Lecture_12.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Lecture 12 Government regulation of economy
Lecture 12 Government regulation of economy
 Plan of the lecture 1. Government regulation: essence, aims, instruments. 2. Monetary-credit system. 3. Financial system 4. Tax and fiscal policy of the RK
Plan of the lecture 1. Government regulation: essence, aims, instruments. 2. Monetary-credit system. 3. Financial system 4. Tax and fiscal policy of the RK
 Aim of the lecture • To understand meaning the government intervention to the economy by using monetary policy and fiscal policy instruments
Aim of the lecture • To understand meaning the government intervention to the economy by using monetary policy and fiscal policy instruments
 • Government regulation of the economy in a market economy is a system of standard measures of legislative, executive and supervisory nature performed by authorized government agencies and civil society organizations in order to stabilize and action existing social and economic system to changing conditions.
• Government regulation of the economy in a market economy is a system of standard measures of legislative, executive and supervisory nature performed by authorized government agencies and civil society organizations in order to stabilize and action existing social and economic system to changing conditions.
 The aim of government regulation • The aim of government regulation is to decrease the influence of market failure because sometimes markets do not allocate resources efficiently, government intervention may improve economic performance and also it tries to stabilize the economy
The aim of government regulation • The aim of government regulation is to decrease the influence of market failure because sometimes markets do not allocate resources efficiently, government intervention may improve economic performance and also it tries to stabilize the economy
 The instruments of government regulation are: • Making transfer payments • Changing the tax rate • Changing money supply
The instruments of government regulation are: • Making transfer payments • Changing the tax rate • Changing money supply
 Using of the type of the instruments depends on the business cycle, especially if the economy is the recession.
Using of the type of the instruments depends on the business cycle, especially if the economy is the recession.
 • “Monetary policy is essentially a programme of action undertaken by the monetary authorities, generally the central bank, to control and regulate the supply of money with the public and the flow of credit with a view to achieving predetermined macroeconomic goals” • The objectives of monetary policy are the same as of macroeconomic policy – price stability, currency stability, financial stability, growth in employment and income
• “Monetary policy is essentially a programme of action undertaken by the monetary authorities, generally the central bank, to control and regulate the supply of money with the public and the flow of credit with a view to achieving predetermined macroeconomic goals” • The objectives of monetary policy are the same as of macroeconomic policy – price stability, currency stability, financial stability, growth in employment and income
 Monetary Policy and Money Supply u. The money supply is controlled by the RBI through: u Changing the reserve requirements u Changing the policy rates (bank rate, repo rate and reverse repo rate) u Open-market u operations Thus the quantity of money supplied does not depend on the interest rate and is vertical
Monetary Policy and Money Supply u. The money supply is controlled by the RBI through: u Changing the reserve requirements u Changing the policy rates (bank rate, repo rate and reverse repo rate) u Open-market u operations Thus the quantity of money supplied does not depend on the interest rate and is vertical
 Monetary system of the country is stated in the law and it has: the following components, such as: 1. National currency 2. Cash system (coins, credit cards and money) 3. System of money emission 4. Government Regulation of money supply (Central bank)
Monetary system of the country is stated in the law and it has: the following components, such as: 1. National currency 2. Cash system (coins, credit cards and money) 3. System of money emission 4. Government Regulation of money supply (Central bank)
 Money supply aggregates • Money supply is the sum of cash, clearing money that is used in the national economy to provide the circulation of goods and services Product quantity=amount of supplied money
Money supply aggregates • Money supply is the sum of cash, clearing money that is used in the national economy to provide the circulation of goods and services Product quantity=amount of supplied money
 Money supply aggregates consists of the following elements: • M 0 - money in cash of people and enterprises • M 1 - M 0+ short term deposits of the people and the enterprises • M 2 - M 1+ long term deposits of the people • M 3 -M 2+ government bonds
Money supply aggregates consists of the following elements: • M 0 - money in cash of people and enterprises • M 1 - M 0+ short term deposits of the people and the enterprises • M 2 - M 1+ long term deposits of the people • M 3 -M 2+ government bonds
 • Instruments of Monetary Policy Credit Control by the Central Bank Instruments of credit control • Broadly categorized into two: – General instruments are intended to regulate the total volume of credit (quantitative) Include (1) policy rates, (2) open market operations, (3) power to vary the reserve requirements – Selective instruments to regulate the purpose for which commercial banks generated credit (qualitative)
• Instruments of Monetary Policy Credit Control by the Central Bank Instruments of credit control • Broadly categorized into two: – General instruments are intended to regulate the total volume of credit (quantitative) Include (1) policy rates, (2) open market operations, (3) power to vary the reserve requirements – Selective instruments to regulate the purpose for which commercial banks generated credit (qualitative)
 Central bank regulates the money supply using a required reserve ratio(r). • It is a minimum ratio of cash reserves to deposits that the central requires commercial banks to hold. e. g. 5%. Bank uses bank multiplier to decide money supply. m= 1/r*100. Taking into consideration our example above m=20, it means that with r money supply increase for 20 times. Suppose the banking system has 100 000 USD in cash. The banking system will create 20 000 USD of deposits against 1 000 USD cash reserve.
