a76500ee1e88df7eff9069e127952f67.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Lecture 1 The English tense system Assistant lecturer : Ahmed Najm Abed
Lecture 1 The English tense system Assistant lecturer : Ahmed Najm Abed
 Simple Present Tense How do we make the simple present tense ? subject + auxiliary verb +main verb e. g. I do . e. g. I sing.
Simple Present Tense How do we make the simple present tense ? subject + auxiliary verb +main verb e. g. I do . e. g. I sing.
 Simple Present Tense is used: • When you are referring to habitual actions-actions that you always or never do • When you are referring to unchanging truths • When you are making general statements of fact
Simple Present Tense is used: • When you are referring to habitual actions-actions that you always or never do • When you are referring to unchanging truths • When you are making general statements of fact
 Examples • (habit) He always comes late to class. • (unchanging truth) The sun rises in the east. • (general statement of fact) They are friendly. simple present tense
Examples • (habit) He always comes late to class. • (unchanging truth) The sun rises in the east. • (general statement of fact) They are friendly. simple present tense
 Indicators simple present tense
Indicators simple present tense
 Form simple present tense
Form simple present tense
 Simple Past Tense How do we make the Simple Past Tense? To make the simple past tense, we use: • Past form only or • Auxiliary did + base form.
Simple Past Tense How do we make the Simple Past Tense? To make the simple past tense, we use: • Past form only or • Auxiliary did + base form.
 The Simple Past Tense is Used: • When an activity or situation began and ended at a particular time in the past--in other words, when an activity or situation is completed in the past • To refer to past habits
The Simple Past Tense is Used: • When an activity or situation began and ended at a particular time in the past--in other words, when an activity or situation is completed in the past • To refer to past habits
 Examples • (Completed action in the past) He was late to class yesterday. • (Completed action in the past) We arrived three weeks ago. • (Past habit) She always wrote a letter to her mother on Sunday night. Simple Past Tense
Examples • (Completed action in the past) He was late to class yesterday. • (Completed action in the past) We arrived three weeks ago. • (Past habit) She always wrote a letter to her mother on Sunday night. Simple Past Tense
 Indicators Simple Past Tense
Indicators Simple Past Tense
 Form Simple Past Tense
Form Simple Past Tense
 The Present Perfect The past perfect tense is quite an easy tense to understand to use. How do we make the Past Perfect Tense? subject + HAVE /HAS + V- in past participle. e. g. I have finished my work. We have bought our house in 2017.
The Present Perfect The past perfect tense is quite an easy tense to understand to use. How do we make the Past Perfect Tense? subject + HAVE /HAS + V- in past participle. e. g. I have finished my work. We have bought our house in 2017.
 The Present Perfect is Used: • When an activity happened at an unspecified time in the past (before the present) • When an activity has been repeated several times before now • When an activity was very recently completed before now • When an activity is not completed in the past
The Present Perfect is Used: • When an activity happened at an unspecified time in the past (before the present) • When an activity has been repeated several times before now • When an activity was very recently completed before now • When an activity is not completed in the past
 Examples • (unspecified time before now) They have already seen that movie. • (repeated activity before now) We have visited New York City many times. • (an action has recently been completed before now) I have just eaten. • (action not completed in the past) I have studied Spanish for many years. Present Perfect Tense
Examples • (unspecified time before now) They have already seen that movie. • (repeated activity before now) We have visited New York City many times. • (an action has recently been completed before now) I have just eaten. • (action not completed in the past) I have studied Spanish for many years. Present Perfect Tense
 Indicators Present Perfect Tense
Indicators Present Perfect Tense
 Form 1 have or has + past participle Present Perfect Tense
Form 1 have or has + past participle Present Perfect Tense
 Form 2 Present Perfect Tense
Form 2 Present Perfect Tense
 The Present Progressive Tense How do we make the Present Continuous Tense? subject + auxiliary verb +main verb …… e. g. I am speaking to you. e. g. I am taking my exam next month. We use the present continuous tense to talk about: 1 - action happening now…. . 2 - action in the future ……. .
The Present Progressive Tense How do we make the Present Continuous Tense? subject + auxiliary verb +main verb …… e. g. I am speaking to you. e. g. I am taking my exam next month. We use the present continuous tense to talk about: 1 - action happening now…. . 2 - action in the future ……. .
 The Present Progressive Tense is Used: • When an activity is in progress now at the moment of speaking • When an activity began before now and continues into the future without stopping. • When an activity is temporary. • When an activity is developing and changing.
