6b49e81d6072195e8d52976c23768fbe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Lecture 1 Reference documentation. Industrial drugs technology according GMP.
Lecture 1 Reference documentation. Industrial drugs technology according GMP.
 Plan 1. Feature of Industrial drugs technology. 2. Some aspects of creation and registration of medicines. 3. Reference documentation. 4. Structure of chemical-pharmaceutical enterprises. 5. Material balance.
Plan 1. Feature of Industrial drugs technology. 2. Some aspects of creation and registration of medicines. 3. Reference documentation. 4. Structure of chemical-pharmaceutical enterprises. 5. Material balance.
 DRUGS TECHNOLOGY is one of the basic disciplines of pharmaceutical education, which main task is study of theoretical bases of manufacturing processing of drugs formulation, their standardizing, storage and release.
DRUGS TECHNOLOGY is one of the basic disciplines of pharmaceutical education, which main task is study of theoretical bases of manufacturing processing of drugs formulation, their standardizing, storage and release.
 Features of Industrial drugs technology: 1. It is characterized by a high degree of development, as wide use machines, devices, mechanized and automated lines lays in its basis. 2. The work of the industrial enterprise is characterized by a strict regulation and planning of manufacture, as the processing of big amount of a material is carried out.
Features of Industrial drugs technology: 1. It is characterized by a high degree of development, as wide use machines, devices, mechanized and automated lines lays in its basis. 2. The work of the industrial enterprise is characterized by a strict regulation and planning of manufacture, as the processing of big amount of a material is carried out.
 Registration of pharmaceutical preparations 1. Chemical-pharmaceutical company can produce medicine only after its state registration. 2. For registration the medicines manufacturer has got to submit the set of documents to the State Pharmacological Center. 3. Ministry of Health provides state registration of medicines on the basis of examination of registrations documents, which is submitted to the State Pharmacological Center. 4. Ministry of Health gives permission in the form of
Registration of pharmaceutical preparations 1. Chemical-pharmaceutical company can produce medicine only after its state registration. 2. For registration the medicines manufacturer has got to submit the set of documents to the State Pharmacological Center. 3. Ministry of Health provides state registration of medicines on the basis of examination of registrations documents, which is submitted to the State Pharmacological Center. 4. Ministry of Health gives permission in the form of
 State registration of medicines - a procedure that is performed in accordance with current legislation in order to approve medical use of medicines.
State registration of medicines - a procedure that is performed in accordance with current legislation in order to approve medical use of medicines.
 The Common Technical Document (CTD) n n n is a set of specification for application dossier for the registration of Medicines and designed to be used across Europe, Japan and the United States. It was developed by the European Medicines Agency (Europe), the Food and Drug Administration and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (Japan). The CTD is maintained by the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH).
The Common Technical Document (CTD) n n n is a set of specification for application dossier for the registration of Medicines and designed to be used across Europe, Japan and the United States. It was developed by the European Medicines Agency (Europe), the Food and Drug Administration and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (Japan). The CTD is maintained by the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH).
