247bd3b41badc3ca151def06288b3e5f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Lecture 1: Introduction Cpr. E 581 Computer Systems Architecture, Fall 2005 Zhao Zhang
Lecture 1: Introduction Cpr. E 581 Computer Systems Architecture, Fall 2005 Zhao Zhang
 Traditional “Computer Architecture” The term architecture is used here to describe the attribute of a system as seen by the programmer, i. e. , the conceptual structure and functional behavior as distinct from the organization of the data flow and controls, the logic design, and the physical implementation. n Gene Amdahl, IBM Journal R&D, April 1964
Traditional “Computer Architecture” The term architecture is used here to describe the attribute of a system as seen by the programmer, i. e. , the conceptual structure and functional behavior as distinct from the organization of the data flow and controls, the logic design, and the physical implementation. n Gene Amdahl, IBM Journal R&D, April 1964
 Contemporary “Computer Architecture” Instruction set architecture Microarchitecture: n n Pipeline structures Cache memories Implementations n Logic design and synthesis
Contemporary “Computer Architecture” Instruction set architecture Microarchitecture: n n Pipeline structures Cache memories Implementations n Logic design and synthesis
 Fundamentals Technology trends Performance evaluation methodologies Instruction Set Architecture
Fundamentals Technology trends Performance evaluation methodologies Instruction Set Architecture
 Technology Drives for High-Performance VLSI technology: faster transistors and larger transistor budget
Technology Drives for High-Performance VLSI technology: faster transistors and larger transistor budget
 CPU Performance For sequential program: CPU time = #Inst CPI Clock cycle time To improve performance w Faster clock time w Reduce #inst w Reduce CPI or increase IPC
CPU Performance For sequential program: CPU time = #Inst CPI Clock cycle time To improve performance w Faster clock time w Reduce #inst w Reduce CPI or increase IPC
 How to use one billion transistors? Bit-level parallelism n Move from 32 -bit to 64 -bit Instruction-level parallelism n n Deep pipeline Execute multiple instructions per cycle Program locality n Large caches, more branch prediction resouces Thread-level parallelism
How to use one billion transistors? Bit-level parallelism n Move from 32 -bit to 64 -bit Instruction-level parallelism n n Deep pipeline Execute multiple instructions per cycle Program locality n Large caches, more branch prediction resouces Thread-level parallelism
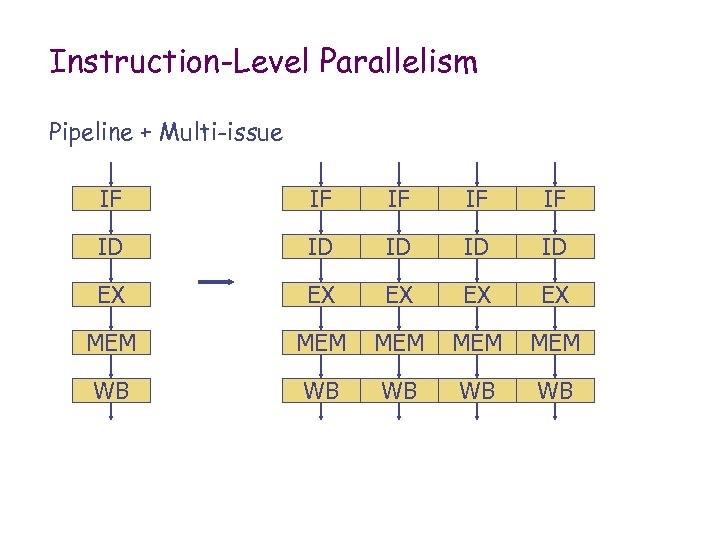 Instruction-Level Parallelism Pipeline + Multi-issue IF IF IF ID ID ID EX EX EX MEM MEM MEM WB WB WB
Instruction-Level Parallelism Pipeline + Multi-issue IF IF IF ID ID ID EX EX EX MEM MEM MEM WB WB WB
