4515f8756a46d615f8092145d1691d38.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Lecture 14 Residential Financing
Lecture 14 Residential Financing
 Items To Consider When Shopping Home Loans l l l l Size of Down Payment Mortgage Interest Rate-Lock Period Length of Grace Period Late Charge for Overdue Payments Prepayment Clauses/Penalties Due-on-Sale Clause Financing Costs/Points
Items To Consider When Shopping Home Loans l l l l Size of Down Payment Mortgage Interest Rate-Lock Period Length of Grace Period Late Charge for Overdue Payments Prepayment Clauses/Penalties Due-on-Sale Clause Financing Costs/Points
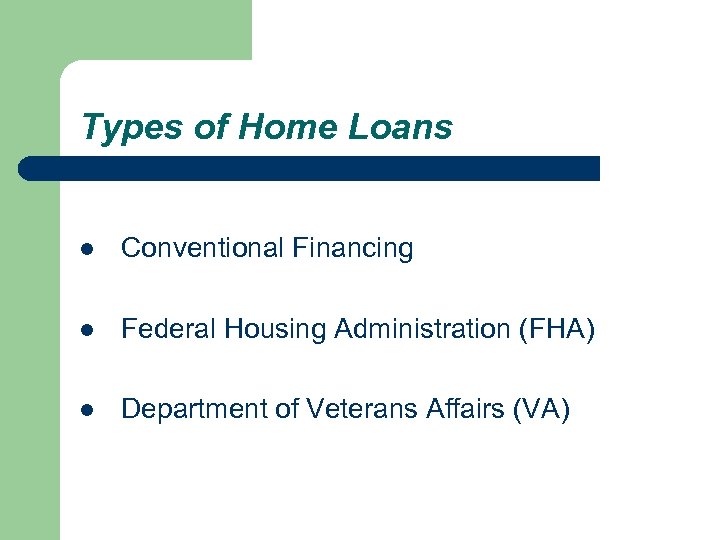 Types of Home Loans l Conventional Financing l Federal Housing Administration (FHA) l Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)
Types of Home Loans l Conventional Financing l Federal Housing Administration (FHA) l Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)
 Residential Mortgage Loans APPLICATION PROCEDURE 1. Complete and Submit Loan Application 2. Within 3 business days, Lender provides the borrower: - Good Faith Estimate of Settlement Costs - Truth-In-Lending disclosure statement, demonstrating costs of mortgage financing considering all financing costs - U. S. HUD booklet explaining RESPA protections to the borrower
Residential Mortgage Loans APPLICATION PROCEDURE 1. Complete and Submit Loan Application 2. Within 3 business days, Lender provides the borrower: - Good Faith Estimate of Settlement Costs - Truth-In-Lending disclosure statement, demonstrating costs of mortgage financing considering all financing costs - U. S. HUD booklet explaining RESPA protections to the borrower
 Residential Mortgage Loans APPLICATION PROCEDURE 3. Lender obtains credit reports of borrower from three sources 4. Borrower provides to the lender W-2 tax information, income statements, verification of employment and history, proof of assets (bank statements), etc. 5. Loan goes through “underwriting” -Borrower’s current and expected debt obligations, credit review