 The Common Technical Document is divided into five modules: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Administrative and prescribing information Overview and summary of modules 3 to 5 Quality (pharmaceutical documentation) Safety (toxicology studies) Efficacy (clinical studies)
The Common Technical Document is divided into five modules: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Administrative and prescribing information Overview and summary of modules 3 to 5 Quality (pharmaceutical documentation) Safety (toxicology studies) Efficacy (clinical studies)
 Documents for state registration of the medicines 1. Statement 2. CTD 3. Proof of payment for registration fee
Documents for state registration of the medicines 1. Statement 2. CTD 3. Proof of payment for registration fee
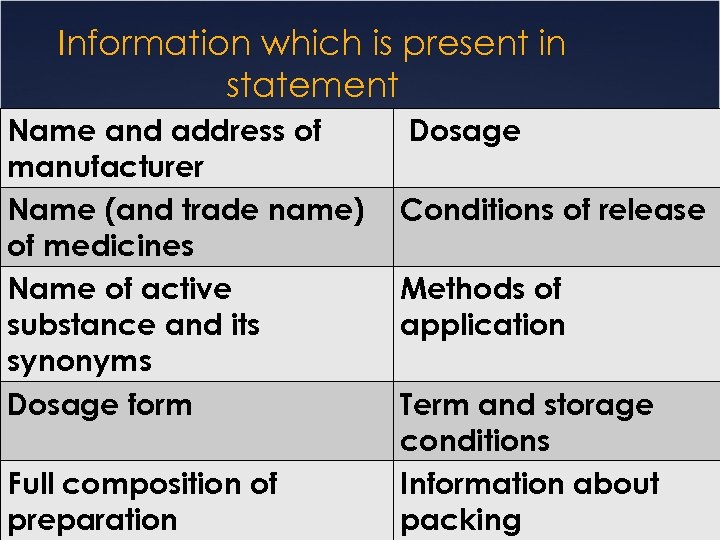 Information which is present in statement Name and address of manufacturer Name (and trade name) of medicines Name of active substance and its synonyms Dosage form Full composition of preparation Dosage Conditions of release Methods of application Term and storage conditions Information about packing
Information which is present in statement Name and address of manufacturer Name (and trade name) of medicines Name of active substance and its synonyms Dosage form Full composition of preparation Dosage Conditions of release Methods of application Term and storage conditions Information about packing
 Reference documentation is any document establishing rules, general principles or characteristics concerning different kinds of activity or its results. They should provide quality and efficiency of medical products on the basis of science and technology advances. There are uniform requirements for design, order of development, coordination and establishing of the reference documents for pharmaceuticals, medical goods, veterinary production and nutrients manufactured on chemical and pharmaceutical enterprises.
Reference documentation is any document establishing rules, general principles or characteristics concerning different kinds of activity or its results. They should provide quality and efficiency of medical products on the basis of science and technology advances. There are uniform requirements for design, order of development, coordination and establishing of the reference documents for pharmaceuticals, medical goods, veterinary production and nutrients manufactured on chemical and pharmaceutical enterprises.
 The reference documents are subdivided into the following categories: 1. Manufacturing and technical rules; 2. State pharmacopoeia (SF); 3. Monographs; 4. Analytical reference documentation (ARD); 5. State standards (St. St); 6. Branch standards (BST); 7. Specifications; 8. Guideline documents - manuals, methodical instructions, etc. ; 9. Operating instructions.
The reference documents are subdivided into the following categories: 1. Manufacturing and technical rules; 2. State pharmacopoeia (SF); 3. Monographs; 4. Analytical reference documentation (ARD); 5. State standards (St. St); 6. Branch standards (BST); 7. Specifications; 8. Guideline documents - manuals, methodical instructions, etc. ; 9. Operating instructions.
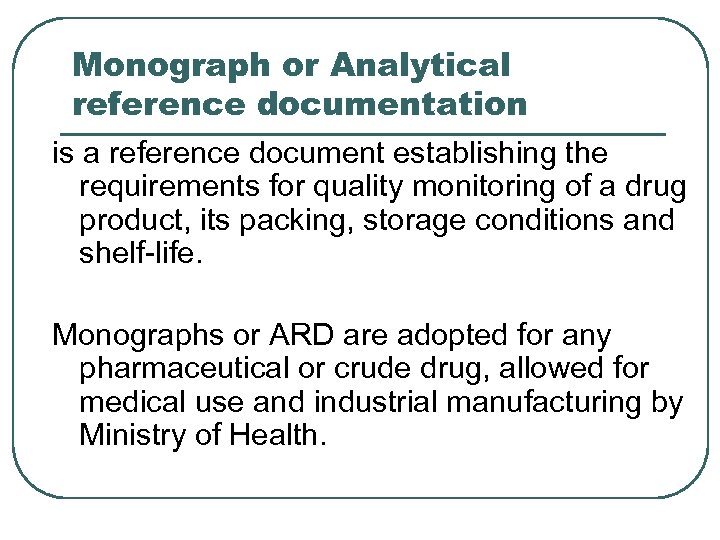 Monograph or Analytical reference documentation is a reference document establishing the requirements for quality monitoring of a drug product, its packing, storage conditions and shelf-life. Monographs or ARD are adopted for any pharmaceutical or crude drug, allowed for medical use and industrial manufacturing by Ministry of Health.
