1.+Introduction+to+Finance.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCE Module: Introduction to Finance
Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCE Module: Introduction to Finance
 What is Finance? Module: Introduction to Finance
What is Finance? Module: Introduction to Finance
 Definition of Finance • According to Oxford dictionary , the word ‘finance’ connotes ‘management of money’. • Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary defines finance as “the Science on study of the management of funds and the management of fund as the system that includes the circulation of money, the granting of credit, the making of investments, and the provision of banking facilities. Module: Introduction to Finance
Definition of Finance • According to Oxford dictionary , the word ‘finance’ connotes ‘management of money’. • Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary defines finance as “the Science on study of the management of funds and the management of fund as the system that includes the circulation of money, the granting of credit, the making of investments, and the provision of banking facilities. Module: Introduction to Finance
 What Is Finance? • Finance is the study of how and under what terms the savings (i. e. money) are allocated between lenders and borrowers. • Finance is distinct from economics in that it addresses not only how resources are allocated but also under what terms and through what channels • Financial contracts or securities occur whenever funds are transferred from issuer to buyer. Module: Introduction to Finance
What Is Finance? • Finance is the study of how and under what terms the savings (i. e. money) are allocated between lenders and borrowers. • Finance is distinct from economics in that it addresses not only how resources are allocated but also under what terms and through what channels • Financial contracts or securities occur whenever funds are transferred from issuer to buyer. Module: Introduction to Finance
 What is Finance? Finance as a discipline is generally divided into three areas: • Financial Institutions • Investments and • Business Finance Module: Introduction to Finance
What is Finance? Finance as a discipline is generally divided into three areas: • Financial Institutions • Investments and • Business Finance Module: Introduction to Finance
 What is Financial Management? • Financial Management studies money and the management of money • Like Economics, it explores allocation of resources. • Because the future is unknown, finance studies the allocation of resources in uncertainty. The uncertain events infuse financial decisions with risk. Module: Introduction to Finance
What is Financial Management? • Financial Management studies money and the management of money • Like Economics, it explores allocation of resources. • Because the future is unknown, finance studies the allocation of resources in uncertainty. The uncertain events infuse financial decisions with risk. Module: Introduction to Finance
