Lecture 1 Wells 01.09.16.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Lecture 1, 2 Oil and gas wells and their functions in petroleum exploration and production
Lecture 1, 2 Oil and gas wells and their functions in petroleum exploration and production
 Historical data The first wells in the history of mankind were drilled in China in 2000 B. C. with the help of cable drilling for extraction of salt water. In the USA the first oil well (depth 25 meters) was drilled in Pennsylvania by Edwin Drake with the use of power plant in 1859. The birth of the Russian petroleum industry was in 1864, when A. N. Novosiltsev began to drill the first oil well (depth 55 meters) on Kuban, in the valley Kudako - river.
Historical data The first wells in the history of mankind were drilled in China in 2000 B. C. with the help of cable drilling for extraction of salt water. In the USA the first oil well (depth 25 meters) was drilled in Pennsylvania by Edwin Drake with the use of power plant in 1859. The birth of the Russian petroleum industry was in 1864, when A. N. Novosiltsev began to drill the first oil well (depth 55 meters) on Kuban, in the valley Kudako - river.
 French engineer Fovell created method of carrying out (removing) the particles fragments of breaked rocks (cutting) with the help of circulating stream of water in 1848 and used this method for the 1 st time for drilling of artesian well in a Saint Dominica monastery. In 1901 in the USA for the first time new way of drilling was used - rotational-rotary drilling with flushing-out of a well by a circulating stream of a liquid (mud). In Russia the first well was drilled by the rotary drilling in 1902 (depth of 345 meters) in Groznensk area. In 1906 Russian engineer A. A. Bogushevsky developed and patented a way of cementing casing string with the help of slurry’s replacement through a casing pipes and casing shoe into borehole
French engineer Fovell created method of carrying out (removing) the particles fragments of breaked rocks (cutting) with the help of circulating stream of water in 1848 and used this method for the 1 st time for drilling of artesian well in a Saint Dominica monastery. In 1901 in the USA for the first time new way of drilling was used - rotational-rotary drilling with flushing-out of a well by a circulating stream of a liquid (mud). In Russia the first well was drilled by the rotary drilling in 1902 (depth of 345 meters) in Groznensk area. In 1906 Russian engineer A. A. Bogushevsky developed and patented a way of cementing casing string with the help of slurry’s replacement through a casing pipes and casing shoe into borehole
 At the beginning of the XX Russia oil industry produced more than 10 million tons per year. It made up about 50 % of the world oil production. In 1923 the graduate of the Tomsk Technological Institute M. A. Kapeljushnikov together with S. M. Volohom and N. A. Korneyev have invented hydraulic downhole motor - the turbodrill. In 1924 in Azerbaijan the first-ever hole was drilled with the help of the one-stage turbodrill which received the name of Kapelyushnikov turbodrill. In 1937 -1940 A. P. Ostrovsky, N. G. Grigoryan, N. V. Aleksandrov and others developed the new downhole motor - an electrodrill.
At the beginning of the XX Russia oil industry produced more than 10 million tons per year. It made up about 50 % of the world oil production. In 1923 the graduate of the Tomsk Technological Institute M. A. Kapeljushnikov together with S. M. Volohom and N. A. Korneyev have invented hydraulic downhole motor - the turbodrill. In 1924 in Azerbaijan the first-ever hole was drilled with the help of the one-stage turbodrill which received the name of Kapelyushnikov turbodrill. In 1937 -1940 A. P. Ostrovsky, N. G. Grigoryan, N. V. Aleksandrov and others developed the new downhole motor - an electrodrill.
 In the Western Siberia the first well gave a gas blowout in 1953 near village Berezovo in the north of the Tyumen area. The first oil exploration drill hole in the Western Siberia gushed on the Mulimlinskaia area in basin of the Konda river in 1960. During the 30 years (1950 -1980) domestic oil production increased more than in 16 times and produced more than 600 million tones.
In the Western Siberia the first well gave a gas blowout in 1953 near village Berezovo in the north of the Tyumen area. The first oil exploration drill hole in the Western Siberia gushed on the Mulimlinskaia area in basin of the Konda river in 1960. During the 30 years (1950 -1980) domestic oil production increased more than in 16 times and produced more than 600 million tones.
