SDU_lecture2_DD_FET_MOS_trans-20130207-101106.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Lecture 2 – Field Effect Transistors (FET): By Karl Lebkuchner Suleyman Demirel University January 2013
Compare Bipolar to FET: 1. FETs are also made of N type and P-type semiconductors. 2. Bipolar transistors use the input current (Ib) to make the output current. FETs use the input voltage (Vg) to make the output current. 3. FETs usually have a much higher input impedance than bipolar transistors. 4. Usually, FET input voltages do not control the output current as exactly as bipolar input currents control the output current.
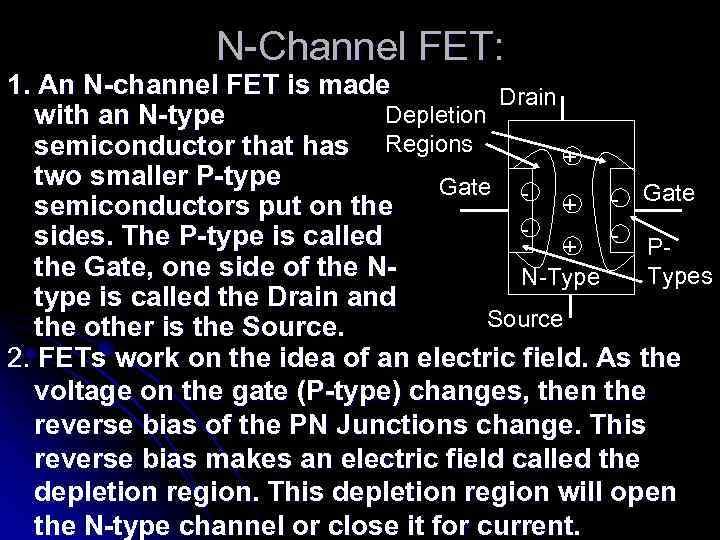
N-Channel FET: 1. An N-channel FET is made Drain Depletion with an N-type semiconductor that has Regions + two smaller P-type Gate + - Gate semiconductors put on the sides. The P-type is called + - Pthe Gate, one side of the NTypes N-Type type is called the Drain and Source the other is the Source. 2. FETs work on the idea of an electric field. As the voltage on the gate (P-type) changes, then the reverse bias of the PN Junctions change. This reverse bias makes an electric field called the depletion region. This depletion region will open the N-type channel or close it for current.
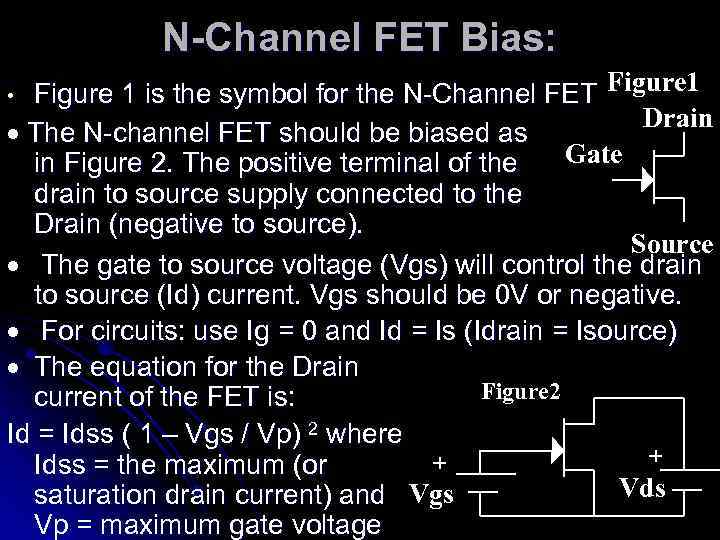
N-Channel FET Bias: Figure 1 is the symbol for the N-Channel FET Figure 1 Drain · The N-channel FET should be biased as Gate in Figure 2. The positive terminal of the drain to source supply connected to the Drain (negative to