Monograph or Analytical reference documentation is a reference document establishing the requirements for quality monitoring of a drug product, its packing, storage conditions and shelf-life. Monographs or ARD are adopted for any pharmaceutical or crude drug, allowed for medical use and industrial manufacturing by Ministry of Health.
 Production process of pharmaceuticals is guided by production rules - the manufacturing and technical ones. Manufacturing rules - the reference document describing the consequence of all operating procedures and used equipment, establishing all manufacturing parameters and sites of quality monitoring and containing specifications on starting materials, intermediates and final products.
Production process of pharmaceuticals is guided by production rules - the manufacturing and technical ones. Manufacturing rules - the reference document describing the consequence of all operating procedures and used equipment, establishing all manufacturing parameters and sites of quality monitoring and containing specifications on starting materials, intermediates and final products.
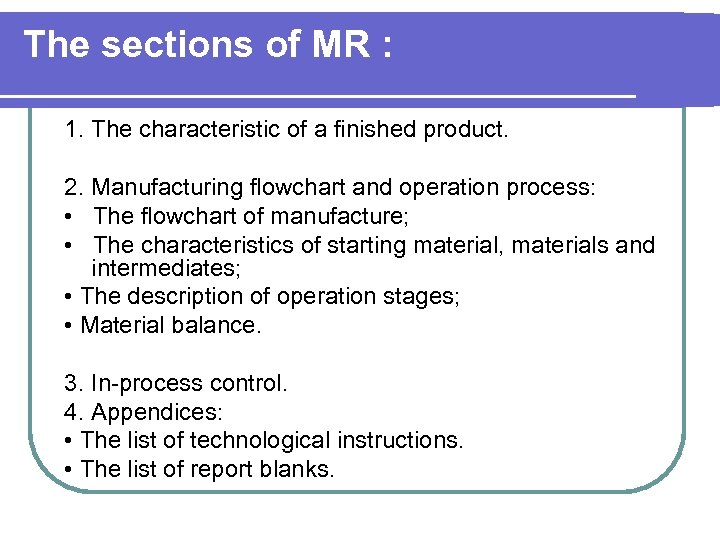 The sections of MR : 1. The characteristic of a finished product. 2. Manufacturing flowchart and operation process: • The flowchart of manufacture; • The characteristics of starting material, materials and intermediates; • The description of operation stages; • Material balance. 3. In-process control. 4. Appendices: • The list of technological instructions. • The list of report blanks.
The sections of MR : 1. The characteristic of a finished product. 2. Manufacturing flowchart and operation process: • The flowchart of manufacture; • The characteristics of starting material, materials and intermediates; • The description of operation stages; • Material balance. 3. In-process control. 4. Appendices: • The list of technological instructions. • The list of report blanks.
 Technical rules represent the reference document establishing the conditions providing an appropriate quality of medical products with respect to a particular complex of the process equipment. Technical rules cover preparing of laboratory, pilot and manufacturing premises and the personnel for work; l sanitary-and-hygienic conditioning of manufacture; l the requirements for occupational safety, l safety precautions, l fire safety, l environment control; l equipment operation etc. Requirements of the given rules guarantee quality of released production, rational carrying out of technical processes, preservation of the equipment, exception of an opportunity of occurrence of failures and environmental contaminations.
