Lecture 11 (11-12).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Lecture 1 1 1901 -1936
Lecture 1 1 1901 -1936
 - Edwardian Britain was the wealthiest country in the world and the biggest investor - the Boer War (the South African War) (18991902); Transvaal Orange Free Natal State the Cape Colony (GB) - the Boer War was the first time the concentration camps were created (to keep th civilians from helping the Boer soldiers) Edward VII (1901 -1910 )
- Edwardian Britain was the wealthiest country in the world and the biggest investor - the Boer War (the South African War) (18991902); Transvaal Orange Free Natal State the Cape Colony (GB) - the Boer War was the first time the concentration camps were created (to keep th civilians from helping the Boer soldiers) Edward VII (1901 -1910 )
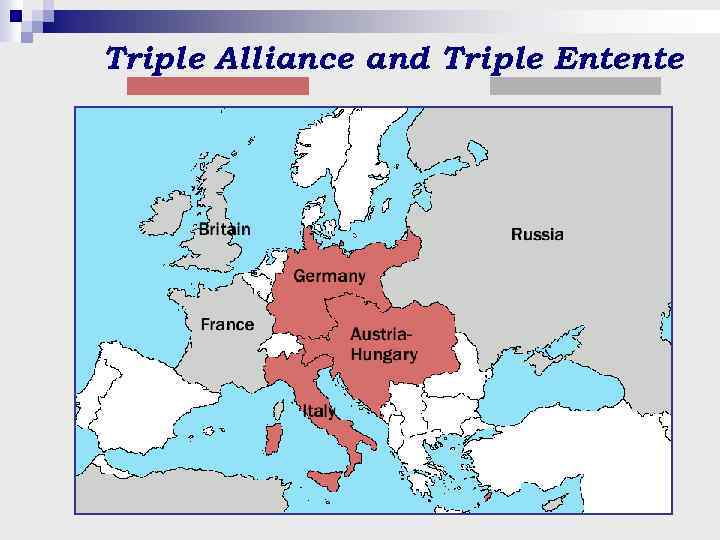 Triple Alliance and Triple Entente
Triple Alliance and Triple Entente
 Australia: The Stolen Generations Rabbit-Proof Fence (a film based on the real events of the time)
Australia: The Stolen Generations Rabbit-Proof Fence (a film based on the real events of the time)
 Labour Party origins James Hardie the 1 st Labour Party leader - in 1900 the TUC established the Labour Representation Committee (LRC) – it was renamed the Labour Party in 1906; - in 1903 the Labourites formed a pact with the Liberals not to contest in the constituencies where the Conservatives had much influence; - Parliament Act of 1911 (any bill passed unchanged by the House of Commons in 3 separate sessions ove 2 years could be presented for the royal assent (necessary for a bill to become law) without the House of Lords’ consent; - in 1911 salaries were instituted fo the MPs, which led many Trades Herbert Asquith Unionists and Labourites be elected a liberal PM into the Commons (1908 -1916)
Labour Party origins James Hardie the 1 st Labour Party leader - in 1900 the TUC established the Labour Representation Committee (LRC) – it was renamed the Labour Party in 1906; - in 1903 the Labourites formed a pact with the Liberals not to contest in the constituencies where the Conservatives had much influence; - Parliament Act of 1911 (any bill passed unchanged by the House of Commons in 3 separate sessions ove 2 years could be presented for the royal assent (necessary for a bill to become law) without the House of Lords’ consent; - in 1911 salaries were instituted fo the MPs, which led many Trades Herbert Asquith Unionists and Labourites be elected a liberal PM into the Commons (1908 -1916)
 George V (1910 -1936)
George V (1910 -1936)
 The Suffrage Movement - in 1903 Emmeline. Pankhurst together with her daughters founded the Women’s Social and Political Union (WSPU), a militant organisation for the universal women’s enfranchisement Emmeline Pankhurst a 1908 WSPU meeting forcefeeding
The Suffrage Movement - in 1903 Emmeline. Pankhurst together with her daughters founded the Women’s Social and Political Union (WSPU), a militant organisation for the universal women’s enfranchisement Emmeline Pankhurst a 1908 WSPU meeting forcefeeding