![Instruction-level Parallelism for (i=0; i<N; i++) X[i] = a*X[i]; // let R 3=&X[0], R Instruction-level Parallelism for (i=0; i<N; i++) X[i] = a*X[i]; // let R 3=&X[0], R](https://present5.com/presentation/247bd3b41badc3ca151def06288b3e5f/image-9.jpg) Instruction-level Parallelism for (i=0; i
Instruction-level Parallelism for (i=0; i
 Instruction-Level Parallelism Find independent instructions through dependence analysis Hardware approaches => Dynamically scheduled superscalar n Most commonly used today: Intel Pentium, AMD, Sun Ultra. Sparc, and MIPS families Software approaches => (1) Static scheduled superscalar, or (2) VLIW
Instruction-Level Parallelism Find independent instructions through dependence analysis Hardware approaches => Dynamically scheduled superscalar n Most commonly used today: Intel Pentium, AMD, Sun Ultra. Sparc, and MIPS families Software approaches => (1) Static scheduled superscalar, or (2) VLIW
 Modern Superscalar Processors Example: Intel Pentium, IBM Power/Power. PC, Sun Ultra. Sparc, SGI MIPS … n n n Multi-issue and Deep pipelining Dynamic scheduling and speculative execution High bandwidth L 1 caches and large L 2/L 3 caches
Modern Superscalar Processors Example: Intel Pentium, IBM Power/Power. PC, Sun Ultra. Sparc, SGI MIPS … n n n Multi-issue and Deep pipelining Dynamic scheduling and speculative execution High bandwidth L 1 caches and large L 2/L 3 caches
 Modern Superscalar Processor Challenges: Complexity!!! n n How Understand how it brings high performance w Will see wield designs w Will use Verilog, simulation to help understanding Have big pictures
Modern Superscalar Processor Challenges: Complexity!!! n n How Understand how it brings high performance w Will see wield designs w Will use Verilog, simulation to help understanding Have big pictures
 Modern Superscalar Processor Maintain register data flow n n Register renaming Instruction scheduling Maintain control flow n n Branch prediction Speculative execution and recovery Maintain memory data flow n n Load and store queues Memory dependence speculation
Modern Superscalar Processor Maintain register data flow n n Register renaming Instruction scheduling Maintain control flow n n Branch prediction Speculative execution and recovery Maintain memory data flow n n Load and store queues Memory dependence speculation
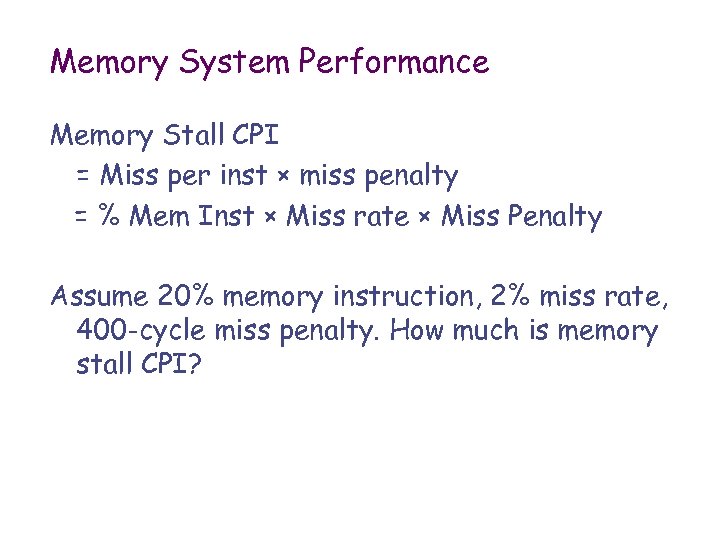 Memory System Performance Memory Stall CPI = Miss per inst × miss penalty = % Mem Inst × Miss rate × Miss Penalty Assume 20% memory instruction, 2% miss rate, 400 -cycle miss penalty. How much is memory stall CPI?
Memory System Performance Memory Stall CPI = Miss per inst × miss penalty = % Mem Inst × Miss rate × Miss Penalty Assume 20% memory instruction, 2% miss rate, 400 -cycle miss penalty. How much is memory stall CPI?
