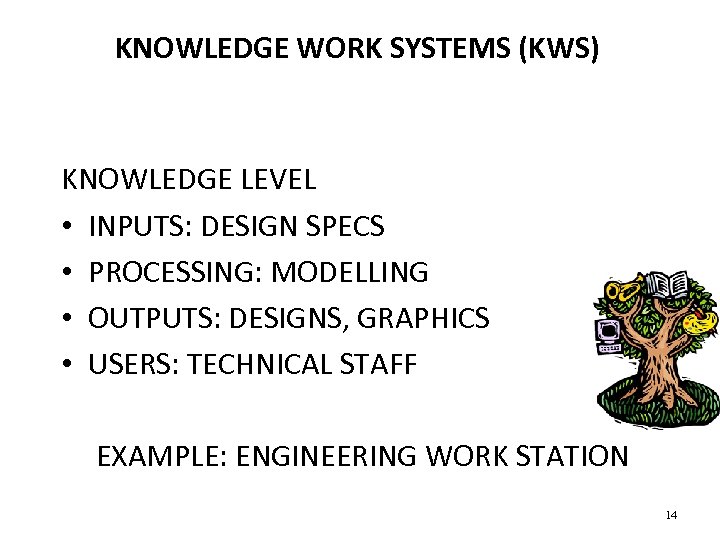 KNOWLEDGE WORK SYSTEMS (KWS) KNOWLEDGE LEVEL • INPUTS: DESIGN SPECS • PROCESSING: MODELLING • OUTPUTS: DESIGNS, GRAPHICS • USERS: TECHNICAL STAFF EXAMPLE: ENGINEERING WORK STATION 14
KNOWLEDGE WORK SYSTEMS (KWS) KNOWLEDGE LEVEL • INPUTS: DESIGN SPECS • PROCESSING: MODELLING • OUTPUTS: DESIGNS, GRAPHICS • USERS: TECHNICAL STAFF EXAMPLE: ENGINEERING WORK STATION 14
 MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS (MIS) MANAGEMENT LEVEL • INPUTS: HIGH VOLUME DATA • PROCESSING: SIMPLE MODELS • OUTPUTS: SUMMARY REPORTS • USERS: MIDDLE MANAGERS EXAMPLE: ANNUAL BUDGETING 15
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS (MIS) MANAGEMENT LEVEL • INPUTS: HIGH VOLUME DATA • PROCESSING: SIMPLE MODELS • OUTPUTS: SUMMARY REPORTS • USERS: MIDDLE MANAGERS EXAMPLE: ANNUAL BUDGETING 15
 MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS (MIS) • Structured & semi-structured decisions • Report control oriented • Past & present data • Internal orientation • Lengthy design process 16
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS (MIS) • Structured & semi-structured decisions • Report control oriented • Past & present data • Internal orientation • Lengthy design process 16
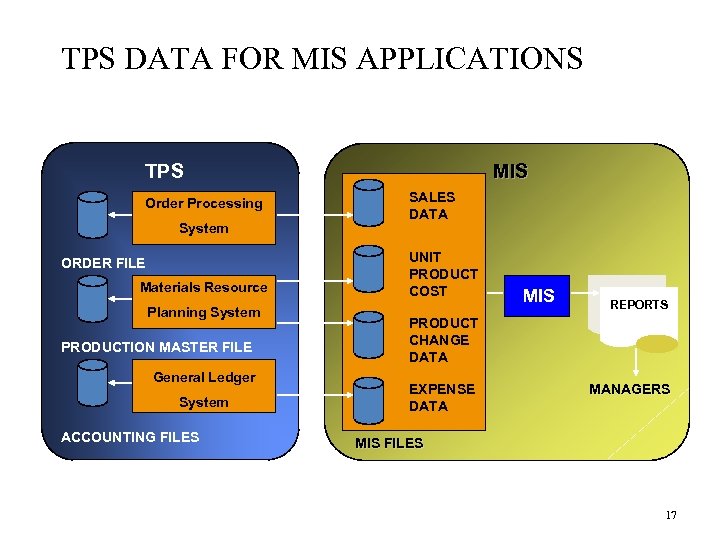 TPS DATA FOR MIS APPLICATIONS TPS Order Processing System ORDER FILE Materials Resource Planning System PRODUCTION MASTER FILE General Ledger System ACCOUNTING FILES MIS SALES DATA UNIT PRODUCT COST MIS REPORTS PRODUCT CHANGE DATA EXPENSE DATA MANAGERS MIS FILES 17
TPS DATA FOR MIS APPLICATIONS TPS Order Processing System ORDER FILE Materials Resource Planning System PRODUCTION MASTER FILE General Ledger System ACCOUNTING FILES MIS SALES DATA UNIT PRODUCT COST MIS REPORTS PRODUCT CHANGE DATA EXPENSE DATA MANAGERS MIS FILES 17
 DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) MANAGEMENT LEVEL • Inputs: low volume data • Processing: interactive • Outputs: decision analysis • Users: professionals, staff EXAMPLE: CONTRACT COST ANALYSIS 18
DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) MANAGEMENT LEVEL • Inputs: low volume data • Processing: interactive • Outputs: decision analysis • Users: professionals, staff EXAMPLE: CONTRACT COST ANALYSIS 18
 DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) • Flexible, adaptable, quick • User controls inputs/outputs • No professional programming • Supports decision process • Sophisticated modeling tools 19
DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) • Flexible, adaptable, quick • User controls inputs/outputs • No professional programming • Supports decision process • Sophisticated modeling tools 19
 EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) STRATEGIC LEVEL • Inputs: aggregate data • Processing: interactive • Outputs: projections • Users: senior managers EXAMPLE: 5 YEAR OPERATING PLAN 20
EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) STRATEGIC LEVEL • Inputs: aggregate data • Processing: interactive • Outputs: projections • Users: senior managers EXAMPLE: 5 YEAR OPERATING PLAN 20
 EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) • Top level management • Designed to the individual • Ties CEO to all levels • Very expensive to keep up • Extensive support staff 21
EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) • Top level management • Designed to the individual • Ties CEO to all levels • Very expensive to keep up • Extensive support staff 21
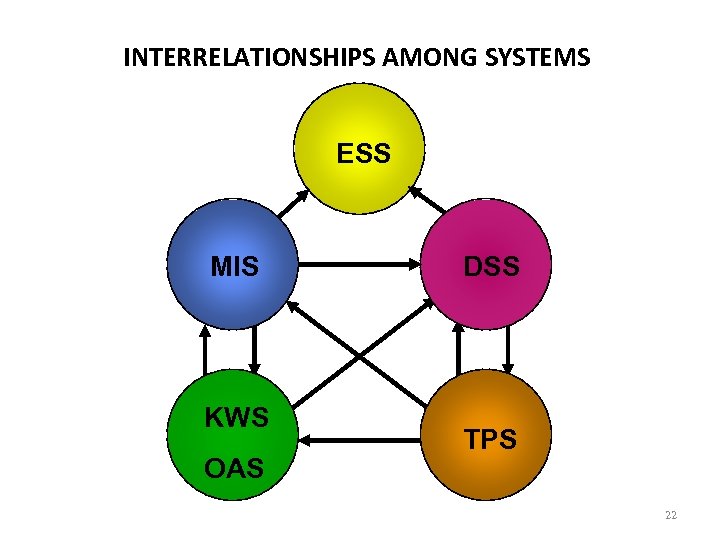 INTERRELATIONSHIPS AMONG SYSTEMS ESS MIS KWS OAS DSS TPS 22
INTERRELATIONSHIPS AMONG SYSTEMS ESS MIS KWS OAS DSS TPS 22
 SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE • Sales & marketing systems • Manufacturing & production systems • Finance & accounting systems • Human resources systems 23
SYSTEMS FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE • Sales & marketing systems • Manufacturing & production systems • Finance & accounting systems • Human resources systems 23
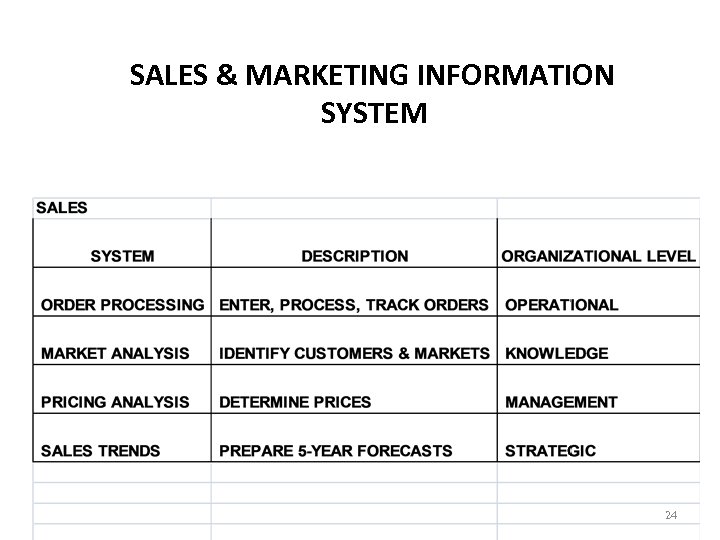 SALES & MARKETING INFORMATION SYSTEM 24
SALES & MARKETING INFORMATION SYSTEM 24
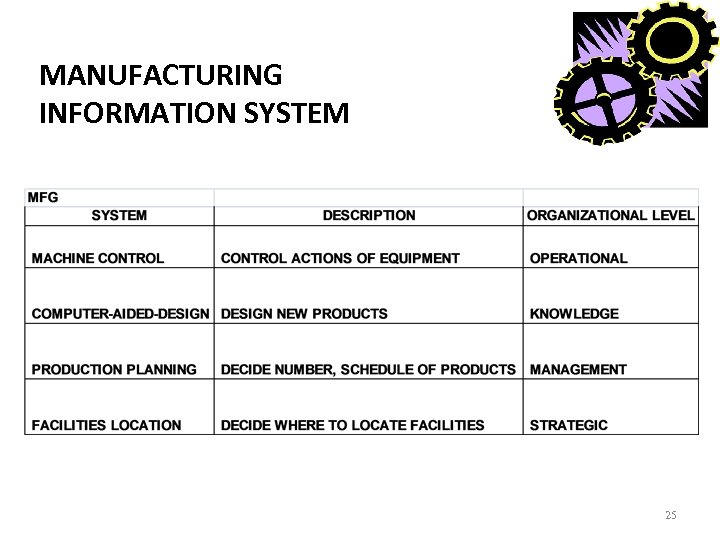 MANUFACTURING INFORMATION SYSTEM 25
MANUFACTURING INFORMATION SYSTEM 25
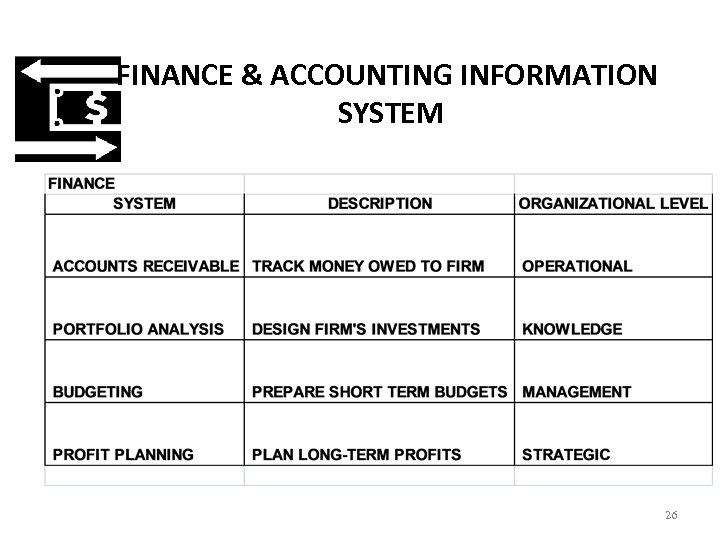 FINANCE & ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM 26
FINANCE & ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM 26
 HUMAN RESOURCES INFORMATION SYSTEM 27
HUMAN RESOURCES INFORMATION SYSTEM 27
 EXAMPLES OF BUSINESS PROCESSES • MANUFACTURING & PRODUCTION: Assembling product, checking quality, producing bills of materials • SALES & MARKETING: Identifying customers, creating customer awareness, selling 28
EXAMPLES OF BUSINESS PROCESSES • MANUFACTURING & PRODUCTION: Assembling product, checking quality, producing bills of materials • SALES & MARKETING: Identifying customers, creating customer awareness, selling 28
 EXAMPLES OF BUSINESS PROCESSES • FINANCE & ACCOUNTING: Paying creditors, creating financial statements, managing cash accounts • HUMAN RESOURCES: Hiring employees, evaluating performance, enrolling employees in benefits plans 29
EXAMPLES OF BUSINESS PROCESSES • FINANCE & ACCOUNTING: Paying creditors, creating financial statements, managing cash accounts • HUMAN RESOURCES: Hiring employees, evaluating performance, enrolling employees in benefits plans 29
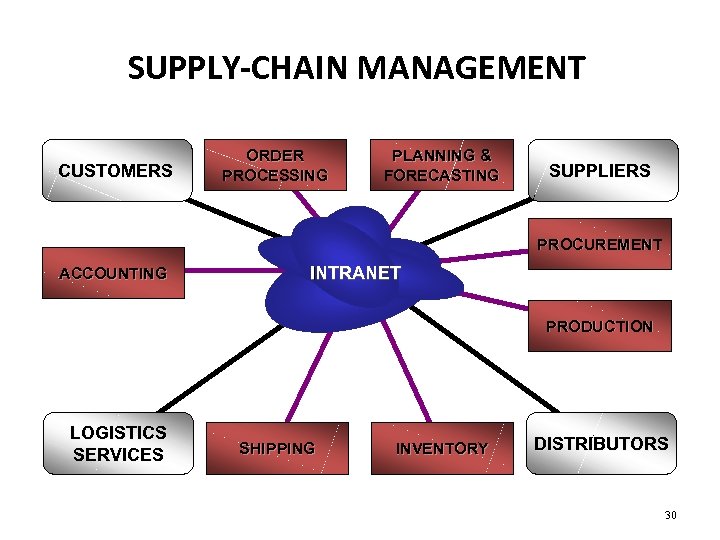 SUPPLY-CHAIN MANAGEMENT CUSTOMERS ORDER PROCESSING PLANNING & FORECASTING SUPPLIERS PROCUREMENT ACCOUNTING INTRANET PRODUCTION LOGISTICS SERVICES SHIPPING INVENTORY DISTRIBUTORS 30
