Lecture 10!.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Lecture 10 Classroom Management
Lecture 10 Classroom Management
 Plan • Introduction • Principles of Classroom Management • Classroom management as time management • Classroom management • Case-study: classroom behavior management
Plan • Introduction • Principles of Classroom Management • Classroom management as time management • Classroom management • Case-study: classroom behavior management
 Definition Classroom management is a term used by teachers to describe the process of ensuring that classroom lessons run smoothly despite disruptive behavior by students. The term also implies the prevention of disruptive behavior.
Definition Classroom management is a term used by teachers to describe the process of ensuring that classroom lessons run smoothly despite disruptive behavior by students. The term also implies the prevention of disruptive behavior.
 According to Moskowitz & Hayman (1976), once a teacher loses control of their classroom, it becomes increasingly more difficult for them to regain that control. Also, research from Berliner (1988) and Brophy & Good (1986) shows that the time a teacher has to take to correct misbehavior caused by poor classroom management skills results in a lower rate of academic engagement in the classroom.
According to Moskowitz & Hayman (1976), once a teacher loses control of their classroom, it becomes increasingly more difficult for them to regain that control. Also, research from Berliner (1988) and Brophy & Good (1986) shows that the time a teacher has to take to correct misbehavior caused by poor classroom management skills results in a lower rate of academic engagement in the classroom.
 Classroom Management • Classroom Management involves establishing procedures, having rules, and reducing discipline problems. • Why do students cause discipline problems?
Classroom Management • Classroom Management involves establishing procedures, having rules, and reducing discipline problems. • Why do students cause discipline problems?
 Students misbehave for several reasons: • They are bored. • They don’t know the purpose of your presentation. • They don’t understand how the information that you are delivering applies to them. • Instruction is uninteresting • The pace of the instruction is incorrect (too fast, or too slow). • Not enough interaction between and among peers.
Students misbehave for several reasons: • They are bored. • They don’t know the purpose of your presentation. • They don’t understand how the information that you are delivering applies to them. • Instruction is uninteresting • The pace of the instruction is incorrect (too fast, or too slow). • Not enough interaction between and among peers.
 "Listen" To The Students’ Misbehavior. • Student misbehavior isn't just an annoying disruption --- it's a secret message the student is (unwittingly) trying to convey to you.
"Listen" To The Students’ Misbehavior. • Student misbehavior isn't just an annoying disruption --- it's a secret message the student is (unwittingly) trying to convey to you.
 Brooks reports that effective classroom managers organized their activities on the first day of school consistent with the emerging needs of the students. methods and assessment systems These middle school student needs for the class? were the following: 7. Is the teacher interested in how I 1. Am I welcome? learn best? 2. What are we going to do today? 8. What interests does the teacher 3. Am I in the right room? have that I can relate to? 4. Is the teacher interested in me? 9. What are we expected to do for 5. What are the rules for this tomorrow? classroom? 10. Will the teacher answer a 6. What are the goals, instructional question I have after class?
Brooks reports that effective classroom managers organized their activities on the first day of school consistent with the emerging needs of the students. methods and assessment systems These middle school student needs for the class? were the following: 7. Is the teacher interested in how I 1. Am I welcome? learn best? 2. What are we going to do today? 8. What interests does the teacher 3. Am I in the right room? have that I can relate to? 4. Is the teacher interested in me? 9. What are we expected to do for 5. What are the rules for this tomorrow? classroom? 10. Will the teacher answer a 6. What are the goals, instructional question I have after class?
 Principles of Classroom Management
Principles of Classroom Management
 Classroom Management Principles • Make a good first impression. • Come in with enthusiasm and show you are excited to be there.
Classroom Management Principles • Make a good first impression. • Come in with enthusiasm and show you are excited to be there.
 Classroom Management Principles Minimize the power differential in everyday communication. • Sitting behind a desk or standing behind a podium can send the message that you want to create some distance between yourself and the students. • Get down to their level when working with them.
Classroom Management Principles Minimize the power differential in everyday communication. • Sitting behind a desk or standing behind a podium can send the message that you want to create some distance between yourself and the students. • Get down to their level when working with them.
 Classroom Management Principles Address problem behavior directly and immediately. • Addressing a problem early lessens the chance that it will expand.
Classroom Management Principles Address problem behavior directly and immediately. • Addressing a problem early lessens the chance that it will expand.
 Classroom Management Principles • Know the power of proximity • You can accomplish more through your body language than through your voice. • Put your body next to problems. • Put your body in-between students who are disruptive. • Know how to work one-on-one with students while not turning your back on the rest of the class.
Classroom Management Principles • Know the power of proximity • You can accomplish more through your body language than through your voice. • Put your body next to problems. • Put your body in-between students who are disruptive. • Know how to work one-on-one with students while not turning your back on the rest of the class.
 Classroom Management Principles Think Prevention • • Consider how you can manage the learning process to prevent undesirable behaviors (i. e. classroom set-up, opportunities for students to interact, active involvement, clear communication of expectations, structuring for success).