 Financial Management “Financial Management is concerned with the acquisition, financing and management of assets with some overall goal in mind” J. C. Van Horne The most popular and acceptable definition of financial management as given by S. C. Kuchal: “Financial Management deals with procurement of funds and their effective utilization in the business”. Financial management “is an area of financial decision-making, harmonizing individual motives and enterprise goals”. Weston and Brigham Financial management “is the operational activity of a business that is responsible for obtaining and effectively utilizing the funds necessary for efficient operations Joshep and Massie Module: Introduction to Finance
Financial Management “Financial Management is concerned with the acquisition, financing and management of assets with some overall goal in mind” J. C. Van Horne The most popular and acceptable definition of financial management as given by S. C. Kuchal: “Financial Management deals with procurement of funds and their effective utilization in the business”. Financial management “is an area of financial decision-making, harmonizing individual motives and enterprise goals”. Weston and Brigham Financial management “is the operational activity of a business that is responsible for obtaining and effectively utilizing the funds necessary for efficient operations Joshep and Massie Module: Introduction to Finance
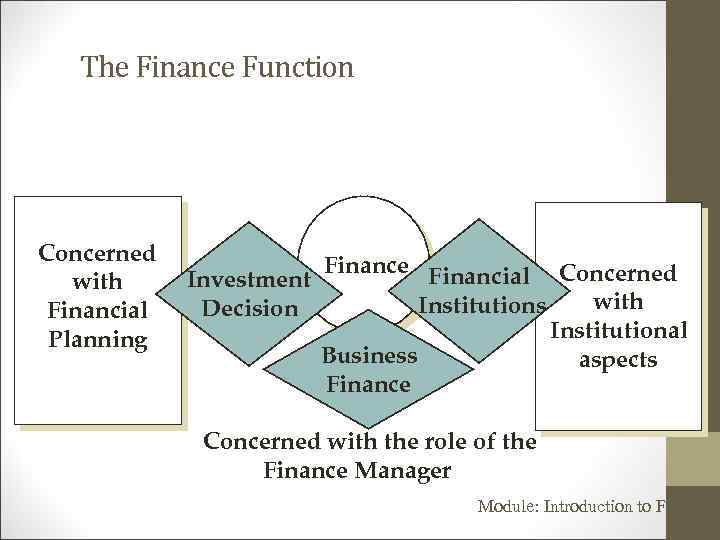 The Finance Function Concerned with Financial Planning Investment Decision Finance Financial Concerned with Institutions Institutional Business aspects Finance Concerned with the role of the Finance Manager Module: Introduction to Finance
The Finance Function Concerned with Financial Planning Investment Decision Finance Financial Concerned with Institutions Institutional Business aspects Finance Concerned with the role of the Finance Manager Module: Introduction to Finance
 Risk and Return in Finance • Risk and return is present in almost every decision. Assessing the returns and risks is an integral part of financial management. • The objective in the decision making process in financial management is not to avoid risk but to properly assess it and to determine whether the risk is worth bearing. Module: Introduction to Finance
Risk and Return in Finance • Risk and return is present in almost every decision. Assessing the returns and risks is an integral part of financial management. • The objective in the decision making process in financial management is not to avoid risk but to properly assess it and to determine whether the risk is worth bearing. Module: Introduction to Finance
 The Role of Interest Rates • Allocate scarce credit • Short-term / Money markets • Long-term / Capital markets Module: Introduction to Finance
The Role of Interest Rates • Allocate scarce credit • Short-term / Money markets • Long-term / Capital markets Module: Introduction to Finance
 Structure of Yields • Yield curve • Generally, long-term debt implies higher rates (positively sloped yield curve). Module: Introduction to Finance
Structure of Yields • Yield curve • Generally, long-term debt implies higher rates (positively sloped yield curve). Module: Introduction to Finance