Technical rules represent the reference document establishing the conditions providing an appropriate quality of medical products with respect to a particular complex of the process equipment. Technical rules cover preparing of laboratory, pilot and manufacturing premises and the personnel for work; l sanitary-and-hygienic conditioning of manufacture; l the requirements for occupational safety, l safety precautions, l fire safety, l environment control; l equipment operation etc. Requirements of the given rules guarantee quality of released production, rational carrying out of technical processes, preservation of the equipment, exception of an opportunity of occurrence of failures and environmental contaminations.
 Material balance (mass balance) is a ratio between starting materials and obtained ones as the result of manufacturing process. It allows to compare theoretically possible and actual yields of final goods. In absence of rejects and by-products the material balance equation is simplified as: m =m + raw materials mlosses finish product
Material balance (mass balance) is a ratio between starting materials and obtained ones as the result of manufacturing process. It allows to compare theoretically possible and actual yields of final goods. In absence of rejects and by-products the material balance equation is simplified as: m =m + raw materials mlosses finish product
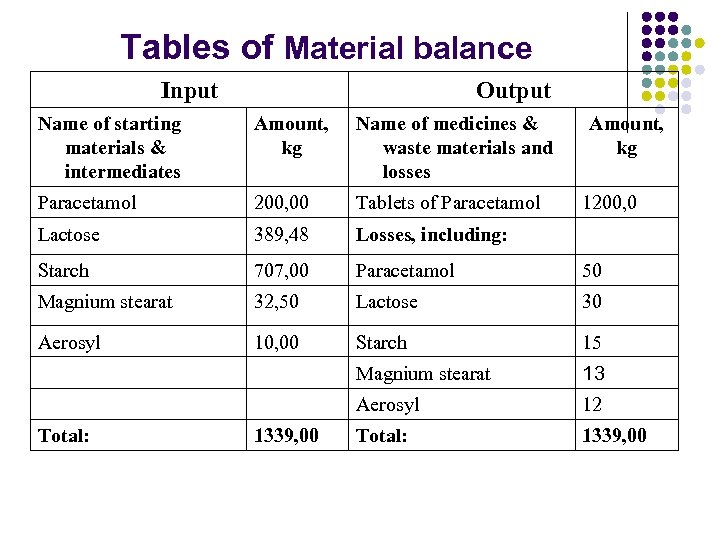 Tables of Material balance Input Output Name of starting materials & intermediates Amount, kg Name of medicines & waste materials and losses Paracetamol 200, 00 Tablets of Paracetamol Lactose 389, 48 Losses, including: Starch 707, 00 Paracetamol 50 Magnium stearat 32, 50 Lactose 30 Aerosyl 10, 00 Starch 15 Magnium stearat 13 Aerosyl 12 Total: 1339, 00 Amount, kg 1200, 0
Tables of Material balance Input Output Name of starting materials & intermediates Amount, kg Name of medicines & waste materials and losses Paracetamol 200, 00 Tablets of Paracetamol Lactose 389, 48 Losses, including: Starch 707, 00 Paracetamol 50 Magnium stearat 32, 50 Lactose 30 Aerosyl 10, 00 Starch 15 Magnium stearat 13 Aerosyl 12 Total: 1339, 00 Amount, kg 1200, 0
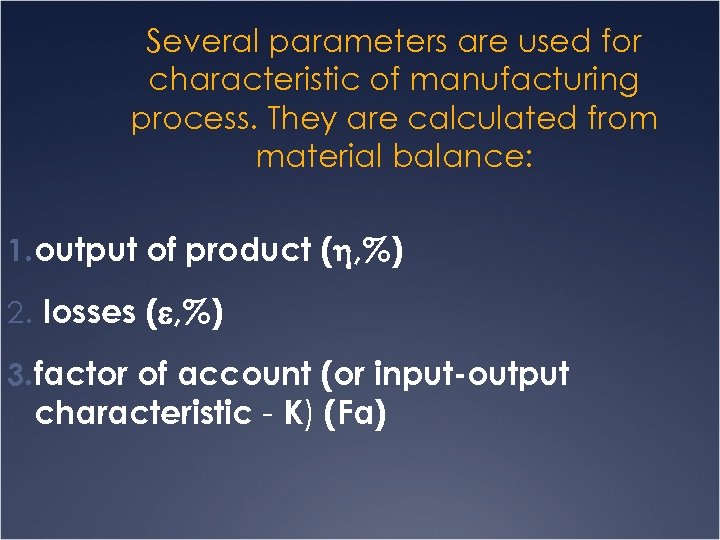 Several parameters are used for characteristic of manufacturing process. They are calculated from material balance: 1. output of product ( , %) 2. losses ( , %) 3. factor of account (or input-output characteristic - K) (Fa)