The Present Progressive Tense is Used: • When an activity is in progress now at the moment of speaking • When an activity began before now and continues into the future without stopping. • When an activity is temporary. • When an activity is developing and changing.
 Examples • I’m explaining something to the class right now. • He’s taking 16 credits this semester. • She is understanding English more and more because she moved into the dorm. Present Progressive Tense
Examples • I’m explaining something to the class right now. • He’s taking 16 credits this semester. • She is understanding English more and more because she moved into the dorm. Present Progressive Tense
 Indicators Present Progressive Tense
Indicators Present Progressive Tense
 Form Present Progressive Tense
Form Present Progressive Tense
 Future Tense
Future Tense
 The Future Tense is Used: • To indicate that an activity or event will take place at a time in the future. • predictions about the future (you think that sth. will happen). •
The Future Tense is Used: • To indicate that an activity or event will take place at a time in the future. • predictions about the future (you think that sth. will happen). •
 Examples • • When I’m retired, I’m going to travel. Next week, we will work on punctuation. He is going to get his car fixed tomorrow. Our plane departs at noon next Friday. Future
Examples • • When I’m retired, I’m going to travel. Next week, we will work on punctuation. He is going to get his car fixed tomorrow. Our plane departs at noon next Friday. Future
 Indicators Future
Indicators Future
 Form 1 Future
Form 1 Future
 Form 2 Future
Form 2 Future
 Form 3 Future Tense
Form 3 Future Tense
 Other English Verb Tenses These tenses are combinations of the tenses we have just reviewed
Other English Verb Tenses These tenses are combinations of the tenses we have just reviewed
 Past Perfect • This tense is not used a lot. It can often be used interchangeably with the simple past because these tenses do not differ much in meaning. The past perfect tense refers to activities that happened before a specific time in the past. it expresses an action in the past before another action in the past. • When we arrived, the train had left. • Example, He had visited her many times before she died. • Form: had + past participle
Past Perfect • This tense is not used a lot. It can often be used interchangeably with the simple past because these tenses do not differ much in meaning. The past perfect tense refers to activities that happened before a specific time in the past. it expresses an action in the past before another action in the past. • When we arrived, the train had left. • Example, He had visited her many times before she died. • Form: had + past participle
 Past Progressive • This tense is used to refer to activities continuously in progress around a time in the past. • Example: They were eating when the taxi arrived. • Form: was or were + verbing
Past Progressive • This tense is used to refer to activities continuously in progress around a time in the past. • Example: They were eating when the taxi arrived. • Form: was or were + verbing
 Past Perfect Progressive • This tense is used when an activity was continuously in progress before a specific time in the past. • Example: I had been thinking about her before she called. • Form: had + been + verbing
Past Perfect Progressive • This tense is used when an activity was continuously in progress before a specific time in the past. • Example: I had been thinking about her before she called. • Form: had + been + verbing