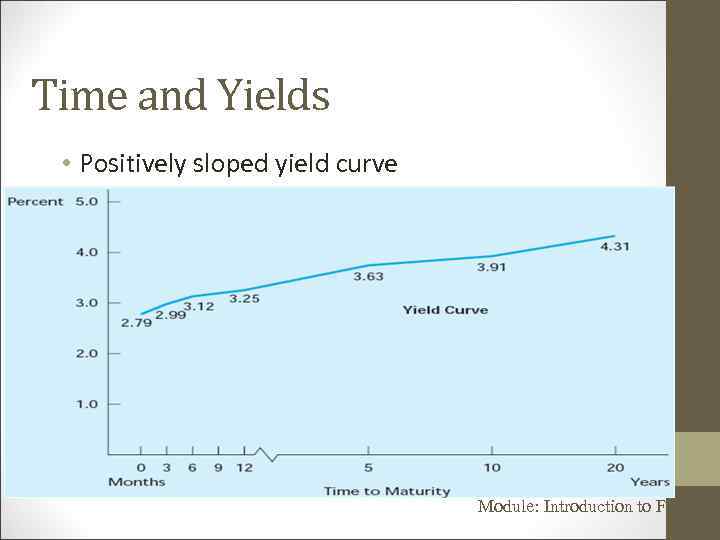 Time and Yields • Positively sloped yield curve Module: Introduction to Finance
Time and Yields • Positively sloped yield curve Module: Introduction to Finance
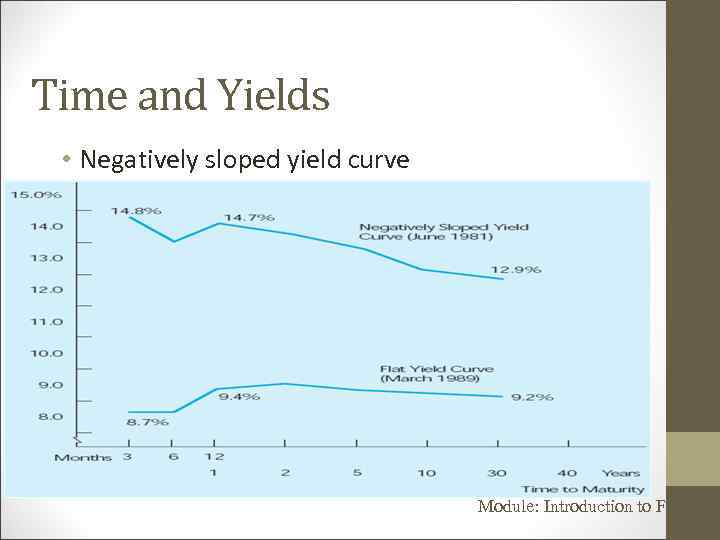 Time and Yields • Negatively sloped yield curve Module: Introduction to Finance
Time and Yields • Negatively sloped yield curve Module: Introduction to Finance
 Determinants of Interest Rates • • Preference for shorter term Marketability Risk Expectations of future rates Module: Introduction to Finance
Determinants of Interest Rates • • Preference for shorter term Marketability Risk Expectations of future rates Module: Introduction to Finance
 Valuation • Assets are acquired in the present, but their returns accrue in the future. • No individual or firm would purchase an asset unless there was an expected return to compensate for the risk. • Since the return is earned in the uncertain future, there has to be a way to express the future in terms of the present. The process of determining what an asset is currently worth is called valuation. Module: Introduction to Finance
Valuation • Assets are acquired in the present, but their returns accrue in the future. • No individual or firm would purchase an asset unless there was an expected return to compensate for the risk. • Since the return is earned in the uncertain future, there has to be a way to express the future in terms of the present. The process of determining what an asset is currently worth is called valuation. Module: Introduction to Finance
 Financial Institutions The study of financial institutions, as the name implies, is concerned with institutional aspects of the discipline, which encompasses the creation of financial assets, the markets for trading securities (for example, the New York Stock Exchange) and the regulation of financial markets. Module: Introduction to Finance
Financial Institutions The study of financial institutions, as the name implies, is concerned with institutional aspects of the discipline, which encompasses the creation of financial assets, the markets for trading securities (for example, the New York Stock Exchange) and the regulation of financial markets. Module: Introduction to Finance
 Investments • The study of investments is primarily concerned with the analysis of individual assets and the construction of well-diversified portfolios. • It encompasses financial planning , specifying the investor’s financial goals, analyzing various securities that the individual may acquire, and constructing diversified portfolios. Module: Introduction to Finance
Investments • The study of investments is primarily concerned with the analysis of individual assets and the construction of well-diversified portfolios. • It encompasses financial planning , specifying the investor’s financial goals, analyzing various securities that the individual may acquire, and constructing diversified portfolios. Module: Introduction to Finance
