594f7c1823172ad07f283ad02d8f4222.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Lecture-1 KNOWLEDGE, INNOVATION & NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 2 UZB 614 Mamurjon Rahimov and Farhod Karimov Academic year 2015 -2016 TW-6 1
Lecture-1 KNOWLEDGE, INNOVATION & NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 2 UZB 614 Mamurjon Rahimov and Farhod Karimov Academic year 2015 -2016 TW-6 1
 New service innovation
New service innovation
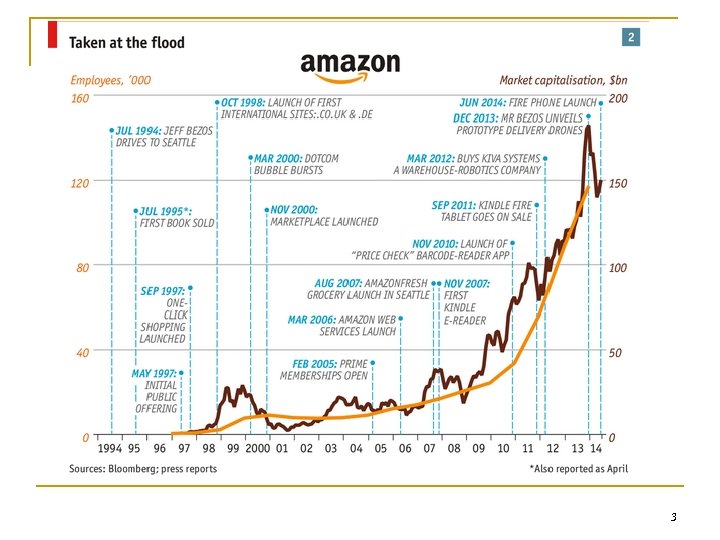 3
3
 New service development (NSD) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction Growth in services Technology and new services Characteristics of services Customer relationship process New service innovations NSD process Summary & recap
New service development (NSD) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction Growth in services Technology and new services Characteristics of services Customer relationship process New service innovations NSD process Summary & recap
 Introduction • Growth in services • Characteristics of services Services are processes where customer is part of it • Viewed differently to products • Services contribute to new business models: e. Bay new way of conducting business Ryanair new way of flying Amazon new way of viewing and buying books i. Tunes new way to buy music
Introduction • Growth in services • Characteristics of services Services are processes where customer is part of it • Viewed differently to products • Services contribute to new business models: e. Bay new way of conducting business Ryanair new way of flying Amazon new way of viewing and buying books i. Tunes new way to buy music
 Categories of service mix 1. 2. 3. 4. Pure tangible good Tangible good with accompanying services Hybrid Major service with accompanying minor goods and services 5. Pure service
Categories of service mix 1. 2. 3. 4. Pure tangible good Tangible good with accompanying services Hybrid Major service with accompanying minor goods and services 5. Pure service
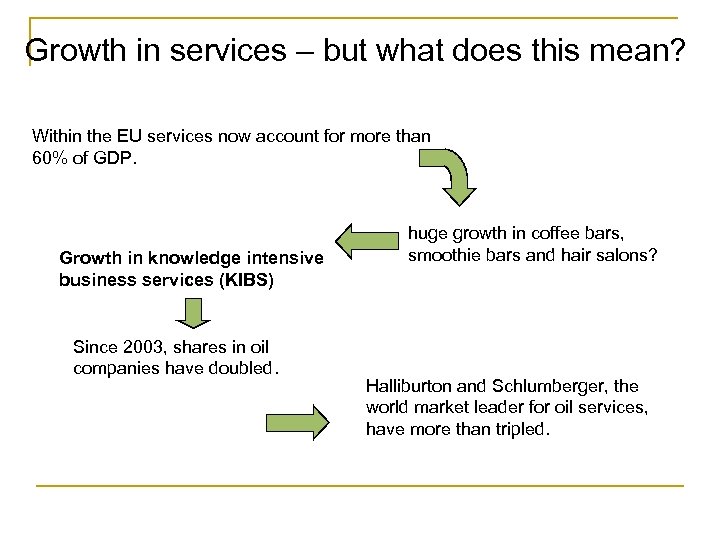 Growth in services – but what does this mean? Within the EU services now account for more than 60% of GDP. Growth in knowledge intensive business services (KIBS) Since 2003, shares in oil companies have doubled. huge growth in coffee bars, smoothie bars and hair salons? Halliburton and Schlumberger, the world market leader for oil services, have more than tripled.