SUPPLY-CHAIN MANAGEMENT CUSTOMERS ORDER PROCESSING PLANNING & FORECASTING SUPPLIERS PROCUREMENT ACCOUNTING INTRANET PRODUCTION LOGISTICS SERVICES SHIPPING INVENTORY DISTRIBUTORS 30
 Supply Chain Management Supply chain management is the streamlining of a business' supply-side activities to maximize customer value and to gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Supply chain management (SCM) represents an effort by suppliers to develop and implement supply chains that are as efficient and economical as possible. 31
Supply Chain Management Supply chain management is the streamlining of a business' supply-side activities to maximize customer value and to gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Supply chain management (SCM) represents an effort by suppliers to develop and implement supply chains that are as efficient and economical as possible. 31
 HOW INFORMATION SYSTEMS FACILITATES SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Decide when, what to produce, store, move… rapidly communicate orders, track order status, check inventory availability, monitor levels, track shipments, plan production based on actual demand…rapidly communicate product design changes…provide product specifications… share information about defect rates, returns. . . 32
HOW INFORMATION SYSTEMS FACILITATES SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Decide when, what to produce, store, move… rapidly communicate orders, track order status, check inventory availability, monitor levels, track shipments, plan production based on actual demand…rapidly communicate product design changes…provide product specifications… share information about defect rates, returns. . . 32
 TRADITIONAL VIEW OF SYSTEMS • WITHIN THE BUSINESS: There are functions, each having its uses of information systems • OUTSIDE THE ORGANIZATION’S BOUNDARIES: There are customers and vendors FUNCTIONS TEND TO WORK IN ISOLATION 33
TRADITIONAL VIEW OF SYSTEMS • WITHIN THE BUSINESS: There are functions, each having its uses of information systems • OUTSIDE THE ORGANIZATION’S BOUNDARIES: There are customers and vendors FUNCTIONS TEND TO WORK IN ISOLATION 33
 BENEFITS OF ENTERPRISE SYSTEMS • FIRM STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION: One organization • MANAGEMENT: Firm wide knowledgebased management processes • TECHNOLOGY: Unified platform • BUSINESS: More efficient operations & customer-driven business processes 34
BENEFITS OF ENTERPRISE SYSTEMS • FIRM STRUCTURE & ORGANIZATION: One organization • MANAGEMENT: Firm wide knowledgebased management processes • TECHNOLOGY: Unified platform • BUSINESS: More efficient operations & customer-driven business processes 34
 CHALLENGES OF ENTERPRISE SYSTEMS • Daunting implementation • High up front costs & future benefits • Inflexibility • Hard to realize strategic value 35
