Lecture #10_ Malware.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Lecture 11 Malware, security, hacking
Lecture 11 Malware, security, hacking
 What is malware? Malware - malicious software Malware is a program that was created to perform unwanted task on user’s computer and with some benefit to creator
What is malware? Malware - malicious software Malware is a program that was created to perform unwanted task on user’s computer and with some benefit to creator
 How malware can harm user? Malware programs can range: ● simple annoyances (pop-up advertising) ● causing serious computer invasion and damage (e. g. , stealing passwords and data or infecting other machines on the network). ● Some malware programs are designed to transmit information about your Webbrowsing habits to advertisers or other third party interests, unbeknownst to you.
How malware can harm user? Malware programs can range: ● simple annoyances (pop-up advertising) ● causing serious computer invasion and damage (e. g. , stealing passwords and data or infecting other machines on the network). ● Some malware programs are designed to transmit information about your Webbrowsing habits to advertisers or other third party interests, unbeknownst to you.
 Types of malware: Virus and worms Virus like biological viruses replicate it’s code into other programs They run each time when other program is running Worms spread themselves through network
Types of malware: Virus and worms Virus like biological viruses replicate it’s code into other programs They run each time when other program is running Worms spread themselves through network
 Types of malware: Trojan horse Like in a story about Troya, program presents itself as a useful program, but has malicious program inside it
Types of malware: Trojan horse Like in a story about Troya, program presents itself as a useful program, but has malicious program inside it
 Types of malware Backdoor - gives remote control for author Trojan banker - steal bank data Trojan DDo. S - conduct DDo. S Fake. AV - simulate activity of antivirus Trojan Ransom - block specific activities of computer, to take ransom money Trojan spy - spies after you
Types of malware Backdoor - gives remote control for author Trojan banker - steal bank data Trojan DDo. S - conduct DDo. S Fake. AV - simulate activity of antivirus Trojan Ransom - block specific activities of computer, to take ransom money Trojan spy - spies after you
 Malware: motivation Computer vandalism Petty theft: stealing passwords for online games and services Cybercrime Grey-market: adware (showing ads), rogueantivirus (user treated by some virus, and suggests to buy antivirus for it)
Malware: motivation Computer vandalism Petty theft: stealing passwords for online games and services Cybercrime Grey-market: adware (showing ads), rogueantivirus (user treated by some virus, and suggests to buy antivirus for it)
 Cybercrime http: //www. securelist. com/en/threats/detect? chapter=72 support for spammers: modern email systems have many different algorithms to find spam out of all mails. There are black-list of emails sending spams. DDo. S attacks: web-sites can handle only limited amount of users, hackers attack website from many computers in one time, to overload work of web-site
Cybercrime http: //www. securelist. com/en/threats/detect? chapter=72 support for spammers: modern email systems have many different algorithms to find spam out of all mails. There are black-list of emails sending spams. DDo. S attacks: web-sites can handle only limited amount of users, hackers attack website from many computers in one time, to overload work of web-site
![Cybercrime[2] botnets: many infected computers are controlled by master. There are black market where Cybercrime[2] botnets: many infected computers are controlled by master. There are black market where](https://present5.com/presentation/-76408184_330686355/image-9.jpg) Cybercrime[2] botnets: many infected computers are controlled by master. There are black market where people can buy access to control that zombie-nets Calls to pay numbers or sending paid SMS Stealing electronic currency Stealing banking information: the most common type of criminal activity. often keyloggers are waiting you to connect to website of bank
Cybercrime[2] botnets: many infected computers are controlled by master. There are black market where people can buy access to control that zombie-nets Calls to pay numbers or sending paid SMS Stealing electronic currency Stealing banking information: the most common type of criminal activity. often keyloggers are waiting you to connect to website of bank
![Cybercrime[3] Stealing other confidential information Cyber blackmail: ciphering files from computer Targeted attacks: some Cybercrime[3] Stealing other confidential information Cyber blackmail: ciphering files from computer Targeted attacks: some](https://present5.com/presentation/-76408184_330686355/image-10.jpg) Cybercrime[3] Stealing other confidential information Cyber blackmail: ciphering files from computer Targeted attacks: some companies e. g. banks can be attacked to steal special information
Cybercrime[3] Stealing other confidential information Cyber blackmail: ciphering files from computer Targeted attacks: some companies e. g. banks can be attacked to steal special information
 Anti-malware strategies Antivirus software Website security scan: Chrome, Firefox has black-list of sites that contain or contained malware
Anti-malware strategies Antivirus software Website security scan: Chrome, Firefox has black-list of sites that contain or contained malware
 Antivirus software Database: Antivirus check for files that are in database of known-viruses e. g. Eset NOD Some anti-virus mutate file to create new file that is not present in database Activity: Checks for all activities of programs e. g. Kaspersky
Antivirus software Database: Antivirus check for files that are in database of known-viruses e. g. Eset NOD Some anti-virus mutate file to create new file that is not present in database Activity: Checks for all activities of programs e. g. Kaspersky
 Social engineering A computer system is no more secure than the human systems responsible for its operation. Malicious individuals have regularly penetrated well-designed, secure computer systems by taking advantage of the carelessness of trusted individuals, or by deliberately deceiving them, for example sending messages that they are the system administrator and asking for passwords.