Growth in services – but what does this mean? Within the EU services now account for more than 60% of GDP. Growth in knowledge intensive business services (KIBS) Since 2003, shares in oil companies have doubled. huge growth in coffee bars, smoothie bars and hair salons? Halliburton and Schlumberger, the world market leader for oil services, have more than tripled.
 Outsourcing and service growth Expected gains that companies can derive from outsourcing include: • • the reduction of operational costs; the ability to transform fixed costs into variable costs; the ability to focus on core competencies; access to the industry-leading external competencies and expertise.
Outsourcing and service growth Expected gains that companies can derive from outsourcing include: • • the reduction of operational costs; the ability to transform fixed costs into variable costs; the ability to focus on core competencies; access to the industry-leading external competencies and expertise.
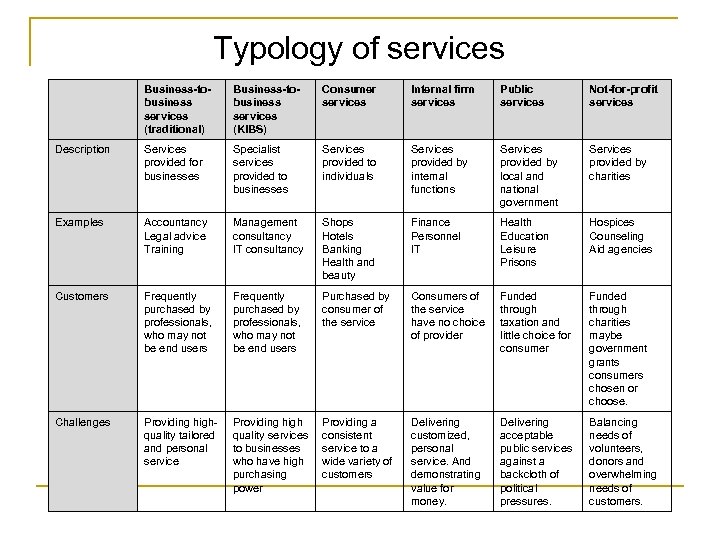 Typology of services Business-tobusiness services (traditional) Business-tobusiness services (KIBS) Consumer services Internal firm services Public services Not-for-profit services Description Services provided for businesses Specialist services provided to businesses Services provided to individuals Services provided by internal functions Services provided by local and national government Services provided by charities Examples Accountancy Legal advice Training Management consultancy IT consultancy Shops Hotels Banking Health and beauty Finance Personnel IT Health Education Leisure Prisons Hospices Counseling Aid agencies Customers Frequently purchased by professionals, who may not be end users Purchased by consumer of the service Consumers of the service have no choice of provider Funded through taxation and little choice for consumer Funded through charities maybe government grants consumers chosen or choose. Challenges Providing highquality tailored and personal service Providing high quality services to businesses who have high purchasing power Providing a consistent service to a wide variety of customers Delivering customized, personal service. And demonstrating value for money. Delivering acceptable public services against a backcloth of political pressures. Balancing needs of volunteers, donors and overwhelming needs of customers.
Typology of services Business-tobusiness services (traditional) Business-tobusiness services (KIBS) Consumer services Internal firm services Public services Not-for-profit services Description Services provided for businesses Specialist services provided to businesses Services provided to individuals Services provided by internal functions Services provided by local and national government Services provided by charities Examples Accountancy Legal advice Training Management consultancy IT consultancy Shops Hotels Banking Health and beauty Finance Personnel IT Health Education Leisure Prisons Hospices Counseling Aid agencies Customers Frequently purchased by professionals, who may not be end users Purchased by consumer of the service Consumers of the service have no choice of provider Funded through taxation and little choice for consumer Funded through charities maybe government grants consumers chosen or choose. Challenges Providing highquality tailored and personal service Providing high quality services to businesses who have high purchasing power Providing a consistent service to a wide variety of customers Delivering customized, personal service. And demonstrating value for money. Delivering acceptable public services against a backcloth of political pressures. Balancing needs of volunteers, donors and overwhelming needs of customers.