CHALLENGES OF ENTERPRISE SYSTEMS • Daunting implementation • High up front costs & future benefits • Inflexibility • Hard to realize strategic value 35
 INDUSTRIAL NETWORKS LINK FIRMS INTO INDUSTRY-WIDE SYSTEM • HORIZONTAL: Link firms in same industry, including competitors • VERTICAL: Link firm with suppliers in same industry 36
INDUSTRIAL NETWORKS LINK FIRMS INTO INDUSTRY-WIDE SYSTEM • HORIZONTAL: Link firms in same industry, including competitors • VERTICAL: Link firm with suppliers in same industry 36
 Emerging information system trends in organisations 37
Emerging information system trends in organisations 37
 Enterprise systems Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning systems(ERP) are software systems for businesses management encompassing modules supporting functional areas such as Manufacturing , Accounting, Finance, Sales & Marketing, Human Resource, ect. 38
Enterprise systems Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning systems(ERP) are software systems for businesses management encompassing modules supporting functional areas such as Manufacturing , Accounting, Finance, Sales & Marketing, Human Resource, ect. 38
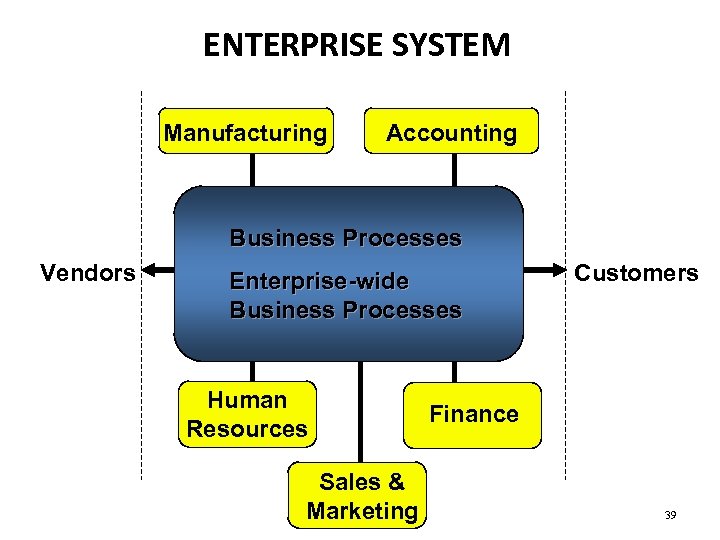 ENTERPRISE SYSTEM Manufacturing Accounting Business Processes Vendors Enterprise-wide Business Processes Human Resources Sales & Marketing Customers Finance 39
ENTERPRISE SYSTEM Manufacturing Accounting Business Processes Vendors Enterprise-wide Business Processes Human Resources Sales & Marketing Customers Finance 39
 ERP system contd. . • ERP is a commodity -- product in the form of software • SAP, Oracle Applications, People. Soft, JD Edwards, Greatplains etc. are world’s leading ERP packages • The market leader is “SAP” 40
ERP system contd. . • ERP is a commodity -- product in the form of software • SAP, Oracle Applications, People. Soft, JD Edwards, Greatplains etc. are world’s leading ERP packages • The market leader is “SAP” 40
 Features of an ERP system • Architecture of ERP system facilitates transparent integration of modules providing flow of information between all function within enterprise in real time. • Many different software replaced by one integrated system. • Reliable information access through common DBMS • Eliminates data and operational redundancies (no duplication of work or data entries etc. ) 41
Features of an ERP system • Architecture of ERP system facilitates transparent integration of modules providing flow of information between all function within enterprise in real time. • Many different software replaced by one integrated system. • Reliable information access through common DBMS • Eliminates data and operational redundancies (no duplication of work or data entries etc. ) 41
