lecture 2.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Lecture 2 Physical-chemical methods of EOR
Lecture 2 Physical-chemical methods of EOR
 Physical-chemical methods provides: • The increase of the displacement coefficient • The increase of sweep efficiency (simultaneously or one of them) • The extraction of the film and capillary hold-up oil from the flooded deposits
Physical-chemical methods provides: • The increase of the displacement coefficient • The increase of sweep efficiency (simultaneously or one of them) • The extraction of the film and capillary hold-up oil from the flooded deposits
 Oil displacement by water solutions of SAR • SAR in the injected water change its physical and chemical properties. They are: 1. The decrease of the surface tension on the boundary "water-oil", 2. The increase of the hydrophilic behavior of pore channels surface, i. e. rock’s grains become more wetted with water.
Oil displacement by water solutions of SAR • SAR in the injected water change its physical and chemical properties. They are: 1. The decrease of the surface tension on the boundary "water-oil", 2. The increase of the hydrophilic behavior of pore channels surface, i. e. rock’s grains become more wetted with water.
 SAR adsorption • Adsorption is a process of separation of SAR from the water solution and its settling-out on the surface of pore channels under the forces of the inter-molecular interactions. • Adhesion is a sticking of molecules of two different bodies, caused by mutual attraction. It occurs between liquid and solid bodies.
SAR adsorption • Adsorption is a process of separation of SAR from the water solution and its settling-out on the surface of pore channels under the forces of the inter-molecular interactions. • Adhesion is a sticking of molecules of two different bodies, caused by mutual attraction. It occurs between liquid and solid bodies.
 • Dupre/ Dupre-Young equations determine the forces work of adhesion Wа • Langmuir isotherm determines the quantity of A, sorbing on the surface of grains of hard rock of SAR A=c/a+bc • Henry isotherm A=c/a Where с - is the specific concentration of SAR in water, kg/m 3, a and b are the coefficients determined experimentally.
• Dupre/ Dupre-Young equations determine the forces work of adhesion Wа • Langmuir isotherm determines the quantity of A, sorbing on the surface of grains of hard rock of SAR A=c/a+bc • Henry isotherm A=c/a Where с - is the specific concentration of SAR in water, kg/m 3, a and b are the coefficients determined experimentally.
 Physical models to describe the processes in the formation: • Reciprocating oil displacement model • Non-reciprocating oil displacement model
Physical models to describe the processes in the formation: • Reciprocating oil displacement model • Non-reciprocating oil displacement model
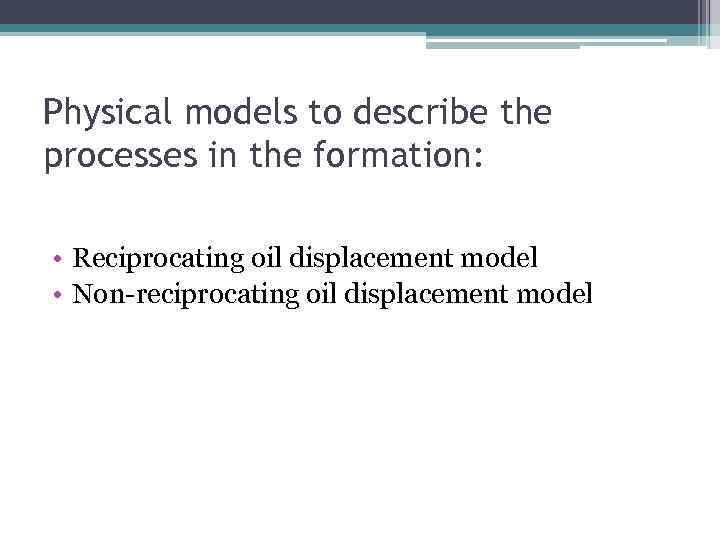
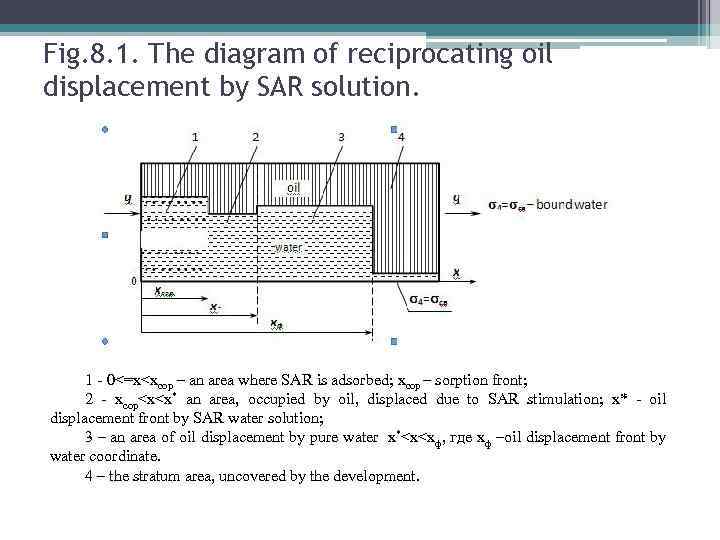 Fig. 8. 1. The diagram of reciprocating oil displacement by SAR solution. 1 - 0<=х<хсор – an area where SAR is adsorbed; хсор – sorption front; 2 - хсор<х<х* an area, occupied by oil, displaced due to SAR stimulation; x* - oil displacement front by SAR water solution; 3 – an area of oil displacement by pure water х*<х<хф, где хф –oil displacement front by water coordinate. 4 – the stratum area, uncovered by the development.