source). Source · The gate to source voltage (Vgs) will control the drain to source (Id) current. Vgs should be 0 V or negative. · For circuits: use Ig = 0 and Id = Is (Idrain = Isource) · The equation for the Drain Figure 2 current of the FET is: Id = Idss ( 1 – Vgs / Vp) 2 where + + Idss = the maximum (or Vds saturation drain current) and Vgs Vp = maximum gate voltage •
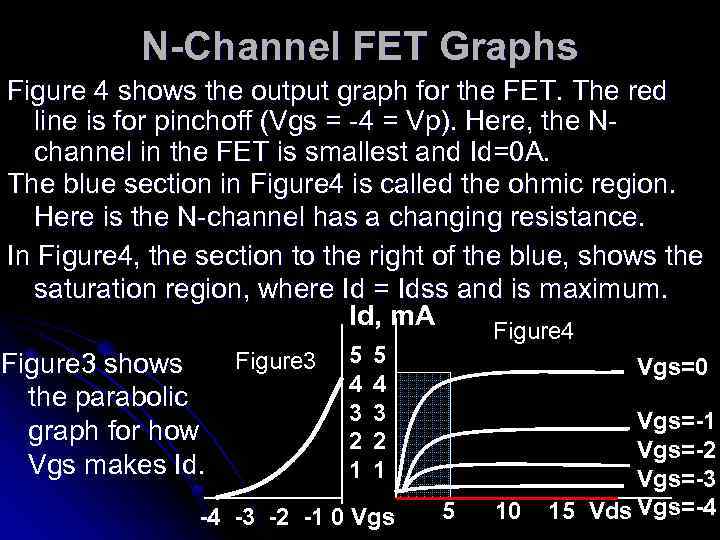
N-Channel FET Graphs Figure 4 shows the output graph for the FET. The red line is for pinchoff (Vgs = -4 = Vp). Here, the Nchannel in the FET is smallest and Id=0 A. The blue section in Figure 4 is called the ohmic region. Here is the N-channel has a changing resistance. In Figure 4, the section to the right of the blue, shows the saturation region, where Id = Idss and is maximum. Id, m. A Figure 3 shows the parabolic graph for how Vgs makes Id. Figure 3 5 4 3 2 1 Figure 4 5 4 3 2 1 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 Vgs=0 5 10 Vgs=-1 Vgs=-2 Vgs=-3 15 Vds Vgs=-4
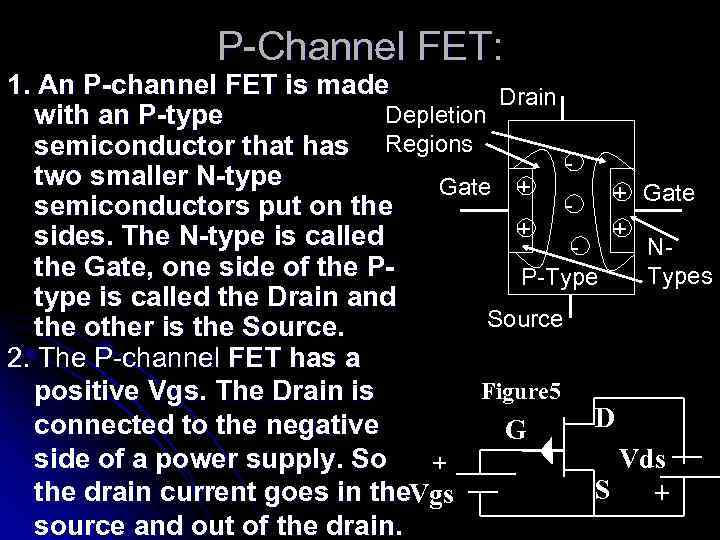
P-Channel FET: 1. An P-channel FET is made Drain Depletion with an P-type semiconductor that has Regions two smaller N-type Gate + + Gate semiconductors put on the + + sides. The N-type is called Nthe Gate, one side of the PTypes P-Type type is called the Drain and Source the other is the Source. 2. The P-channel FET has a Figure 5 positive Vgs. The Drain is D connected to the negative G side of a power supply. So Vds + S the drain current goes in the. Vgs + source and out of the drain.