 Business Finance • The study of business finance or corporate emphasizes the role of a finance manager. • The finance manager must make certain that the firm can meet its obligations as it become due, determine which are the best sources of financing for the firm, and allocate the firms’s resources among the competing investment alternatives. Module: Introduction to Finance
Business Finance • The study of business finance or corporate emphasizes the role of a finance manager. • The finance manager must make certain that the firm can meet its obligations as it become due, determine which are the best sources of financing for the firm, and allocate the firms’s resources among the competing investment alternatives. Module: Introduction to Finance
 The Role of Finance Manager • One of the finance manager’s role is to help others see how their actions affect the company’s ability to generate cash flow and hence its fundamental value. • Finance managers must also decide how to finance the firm. • In particular they must choose what mix of debt and equity should be used, and what specific types of debt and security should be issued. Module: Introduction to Finance
The Role of Finance Manager • One of the finance manager’s role is to help others see how their actions affect the company’s ability to generate cash flow and hence its fundamental value. • Finance managers must also decide how to finance the firm. • In particular they must choose what mix of debt and equity should be used, and what specific types of debt and security should be issued. Module: Introduction to Finance
 The Role of Finance Manager (Cont’d) • They must also decide what percentage of current earnings should be retained and reinvested rather than paid out as dividends. • Along with these financing decisions, the general level of interest rates in the economy, the risk of the firm’s operations and stock market investors’ overall attitude towards risk determine the rate of return that is required to satisfy a firm’s investors. Module: Introduction to Finance
The Role of Finance Manager (Cont’d) • They must also decide what percentage of current earnings should be retained and reinvested rather than paid out as dividends. • Along with these financing decisions, the general level of interest rates in the economy, the risk of the firm’s operations and stock market investors’ overall attitude towards risk determine the rate of return that is required to satisfy a firm’s investors. Module: Introduction to Finance
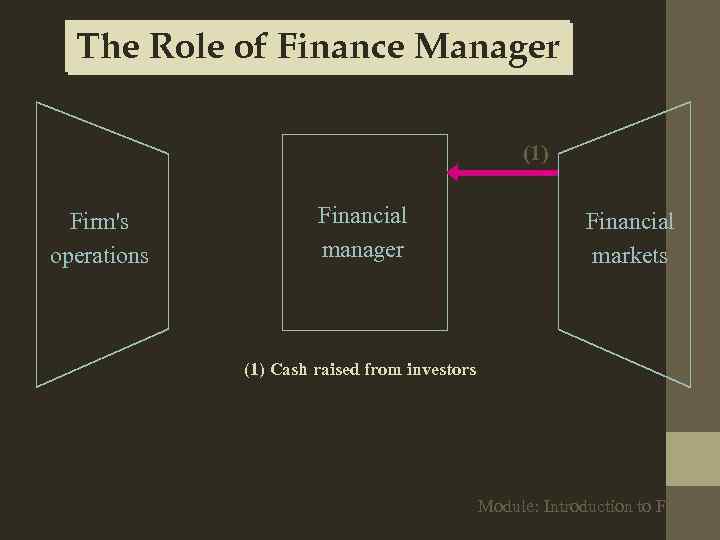 The Role of Finance Manager (1) Firm's operations Financial manager Financial markets (1) Cash raised from investors Module: Introduction to Finance
The Role of Finance Manager (1) Firm's operations Financial manager Financial markets (1) Cash raised from investors Module: Introduction to Finance
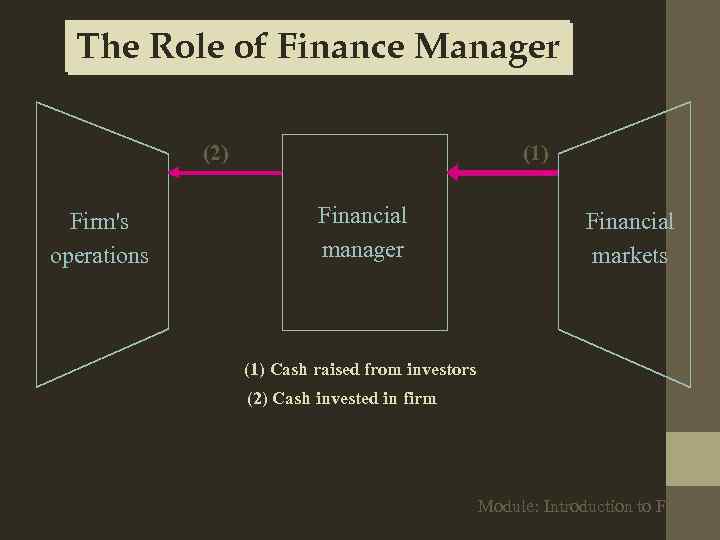 The Role of Finance Manager (2) Firm's operations (1) Financial manager Financial markets (1) Cash raised from investors (2) Cash invested in firm Module: Introduction to Finance
The Role of Finance Manager (2) Firm's operations (1) Financial manager Financial markets (1) Cash raised from investors (2) Cash invested in firm Module: Introduction to Finance