 Present Perfect Progressive • This tense is used to describe actions that have been continuously in progress before now. These actions are not completed. • Example: I have been waiting here for the last two hours. • Form: have or has + been + verbing
Present Perfect Progressive • This tense is used to describe actions that have been continuously in progress before now. These actions are not completed. • Example: I have been waiting here for the last two hours. • Form: have or has + been + verbing
 Future Perfect • The future perfect expresses the idea that an activity will occur before some future time. • Example: She will have finished dinner before the game starts. • Form: will + have + past participle
Future Perfect • The future perfect expresses the idea that an activity will occur before some future time. • Example: She will have finished dinner before the game starts. • Form: will + have + past participle
 Future Progressive Tense • This tense is used to refer to activities that will be continuously in progress around some future time. • Example: We will be flying over New York at noon tomorrow. • Form: will + be + verbing
Future Progressive Tense • This tense is used to refer to activities that will be continuously in progress around some future time. • Example: We will be flying over New York at noon tomorrow. • Form: will + be + verbing
 Future Perfect Progressive • This tense is used to refer to activities that will be continuously in progress before a future time. • Example: He will have been working for 3 hours before you arrive. • Form: will + have + been + verbing
Future Perfect Progressive • This tense is used to refer to activities that will be continuously in progress before a future time. • Example: He will have been working for 3 hours before you arrive. • Form: will + have + been + verbing
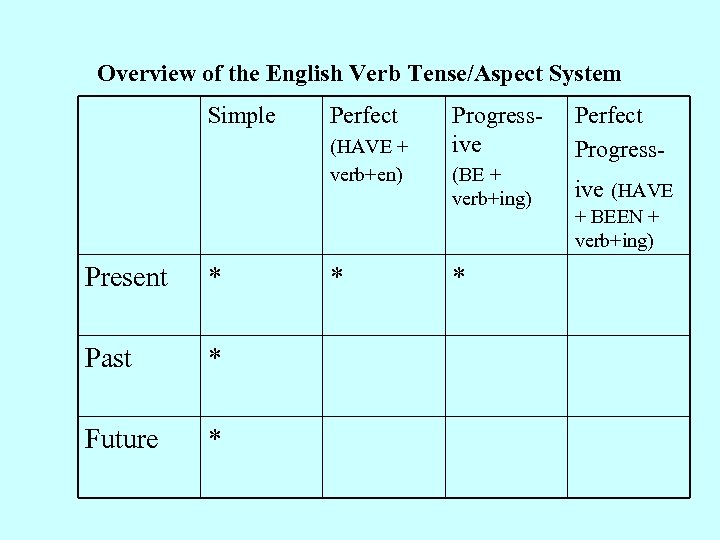 Overview of the English Verb Tense/Aspect System Simple Perfect (HAVE + verb+en) Present * Past * Future * * Progressive Perfect Progress- (BE + verb+ing) ive (HAVE * + BEEN + verb+ing)
Overview of the English Verb Tense/Aspect System Simple Perfect (HAVE + verb+en) Present * Past * Future * * Progressive Perfect Progress- (BE + verb+ing) ive (HAVE * + BEEN + verb+ing)
 Thank you
Thank you
 Lecture 2 Types of sentences In English Grammar Assistant Lecturer : Ahmed Najm Abed University of Kufa , Faculty of Education / Department of English.
Lecture 2 Types of sentences In English Grammar Assistant Lecturer : Ahmed Najm Abed University of Kufa , Faculty of Education / Department of English.
 Sentence In English grammar, a sentence is a group of words which make a complete sense. The sentences by form are of four types. Ø Simple Ø Compound Ø Complex Ø Compound –complex
Sentence In English grammar, a sentence is a group of words which make a complete sense. The sentences by form are of four types. Ø Simple Ø Compound Ø Complex Ø Compound –complex
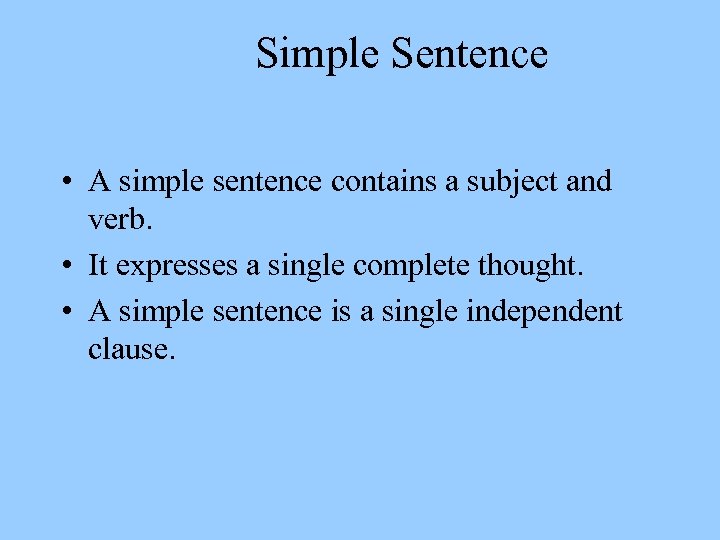 Simple Sentence • A simple sentence contains a subject and verb. • It expresses a single complete thought. • A simple sentence is a single independent clause.
Simple Sentence • A simple sentence contains a subject and verb. • It expresses a single complete thought. • A simple sentence is a single independent clause.
 Sample Simple Sentences • • peter went to the store. The music is too loud for my ears. Sarah and peter are going swimming. The pizza smells delicious.
Sample Simple Sentences • • peter went to the store. The music is too loud for my ears. Sarah and peter are going swimming. The pizza smells delicious.
 Compound Sentences • A compound sentence contains two independent clauses. • Conjunctions (for, and, nor, but, or, and yet, so) join these independent clauses. • The conjunction can impact the meaning of the sentence.