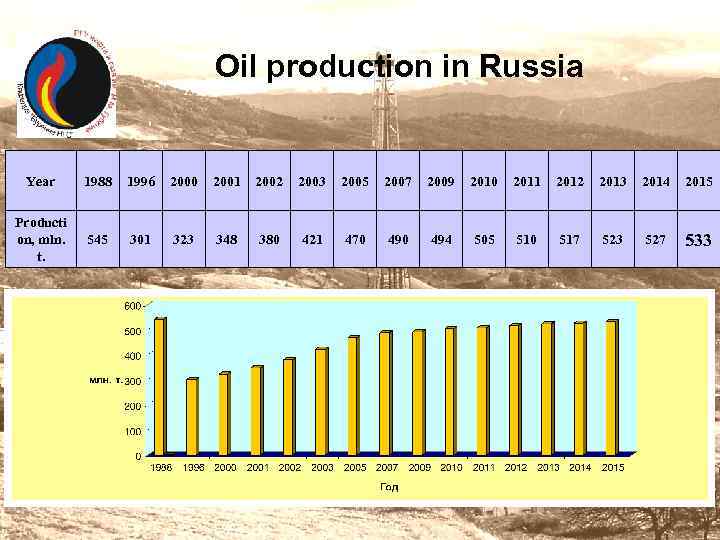 Oil production in Russia Year 1988 1996 2000 2001 2002 2003 2005 2007 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Producti on, mln. t. 545 301 323 348 380 421 470 494 505 510 517 523 527 533
Oil production in Russia Year 1988 1996 2000 2001 2002 2003 2005 2007 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Producti on, mln. t. 545 301 323 348 380 421 470 494 505 510 517 523 527 533
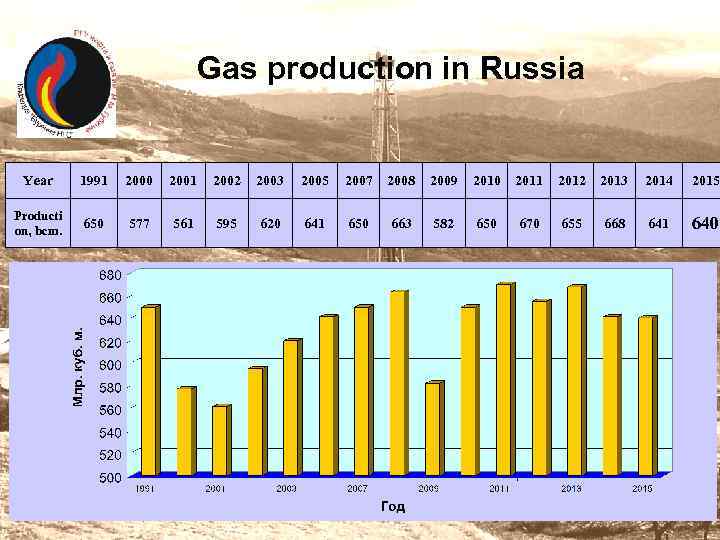 Gas production in Russia Year 1991 2000 2001 2002 2003 2005 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Producti on, bcm. 650 577 561 595 620 641 650 663 582 650 670 655 668 641 640
Gas production in Russia Year 1991 2000 2001 2002 2003 2005 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Producti on, bcm. 650 577 561 595 620 641 650 663 582 650 670 655 668 641 640
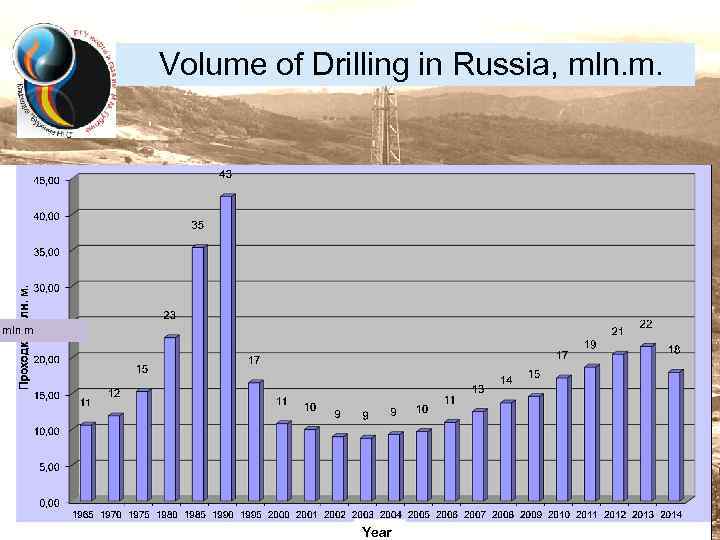 Volume of Drilling in Russia, mln. m. mln m Year
Volume of Drilling in Russia, mln. m. mln m Year
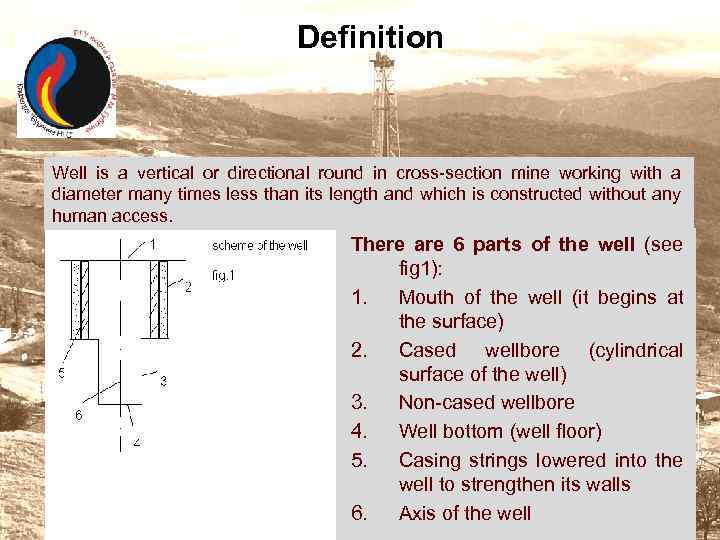 Definition Well is a vertical or directional round in cross-section mine working with a diameter many times less than its length and which is constructed without any human access. There are 6 parts of the well (see fig 1): 1. Mouth of the well (it begins at the surface) 2. Cased wellbore (cylindrical surface of the well) 3. Non-cased wellbore 4. Well bottom (well floor) 5. Casing strings lowered into the well to strengthen its walls 6. Axis of the well
Definition Well is a vertical or directional round in cross-section mine working with a diameter many times less than its length and which is constructed without any human access. There are 6 parts of the well (see fig 1): 1. Mouth of the well (it begins at the surface) 2. Cased wellbore (cylindrical surface of the well) 3. Non-cased wellbore 4. Well bottom (well floor) 5. Casing strings lowered into the well to strengthen its walls 6. Axis of the well