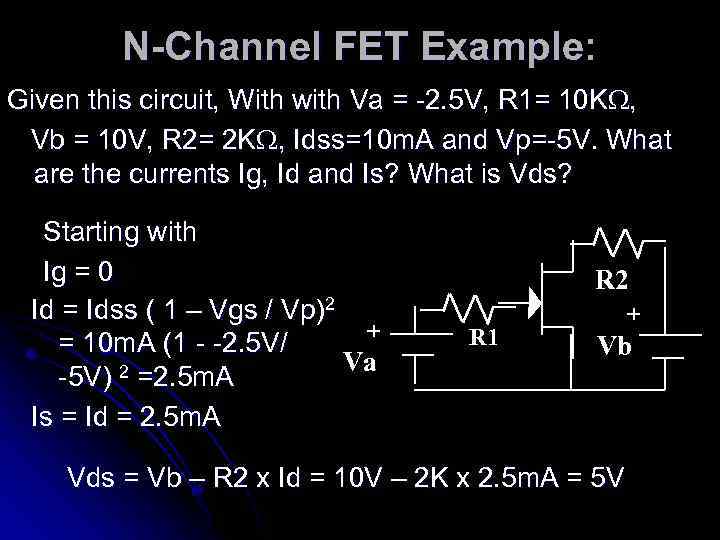
N-Channel FET Example: Given this circuit, With with Va = -2. 5 V, R 1= 10 K , Vb = 10 V, R 2= 2 K , Idss=10 m. A and Vp=-5 V. What are the currents Ig, Id and Is? What is Vds? Starting with Ig = 0 Id = Idss ( 1 – Vgs / Vp)2 + = 10 m. A (1 - -2. 5 V/ Va 2 =2. 5 m. A -5 V) Is = Id = 2. 5 m. A R 2 R 1 + Vb Vds = Vb – R 2 x Id = 10 V – 2 K x 2. 5 m. A = 5 V
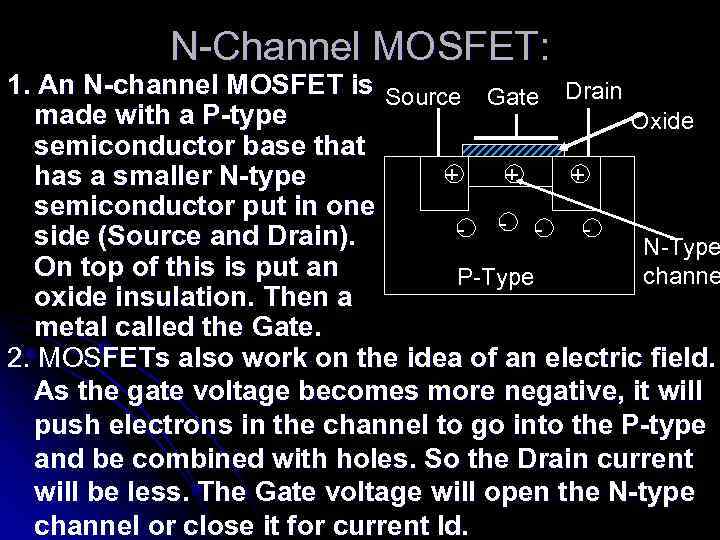
N-Channel MOSFET: 1. An N-channel MOSFET is Source Gate Drain made with a P-type Oxide semiconductor base that + + + has a smaller N-type semiconductor put in one - - side (Source and Drain). N-Type On top of this is put an channe P-Type oxide insulation. Then a metal called the Gate. 2. MOSFETs also work on the idea of an electric field. As the gate voltage becomes more negative, it will push electrons in the channel to go into the P-type and be combined with holes. So the Drain current will be less. The Gate voltage will open the N-type channel or close it for current Id.