 Great Britain in WWI British recruits August 1914 Troops landing at Gallipoli 1915 West Front Battles: 1915 Marne 1916 Somme 1916 Jutland Dardanelles Battles: 1915 Gallipoli Campaign
Great Britain in WWI British recruits August 1914 Troops landing at Gallipoli 1915 West Front Battles: 1915 Marne 1916 Somme 1916 Jutland Dardanelles Battles: 1915 Gallipoli Campaign
 - on June 28, 1919 the sides signed the Treaty of Versailles David Lloyd George PM (1916 -1922)
- on June 28, 1919 the sides signed the Treaty of Versailles David Lloyd George PM (1916 -1922)
 Canada in WWI 1917: Battle of Passchendaele Battle of Ypres (1915) Battle of the Somme (1916) 1918: Canada’s 1000 days Battle of the Vimy Ridge
Canada in WWI 1917: Battle of Passchendaele Battle of Ypres (1915) Battle of the Somme (1916) 1918: Canada’s 1000 days Battle of the Vimy Ridge
 Australia in WWI ANZAC (Australian and New Zealand Armed Corps) 1918: Hamel Spur, Hindenburg Line 1915 Gallipoli Campaign 1916 Bullercourt. Messines , 1917 Passchendaele
Australia in WWI ANZAC (Australian and New Zealand Armed Corps) 1918: Hamel Spur, Hindenburg Line 1915 Gallipoli Campaign 1916 Bullercourt. Messines , 1917 Passchendaele
 New Zealand in WWI 1915 Gallipoli Campaign 1916 Somme NZEF buckle NZEF (New Zealand Expeditionary Forces) took Western Samoa from Germany and administered it till 1962
New Zealand in WWI 1915 Gallipoli Campaign 1916 Somme NZEF buckle NZEF (New Zealand Expeditionary Forces) took Western Samoa from Germany and administered it till 1962
 Women’s Movement progress - WWI created many more opportunities for the British women to work outside home; - black women found jobs in industry; - in the 1920 s contraception became widespread; - the 1918 Reform Act gave women over 30 the right to vote and run for Parliament; it also granted vote to all men over 21; - in 1919 a Conservative Nancy Astor was elected into the Commons – the 1 st woman in British Parliament; - in 1928 the British women were given full voting rights Nancy Astor
Women’s Movement progress - WWI created many more opportunities for the British women to work outside home; - black women found jobs in industry; - in the 1920 s contraception became widespread; - the 1918 Reform Act gave women over 30 the right to vote and run for Parliament; it also granted vote to all men over 21; - in 1919 a Conservative Nancy Astor was elected into the Commons – the 1 st woman in British Parliament; - in 1928 the British women were given full voting rights Nancy Astor
 General Strike 1926 Ramsay Macdonald a Labour. PM (1924; 1929 -1931; 1931 - Great Depression 1929 -1932 1935)
General Strike 1926 Ramsay Macdonald a Labour. PM (1924; 1929 -1931; 1931 - Great Depression 1929 -1932 1935)
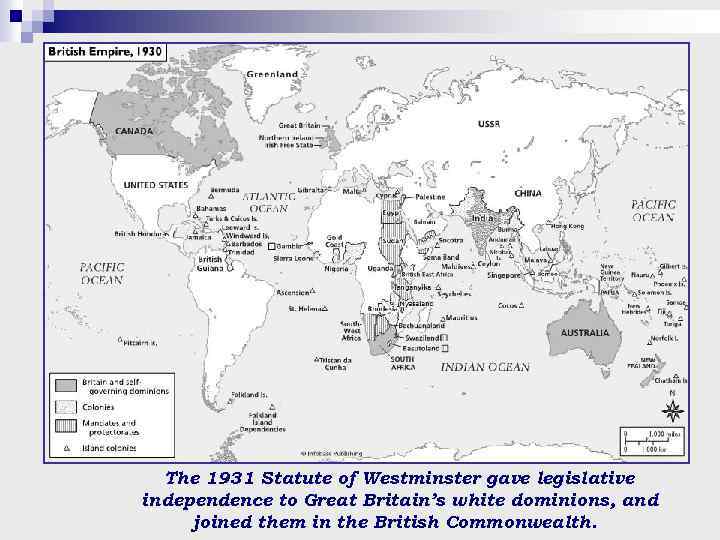 The 1931 Statute of Westminster gave legislative independence to Great Britain’s white dominions, and joined them in the British Commonwealth.
The 1931 Statute of Westminster gave legislative independence to Great Britain’s white dominions, and joined them in the British Commonwealth.