 Features of an ERP system contd. . • Cost reduction through time saving, improved control by organizational wise analysis of organizational decisions. • Delivery and cycle time reduction • Scalable systems • Global outreach through extended modules such as CRM or SCM • E-Business • Providing business solutions in support of core processes • Process-oriented view cutting across functions of an enterprise • Huge potential for customizing 42
Features of an ERP system contd. . • Cost reduction through time saving, improved control by organizational wise analysis of organizational decisions. • Delivery and cycle time reduction • Scalable systems • Global outreach through extended modules such as CRM or SCM • E-Business • Providing business solutions in support of core processes • Process-oriented view cutting across functions of an enterprise • Huge potential for customizing 42
 Business and Technical Benefits • Automation of business transactions • Flexibility in changing the system catering to newer business processes. • Coordination across business functions • Coordination across geographical distances resulting in better Managerial control • Consistent information and interface thus easier to understand work in • Single system 43
Business and Technical Benefits • Automation of business transactions • Flexibility in changing the system catering to newer business processes. • Coordination across business functions • Coordination across geographical distances resulting in better Managerial control • Consistent information and interface thus easier to understand work in • Single system 43
 Prime Reasons for Implementing ERP • Need for common platform • Process improvement. • Data visibility that could be used to improve operating decisions. • Operation cost reductions. • Increased customer responsiveness. • Improved strategic decision making • Personal Improvement 44
Prime Reasons for Implementing ERP • Need for common platform • Process improvement. • Data visibility that could be used to improve operating decisions. • Operation cost reductions. • Increased customer responsiveness. • Improved strategic decision making • Personal Improvement 44
 Knowledge Management • Knowledge management is the process of capturing, distributing, and effectively using knowledge. • So it’s a discipline that promotes an integrated approach to identifying, capturing, evaluating, retrieving, and sharing all of an enterprise's information assets. • These assets may include databases, documents, policies, procedures, and previously un-captured expertise and experience in individual workers. 45
Knowledge Management • Knowledge management is the process of capturing, distributing, and effectively using knowledge. • So it’s a discipline that promotes an integrated approach to identifying, capturing, evaluating, retrieving, and sharing all of an enterprise's information assets. • These assets may include databases, documents, policies, procedures, and previously un-captured expertise and experience in individual workers. 45