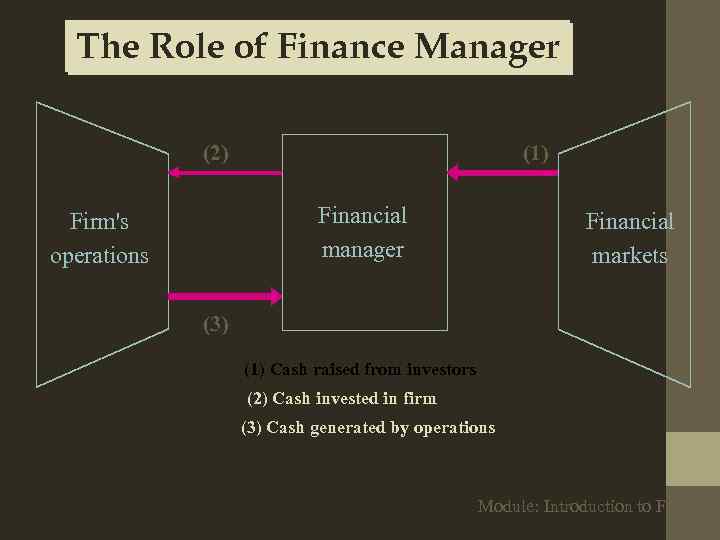 The Role of Finance Manager (2) (1) Financial manager Firm's operations Financial markets (3) (1) Cash raised from investors (2) Cash invested in firm (3) Cash generated by operations Module: Introduction to Finance
The Role of Finance Manager (2) (1) Financial manager Firm's operations Financial markets (3) (1) Cash raised from investors (2) Cash invested in firm (3) Cash generated by operations Module: Introduction to Finance
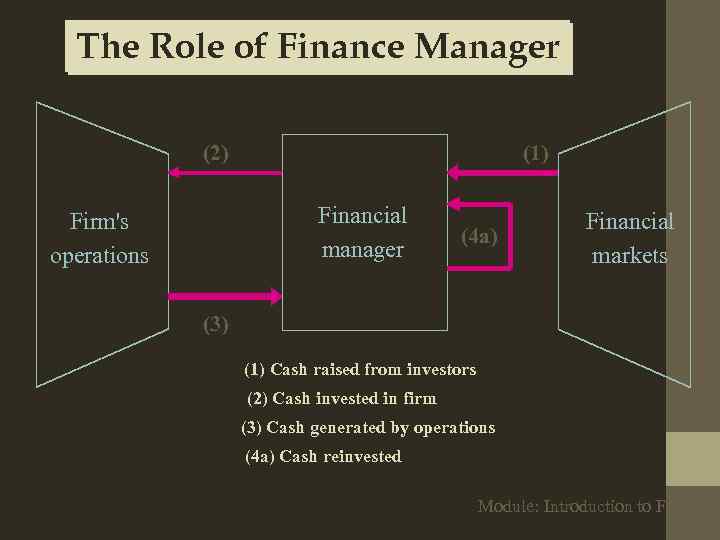 The Role of Finance Manager (2) (1) Financial manager Firm's operations (4 a) Financial markets (3) (1) Cash raised from investors (2) Cash invested in firm (3) Cash generated by operations (4 a) Cash reinvested Module: Introduction to Finance
The Role of Finance Manager (2) (1) Financial manager Firm's operations (4 a) Financial markets (3) (1) Cash raised from investors (2) Cash invested in firm (3) Cash generated by operations (4 a) Cash reinvested Module: Introduction to Finance
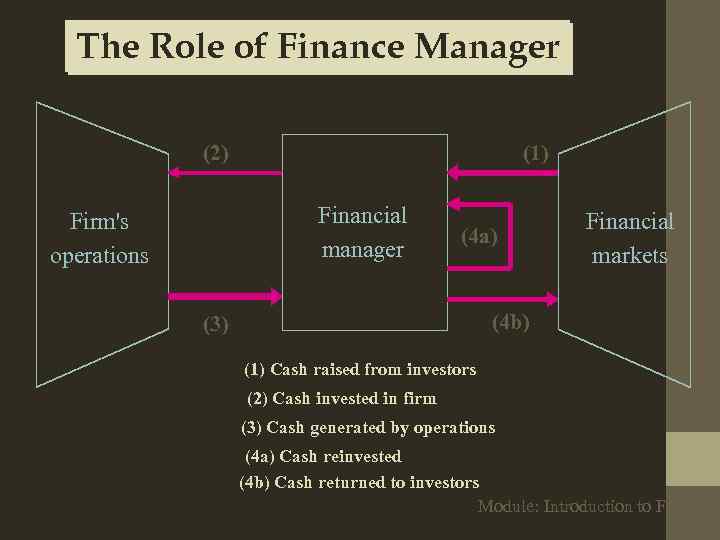 The Role of Finance Manager (2) (1) Financial manager Firm's operations (4 a) Financial markets (4 b) (3) (1) Cash raised from investors (2) Cash invested in firm (3) Cash generated by operations (4 a) Cash reinvested (4 b) Cash returned to investors Module: Introduction to Finance
The Role of Finance Manager (2) (1) Financial manager Firm's operations (4 a) Financial markets (4 b) (3) (1) Cash raised from investors (2) Cash invested in firm (3) Cash generated by operations (4 a) Cash reinvested (4 b) Cash returned to investors Module: Introduction to Finance
 Finance from Different Perspectives • Finance may be studied from a business perspective and also from an investor’s perspective. This ability to approach finance from more than one perspective is important. • Corporate finance or financial management approaches finance from a business perspective. • While corporate finance emphasizes raising funds and their subsequent allocation, investment emphasizes the construction of diversified portfolios and the allocation of wealth among competing securities. Thus, both perspectives are often the opposite sides of the same coin. Module: Introduction to Finance
Finance from Different Perspectives • Finance may be studied from a business perspective and also from an investor’s perspective. This ability to approach finance from more than one perspective is important. • Corporate finance or financial management approaches finance from a business perspective. • While corporate finance emphasizes raising funds and their subsequent allocation, investment emphasizes the construction of diversified portfolios and the allocation of wealth among competing securities. Thus, both perspectives are often the opposite sides of the same coin. Module: Introduction to Finance
 Objectives of Financial Management • Objectives of Financial Management may be broadly divided into two parts such as: • 1. Profit maximization • 2. Wealth maximization Module: Introduction to Finance