 Well design is characterized by the number and the locations of casing strings, their diameters and total lengths to be lowered (RIH), diameters of the bits used for each interval of drilling, and also by the location of cemented intervals.
Well design is characterized by the number and the locations of casing strings, their diameters and total lengths to be lowered (RIH), diameters of the bits used for each interval of drilling, and also by the location of cemented intervals.
 Abbreviations • RIH - run into hole (insert, lower) • POOH - pool out of hole (lift, raise) • ROP - rate of penetration • WOB - weight on the bit (load) • RPM - revolutions per minute
Abbreviations • RIH - run into hole (insert, lower) • POOH - pool out of hole (lift, raise) • ROP - rate of penetration • WOB - weight on the bit (load) • RPM - revolutions per minute
 Casing strings types 1. 2. 3. 4. Protective casing (only oblong) Surface casing Intermediate casing Production casing • • Complications: Lost circulation Oil, gas and water shows Shale instability, hole sloughing Sticking
Casing strings types 1. 2. 3. 4. Protective casing (only oblong) Surface casing Intermediate casing Production casing • • Complications: Lost circulation Oil, gas and water shows Shale instability, hole sloughing Sticking
 Protective casing It serves in strengthening the mouth of well, to avoid flushing the mouth of well by mud and to provide the vertical direction of the well while drilling in the top part of geological crosssection. As a rule, protective casing is RIH to the depth of 3 -10 meters. Sometimes in West Siberia, longer protective casings are used. Their length equals to approximately 30 -80 meters.