Classroom Management Principles Think Prevention • • Consider how you can manage the learning process to prevent undesirable behaviors (i. e. classroom set-up, opportunities for students to interact, active involvement, clear communication of expectations, structuring for success).
 Classroom Management Principles • Model behaviors you expect from the students: mutual respect, active listening, interest in learning, subject enthusiasm, open mindedness, positive attitude.
Classroom Management Principles • Model behaviors you expect from the students: mutual respect, active listening, interest in learning, subject enthusiasm, open mindedness, positive attitude.
 Classroom Management Principles • Know the schools’ procedures regarding such things as code of conduct • Make your lessons relevant and interesting to your students. Use examples that interest students. • Teach positively and show your enthusiasm. Passion is contagious.
Classroom Management Principles • Know the schools’ procedures regarding such things as code of conduct • Make your lessons relevant and interesting to your students. Use examples that interest students. • Teach positively and show your enthusiasm. Passion is contagious.
 Classroom Management Principles • Non-Verbal Cuing. • Non-verbal cues can be effective to show the class that the noise level is too high. • Tell the student up-front what is your cue, and use it throughout the presentation. • Cues can be a bell, a clicker, flipping the light switches. • They can also be facial expressions, body posture and hand signals.
Classroom Management Principles • Non-Verbal Cuing. • Non-verbal cues can be effective to show the class that the noise level is too high. • Tell the student up-front what is your cue, and use it throughout the presentation. • Cues can be a bell, a clicker, flipping the light switches. • They can also be facial expressions, body posture and hand signals.
 Classroom Management Principles • Focusing. Be sure you have the attention of everyone in your classroom before you start your lesson. Don’t attempt to teach over the chatter of students who are not paying attention.
Classroom Management Principles • Focusing. Be sure you have the attention of everyone in your classroom before you start your lesson. Don’t attempt to teach over the chatter of students who are not paying attention.
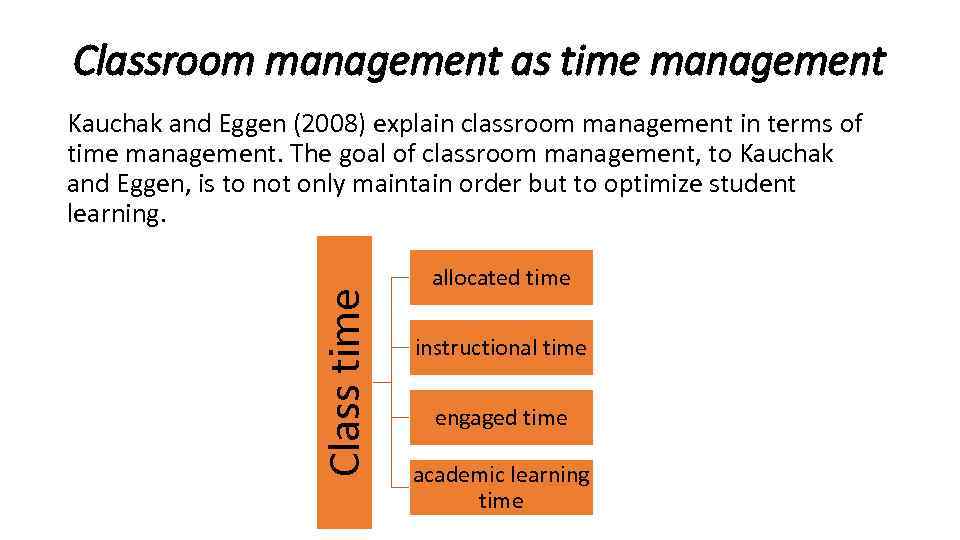 Classroom management as time management Class time Kauchak and Eggen (2008) explain classroom management in terms of time management. The goal of classroom management, to Kauchak and Eggen, is to not only maintain order but to optimize student learning. allocated time instructional time engaged time academic learning time
Classroom management as time management Class time Kauchak and Eggen (2008) explain classroom management in terms of time management. The goal of classroom management, to Kauchak and Eggen, is to not only maintain order but to optimize student learning. allocated time instructional time engaged time academic learning time
 • Allocated time is the total time allotted for teaching, learning, and routine classroom procedures like attendance and announcements. Allocated time is also what appears on a student's schedule, for example "Introductory Algebra: 9: 5010: 30 a. m. " or "Fine Arts 1: 15 -2: 00 p. m. " • Instructional time is what remains after routine classroom procedures are completed. That is to say, instructional time is the time wherein teaching and learning actually takes place. Teachers may spend two or three minutes taking attendance, for example, before their instruction begins.
• Allocated time is the total time allotted for teaching, learning, and routine classroom procedures like attendance and announcements. Allocated time is also what appears on a student's schedule, for example "Introductory Algebra: 9: 5010: 30 a. m. " or "Fine Arts 1: 15 -2: 00 p. m. " • Instructional time is what remains after routine classroom procedures are completed. That is to say, instructional time is the time wherein teaching and learning actually takes place. Teachers may spend two or three minutes taking attendance, for example, before their instruction begins.