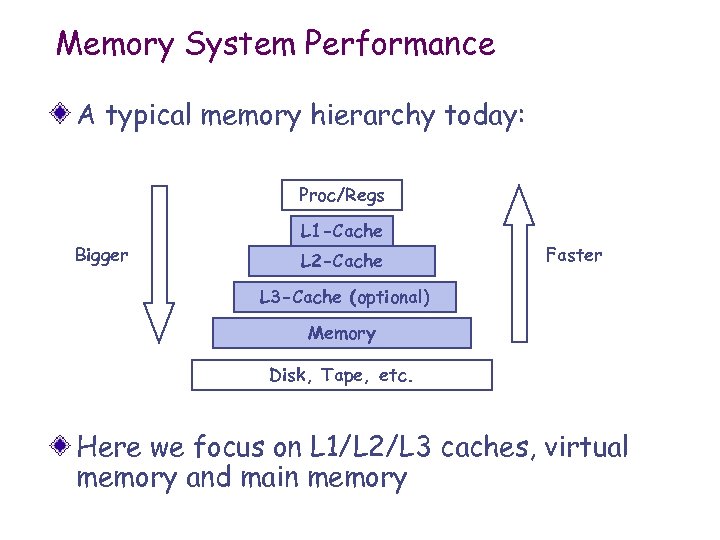 Memory System Performance A typical memory hierarchy today: Proc/Regs Bigger L 1 -Cache L 2 -Cache Faster L 3 -Cache (optional) Memory Disk, Tape, etc. Here we focus on L 1/L 2/L 3 caches, virtual memory and main memory
Memory System Performance A typical memory hierarchy today: Proc/Regs Bigger L 1 -Cache L 2 -Cache Faster L 3 -Cache (optional) Memory Disk, Tape, etc. Here we focus on L 1/L 2/L 3 caches, virtual memory and main memory
 Cache Design Many applications are memory-bound n CPU speeds increases fast; memory speed cannot match up Cache hierarchy: exploits program locality n n Basic principles of cache designs Hardware cache optimizations Application cache optimizations Prefetching techniques Also talk about virtual memory
Cache Design Many applications are memory-bound n CPU speeds increases fast; memory speed cannot match up Cache hierarchy: exploits program locality n n Basic principles of cache designs Hardware cache optimizations Application cache optimizations Prefetching techniques Also talk about virtual memory
 High Performance Storage Systems What limits the performance of web servers? Storage! Storage technology trends RAID: Redundant array of inexpensive disks
High Performance Storage Systems What limits the performance of web servers? Storage! Storage technology trends RAID: Redundant array of inexpensive disks
 Multiprocessor Systems Must exploit thread-level parallelism for further performance improvement Shared-memory multiprocessors: Cooperating programs see the same memory address How to build them? n n Cache coherence Memory consistency
Multiprocessor Systems Must exploit thread-level parallelism for further performance improvement Shared-memory multiprocessors: Cooperating programs see the same memory address How to build them? n n Cache coherence Memory consistency
 Emerging Techniques Low power design Multicore and multithreaded processors Secure processor Reliable design
Emerging Techniques Low power design Multicore and multithreaded processors Secure processor Reliable design
 Why Study Computer Architecture As a hardware designer/researcher – know how to design processor, cache, storage, graphics, interconnect, and so on As a system designer – know how to build a computer system using the best components available As a software designer – know how to get the best performance from the hardware
Why Study Computer Architecture As a hardware designer/researcher – know how to design processor, cache, storage, graphics, interconnect, and so on As a system designer – know how to build a computer system using the best components available As a software designer – know how to get the best performance from the hardware
 Class Web Site www. ece. iastate. edu/~zzhang/cpre 585/ Syllabus Schedule Homework assignments Readings Web. CT: Grades, Assignments and Discussions
Class Web Site www. ece. iastate. edu/~zzhang/cpre 585/ Syllabus Schedule Homework assignments Readings Web. CT: Grades, Assignments and Discussions