 Edward VIII(1936) and Wallis Simpson George VI (1936 -1952)
Edward VIII(1936) and Wallis Simpson George VI (1936 -1952)
 British Prose Arthur Conan Doyle the Sherlock Holmes series Joseph Conrad Nostromo Dorothy Sayers Strong Poison Kenneth Graham The Wind in the Willows Katherine Mansfield short stories writer Virginia Woolf Mrs Dalloway James Joyce The Dubliners John Galsworthy The Forsyte. Saga
British Prose Arthur Conan Doyle the Sherlock Holmes series Joseph Conrad Nostromo Dorothy Sayers Strong Poison Kenneth Graham The Wind in the Willows Katherine Mansfield short stories writer Virginia Woolf Mrs Dalloway James Joyce The Dubliners John Galsworthy The Forsyte. Saga
 British Prose Aldous Huxley Brave New World Evelyn Waugh A Handful of Dust G. K. Chesterton The Man Who Was Thursday D. H. Lawrence Sons and Lovers Enid Blyton Child Whispers Alan Milne Winnie -the-Pooh P. G. Wodehouse Jeeves Takes Charge Hugh Lofting Dr Doolitle series
British Prose Aldous Huxley Brave New World Evelyn Waugh A Handful of Dust G. K. Chesterton The Man Who Was Thursday D. H. Lawrence Sons and Lovers Enid Blyton Child Whispers Alan Milne Winnie -the-Pooh P. G. Wodehouse Jeeves Takes Charge Hugh Lofting Dr Doolitle series
 British Poetry William Butler Yeats The Winding Stair Thomas Stearns Eliot The Waste Land Wilfred Owen a war poet Siegfried Sassoon a war poet
British Poetry William Butler Yeats The Winding Stair Thomas Stearns Eliot The Waste Land Wilfred Owen a war poet Siegfried Sassoon a war poet
 British Theatre Augusta Gregory a Seven Short Plays collection William Butler Yeats Deirdre Sean O’Casey The Shadow of a Gunman James M. Barrie Peter Pan, the Boy Who Wouldn’t Grow Up
British Theatre Augusta Gregory a Seven Short Plays collection William Butler Yeats Deirdre Sean O’Casey The Shadow of a Gunman James M. Barrie Peter Pan, the Boy Who Wouldn’t Grow Up
 British Art (pictorialism ) Zonnebeke William Orpen Lily Carstairs Bath Self- ortait P
British Art (pictorialism ) Zonnebeke William Orpen Lily Carstairs Bath Self- ortait P
 British Art (vorticism ) Self-Portrait Wyndham Lewis Creditors Vorticist Composition Workshop A Battery Shelled
British Art (vorticism ) Self-Portrait Wyndham Lewis Creditors Vorticist Composition Workshop A Battery Shelled
 British Art (vorticism ) the Rock Drill sculpture Jacob Epstein Nan Christ in Majesty the tomb of Oscar Wilde
British Art (vorticism ) the Rock Drill sculpture Jacob Epstein Nan Christ in Majesty the tomb of Oscar Wilde
 British Art (the Bloomsbury Group) Dora Carrington Flowering Cactus The Mill at Tidmarsh Mountain Church, Larrau The Spanish Boy
British Art (the Bloomsbury Group) Dora Carrington Flowering Cactus The Mill at Tidmarsh Mountain Church, Larrau The Spanish Boy
 British Art (modernism) White Relief Ben Nicholson Porthmeor Window Porthmeor Beach, St Ives
British Art (modernism) White Relief Ben Nicholson Porthmeor Window Porthmeor Beach, St Ives
 British Art (surrealism) Stanley. Hayter Confluence Runner Cronos Prestige of the Insect
British Art (surrealism) Stanley. Hayter Confluence Runner Cronos Prestige of the Insect
 British Music Ethel Smyth composer The Wreckers March of the Women The Boatswain’s Mate William Walton composer Ralph Vaughan Williams composer Belshazzar’s. Feast music for Edith Sitwell’spoems Sea Symphony Sinfonia Antarctica Riders to the Sea (opera)
British Music Ethel Smyth composer The Wreckers March of the Women The Boatswain’s Mate William Walton composer Ralph Vaughan Williams composer Belshazzar’s. Feast music for Edith Sitwell’spoems Sea Symphony Sinfonia Antarctica Riders to the Sea (opera)
 British Cinema Alfred Hitchcock Basil Rathbone Charles Chaplin Peggy Ashcroft Leslie Howard Vivien Leigh
British Cinema Alfred Hitchcock Basil Rathbone Charles Chaplin Peggy Ashcroft Leslie Howard Vivien Leigh
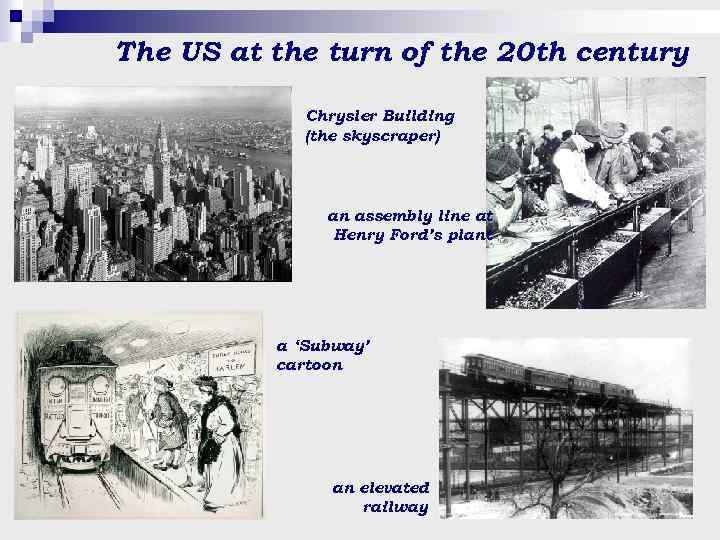 The US at the turn of the 20 th century Chrysler Building (the skyscraper) an assembly line at Henry Ford’s plant a ‘Subway’ cartoon an elevated railway
The US at the turn of the 20 th century Chrysler Building (the skyscraper) an assembly line at Henry Ford’s plant a ‘Subway’ cartoon an elevated railway