Residential Mortgage Loans APPLICATION PROCEDURE 3. Lender obtains credit reports of borrower from three sources 4. Borrower provides to the lender W-2 tax information, income statements, verification of employment and history, proof of assets (bank statements), etc. 5. Loan goes through “underwriting” -Borrower’s current and expected debt obligations, credit review
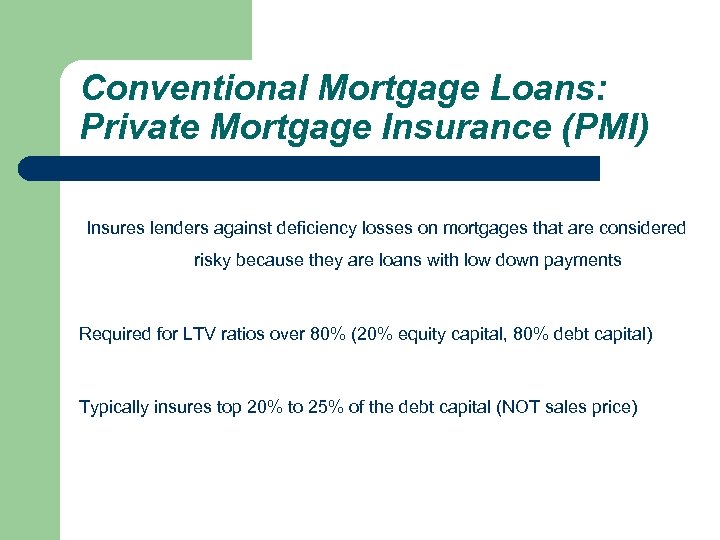 Conventional Mortgage Loans: Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) Insures lenders against deficiency losses on mortgages that are considered risky because they are loans with low down payments Required for LTV ratios over 80% (20% equity capital, 80% debt capital) Typically insures top 20% to 25% of the debt capital (NOT sales price)
Conventional Mortgage Loans: Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) Insures lenders against deficiency losses on mortgages that are considered risky because they are loans with low down payments Required for LTV ratios over 80% (20% equity capital, 80% debt capital) Typically insures top 20% to 25% of the debt capital (NOT sales price)
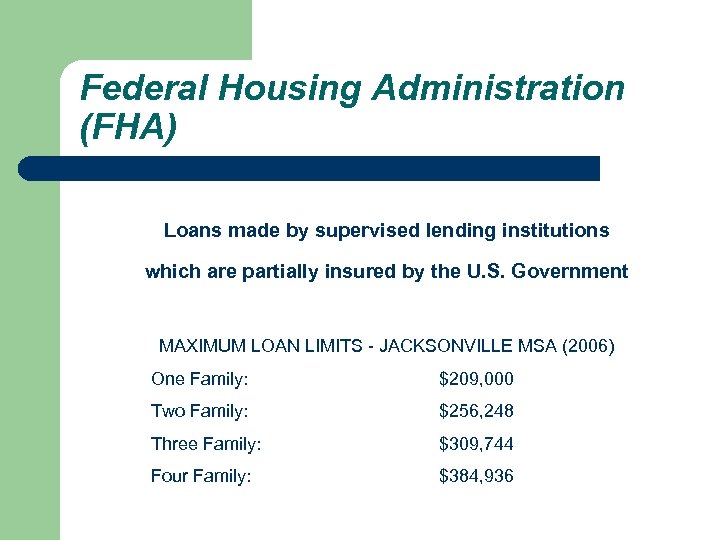 Federal Housing Administration (FHA) Loans made by supervised lending institutions which are partially insured by the U. S. Government MAXIMUM LOAN LIMITS - JACKSONVILLE MSA (2006) One Family: $209, 000 Two Family: $256, 248 Three Family: $309, 744 Four Family: $384, 936
Federal Housing Administration (FHA) Loans made by supervised lending institutions which are partially insured by the U. S. Government MAXIMUM LOAN LIMITS - JACKSONVILLE MSA (2006) One Family: $209, 000 Two Family: $256, 248 Three Family: $309, 744 Four Family: $384, 936
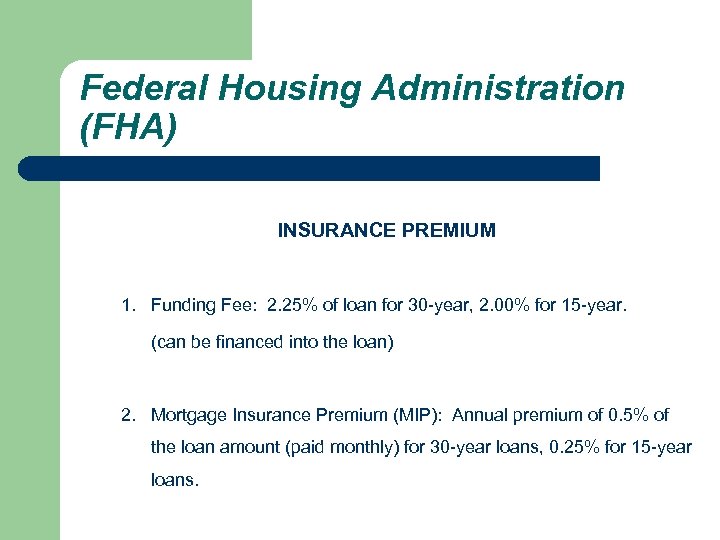 Federal Housing Administration (FHA) INSURANCE PREMIUM 1. Funding Fee: 2. 25% of loan for 30 -year, 2. 00% for 15 -year. (can be financed into the loan) 2. Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP): Annual premium of 0. 5% of the loan amount (paid monthly) for 30 -year loans, 0. 25% for 15 -year loans.
Federal Housing Administration (FHA) INSURANCE PREMIUM 1. Funding Fee: 2. 25% of loan for 30 -year, 2. 00% for 15 -year. (can be financed into the loan) 2. Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP): Annual premium of 0. 5% of the loan amount (paid monthly) for 30 -year loans, 0. 25% for 15 -year loans.
 Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Loans made by supervised lending institutions which are partially guaranteed by the U. S. Government Primary Benefit: Zero-Down Payment Financing Loan applicant must be active for 181 days if currently listed in armed forces Discharged Personnel: Must have served at least two years to apply Application for a VA loan the same as conventional or FHA financing, but further requires a Certificate of Eligibility
Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Loans made by supervised lending institutions which are partially guaranteed by the U. S. Government Primary Benefit: Zero-Down Payment Financing Loan applicant must be active for 181 days if currently listed in armed forces Discharged Personnel: Must have served at least two years to apply Application for a VA loan the same as conventional or FHA financing, but further requires a Certificate of Eligibility
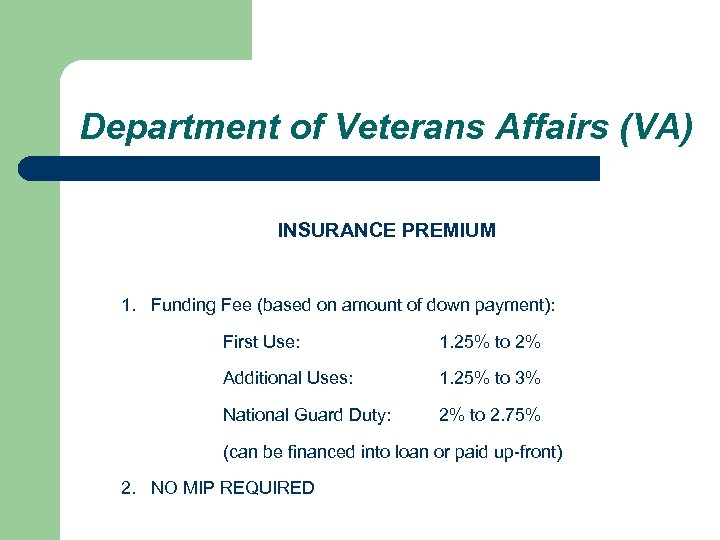 Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) INSURANCE PREMIUM 1. Funding Fee (based on amount of down payment): First Use: 1. 25% to 2% Additional Uses: 1. 25% to 3% National Guard Duty: 2% to 2. 75% (can be financed into loan or paid up-front) 2. NO MIP REQUIRED
Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) INSURANCE PREMIUM 1. Funding Fee (based on amount of down payment): First Use: 1. 25% to 2% Additional Uses: 1. 25% to 3% National Guard Duty: 2% to 2. 75% (can be financed into loan or paid up-front) 2. NO MIP REQUIRED
 Lecture 14 Other Types of Residential Financing
Lecture 14 Other Types of Residential Financing
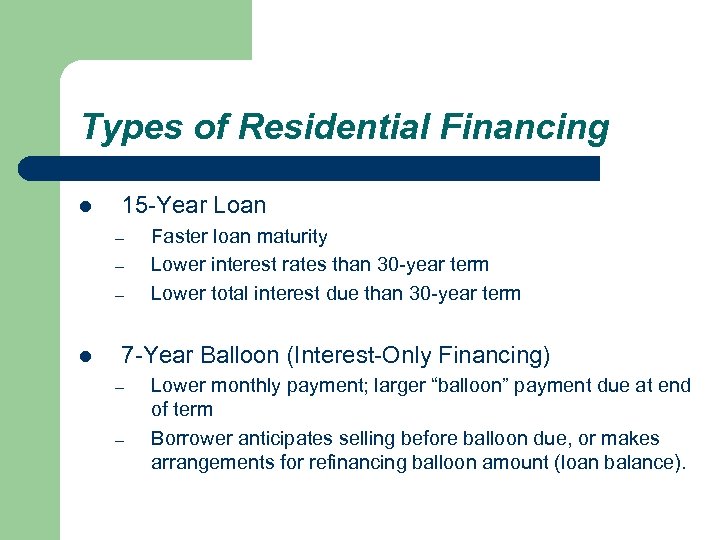 Types of Residential Financing l 15 -Year Loan – – – l Faster loan maturity Lower interest rates than 30 -year term Lower total interest due than 30 -year term 7 -Year Balloon (Interest-Only Financing) – – Lower monthly payment; larger “balloon” payment due at end of term Borrower anticipates selling before balloon due, or makes arrangements for refinancing balloon amount (loan balance).
Types of Residential Financing l 15 -Year Loan – – – l Faster loan maturity Lower interest rates than 30 -year term Lower total interest due than 30 -year term 7 -Year Balloon (Interest-Only Financing) – – Lower monthly payment; larger “balloon” payment due at end of term Borrower anticipates selling before balloon due, or makes arrangements for refinancing balloon amount (loan balance).