N-Channel MOSFET Bias: Figure 6 is the symbol for the N-Channel Drain MOSFET Gate · The N-channel MOSFET should be biased as in Figure 7. The positive terminal of the drain to source supply Source connected to the Drain. · The gate to source voltage (Vgs) will control the drain to source (Id) current. For depletion mode, Vgs should be 0 V or negative. For enhancement mode, Vgs is >0. • Figure 7 · The equation for the Drain current of the MOSFET is: Id = Idss ( 1 – Vgs / Vp) 2 where + Vgs Idss = the saturation drain current. Vp = maximum gate voltage + Vds
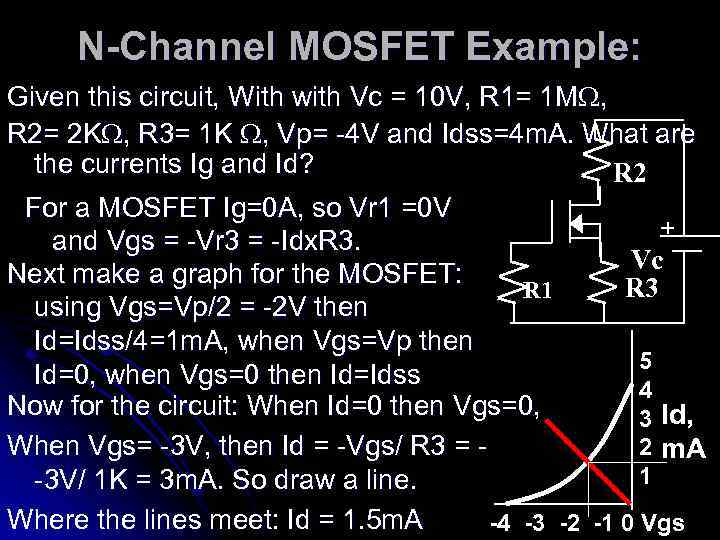
N-Channel MOSFET Example: Given this circuit, With with Vc = 10 V, R 1= 1 M , R 2= 2 K , R 3= 1 K , Vp= -4 V and Idss=4 m. A. What are the currents Ig and Id? R 2 For a MOSFET Ig=0 A, so Vr 1 =0 V + and Vgs = -Vr 3 = -Idx. R 3. Vc Next make a graph for the MOSFET: R 3 R 1 using Vgs=Vp/2 = -2 V then Id=Idss/4=1 m. A, when Vgs=Vp then 5 Id=0, when Vgs=0 then Id=Idss 4 Now for the circuit: When Id=0 then Vgs=0, 3 Id, When Vgs= -3 V, then Id = -Vgs/ R 3 = 2 m. A 1 -3 V/ 1 K = 3 m. A. So draw a line. Where the lines meet: Id = 1. 5 m. A -4 -3 -2 -1 0 Vgs
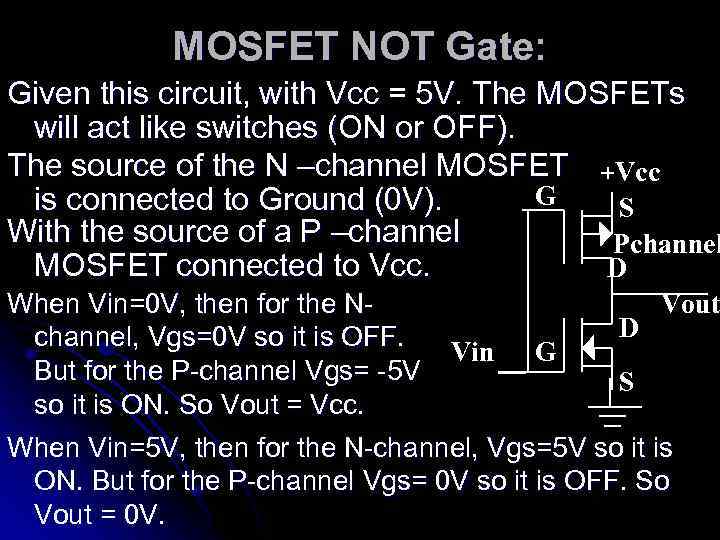
MOSFET NOT Gate: Given this circuit, with Vcc = 5 V. The MOSFETs will act like switches (ON or OFF). The source of the N –channel MOSFET +Vcc G is connected to Ground (0 V). S With the source of a P –channel Pchannel MOSFET connected to Vcc. D When Vin=0 V, then for the Nchannel, Vgs=0 V so it is OFF. But for the P-channel Vgs= -5 V so it is ON. So Vout = Vcc. Vin G D Vout S When Vin=5 V, then for the N-channel, Vgs=5 V so it is ON. But for the P-channel Vgs= 0 V so it is OFF. So Vout = 0 V.