Compound Sentences • A compound sentence contains two independent clauses. • Conjunctions (for, and, nor, but, or, and yet, so) join these independent clauses. • The conjunction can impact the meaning of the sentence.
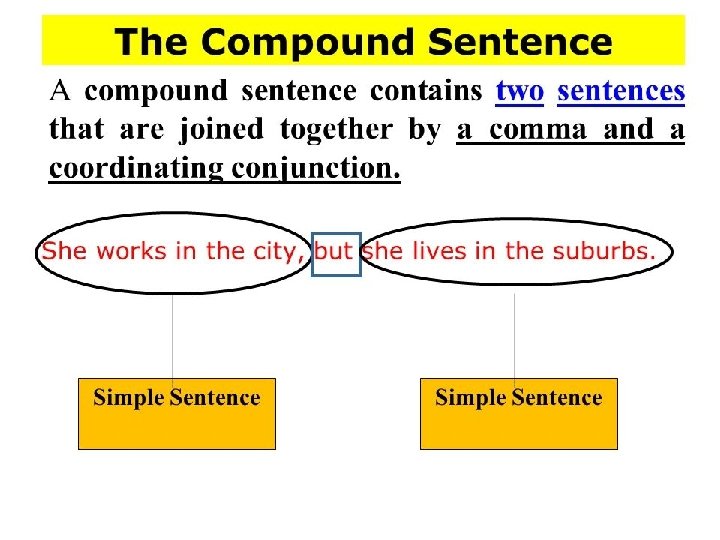
 Sample Compound Sentences • My husband was working, so I went shopping. • I like chocolate ice cream but don't have it very often. • They wanted to go to Italy, for they wanted to see Venice. • I am on a diet yet still want a cookie. • She is a good administrator, and everybody knows that.
Sample Compound Sentences • My husband was working, so I went shopping. • I like chocolate ice cream but don't have it very often. • They wanted to go to Italy, for they wanted to see Venice. • I am on a diet yet still want a cookie. • She is a good administrator, and everybody knows that.
 Complex Sentences • A complex sentence is an independent clause joined by one or more dependent clauses. • A subordinating conjunction begins the dependent clauses. • A dependent clause that begins a sentence must be followed by comma. • A dependent clause has a subject and a verb, but it does not make sense on its own.
Complex Sentences • A complex sentence is an independent clause joined by one or more dependent clauses. • A subordinating conjunction begins the dependent clauses. • A dependent clause that begins a sentence must be followed by comma. • A dependent clause has a subject and a verb, but it does not make sense on its own.
 Subordinating Conjunctions After Although As in order that At least now that wherever While Before even though how if in as much Whenever whereas as though because even if though Until Unless as if as long as as much as soon Since so that That
Subordinating Conjunctions After Although As in order that At least now that wherever While Before even though how if in as much Whenever whereas as though because even if though Until Unless as if as long as as much as soon Since so that That
 Sample Complex Sentences • Everybody knows that she is a good administrator. • I am glad that you are joining our company. • Stay in the bath until the phone rings. • Leave while you can. • The human brain never stops working until you stand up to speak in public.
Sample Complex Sentences • Everybody knows that she is a good administrator. • I am glad that you are joining our company. • Stay in the bath until the phone rings. • Leave while you can. • The human brain never stops working until you stand up to speak in public.
 Compound-Complex Sentences Ø A compound-complex sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause. Ø The dependent clause is introduced by either a subordinate conjunction (until, when, while, because ) or a relative pronoun (that, which , who ).
Compound-Complex Sentences Ø A compound-complex sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause. Ø The dependent clause is introduced by either a subordinate conjunction (until, when, while, because ) or a relative pronoun (that, which , who ).
 Sample- Compound-Complex Sentence. • Although I like to go camping, I haven't had the time to go lately, and I haven't found anyone to go with. • independent clause: "I haven't had the time to go lately“ • independent clause: "I haven't found anyone to go with“ • dependent clause: "Although I like to go camping. . . "
Sample- Compound-Complex Sentence. • Although I like to go camping, I haven't had the time to go lately, and I haven't found anyone to go with. • independent clause: "I haven't had the time to go lately“ • independent clause: "I haven't found anyone to go with“ • dependent clause: "Although I like to go camping. . . "
 Test Yourself – Simple, Compound, Complex, or Compound-Complex? 1. The teacher walked into the classroom, greeted the students, and took attendance. 2. Peter played football while Jane went shopping. 3. jack played football, yet Jim went shopping. 4. Although Mexico has a better team, they lost the tournament, and their more aggressive style did not pay off. 5. Because I am an English teacher, some people expect me to speak perfectly, and other people expect me to write perfectly. 6. We decided that the movie was too violent, but our children, who like to watch scary movies, thought that we were wrong.