Several parameters are used for characteristic of manufacturing process. They are calculated from material balance: 1. output of product ( , %) 2. losses ( , %) 3. factor of account (or input-output characteristic - K) (Fa)
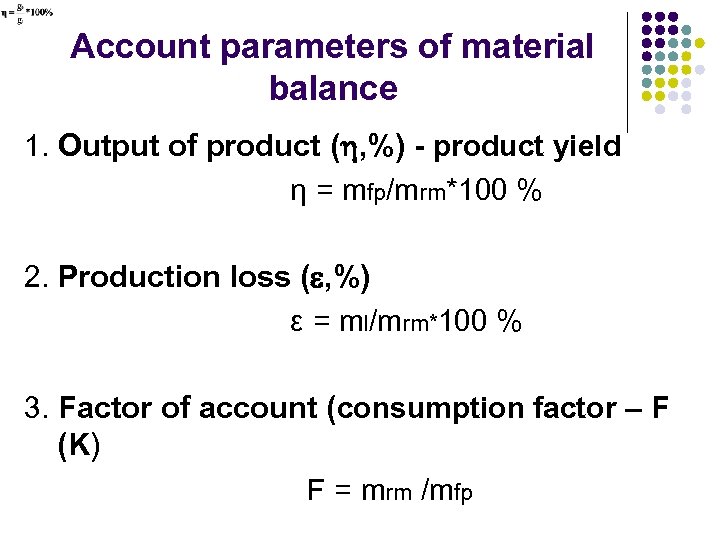 Account parameters of material balance 1. Output of product ( , %) - product yield η = mfp/mrm*100 % 2. Production loss ( , %) ε = ml/mrm*100 % 3. Factor of account (consumption factor – F (K) F = mrm /mfp
Account parameters of material balance 1. Output of product ( , %) - product yield η = mfp/mrm*100 % 2. Production loss ( , %) ε = ml/mrm*100 % 3. Factor of account (consumption factor – F (K) F = mrm /mfp
 Process flowsheet (flowchart) - a sequence and description of all stages in manufacturing of a product.
Process flowsheet (flowchart) - a sequence and description of all stages in manufacturing of a product.
 FLOCHART Principle of flowcharts composition
FLOCHART Principle of flowcharts composition
 A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents an algorithm or process, showing the steps as boxes of various kinds, and their order by connecting these with arrows.
A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents an algorithm or process, showing the steps as boxes of various kinds, and their order by connecting these with arrows.
 This diagrammatic representation can give a step-by-step solution to a given problem.
This diagrammatic representation can give a step-by-step solution to a given problem.
 Data flows are not typically represented in a flowchart, in contrast with data flow diagrams; rather, they are implied by the sequencing of operations.
Data flows are not typically represented in a flowchart, in contrast with data flow diagrams; rather, they are implied by the sequencing of operations.
 Flowcharts are used in analyzing, designing, documenting or managing a process or program in various fields.
Flowcharts are used in analyzing, designing, documenting or managing a process or program in various fields.
 Flowcharts are used in designing and documenting complex processes. l Like other types of diagram, they help visualize what is going on and thereby help the viewer to understand a process, and perhaps also find flaws.
Flowcharts are used in designing and documenting complex processes. l Like other types of diagram, they help visualize what is going on and thereby help the viewer to understand a process, and perhaps also find flaws.