Protective casing It serves in strengthening the mouth of well, to avoid flushing the mouth of well by mud and to provide the vertical direction of the well while drilling in the top part of geological crosssection. As a rule, protective casing is RIH to the depth of 3 -10 meters. Sometimes in West Siberia, longer protective casings are used. Their length equals to approximately 30 -80 meters.
 Surface casing It is RIH for the following objectives: – – – to prevent caving; to minimize lost circulation into shallow permeable zones; to cover weak zone where fracturing may occur; to provide means for attaching the blowout preventers (BOP); to support the weight of casing strings located below.
Surface casing It is RIH for the following objectives: – – – to prevent caving; to minimize lost circulation into shallow permeable zones; to cover weak zone where fracturing may occur; to provide means for attaching the blowout preventers (BOP); to support the weight of casing strings located below.
 Intermediate casing The basic application of these strings is the prevention of various complications while drilling. The number of these strings depends on complexity of geological cross-section and hydro geological conditions.
Intermediate casing The basic application of these strings is the prevention of various complications while drilling. The number of these strings depends on complexity of geological cross-section and hydro geological conditions.
 Production casing This string connects pay zone and the mouth of the well. With the help of this string oil and gas come to the surface of the earth from pay zone. Other purposes: – to isolate the producing zone from the other formations (to prevent cross-flow between layers) – to provide a work of the given diameter pump to extract oil from the pay zone; – to protect the production tubing equipment.
Production casing This string connects pay zone and the mouth of the well. With the help of this string oil and gas come to the surface of the earth from pay zone. Other purposes: – to isolate the producing zone from the other formations (to prevent cross-flow between layers) – to provide a work of the given diameter pump to extract oil from the pay zone; – to protect the production tubing equipment.
 Well design drawing Casing strings: 1. Surface casing 2. Intermediate casing 3. Production casing D 1, D 2, D 3 – diameters of casing strings L 1, L 2, L 3 – depth of casing shoe d 1, d 2, d 3 – diameters of the bits H 1, H 2, H 3 – coordinate of the top end of cement stone column of the casing
Well design drawing Casing strings: 1. Surface casing 2. Intermediate casing 3. Production casing D 1, D 2, D 3 – diameters of casing strings L 1, L 2, L 3 – depth of casing shoe d 1, d 2, d 3 – diameters of the bits H 1, H 2, H 3 – coordinate of the top end of cement stone column of the casing
 Liner and tail pipe To economize metal and to reduce the cost of a well we often use special intermediate casing called liner. This string does not reach the mouth of the well. It is hung up into preceding casing string with the help of special equipment. The interval of the well, where casing string is absent, is shown as dotted line. Look at the following picture.
Liner and tail pipe To economize metal and to reduce the cost of a well we often use special intermediate casing called liner. This string does not reach the mouth of the well. It is hung up into preceding casing string with the help of special equipment. The interval of the well, where casing string is absent, is shown as dotted line. Look at the following picture.
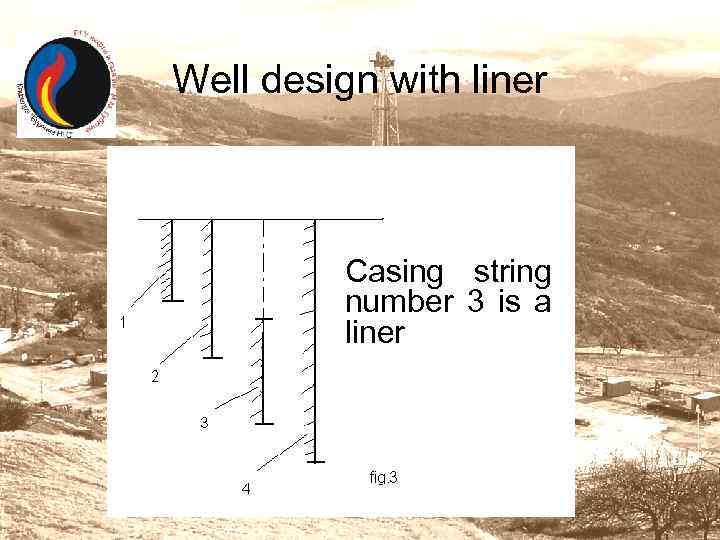 Well design with liner Casing string number 3 is a liner
Well design with liner Casing string number 3 is a liner
 Requirements of well planning It is very important to plan the design of a well in such way that allows drilling of the well to the project depth without any complications; the well must be reliable within all period of its operation. Engineers consider planning of a well as a very important task.