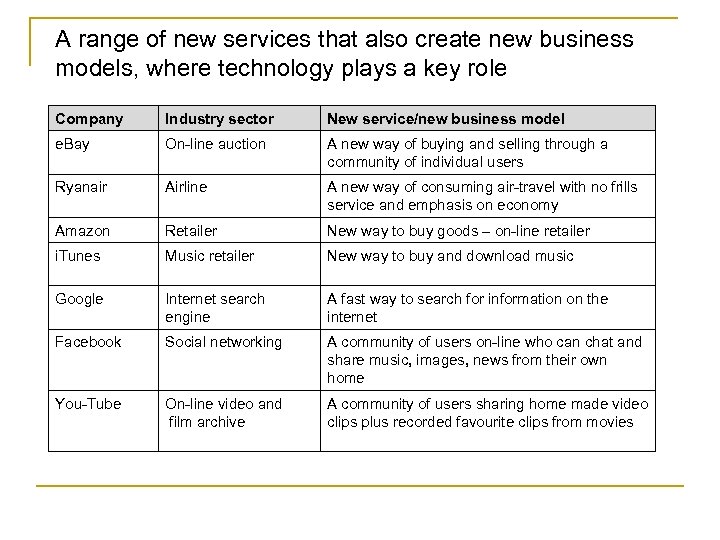 A range of new services that also create new business models, where technology plays a key role Company Industry sector New service/new business model e. Bay On-line auction A new way of buying and selling through a community of individual users Ryanair Airline A new way of consuming air-travel with no frills service and emphasis on economy Amazon Retailer New way to buy goods – on-line retailer i. Tunes Music retailer New way to buy and download music Google Internet search engine A fast way to search for information on the internet Facebook Social networking A community of users on-line who can chat and share music, images, news from their own home You-Tube On-line video and film archive A community of users sharing home made video clips plus recorded favourite clips from movies
A range of new services that also create new business models, where technology plays a key role Company Industry sector New service/new business model e. Bay On-line auction A new way of buying and selling through a community of individual users Ryanair Airline A new way of consuming air-travel with no frills service and emphasis on economy Amazon Retailer New way to buy goods – on-line retailer i. Tunes Music retailer New way to buy and download music Google Internet search engine A fast way to search for information on the internet Facebook Social networking A community of users on-line who can chat and share music, images, news from their own home You-Tube On-line video and film archive A community of users sharing home made video clips plus recorded favourite clips from movies
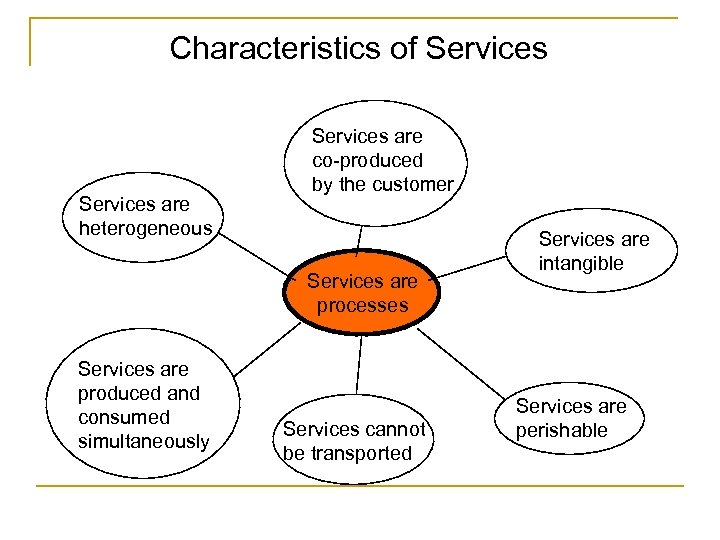 Characteristics of Services are heterogeneous Services are co-produced by the customer Services are processes Services are produced and consumed simultaneously Services cannot be transported Services are intangible Services are perishable
Characteristics of Services are heterogeneous Services are co-produced by the customer Services are processes Services are produced and consumed simultaneously Services cannot be transported Services are intangible Services are perishable
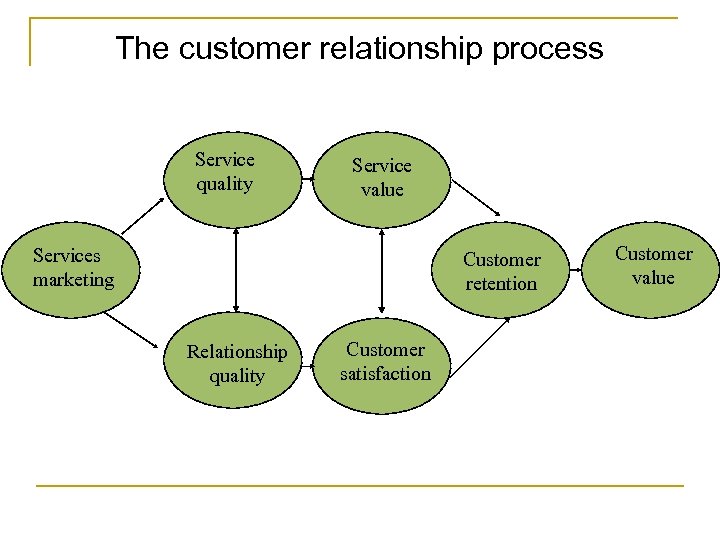 The customer relationship process Service quality Service value Services marketing Customer retention Relationship quality Customer satisfaction Customer value
The customer relationship process Service quality Service value Services marketing Customer retention Relationship quality Customer satisfaction Customer value
 New service innovation As with products, service innovations can be classified in many ways: • e. Bay was new to the market; Google’s on-line auction is new to Google; • Internal process innovations, e. g. Amazon: delivering books to consumer is not new, but using internet; • Line extensions to services, e. g. banks offering insurance; • Service modifications, e. g internet access to airline passengers.
New service innovation As with products, service innovations can be classified in many ways: • e. Bay was new to the market; Google’s on-line auction is new to Google; • Internal process innovations, e. g. Amazon: delivering books to consumer is not new, but using internet; • Line extensions to services, e. g. banks offering insurance; • Service modifications, e. g internet access to airline passengers.