 The two most common types of boxes in a flowchart are: l l a processing step, usually called activity, and denoted as a rectangular box; a decision, usually denoted as a diamond.
The two most common types of boxes in a flowchart are: l l a processing step, usually called activity, and denoted as a rectangular box; a decision, usually denoted as a diamond.
 l l l flowchart, Common alternate names include: process flowchart, functional flowchart, process map, process chart, functional process chart, business process model, process flow diagram, work flow diagram, business flow diagram.
l l l flowchart, Common alternate names include: process flowchart, functional flowchart, process map, process chart, functional process chart, business process model, process flow diagram, work flow diagram, business flow diagram.
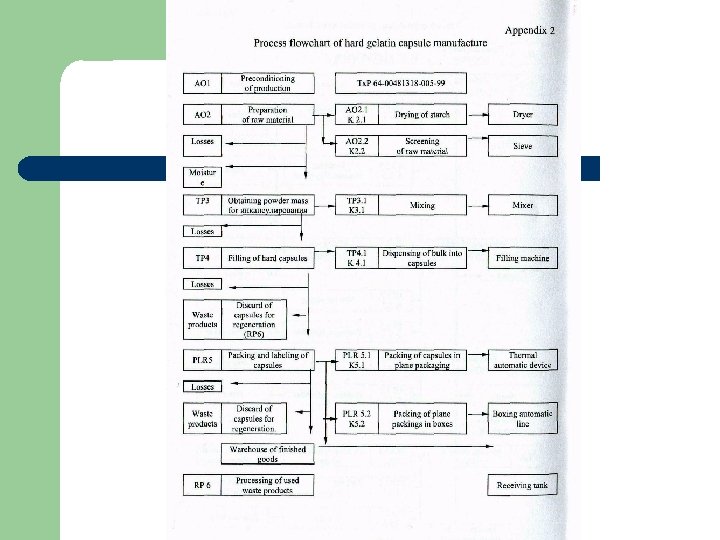
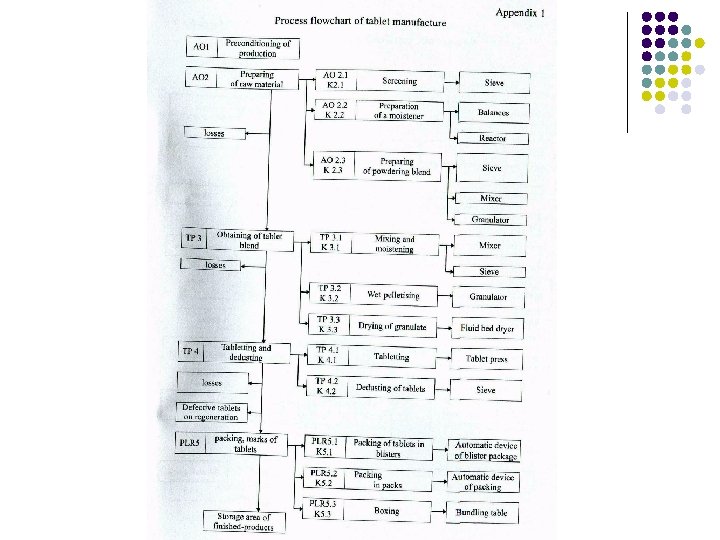
 Technological flowchart is the visual display of dosage production. l Technological flowchart (Process flowsheet) - a sequence and description of all stages in manufacturing of a product.
Technological flowchart is the visual display of dosage production. l Technological flowchart (Process flowsheet) - a sequence and description of all stages in manufacturing of a product.
 Arrows l l Showing "flow of control". An arrow coming from one symbol and ending at another symbol represents that control passes to the symbol the arrow points to.
Arrows l l Showing "flow of control". An arrow coming from one symbol and ending at another symbol represents that control passes to the symbol the arrow points to.