Test Yourself – Simple, Compound, Complex, or Compound-Complex? 1. The teacher walked into the classroom, greeted the students, and took attendance. 2. Peter played football while Jane went shopping. 3. jack played football, yet Jim went shopping. 4. Although Mexico has a better team, they lost the tournament, and their more aggressive style did not pay off. 5. Because I am an English teacher, some people expect me to speak perfectly, and other people expect me to write perfectly. 6. We decided that the movie was too violent, but our children, who like to watch scary movies, thought that we were wrong.
 Sentence by function The sentences are of four types. Ø Assertive : Ø Interrogative: Ø Imperative: Ø Exclamatory sentence:
Sentence by function The sentences are of four types. Ø Assertive : Ø Interrogative: Ø Imperative: Ø Exclamatory sentence:
 Assertive sentences : Ø Those which make statements or assertion; as Ø A declarative sentence tells something. It ends with a period. e. g. My friend loves to write and explores English language.
Assertive sentences : Ø Those which make statements or assertion; as Ø A declarative sentence tells something. It ends with a period. e. g. My friend loves to write and explores English language.
 Sample – Assertive sentences Ø Jan is a student. She lives in a big city. Ø She is a good student . Ø jack was a great leader. Ø India is a Very Vast country. Ø The principal did not punish him.
Sample – Assertive sentences Ø Jan is a student. She lives in a big city. Ø She is a good student . Ø jack was a great leader. Ø India is a Very Vast country. Ø The principal did not punish him.
 Imperative sentence Ø A sentence that expresses a command or an entreaty e. g. , Be quiet. Ø An imperative sentence gives an order. It ends with a period OR an exclamation point.
Imperative sentence Ø A sentence that expresses a command or an entreaty e. g. , Be quiet. Ø An imperative sentence gives an order. It ends with a period OR an exclamation point.
 Sample – imperative sentences Ø Do Not Enter ! Ø Please be quiet in the library. Ø Let’s eat. Ø Come with me. Ø Be nice ! Ø Help me!
Sample – imperative sentences Ø Do Not Enter ! Ø Please be quiet in the library. Ø Let’s eat. Ø Come with me. Ø Be nice ! Ø Help me!
 Interrogative sentence : Ø Those which ask questions; as Ø Where do you live? Ø An interrogative sentence asks a question. It ends with a question mark.
Interrogative sentence : Ø Those which ask questions; as Ø Where do you live? Ø An interrogative sentence asks a question. It ends with a question mark.
 Interrogative sentence Ø There are 4 types of Interrogative. Ø Yes /No interrogatives Ø Alternative interrogatives. Ø Wh-interrogatives Ø Tag questions.
Interrogative sentence Ø There are 4 types of Interrogative. Ø Yes /No interrogatives Ø Alternative interrogatives. Ø Wh-interrogatives Ø Tag questions.
 Here are some examples- interrogative sentences: Ø Did you go to the game Friday night? Ø Should I call or email you? Ø What are you doing? Ø You live in the city, don’t you?
Here are some examples- interrogative sentences: Ø Did you go to the game Friday night? Ø Should I call or email you? Ø What are you doing? Ø You live in the city, don’t you?
 Exclamatory sentence: Ø A sentence that expresses a strong feeling is called exclamatory sentence. Ø e. g. , How cold the night is! Ø What a shame! Ø An exclamatory sentence ends with an exclamation point. ( ! )
Exclamatory sentence: Ø A sentence that expresses a strong feeling is called exclamatory sentence. Ø e. g. , How cold the night is! Ø What a shame! Ø An exclamatory sentence ends with an exclamation point. ( ! )
 Sample -Exclamatory sentences Ø No, you did not have permission to stay out this late ! Ø I can’t figure this out ! Ø Our team won the championship ! Ø I don’t know what happened here ! Ø I simply adore you ! Ø How a brave man !
Sample -Exclamatory sentences Ø No, you did not have permission to stay out this late ! Ø I can’t figure this out ! Ø Our team won the championship ! Ø I don’t know what happened here ! Ø I simply adore you ! Ø How a brave man !