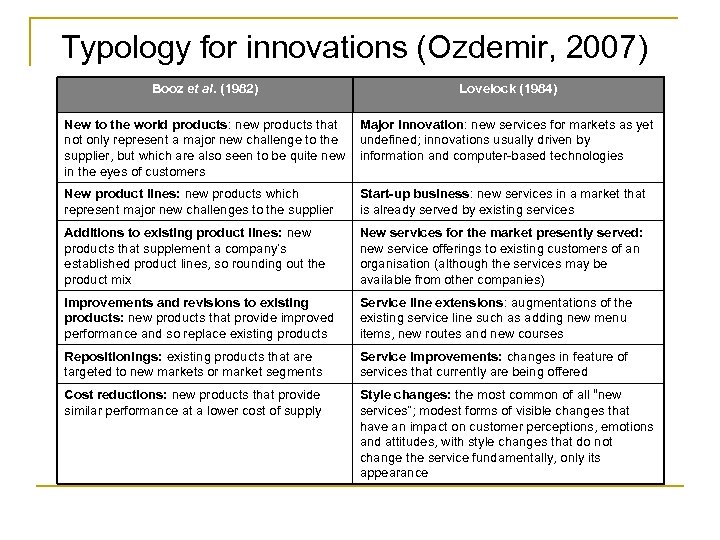 Typology for innovations (Ozdemir, 2007) Booz et al. (1982) Lovelock (1984) New to the world products: new products that not only represent a major new challenge to the supplier, but which are also seen to be quite new in the eyes of customers Major innovation: new services for markets as yet undefined; innovations usually driven by information and computer-based technologies New product lines: new products which represent major new challenges to the supplier Start-up business: new services in a market that is already served by existing services Additions to existing product lines: new products that supplement a company’s established product lines, so rounding out the product mix New services for the market presently served: new service offerings to existing customers of an organisation (although the services may be available from other companies) Improvements and revisions to existing products: new products that provide improved performance and so replace existing products Service line extensions: augmentations of the existing service line such as adding new menu items, new routes and new courses Repositionings: existing products that are targeted to new markets or market segments Service improvements: changes in feature of services that currently are being offered Cost reductions: new products that provide similar performance at a lower cost of supply Style changes: the most common of all “new services”; modest forms of visible changes that have an impact on customer perceptions, emotions and attitudes, with style changes that do not change the service fundamentally, only its appearance
Typology for innovations (Ozdemir, 2007) Booz et al. (1982) Lovelock (1984) New to the world products: new products that not only represent a major new challenge to the supplier, but which are also seen to be quite new in the eyes of customers Major innovation: new services for markets as yet undefined; innovations usually driven by information and computer-based technologies New product lines: new products which represent major new challenges to the supplier Start-up business: new services in a market that is already served by existing services Additions to existing product lines: new products that supplement a company’s established product lines, so rounding out the product mix New services for the market presently served: new service offerings to existing customers of an organisation (although the services may be available from other companies) Improvements and revisions to existing products: new products that provide improved performance and so replace existing products Service line extensions: augmentations of the existing service line such as adding new menu items, new routes and new courses Repositionings: existing products that are targeted to new markets or market segments Service improvements: changes in feature of services that currently are being offered Cost reductions: new products that provide similar performance at a lower cost of supply Style changes: the most common of all “new services”; modest forms of visible changes that have an impact on customer perceptions, emotions and attitudes, with style changes that do not change the service fundamentally, only its appearance