Social engineering A computer system is no more secure than the human systems responsible for its operation. Malicious individuals have regularly penetrated well-designed, secure computer systems by taking advantage of the carelessness of trusted individuals, or by deliberately deceiving them, for example sending messages that they are the system administrator and asking for passwords.
 Phishing Creating web-sites that are totally same design as some popular web-site and ask you to enter login and password Mostly URL of page can be: ● in the beginning same as real websites address. e. g. vk. com. adfasf. com ● or there are redirects in “hosts. txt” file to other web-site
Phishing Creating web-sites that are totally same design as some popular web-site and ask you to enter login and password Mostly URL of page can be: ● in the beginning same as real websites address. e. g. vk. com. adfasf. com ● or there are redirects in “hosts. txt” file to other web-site
 Exploit is a piece of software that allows some unintended behaviour. It gives ability to make some operations 0 -day exploit: exploit that haven’t been found by developers, so hackers who have found it, can sell it to others who want to use them
Exploit is a piece of software that allows some unintended behaviour. It gives ability to make some operations 0 -day exploit: exploit that haven’t been found by developers, so hackers who have found it, can sell it to others who want to use them
 Hacker
Hacker
 Law Статья 227 – неправомерный доступ к программам ЭВМ, использование или распостранение программ наказывается штрафом в размере от 500 до 1000 тысячи МРП, или в размере заработной платы или иного дохода за период от пяти месяцев до двух лет, либо лишением свободы на тот же срок
Law Статья 227 – неправомерный доступ к программам ЭВМ, использование или распостранение программ наказывается штрафом в размере от 500 до 1000 тысячи МРП, или в размере заработной платы или иного дохода за период от пяти месяцев до двух лет, либо лишением свободы на тот же срок
 TOR The Onion Router or Tor is a server that keeps users anonymous on the Internet. It works by moving data across many Tor servers, called "hops". The role of each server is to only move that data to another server. With the final hop moving data to the end site. As a result, information transmitted in this way is hard to trace.
TOR The Onion Router or Tor is a server that keeps users anonymous on the Internet. It works by moving data across many Tor servers, called "hops". The role of each server is to only move that data to another server. With the final hop moving data to the end site. As a result, information transmitted in this way is hard to trace.
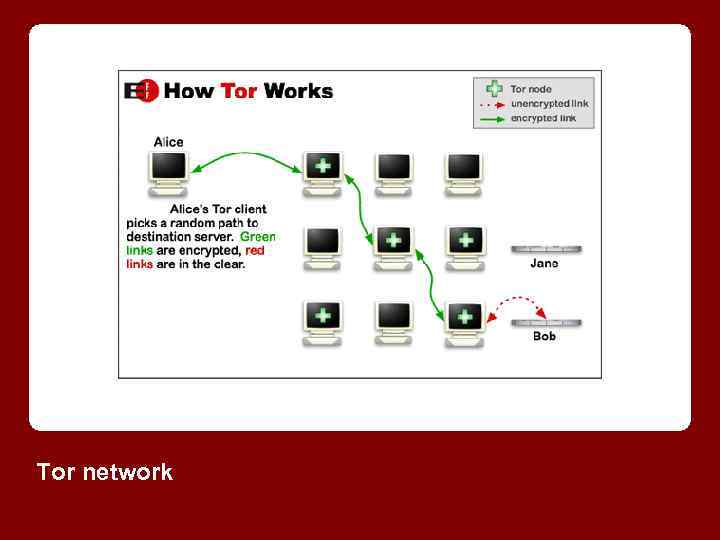 Tor network
Tor network