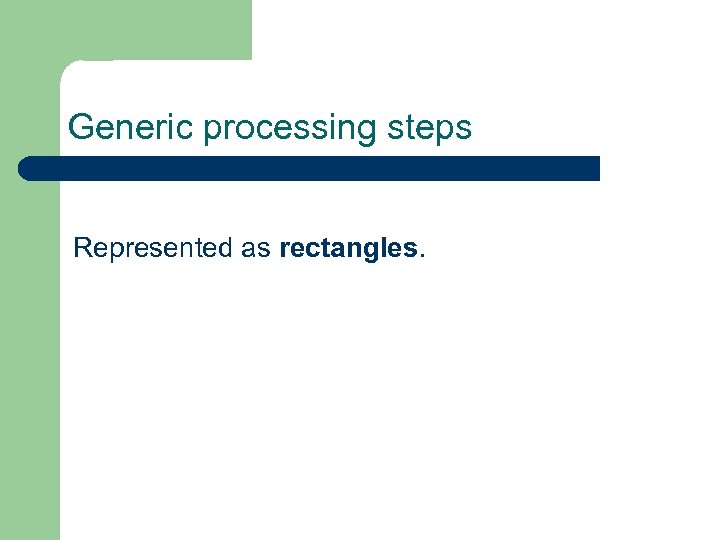 Generic processing steps Represented as rectangles.
Generic processing steps Represented as rectangles.
 Direct compression - a method obtaining of tablets without granulation. Stages of Direct compression: 1. Mixing active and auxiliaries substances 2. Compressing tablets
Direct compression - a method obtaining of tablets without granulation. Stages of Direct compression: 1. Mixing active and auxiliaries substances 2. Compressing tablets
 Stages of wet granulation: 1. Mixing components (drum mixer); 2. Granulation: l Adding solutions of binders (moistening of powder); l Granulation of the moistened mass – obtaining of wet granules; l Drying of wet granules; l Granulation of the dried granules; 3. Powdering (dusting) of dry granules 4. Compressing tablets and dust control (tablets machine);
Stages of wet granulation: 1. Mixing components (drum mixer); 2. Granulation: l Adding solutions of binders (moistening of powder); l Granulation of the moistened mass – obtaining of wet granules; l Drying of wet granules; l Granulation of the dried granules; 3. Powdering (dusting) of dry granules 4. Compressing tablets and dust control (tablets machine);
 Stages of Dry granulation: 1. Mixing components (drum mixer); 2. Granulation: l Adding solutions of binders (moistening of powder); l Drying of wet granules; l Granulation of the dried granules; 3. Powdering ((dusting)of dry granules 4. Compressing tablets and dust control (tablets machine).
Stages of Dry granulation: 1. Mixing components (drum mixer); 2. Granulation: l Adding solutions of binders (moistening of powder); l Drying of wet granules; l Granulation of the dried granules; 3. Powdering ((dusting)of dry granules 4. Compressing tablets and dust control (tablets machine).
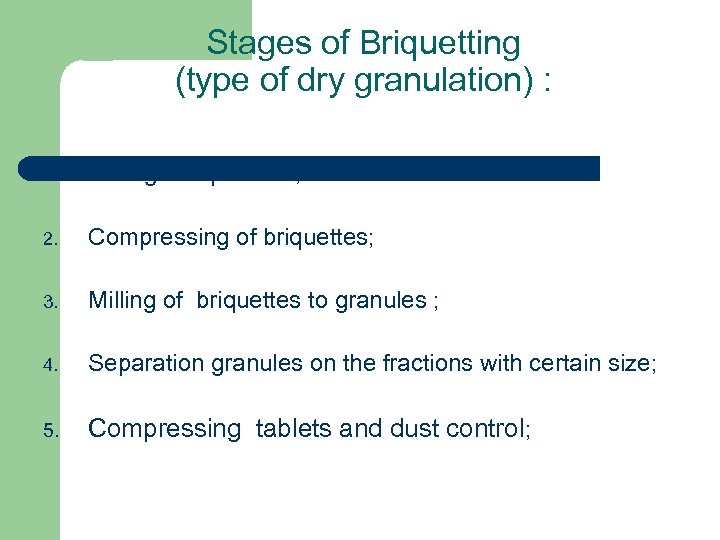 Stages of Briquetting (type of dry granulation) : 1. Mixing components; 2. Compressing of briquettes; 3. Milling of briquettes to granules ; 4. Separation granules on the fractions with certain size; 5. Compressing tablets and dust control;
Stages of Briquetting (type of dry granulation) : 1. Mixing components; 2. Compressing of briquettes; 3. Milling of briquettes to granules ; 4. Separation granules on the fractions with certain size; 5. Compressing tablets and dust control;
 Granulation in dragee pan Stages: 1. Mixing components (medicinal and auxiliary); 2. Moistening of powder; 3. Drying wet binder and formation granules; 4. Powdering granules; 5. Compression tablets and dust control; 6. Packing.