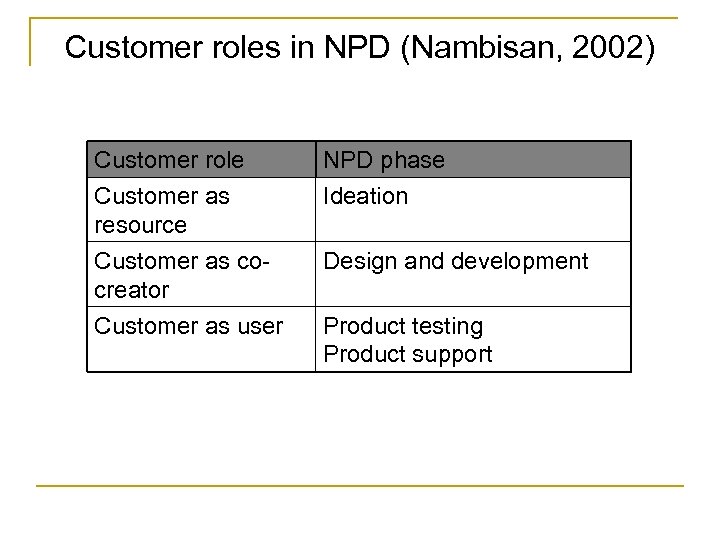 Customer roles in NPD (Nambisan, 2002) Customer role Customer as resource Customer as cocreator Customer as user NPD phase Ideation Design and development Product testing Product support
Customer roles in NPD (Nambisan, 2002) Customer role Customer as resource Customer as cocreator Customer as user NPD phase Ideation Design and development Product testing Product support
 The service innovation process Different from NPD: customer is part of the process • Blueprinting the service Identify every activity and every possible outcome in the process • ‘Prick-eared’ market research Direct contact facilitates dialogue • Service prototypes Difficult because customer is part of process Level of integration determines ability to prototype E. g. a doctor’s home visit a visit to the cinema
The service innovation process Different from NPD: customer is part of the process • Blueprinting the service Identify every activity and every possible outcome in the process • ‘Prick-eared’ market research Direct contact facilitates dialogue • Service prototypes Difficult because customer is part of process Level of integration determines ability to prototype E. g. a doctor’s home visit a visit to the cinema
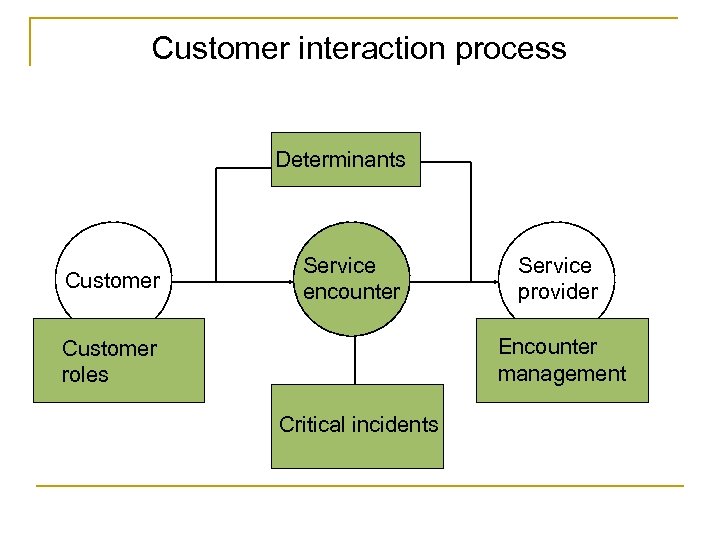 Customer interaction process Determinants Customer Service encounter Service provider Encounter management Customer roles Critical incidents
Customer interaction process Determinants Customer Service encounter Service provider Encounter management Customer roles Critical incidents
 How do customers evaluate services? Perceived service quality. . . Perceived service value. . . Customer expectations. . . • • • Reliability Responsiveness Assurance Empathy Tangibles
How do customers evaluate services? Perceived service quality. . . Perceived service value. . . Customer expectations. . . • • • Reliability Responsiveness Assurance Empathy Tangibles
 • Reliability – Providing service as promised – Dependability in handling customers’ problems – Performing services right first time – Performing services at the promised time – Maintaining error free records • Responsiveness – Keeping customer informed when service will be performed – Prompt service to customers – Willingness to help customers – Readiness to respond to customers’ requests • Assurance – Employees who instil confidence in customers – Making customers feel safe in their transactions – Employees who are consistently courteous – Employees who have knowledge to answer questions
• Reliability – Providing service as promised – Dependability in handling customers’ problems – Performing services right first time – Performing services at the promised time – Maintaining error free records • Responsiveness – Keeping customer informed when service will be performed – Prompt service to customers – Willingness to help customers – Readiness to respond to customers’ requests • Assurance – Employees who instil confidence in customers – Making customers feel safe in their transactions – Employees who are consistently courteous – Employees who have knowledge to answer questions