 Explicit, Implicit and Tacit Knowledge • Explicit: information or knowledge that is set out in tangible form. (this is the knowledge that is written down and is accessible in one way or another. ) • Implicit: information or knowledge that is not set out in tangible form but could be made explicit. (this is knowledge that isn’t written down yet but is largely procedural and not dependent on an individual’s context) • Tacit: information or knowledge that one would have extreme difficulty operationally setting out in tangible form. (this is the knowledge in our heads that is made up from experience and personal contexts. It’s not written down and is hard to articulate) 46
Explicit, Implicit and Tacit Knowledge • Explicit: information or knowledge that is set out in tangible form. (this is the knowledge that is written down and is accessible in one way or another. ) • Implicit: information or knowledge that is not set out in tangible form but could be made explicit. (this is knowledge that isn’t written down yet but is largely procedural and not dependent on an individual’s context) • Tacit: information or knowledge that one would have extreme difficulty operationally setting out in tangible form. (this is the knowledge in our heads that is made up from experience and personal contexts. It’s not written down and is hard to articulate) 46
 Customer Relationship Management (CRM) • Customer relationship management (CRM) refers to the practices, strategies and technologies that companies use to manage, record and evaluate customer interactions in order to drive sales growth by deepening and enriching relationships with their customer bases. 47
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) • Customer relationship management (CRM) refers to the practices, strategies and technologies that companies use to manage, record and evaluate customer interactions in order to drive sales growth by deepening and enriching relationships with their customer bases. 47
 The CRM Strategy The CRM strategy allows you to following: • Understand the customer • Retain customers through better customer experience • Attract new customers • Win new clients and contracts • Increase profitably • Decrease customer management costs 48
The CRM Strategy The CRM strategy allows you to following: • Understand the customer • Retain customers through better customer experience • Attract new customers • Win new clients and contracts • Increase profitably • Decrease customer management costs 48