 • Engaged time is also called time on task. During engaged time, students are participating actively in learning activities—asking and responding to questions, completing worksheets and exercises, preparing skits and presentations, etc. • Academic learning time occurs when students 1) participate actively and 2) are successful in learning activities. Effective classroom management maximizes academic learning time.
• Engaged time is also called time on task. During engaged time, students are participating actively in learning activities—asking and responding to questions, completing worksheets and exercises, preparing skits and presentations, etc. • Academic learning time occurs when students 1) participate actively and 2) are successful in learning activities. Effective classroom management maximizes academic learning time.
 Classroom Language • What is it? • Give the examples.
Classroom Language • What is it? • Give the examples.

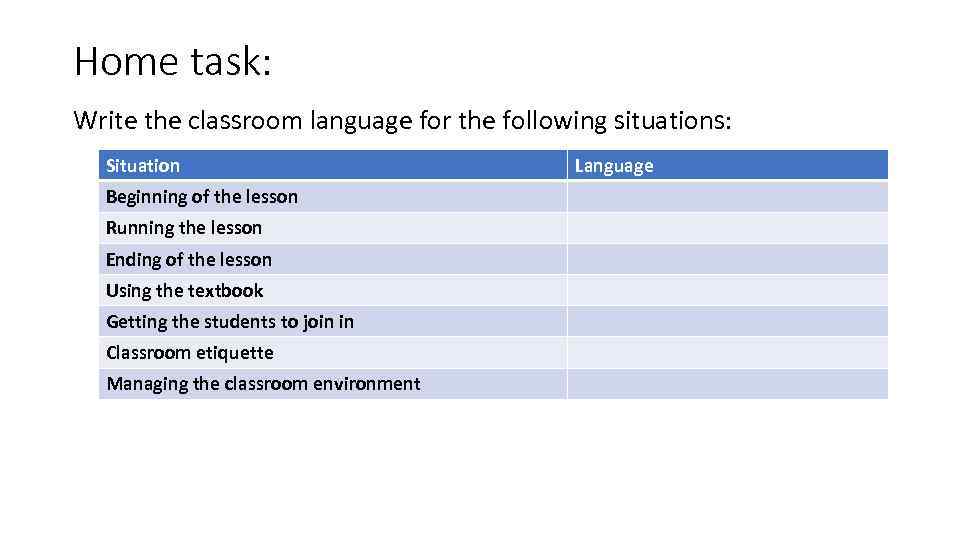 Home task: Write the classroom language for the following situations: Situation Beginning of the lesson Running the lesson Ending of the lesson Using the textbook Getting the students to join in Classroom etiquette Managing the classroom environment Language
Home task: Write the classroom language for the following situations: Situation Beginning of the lesson Running the lesson Ending of the lesson Using the textbook Getting the students to join in Classroom etiquette Managing the classroom environment Language
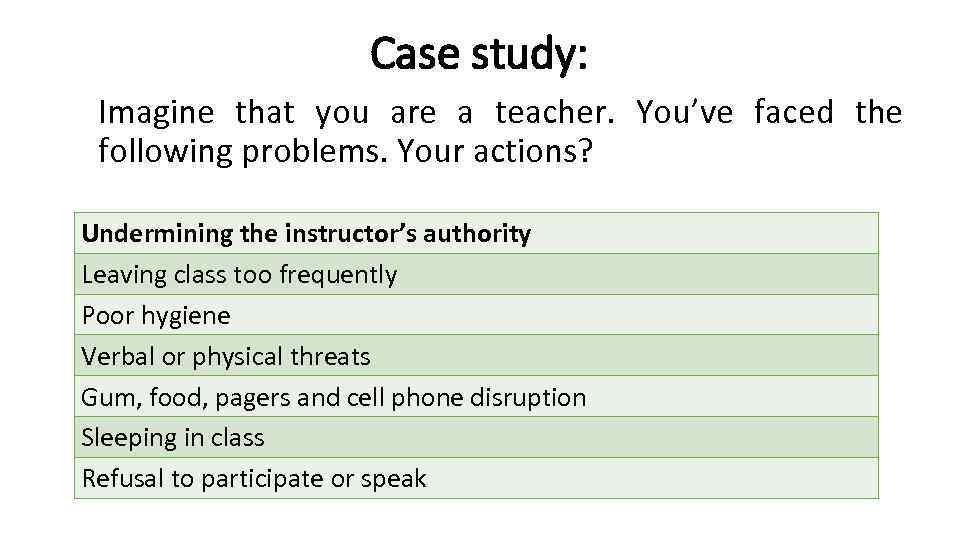 Case study: Imagine that you are a teacher. You’ve faced the following problems. Your actions? Undermining the instructor’s authority Leaving class too frequently Poor hygiene Verbal or physical threats Gum, food, pagers and cell phone disruption Sleeping in class Refusal to participate or speak
Case study: Imagine that you are a teacher. You’ve faced the following problems. Your actions? Undermining the instructor’s authority Leaving class too frequently Poor hygiene Verbal or physical threats Gum, food, pagers and cell phone disruption Sleeping in class Refusal to participate or speak
 Thank you!
Thank you!