Objectives of Financial Management • Objectives of Financial Management may be broadly divided into two parts such as: • 1. Profit maximization • 2. Wealth maximization Module: Introduction to Finance
 Profit Maximization Favourable Arguments for Profit Maximization • (i) Main aim is earning profit. • (ii) Profit is the parameter of the business operation. • (iv) Profit is the main source of finance. • (v) Profitability meets the social needs also. Unfavourable Arguments for Profit Maximization • (i) Profit maximization creates immoral practices such as corrupt practice, unfair trade practice, etc. • (ii) Profit maximization objectives leads to inequalities among the sake holders such as customers, suppliers, public shareholders, etc. Module: Introduction to Finance
Profit Maximization Favourable Arguments for Profit Maximization • (i) Main aim is earning profit. • (ii) Profit is the parameter of the business operation. • (iv) Profit is the main source of finance. • (v) Profitability meets the social needs also. Unfavourable Arguments for Profit Maximization • (i) Profit maximization creates immoral practices such as corrupt practice, unfair trade practice, etc. • (ii) Profit maximization objectives leads to inequalities among the sake holders such as customers, suppliers, public shareholders, etc. Module: Introduction to Finance
 Limitations of P. M. Objective • (i) It is vague: In this objective, profit is not defined precisely or correctly. It creates some unnecessary opinion regarding earning habits of the business concern. • (ii) It ignores the time value of money: Profit maximization does not consider the time value of money or the net present value of the cash inflow. It leads certain differences between the actual cash inflow and net present cash flow during a particular period. • (iii) It ignores risk: Profit maximization does not consider risk of the business concern. Risks may be internal or external which will affect the overall operation of the business concern Module: Introduction to Finance
Limitations of P. M. Objective • (i) It is vague: In this objective, profit is not defined precisely or correctly. It creates some unnecessary opinion regarding earning habits of the business concern. • (ii) It ignores the time value of money: Profit maximization does not consider the time value of money or the net present value of the cash inflow. It leads certain differences between the actual cash inflow and net present cash flow during a particular period. • (iii) It ignores risk: Profit maximization does not consider risk of the business concern. Risks may be internal or external which will affect the overall operation of the business concern Module: Introduction to Finance
 Wealth Maximization • Wealth maximization is one of the modern approaches, which involves latest innovations and improvements in the field of the business concern. • The term wealth means shareholder wealth or the wealth of the persons those who are involved in the business concern. • Wealth maximization is also known as value maximization or net present worth maximization. This objective is an universally accepted concept in the field of business. Module: Introduction to Finance