Central bank regulates the money supply using a required reserve ratio(r). • It is a minimum ratio of cash reserves to deposits that the central requires commercial banks to hold. e. g. 5%. Bank uses bank multiplier to decide money supply. m= 1/r*100. Taking into consideration our example above m=20, it means that with r money supply increase for 20 times. Suppose the banking system has 100 000 USD in cash. The banking system will create 20 000 USD of deposits against 1 000 USD cash reserve.
 Bank Rate • The minimum rate at which the central bank of a country provided financial assistance to commercial banks • By raising or lowering bank rate, the central bank can reduce or expand credit granted by banks • Currently bank rate in Kazakhstan is 5. 0%
Bank Rate • The minimum rate at which the central bank of a country provided financial assistance to commercial banks • By raising or lowering bank rate, the central bank can reduce or expand credit granted by banks • Currently bank rate in Kazakhstan is 5. 0%
 • Credit is a sum of money that has to be returned, be payed according to the agreement. There are forms of the credit such as commercial credit, consumer credit, mortgage (ипотека), international credit, leasing, factoring, and etc.
• Credit is a sum of money that has to be returned, be payed according to the agreement. There are forms of the credit such as commercial credit, consumer credit, mortgage (ипотека), international credit, leasing, factoring, and etc.
 • Commercial credit is form of credit when it is used to let pay enterprise for the goods after buying them. This form is used only between enterprises.
• Commercial credit is form of credit when it is used to let pay enterprise for the goods after buying them. This form is used only between enterprises.
 • Consumer credit is a credit that is taken by person to buy long term goods. • Mortgage is a form credit when person can get money but should give mortgage to the bank (house, land) • Factoring means the bank covers all debts of the enterprise, then requires the money from the enterprise.
• Consumer credit is a credit that is taken by person to buy long term goods. • Mortgage is a form credit when person can get money but should give mortgage to the bank (house, land) • Factoring means the bank covers all debts of the enterprise, then requires the money from the enterprise.