Fig. 8. 1. The diagram of reciprocating oil displacement by SAR solution. 1 - 0<=х<хсор – an area where SAR is adsorbed; хсор – sorption front; 2 - хсор<х<х* an area, occupied by oil, displaced due to SAR stimulation; x* - oil displacement front by SAR water solution; 3 – an area of oil displacement by pure water х*<х<хф, где хф –oil displacement front by water coordinate. 4 – the stratum area, uncovered by the development.
 SAR compositions Surface-active reagents (SAR) are chemical compositions capable due to adsorption to change the phase and energy interaction on the various boundary surfaces sections: liquid air, liquid - solid, oil - water. 1. According to the ionic characteristic SAR are divided into: • non-ionic compounds • ionic compounds can be: ü anionic SAR, cationic SAR and ampholytic SAR 2. According to solubility in water and oils, SAR can be: • water-, water-oil - and oil-soluble
SAR compositions Surface-active reagents (SAR) are chemical compositions capable due to adsorption to change the phase and energy interaction on the various boundary surfaces sections: liquid air, liquid - solid, oil - water. 1. According to the ionic characteristic SAR are divided into: • non-ionic compounds • ionic compounds can be: ü anionic SAR, cationic SAR and ampholytic SAR 2. According to solubility in water and oils, SAR can be: • water-, water-oil - and oil-soluble
 Polymer oil displacement • Mobility coefficient is the ratio of the relative permeability to the viscosity of the liquid. For oil and water the coefficients of mobility are the following: Koil =koil/µoil Kwater=kwater/ µwater • Darcy law for water and oil has the following view: V= - (k/ µ)*gradp • Darcy law for dilatant liquid: V= - (k/µbp)* (gradp)n
Polymer oil displacement • Mobility coefficient is the ratio of the relative permeability to the viscosity of the liquid. For oil and water the coefficients of mobility are the following: Koil =koil/µoil Kwater=kwater/ µwater • Darcy law for water and oil has the following view: V= - (k/ µ)*gradp • Darcy law for dilatant liquid: V= - (k/µbp)* (gradp)n
 Micellar-polymer flooding method • Is the method of complex stimulation on oil reservoir by injection of surfactants mixture, alcohols, oil solvents, water solution of PAA (polyacrylamide)and water. • the micellar solutions are transparent or translucent liquids that refer to the Newtonian liquids
Micellar-polymer flooding method • Is the method of complex stimulation on oil reservoir by injection of surfactants mixture, alcohols, oil solvents, water solution of PAA (polyacrylamide)and water. • the micellar solutions are transparent or translucent liquids that refer to the Newtonian liquids
 oil water а) oil б) The schemes of micellar structure on - а) oil base and б) water base
oil water а) oil б) The schemes of micellar structure on - а) oil base and б) water base
 Conformance change or control (straightening the injectability profile) (CC) • Conformance change or control of the injection wells is sometimes called diverter technologies that is not correct from our point of view, since the flow direction of the injected water can stay unchangeable. But the increase of the injectability interval, where the injected water comes, occurs. Or it should happen if the chemicals are chosen in a correct way and reliable geophysical data about the injectability interval are given.