Wealth Maximization • Wealth maximization is one of the modern approaches, which involves latest innovations and improvements in the field of the business concern. • The term wealth means shareholder wealth or the wealth of the persons those who are involved in the business concern. • Wealth maximization is also known as value maximization or net present worth maximization. This objective is an universally accepted concept in the field of business. Module: Introduction to Finance
 Wealth Maximization Cont. Unfavourable Arguments for Wealth Maximization • (i) Wealth maximization is leads to prescriptive idea of superior to the profit the business concern but it maximization because the may not be suitable to main aim of the business present day business concern under this concept is activities. to improve the value or wealth • (ii) Wealth maximization is of the shareholders. nothing, it is also profit • (ii) Wealth maximization, it is the indirect name of the profit considers the comparison of maximization. the value to cost associated • (iii) Wealth maximization with the business concern. creates ownershipmanagement controversy. Favourable Arguments for Wealth Maximization Module: Introduction to Finance
Wealth Maximization Cont. Unfavourable Arguments for Wealth Maximization • (i) Wealth maximization is leads to prescriptive idea of superior to the profit the business concern but it maximization because the may not be suitable to main aim of the business present day business concern under this concept is activities. to improve the value or wealth • (ii) Wealth maximization is of the shareholders. nothing, it is also profit • (ii) Wealth maximization, it is the indirect name of the profit considers the comparison of maximization. the value to cost associated • (iii) Wealth maximization with the business concern. creates ownershipmanagement controversy. Favourable Arguments for Wealth Maximization Module: Introduction to Finance
 Wealth Maximization Cont. (iii) Wealth maximization considers both time and risk of the business concern. • (iv) Wealth maximization provides efficient allocation of resources. • (v) It ensures the economic interest of the society. • (iv) Management alone enjoy certain benefits. • (v) The ultimate aim of the wealth maximization objectives is to maximize the profit. • (vi) Wealth maximization can be activated only with the help of the profitable position of the business concern Module: Introduction to Finance
Wealth Maximization Cont. (iii) Wealth maximization considers both time and risk of the business concern. • (iv) Wealth maximization provides efficient allocation of resources. • (v) It ensures the economic interest of the society. • (iv) Management alone enjoy certain benefits. • (v) The ultimate aim of the wealth maximization objectives is to maximize the profit. • (vi) Wealth maximization can be activated only with the help of the profitable position of the business concern Module: Introduction to Finance