 The Impact of Technology on CRM • Technology and the Internet have changed the way companies approach customer relationship strategies. Advances in technology have changed consumer buying behavior, and today there are many ways for companies to communicate with customers and to collect data about them. With each new advance in technology — especially the proliferation of self-service channels like the Web and smartphones — customer relationships are being managed electronically. 49
The Impact of Technology on CRM • Technology and the Internet have changed the way companies approach customer relationship strategies. Advances in technology have changed consumer buying behavior, and today there are many ways for companies to communicate with customers and to collect data about them. With each new advance in technology — especially the proliferation of self-service channels like the Web and smartphones — customer relationships are being managed electronically. 49
 The Benefits of CRM • The biggest benefit most businesses realize when moving to a CRM system comes directly from having all your business data stored and accessed from a single location. Before CRM systems, customer data was spread out over office productivity suite documents, email systems, mobile phone data and even paper note cards and Rolodex entries 50
The Benefits of CRM • The biggest benefit most businesses realize when moving to a CRM system comes directly from having all your business data stored and accessed from a single location. Before CRM systems, customer data was spread out over office productivity suite documents, email systems, mobile phone data and even paper note cards and Rolodex entries 50
 • Storing all the data from all departments (e. g. , sales, marketing, customer service and HR) in a central location gives management and employees immediate access to the most recent data when they need it. • Departments can collaborate with ease, and CRM systems help organization to develop efficient automated processes to improve business processes. 51
• Storing all the data from all departments (e. g. , sales, marketing, customer service and HR) in a central location gives management and employees immediate access to the most recent data when they need it. • Departments can collaborate with ease, and CRM systems help organization to develop efficient automated processes to improve business processes. 51
 • Other benefits include a 360 -degree view of all customer information, knowledge of what customers and the general market want, and integration with your existing applications to consolidate all business information. 52
• Other benefits include a 360 -degree view of all customer information, knowledge of what customers and the general market want, and integration with your existing applications to consolidate all business information. 52