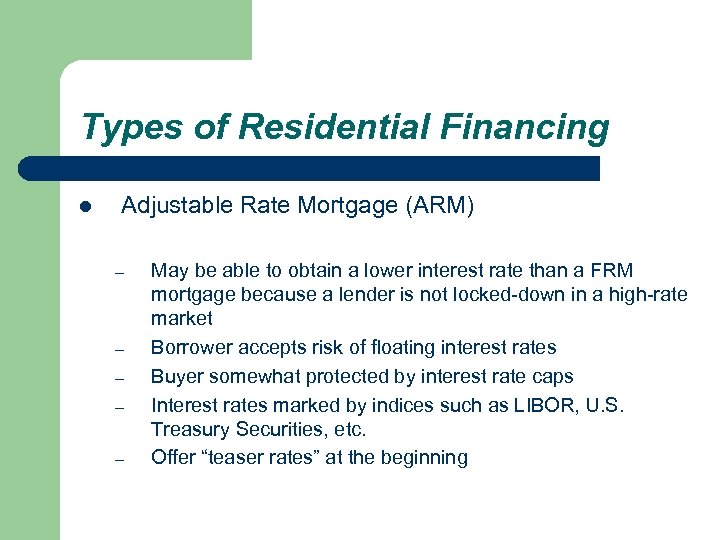 Types of Residential Financing l Adjustable Rate Mortgage (ARM) – – – May be able to obtain a lower interest rate than a FRM mortgage because a lender is not locked-down in a high-rate market Borrower accepts risk of floating interest rates Buyer somewhat protected by interest rate caps Interest rates marked by indices such as LIBOR, U. S. Treasury Securities, etc. Offer “teaser rates” at the beginning
Types of Residential Financing l Adjustable Rate Mortgage (ARM) – – – May be able to obtain a lower interest rate than a FRM mortgage because a lender is not locked-down in a high-rate market Borrower accepts risk of floating interest rates Buyer somewhat protected by interest rate caps Interest rates marked by indices such as LIBOR, U. S. Treasury Securities, etc. Offer “teaser rates” at the beginning
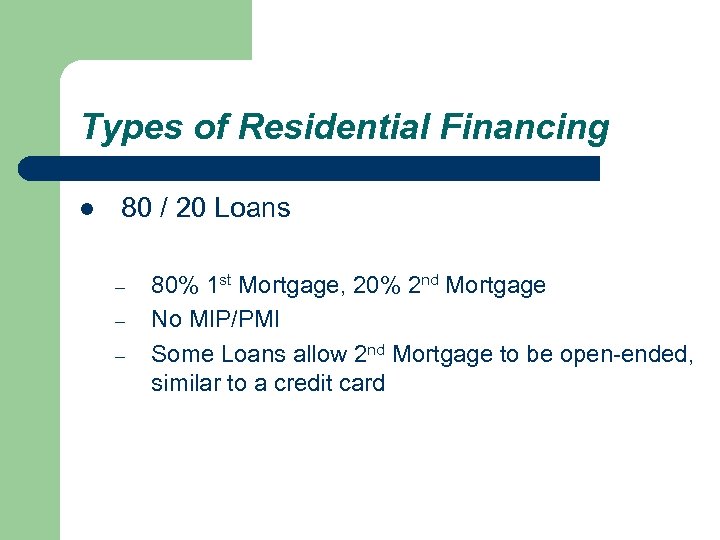 Types of Residential Financing l 80 / 20 Loans – – – 80% 1 st Mortgage, 20% 2 nd Mortgage No MIP/PMI Some Loans allow 2 nd Mortgage to be open-ended, similar to a credit card
Types of Residential Financing l 80 / 20 Loans – – – 80% 1 st Mortgage, 20% 2 nd Mortgage No MIP/PMI Some Loans allow 2 nd Mortgage to be open-ended, similar to a credit card
 Lecture 14 Borrower Competition for Mortgage Money
Lecture 14 Borrower Competition for Mortgage Money
 Competition For Mortgage Money l Government l Business l Households
Competition For Mortgage Money l Government l Business l Households
 Lecture 14 Types of Mortgage Lenders
Lecture 14 Types of Mortgage Lenders
 Mortgage Lenders l Mortgage Companies – l l Commercial Bank Thrift Institutions – l Mortgage Bankers, Mortgage Brokers Savings & Loan Associations, Savings Banks, Mutual Savings Banks, Credit Unions Individuals
Mortgage Lenders l Mortgage Companies – l l Commercial Bank Thrift Institutions – l Mortgage Bankers, Mortgage Brokers Savings & Loan Associations, Savings Banks, Mutual Savings Banks, Credit Unions Individuals