 • Empathy – Giving customers individual attention – Employees who deal with customers in a caring manner – Having the customers best interests at heart – Employees who understand the needs of their customers – Convenient business hours • Tangibles – Modern equipment – Visually appealing facilities – Employees who have neat, professional appearance – Visually appealing materials associated with service
• Empathy – Giving customers individual attention – Employees who deal with customers in a caring manner – Having the customers best interests at heart – Employees who understand the needs of their customers – Convenient business hours • Tangibles – Modern equipment – Visually appealing facilities – Employees who have neat, professional appearance – Visually appealing materials associated with service
 New service innovation For many years the literature overlooked this concept! Innovation deemed to require a new physical “thing” But, the world of business suggested new services could deliver even more significant changes (new business models): First Direct Ryanair e. Bay Apple’s i. Tunes
New service innovation For many years the literature overlooked this concept! Innovation deemed to require a new physical “thing” But, the world of business suggested new services could deliver even more significant changes (new business models): First Direct Ryanair e. Bay Apple’s i. Tunes
 Recommended Reading Essential Reading Trott, P. (2012) Innovation Management & New Product Development. FT Prentice Hall. Recommended Reading • Davis, S. M. & Moe, K. (1997). Bringing innovation to life. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 14 (5), 338 -361. • Kao, S-C. , Wu, S-H. & Su, P-H. (2011). Which mode is better for knowledge creation? Management Decision, 49 (7), 1037 -1060. • Mitchell, R. & Boyle, B. (2010). Knowledge creation measurement methods. Journal of Knowledge Management, 14 (1), 62 -87. • Witell, L. , Kristensson, P. , Gustafsson, A. & Löfgren, M. (2011). Idea generation: customer co-creation versus traditional market research techniques. Journal of Service Management, 22 (2), 140 -159. • Yelkur, R. & Herbig, P. (1996). Global markets and the new product development process. Journal of Product and Brand Management, 5 (6), 3847. KNOWLEDGE, INNOVATION & NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 22
Recommended Reading Essential Reading Trott, P. (2012) Innovation Management & New Product Development. FT Prentice Hall. Recommended Reading • Davis, S. M. & Moe, K. (1997). Bringing innovation to life. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 14 (5), 338 -361. • Kao, S-C. , Wu, S-H. & Su, P-H. (2011). Which mode is better for knowledge creation? Management Decision, 49 (7), 1037 -1060. • Mitchell, R. & Boyle, B. (2010). Knowledge creation measurement methods. Journal of Knowledge Management, 14 (1), 62 -87. • Witell, L. , Kristensson, P. , Gustafsson, A. & Löfgren, M. (2011). Idea generation: customer co-creation versus traditional market research techniques. Journal of Service Management, 22 (2), 140 -159. • Yelkur, R. & Herbig, P. (1996). Global markets and the new product development process. Journal of Product and Brand Management, 5 (6), 3847. KNOWLEDGE, INNOVATION & NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 22