 Electronic Commerce • Electronic Commerce (EC) is where business transactions take place via telecommunications networks, especially the Internet. – Electronic commerce describes the buying and selling of products, services, and information via computer networks including the Internet. – The infrastructure for EC is a networked computing environment in business, home, and government. – E-Business describes the broadest definition of EC. It includes customer service and intrabusiness tasks. It is frequently used interchangeably with EC. 53
Electronic Commerce • Electronic Commerce (EC) is where business transactions take place via telecommunications networks, especially the Internet. – Electronic commerce describes the buying and selling of products, services, and information via computer networks including the Internet. – The infrastructure for EC is a networked computing environment in business, home, and government. – E-Business describes the broadest definition of EC. It includes customer service and intrabusiness tasks. It is frequently used interchangeably with EC. 53
 The Driving Forces of Electronic Commerce • The New World of Business – Business pressures – Organizational responses – The role of Information Technology (including electronic commerce) 54
The Driving Forces of Electronic Commerce • The New World of Business – Business pressures – Organizational responses – The role of Information Technology (including electronic commerce) 54
 Electronic Commerce Terms • Business-to-business (B 2 B) – Businesses make online transactions purchases with other business • Business-to-consumer (B 2 C) – Online transactions between businesses and consumers • Consumer-to-Consumer (C 2 C) – Online auctions, posting to newspaper sites, personal websites, e-commerce portals 55
Electronic Commerce Terms • Business-to-business (B 2 B) – Businesses make online transactions purchases with other business • Business-to-consumer (B 2 C) – Online transactions between businesses and consumers • Consumer-to-Consumer (C 2 C) – Online auctions, posting to newspaper sites, personal websites, e-commerce portals 55
 Electronic Commerce Terms (cont. ) • Pure vs. Partial EC: based on the degree of digitization of – Product – Process – Delivery agent • Traditional commerce: all dimensions are physical • Pure EC: all dimensions are digital • Partial EC: all other possibilities include a mix of digital and physical dimensions 56
Electronic Commerce Terms (cont. ) • Pure vs. Partial EC: based on the degree of digitization of – Product – Process – Delivery agent • Traditional commerce: all dimensions are physical • Pure EC: all dimensions are digital • Partial EC: all other possibilities include a mix of digital and physical dimensions 56
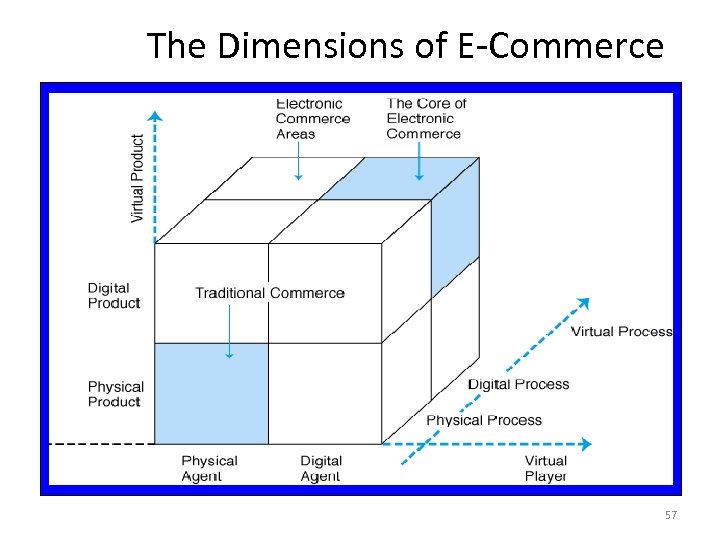 The Dimensions of E-Commerce 57
The Dimensions of E-Commerce 57
 Benefits of ecommerce • Discuss the benefits to • Business • Customer 58
Benefits of ecommerce • Discuss the benefits to • Business • Customer 58