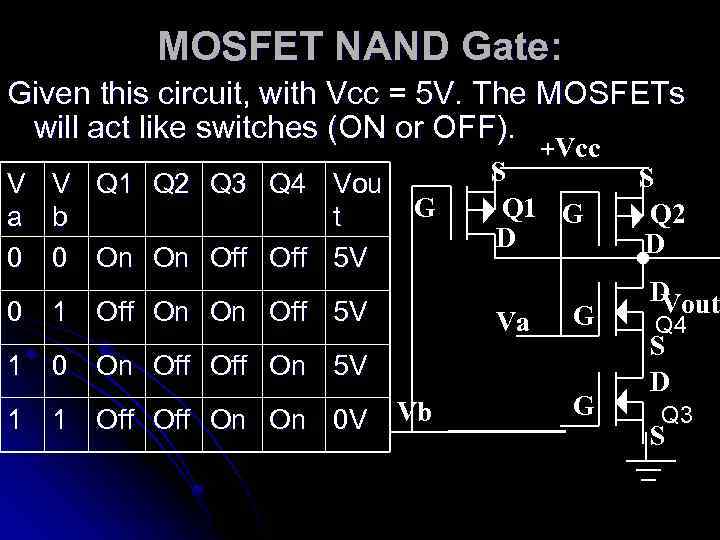
MOSFET NAND Gate: Given this circuit, with Vcc = 5 V. The MOSFETs will act like switches (ON or OFF). +Vcc V a 0 V Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Vou b t 0 On On Off 5 V G 0 1 Off On On Off 5 V S Q 1 G D Va G 1 0 On Off On 5 V 1 1 Off On On 0 V Vb G S Q 2 D D Vout Q 4 S D Q 3 S
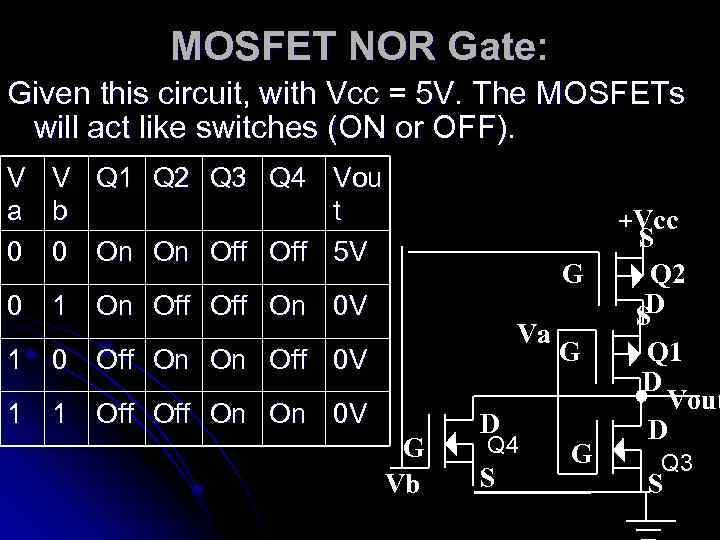
MOSFET NOR Gate: Given this circuit, with Vcc = 5 V. The MOSFETs will act like switches (ON or OFF). V V Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Vou a b t 0 0 On On Off 5 V +Vcc G 0 1 On Off On 0 V Va 1 0 Off On On Off 0 V 1 1 Off On On 0 V G Vb D Q 4 S G G S Q 2 D S Q 1 D Vout D Q 3 S
SDU_lecture2_DD_FET_MOS_trans-20130207-101106.ppt