Requirements of well planning It is very important to plan the design of a well in such way that allows drilling of the well to the project depth without any complications; the well must be reliable within all period of its operation. Engineers consider planning of a well as a very important task.
 Requirements of well planning During the planning of the well following demands have to be satisfied: –well safety –minimum cost of well construction –usable for particular conditions Safety should be the highest priority in well planning. Personal consideration of this item must be placed above all other aspects of the plan. The well plan must be designed to minimize the risk of blowout and other factors that could create problems.
Requirements of well planning During the planning of the well following demands have to be satisfied: –well safety –minimum cost of well construction –usable for particular conditions Safety should be the highest priority in well planning. Personal consideration of this item must be placed above all other aspects of the plan. The well plan must be designed to minimize the risk of blowout and other factors that could create problems.
 Requirements of well planning Another objective of the well planning process is to minimize the cost of the well. Usually costs can be reduced to a certain level as additional efforts are given to the planning.
Requirements of well planning Another objective of the well planning process is to minimize the cost of the well. Usually costs can be reduced to a certain level as additional efforts are given to the planning.
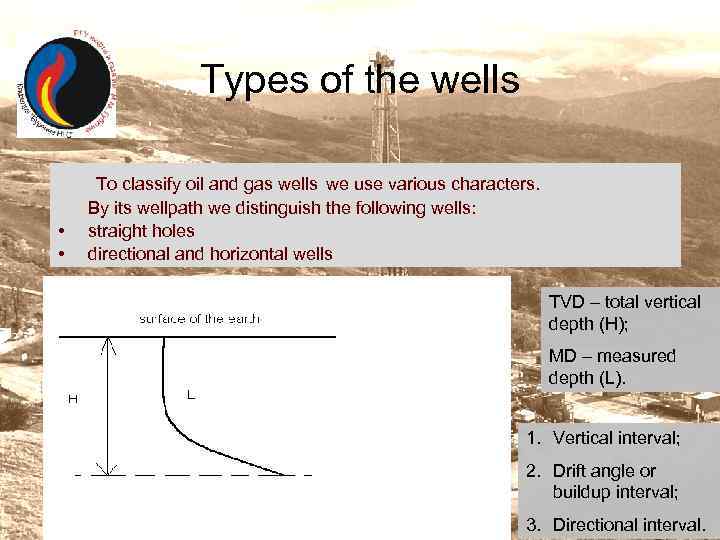 Types of the wells • • To classify oil and gas wells we use various characters. By its wellpath we distinguish the following wells: straight holes directional and horizontal wells TVD – total vertical depth (H); MD – measured depth (L). 1. Vertical interval; 2. Drift angle or buildup interval; 3. Directional interval.
Types of the wells • • To classify oil and gas wells we use various characters. By its wellpath we distinguish the following wells: straight holes directional and horizontal wells TVD – total vertical depth (H); MD – measured depth (L). 1. Vertical interval; 2. Drift angle or buildup interval; 3. Directional interval.
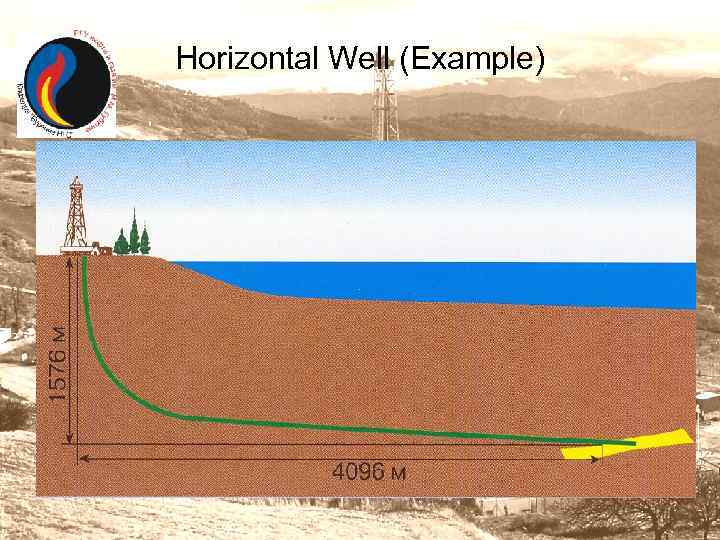 Horizontal Well (Example)
Horizontal Well (Example)
 Classification of the wells according to the well depth • • The depth of oil and gas wells – from several hundred to several thousand meters. In terms of the depth of well there are existing 4 types of the wells: Short wells (up to 1500 m); Wells of intermediate depth (up to 4500 m); Deep wells (up to 6000 m); Super deep wells (more then 6000 m).
