 LECTURE 2 - PRE-SCIENTIFIC MANAGEMENT ERA OUTLINE: 1. Items of Pre-Scientific management era 2. Early contributors of management thought
LECTURE 2 - PRE-SCIENTIFIC MANAGEMENT ERA OUTLINE: 1. Items of Pre-Scientific management era 2. Early contributors of management thought
 1. 1 Management in antiquity
1. 1 Management in antiquity
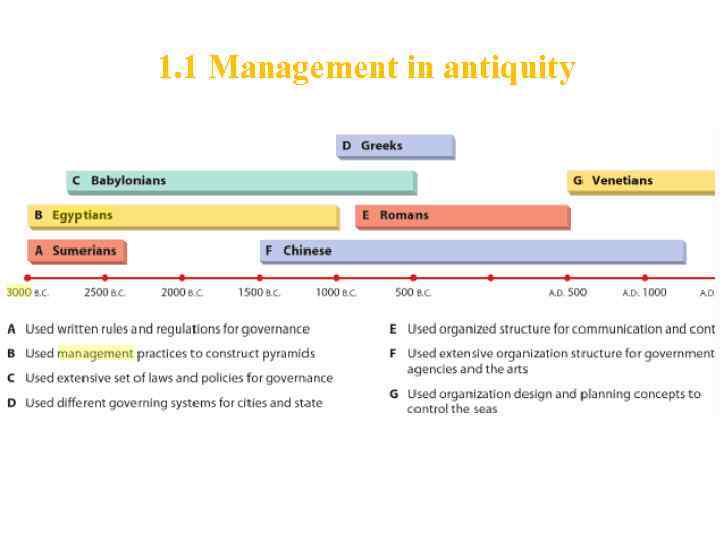
 1. 2 Management in antiquity - administration of mohenjodaro & harappa Cities Of ancient aryan in 2000 B. C. ; - buddha order and the sangha; - 3000 В. С. – Sumerians used written rules and regulations for governance; - 3000 B. C. – Egyptians used many management practices still used today in building pyramids; - 1500 B. C. – Chinese used extensive organizational structure for government agencies and the arts; - 1000 B. C. – Romans used organizational structure for communication and control.
1. 2 Management in antiquity - administration of mohenjodaro & harappa Cities Of ancient aryan in 2000 B. C. ; - buddha order and the sangha; - 3000 В. С. – Sumerians used written rules and regulations for governance; - 3000 B. C. – Egyptians used many management practices still used today in building pyramids; - 1500 B. C. – Chinese used extensive organizational structure for government agencies and the arts; - 1000 B. C. – Romans used organizational structure for communication and control.
 2. 1 Early contributors of management thought Prominent among the pioneers who made significant contributions to management thought were: Robert Owen (1771 -1858) He believed workers performance was influenced by the total environment in which they worked. Owen suggested that investment in human beings is more profitable than investment in machinery and other physical resources. He introduced new ideas of human relations, e. g. shorter working hours, housing facilities, education of children, provision of canteen, rest pauses, training of workers in hygiene etc. Charles Babbage (1792 -1891) Babbage perceived that the methods of science and mathematics could be applied to operations of factories. He laid considerable emphasis on specialisation, work measurement, optimum utilisation of machines, cost reduction and wage incentives. Henry Vamun Poor advocated a "managerial system" with a clear organization structure in which people could be held completely accountable and the need for a set of operating reports summarising costs, revenues and rates.
2. 1 Early contributors of management thought Prominent among the pioneers who made significant contributions to management thought were: Robert Owen (1771 -1858) He believed workers performance was influenced by the total environment in which they worked. Owen suggested that investment in human beings is more profitable than investment in machinery and other physical resources. He introduced new ideas of human relations, e. g. shorter working hours, housing facilities, education of children, provision of canteen, rest pauses, training of workers in hygiene etc. Charles Babbage (1792 -1891) Babbage perceived that the methods of science and mathematics could be applied to operations of factories. He laid considerable emphasis on specialisation, work measurement, optimum utilisation of machines, cost reduction and wage incentives. Henry Vamun Poor advocated a "managerial system" with a clear organization structure in which people could be held completely accountable and the need for a set of operating reports summarising costs, revenues and rates.
 Conclusion: • The practice of management is as old as the human race but its theories and conceptual frameworks are of recent origin. • This early 'autocratic period' of management is characterized by the use of strategies like 'fear of punishment' and 'fear of God', absolute authority, coercion and force on the human side of management.
Conclusion: • The practice of management is as old as the human race but its theories and conceptual frameworks are of recent origin. • This early 'autocratic period' of management is characterized by the use of strategies like 'fear of punishment' and 'fear of God', absolute authority, coercion and force on the human side of management.