Conformance change or control (straightening the injectability profile) (CC) • Conformance change or control of the injection wells is sometimes called diverter technologies that is not correct from our point of view, since the flow direction of the injected water can stay unchangeable. But the increase of the injectability interval, where the injected water comes, occurs. Or it should happen if the chemicals are chosen in a correct way and reliable geophysical data about the injectability interval are given.
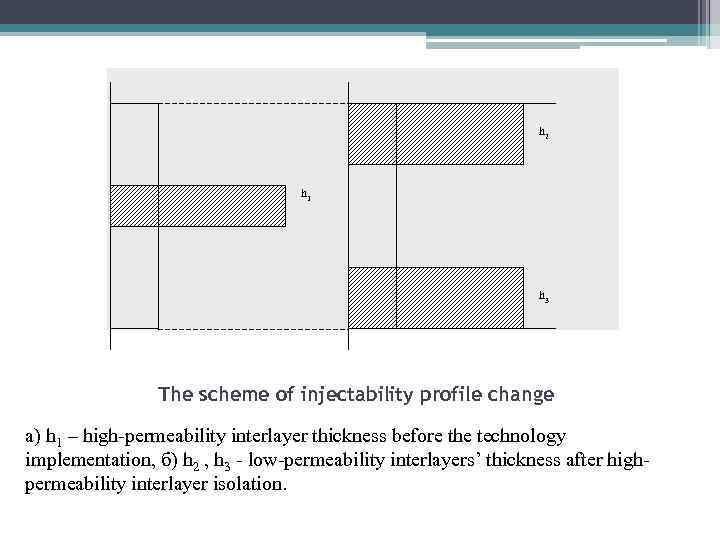 h 2 h 1 h 3 The scheme of injectability profile change а) h 1 – high-permeability interlayer thickness before the technology implementation, б) h 2 , h 3 - low-permeability interlayers’ thickness after highpermeability interlayer isolation.
h 2 h 1 h 3 The scheme of injectability profile change а) h 1 – high-permeability interlayer thickness before the technology implementation, б) h 2 , h 3 - low-permeability interlayers’ thickness after highpermeability interlayer isolation.
 Chemicals, according to the composition, can be: • Dispersed • Deposition-gel-forming • Complex composition
Chemicals, according to the composition, can be: • Dispersed • Deposition-gel-forming • Complex composition
 The criteria to use injectability profile enhancement technologies • The presence of the distinct geological filtration heterogeneity of the reservoir profile • The correspondence of the development degree of oil reserves to the production watering: the smaller the correspondence, the first the necessity of the work is considered (it indicates the presence of the trapped residual recoverable reserves). • The ratio between the degree of pumping (in percents from the pore volume of the area) and initial recoverable reserves extraction (the efficiency of the reservoir pressure maintenance system). • When all the other conditions are equal, first of all the areas of the production facility, corresponding to Kazemi model are processed. These are the areas, with high - and - low permeability interlayers. • In the conditions of the homogeneous geological structure, for example in the monolithic deposits, permabilities, defined on producing and injection wells, are compared respectively with pressure build-up curve (PBU) and pressure drawdown curve (PDD).
The criteria to use injectability profile enhancement technologies • The presence of the distinct geological filtration heterogeneity of the reservoir profile • The correspondence of the development degree of oil reserves to the production watering: the smaller the correspondence, the first the necessity of the work is considered (it indicates the presence of the trapped residual recoverable reserves). • The ratio between the degree of pumping (in percents from the pore volume of the area) and initial recoverable reserves extraction (the efficiency of the reservoir pressure maintenance system). • When all the other conditions are equal, first of all the areas of the production facility, corresponding to Kazemi model are processed. These are the areas, with high - and - low permeability interlayers. • In the conditions of the homogeneous geological structure, for example in the monolithic deposits, permabilities, defined on producing and injection wells, are compared respectively with pressure build-up curve (PBU) and pressure drawdown curve (PDD).
 Thanks for your attention!!!
Thanks for your attention!!!