Classification of the wells according to the well depth • • The depth of oil and gas wells – from several hundred to several thousand meters. In terms of the depth of well there are existing 4 types of the wells: Short wells (up to 1500 m); Wells of intermediate depth (up to 4500 m); Deep wells (up to 6000 m); Super deep wells (more then 6000 m).
 Ultra deep well on Kolskyi peninsula (TVD is 12 262 m. )
Ultra deep well on Kolskyi peninsula (TVD is 12 262 m. )
 Types of wells (continuation) Wells are drilled on land (onshore) and on sea (offshore) by using special drilling rigs. We often drill not only oil and gas wells but special wells too. For example special wells are drilled in coal and ore industry. Very often the wells are drilled to get mineral water and water for drinking.
Types of wells (continuation) Wells are drilled on land (onshore) and on sea (offshore) by using special drilling rigs. We often drill not only oil and gas wells but special wells too. For example special wells are drilled in coal and ore industry. Very often the wells are drilled to get mineral water and water for drinking.
 Maximum measured depth well Maximum measured depth of the well was reached on oilfield Chayvo by company Rosneft (in "Sakhalin -1" Project) with the help of Fixed Offshore Platform "Orlan". Measured depth (MD) of this well reached 13 500 meters and horizontal displacement reached 12033 meters. Today it's the world record.
Maximum measured depth well Maximum measured depth of the well was reached on oilfield Chayvo by company Rosneft (in "Sakhalin -1" Project) with the help of Fixed Offshore Platform "Orlan". Measured depth (MD) of this well reached 13 500 meters and horizontal displacement reached 12033 meters. Today it's the world record.
 The modern onshore Drill Rig Ull. Rig in IRIS (Stavanger, Norway)
The modern onshore Drill Rig Ull. Rig in IRIS (Stavanger, Norway)
 THE FIRST RUSSIAN EXPLORATORY WELL IN THE KARA SEA Russian oil company, Rosneft and American oil and gas corporation Exxon. Mobil have discovered oil during drilling on the Universitetskaya-1 well in the Kara Sea. Drilling was carried out in record time - one and a half months. Preliminary assessment of the resource base only for this first opening has trapped 338 million cubic meters of gas and 100 million tons of oil , and this is only one of the structures in this field. The total expenses of this well construction is evaluated approximately 600 MUSD. The water depth is 81 meters at this site, TVD of exploratory well is 2113 meters.
THE FIRST RUSSIAN EXPLORATORY WELL IN THE KARA SEA Russian oil company, Rosneft and American oil and gas corporation Exxon. Mobil have discovered oil during drilling on the Universitetskaya-1 well in the Kara Sea. Drilling was carried out in record time - one and a half months. Preliminary assessment of the resource base only for this first opening has trapped 338 million cubic meters of gas and 100 million tons of oil , and this is only one of the structures in this field. The total expenses of this well construction is evaluated approximately 600 MUSD. The water depth is 81 meters at this site, TVD of exploratory well is 2113 meters.