 • There are 2 levels of banking system in the economy. They are Central bank and commercial bank. •
• There are 2 levels of banking system in the economy. They are Central bank and commercial bank. •
 The functions of Central bank: • Banknotes emission • Saving of government gold-currency reserve • Saving reserve funds of commercial and noncommercial organizations (pawnshopы (ломбарды), micro-credit organizations, investment funds, pension funds, insurance companies and others) • Regulating economy by using money-credit system instruments(changing reserve ratio, credit interest rate ) • Control the actions of the commercial banks
The functions of Central bank: • Banknotes emission • Saving of government gold-currency reserve • Saving reserve funds of commercial and noncommercial organizations (pawnshopы (ломбарды), micro-credit organizations, investment funds, pension funds, insurance companies and others) • Regulating economy by using money-credit system instruments(changing reserve ratio, credit interest rate ) • Control the actions of the commercial banks
 The main functions of the commercial banks: • To give credits for the individuals and enterprises (active part operation) • To attract deposits of the individuals and enterprises (passive part operation) • To transfer money cash of the individuals and enterprises (active part operation)
The main functions of the commercial banks: • To give credits for the individuals and enterprises (active part operation) • To attract deposits of the individuals and enterprises (passive part operation) • To transfer money cash of the individuals and enterprises (active part operation)
 Types of the bank • According to the type of the services that offers bank it is classified as Deposit bank Investment bank Mortgage bank Universal bank Specialized bank(жилищно сберегательный строительный банк) and others
Types of the bank • According to the type of the services that offers bank it is classified as Deposit bank Investment bank Mortgage bank Universal bank Specialized bank(жилищно сберегательный строительный банк) and others
 Fiscal Policy-Meaning • • The word fisc means ‘state treasury’ and fiscal policy refers to policy concerning the use of ‘state treasury’ or the govt. finances to achieve the macroeconomic goals. “any decision to change the level, composition or timing of govt. expenditure or to vary the burden , the structure or frequency of the tax payment is fiscal policy. ” - G. K. Shaw
Fiscal Policy-Meaning • • The word fisc means ‘state treasury’ and fiscal policy refers to policy concerning the use of ‘state treasury’ or the govt. finances to achieve the macroeconomic goals. “any decision to change the level, composition or timing of govt. expenditure or to vary the burden , the structure or frequency of the tax payment is fiscal policy. ” - G. K. Shaw
 Financial system • Important system in any economy is financial system. • Finance is a system concerning the distribution and usage of money
Financial system • Important system in any economy is financial system. • Finance is a system concerning the distribution and usage of money
 Financial system consists the following parts 1. 2. 3. 4. Government budget Insurance fund Currency reserve Money fund of commercial and non commercial organisations 5. Other special funds
Financial system consists the following parts 1. 2. 3. 4. Government budget Insurance fund Currency reserve Money fund of commercial and non commercial organisations 5. Other special funds
 Objectives of Fiscal Policy • It has 2 major objectives: • GENERAL obj-. aimed at achieving macroeconomic goals • SPECIFIC obj-. relating to any typical problems of an economy
Objectives of Fiscal Policy • It has 2 major objectives: • GENERAL obj-. aimed at achieving macroeconomic goals • SPECIFIC obj-. relating to any typical problems of an economy
 Instruments of Fiscal Policy • • • Budgetary surplus and deficit Government expenditure Taxation- direct and indirect Public debt Deficit financing
Instruments of Fiscal Policy • • • Budgetary surplus and deficit Government expenditure Taxation- direct and indirect Public debt Deficit financing
 Government budget • Government budget is centralized fund of money resources
Government budget • Government budget is centralized fund of money resources
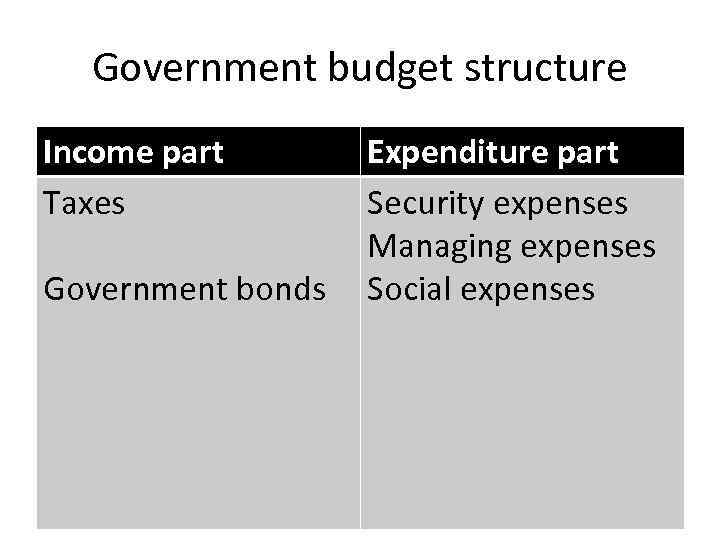 Government budget structure Income part Taxes Government bonds Expenditure part Security expenses Managing expenses Social expenses
Government budget structure Income part Taxes Government bonds Expenditure part Security expenses Managing expenses Social expenses