Granulation in dragee pan Stages: 1. Mixing components (medicinal and auxiliary); 2. Moistening of powder; 3. Drying wet binder and formation granules; 4. Powdering granules; 5. Compression tablets and dust control; 6. Packing.
 Granulation by spray drying 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Preparation suspension of the auxiliary and sometimes of medicines substances; Serving suspension throw nozzles in camera of dryer and formation granules under hire temperature; Fractionation granules; Mixing granules and medicines substances; Compression tablets and dust control.
Granulation by spray drying 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Preparation suspension of the auxiliary and sometimes of medicines substances; Serving suspension throw nozzles in camera of dryer and formation granules under hire temperature; Fractionation granules; Mixing granules and medicines substances; Compression tablets and dust control.
 Stages of the granulation in the fluidized layer 1. l l l Mixing components (medicinal and auxiliary); Moistening of powder; Drying and formation of granules; Powdering of granules; Compression tablets and dust control; Packing.
Stages of the granulation in the fluidized layer 1. l l l Mixing components (medicinal and auxiliary); Moistening of powder; Drying and formation of granules; Powdering of granules; Compression tablets and dust control; Packing.
 Stage of capsules production: 1. 2. 3. 4. Preparing of gelatin solutions. Preparing of gelatin shells. Hard-gelatin capsule filling. Packing and labeling. 2. Preparing of gelatin solutions. Preparing and filling of soft-gelatin capsules. 3. Packing and labeling. 1.
Stage of capsules production: 1. 2. 3. 4. Preparing of gelatin solutions. Preparing of gelatin shells. Hard-gelatin capsule filling. Packing and labeling. 2. Preparing of gelatin solutions. Preparing and filling of soft-gelatin capsules. 3. Packing and labeling. 1.
 Obtaining of gelatin solutions with stage of swelling 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Swelling of gelatin in cold water (15 - 18 °C, 1. 5 - 2 hours). Dissolving of gelatin. Adding preservatives, plasticizers and others excipients. Remove of air bubbles from the solution of the gelatin by the vacuum. Stabilization of solution of the gelatin (45 -60 °C).
Obtaining of gelatin solutions with stage of swelling 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Swelling of gelatin in cold water (15 - 18 °C, 1. 5 - 2 hours). Dissolving of gelatin. Adding preservatives, plasticizers and others excipients. Remove of air bubbles from the solution of the gelatin by the vacuum. Stabilization of solution of the gelatin (45 -60 °C).
 Obtaining of gelatin solutions without stage of swelling 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Heating of purified water (70 -75 °C). Dissolution of preservatives, plasticizers and others excipients in the water. Dissolution of the gelatin. Remove of air bubbles from the solution of the gelatin by a vacuum. Stabilization of the solution of the gelatin (45 -60 °C).
Obtaining of gelatin solutions without stage of swelling 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Heating of purified water (70 -75 °C). Dissolution of preservatives, plasticizers and others excipients in the water. Dissolution of the gelatin. Remove of air bubbles from the solution of the gelatin by a vacuum. Stabilization of the solution of the gelatin (45 -60 °C).
 Thank you for your attention
Thank you for your attention