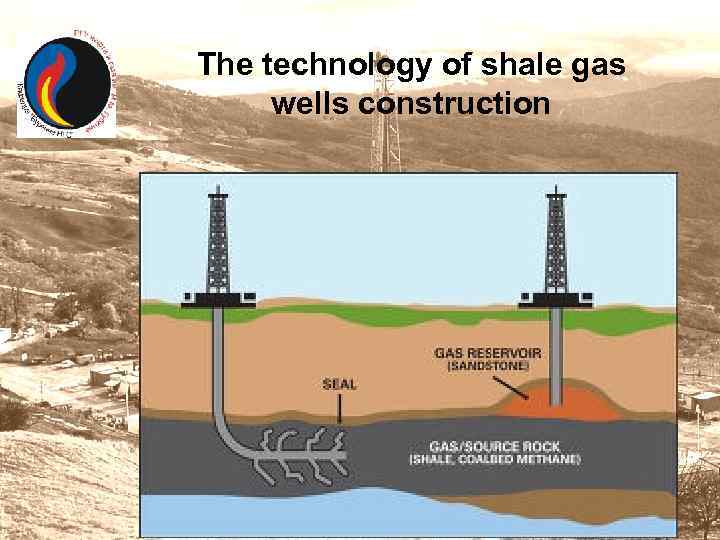 The technology of shale gas wells construction
The technology of shale gas wells construction
 Classification of oil and gas wells • Key boreholes (in American classification – wild cats) • Parameter well • Structure boreholes • Prospecting well • Exploratory wells • Production well (recovery well) • Special wells
Classification of oil and gas wells • Key boreholes (in American classification – wild cats) • Parameter well • Structure boreholes • Prospecting well • Exploratory wells • Production well (recovery well) • Special wells
 Main types of the wells (according their function) Key wells (wild cat)- These wells are drilled on a significant distance one from another to get general picture of geological structure of large regions where there are little geological information is available. Parameter wells - They are intended for a more detailed study of geological cross-section, especially at great depth and for identification of the most promising areas of geological prospecting work. Structure wells - They serve the purpose of investigating more properly the structures encountered in drilling by key and parameter boreholes and to make up a plan of exploratoryprospecting drilling into these structures. Prospecting wells - Their general purpose is to discover new oil and gas deposits.
Main types of the wells (according their function) Key wells (wild cat)- These wells are drilled on a significant distance one from another to get general picture of geological structure of large regions where there are little geological information is available. Parameter wells - They are intended for a more detailed study of geological cross-section, especially at great depth and for identification of the most promising areas of geological prospecting work. Structure wells - They serve the purpose of investigating more properly the structures encountered in drilling by key and parameter boreholes and to make up a plan of exploratoryprospecting drilling into these structures. Prospecting wells - Their general purpose is to discover new oil and gas deposits.
 Well types Exploratory wells - The aim of these wells are to delineate the pool and to collect the initial basic data for planning its development. Production wells - They are drilled into completely prospective oil and gas fields. The category of producing wells includes not only the wells through which oil and gas are recovered in a particular reservoir according to the plan.
Well types Exploratory wells - The aim of these wells are to delineate the pool and to collect the initial basic data for planning its development. Production wells - They are drilled into completely prospective oil and gas fields. The category of producing wells includes not only the wells through which oil and gas are recovered in a particular reservoir according to the plan.
 Producing wells also include: • Injection wells. They serve to maintain the formation pressure. For this aim water injection is made into the formation through these wells. Injection can be made into an aquifer, in this case injection wells are located out of boundaries of particular oil field. • Observation wells. They are drilled to control formation pressure, the position of the water-oil, gaswater and gas-oil contacts during the reservoir development.
Producing wells also include: • Injection wells. They serve to maintain the formation pressure. For this aim water injection is made into the formation through these wells. Injection can be made into an aquifer, in this case injection wells are located out of boundaries of particular oil field. • Observation wells. They are drilled to control formation pressure, the position of the water-oil, gaswater and gas-oil contacts during the reservoir development.
 Well types Special wells are often drilled: • for liquid waste products escape into unproductive absorbing layers, • for exploration and production of water, • geological structures preparation for underground gas storages and gas injection into them, • for elimination of oil and gas blowouts.
Well types Special wells are often drilled: • for liquid waste products escape into unproductive absorbing layers, • for exploration and production of water, • geological structures preparation for underground gas storages and gas injection into them, • for elimination of oil and gas blowouts.
 Thank you for your attention Next lection will include next questions: Methods of Drilling
Thank you for your attention Next lection will include next questions: Methods of Drilling


