 LECTURE 2: COMPUTER REVOLUTION Computer Science Alemany High School Summer 2008 Mr. Galla
LECTURE 2: COMPUTER REVOLUTION Computer Science Alemany High School Summer 2008 Mr. Galla
 I. REVOLUTION! industrial revolution – led to surplus of technology and the computer revolution Computer revolution – each household having a computer information revolution – mental work is being automated
I. REVOLUTION! industrial revolution – led to surplus of technology and the computer revolution Computer revolution – each household having a computer information revolution – mental work is being automated
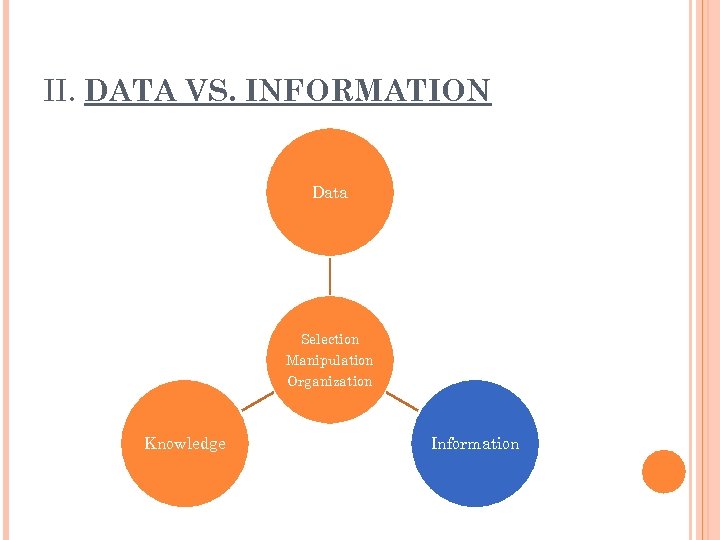 II. DATA VS. INFORMATION Data Selection Manipulation Organization Knowledge Information
II. DATA VS. INFORMATION Data Selection Manipulation Organization Knowledge Information
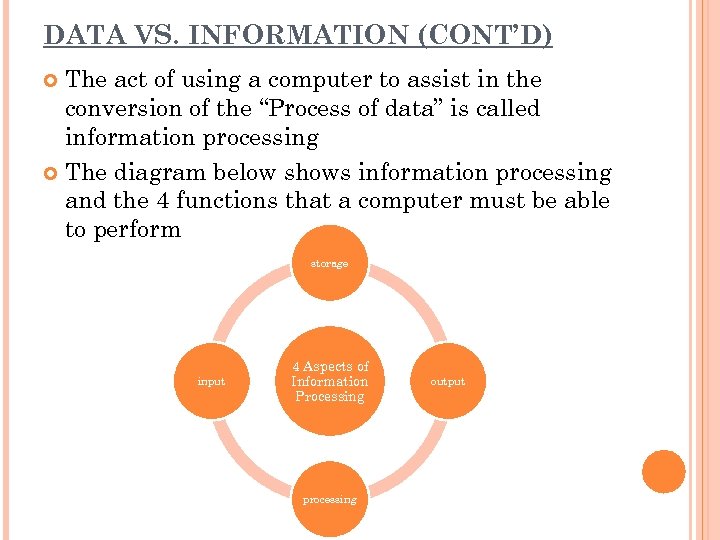 DATA VS. INFORMATION (CONT’D) The act of using a computer to assist in the conversion of the “Process of data” is called information processing The diagram below shows information processing and the 4 functions that a computer must be able to perform storage input 4 Aspects of Information Processing processing output
DATA VS. INFORMATION (CONT’D) The act of using a computer to assist in the conversion of the “Process of data” is called information processing The diagram below shows information processing and the 4 functions that a computer must be able to perform storage input 4 Aspects of Information Processing processing output
 III. WHAT IS A COMPUTER? Micro – electronics – refers to the miniaturization of the components of an electronic circuit “IC” integrated circuit – all of the components of an electric circuit on a single piece of semiconduction material called silicon. Computer/microprocessor/microchip/processor – thousands of electrical circuits etched onto a very small piece of silicon
III. WHAT IS A COMPUTER? Micro – electronics – refers to the miniaturization of the components of an electronic circuit “IC” integrated circuit – all of the components of an electric circuit on a single piece of semiconduction material called silicon. Computer/microprocessor/microchip/processor – thousands of electrical circuits etched onto a very small piece of silicon
 IV. A COMPUTER “SYSTEM” a computer system is a collection of at least 4 basic components: 1. computer – the tower (desktop/box) 2. input device – keyboard, mouse , etc. 3. output devices – printer, speakers, etc. 4. storage – divided into primary & secondary storage
IV. A COMPUTER “SYSTEM” a computer system is a collection of at least 4 basic components: 1. computer – the tower (desktop/box) 2. input device – keyboard, mouse , etc. 3. output devices – printer, speakers, etc. 4. storage – divided into primary & secondary storage
 V. AN INFORMATION “SYSTEM” hardware 2. software 3. data 4. people 5. procedures 1.
V. AN INFORMATION “SYSTEM” hardware 2. software 3. data 4. people 5. procedures 1.
 VI. PROCESSING POWER processing power depends on processor speed and processor memory
VI. PROCESSING POWER processing power depends on processor speed and processor memory
 VII. CLASSIFYING COMPUTER SYSTEMS Computer systems can be classified - Supercomputer system - Mainframe system - Mini Computer system - Workstation system - Microprocessor system - Laptop/notebook - Handheld - Smartphone
VII. CLASSIFYING COMPUTER SYSTEMS Computer systems can be classified - Supercomputer system - Mainframe system - Mini Computer system - Workstation system - Microprocessor system - Laptop/notebook - Handheld - Smartphone