 Immigration and living conditions
Immigration and living conditions
 - trusts and syndicates in fact ruled the US; - Progressivism; - Progressives demanded anti-trust laws and state control over vital industries (railroad, energy, munitions, etc. ), more open politics an an end to corruption; - a ‘muckracker– a Progressive journalist who ’ openly wrote about the ills of the society; - Roosevelt supported the Progressives; - more than 20 trials against trusts; - the Panama Canal (1904 -1914); Theodore Roosevelt 26 th US President (1901 -1909) - the Russo-Japanese War (1904 -1905)
- trusts and syndicates in fact ruled the US; - Progressivism; - Progressives demanded anti-trust laws and state control over vital industries (railroad, energy, munitions, etc. ), more open politics an an end to corruption; - a ‘muckracker– a Progressive journalist who ’ openly wrote about the ills of the society; - Roosevelt supported the Progressives; - more than 20 trials against trusts; - the Panama Canal (1904 -1914); Theodore Roosevelt 26 th US President (1901 -1909) - the Russo-Japanese War (1904 -1905)
 - continued Roosevelt’s reforms; - in 1913 the 16 th (the introduction of a federal income tax), and 17 th (direct election of US senators) Amendments were ratified; - child labour and working weeks duration were restricted; - workers’ were provided with a compensations in case of a working accident or job-related illness; - Oklahoma (1907), Arizona and New Mexico (1913) were added to the US; - ‘Dollar Diplomacy’ – investing in a country’s trade or banks to control its politics afterwards William Howard Taft 27 th US President (1909 -1913)
- continued Roosevelt’s reforms; - in 1913 the 16 th (the introduction of a federal income tax), and 17 th (direct election of US senators) Amendments were ratified; - child labour and working weeks duration were restricted; - workers’ were provided with a compensations in case of a working accident or job-related illness; - Oklahoma (1907), Arizona and New Mexico (1913) were added to the US; - ‘Dollar Diplomacy’ – investing in a country’s trade or banks to control its politics afterwards William Howard Taft 27 th US President (1909 -1913)
 - when the Great War (World War I) began in 1914, Wilson supported the policy of strict neutrality (military only for the US still continued trading with the Allies and supplying them with food and munitions); - in 1915 -1917 German submarines drowned several US vessels; - on April 6, 1917 the US declared war on Germany; - May 1917: mobilisation begins; - June 1917: first US troops arrive in France; - 1917 -1918: the American troops fight several battles in France; Woodrow Wilson - the US Senate didn’t ratify the Treaty of Versailles, so the US could not join US President the League of Nations Thomas 28 th (1913 -1921)
- when the Great War (World War I) began in 1914, Wilson supported the policy of strict neutrality (military only for the US still continued trading with the Allies and supplying them with food and munitions); - in 1915 -1917 German submarines drowned several US vessels; - on April 6, 1917 the US declared war on Germany; - May 1917: mobilisation begins; - June 1917: first US troops arrive in France; - 1917 -1918: the American troops fight several battles in France; Woodrow Wilson - the US Senate didn’t ratify the Treaty of Versailles, so the US could not join US President the League of Nations Thomas 28 th (1913 -1921)
 ‘Post-war’ US: Prohibition and Women’s votes an anti-smuggling raid women voting in New York - the US turned from the world’s debtor to the creditor; - in 1920 the 18 th Amendment was ratified, which introduced the ‘dry law’ – a complete prohibition to produce and consume alcohol in the US; - ‘moonshine’ – home-made alcohol; - a ‘speakeasy’ – an illegal place during the Prohibition years where people could find drinks; - in 1920 women in all US states finally gained the right to vote; - after the Great War American women were encouraged to drop their jobs and return to the housekeeping
‘Post-war’ US: Prohibition and Women’s votes an anti-smuggling raid women voting in New York - the US turned from the world’s debtor to the creditor; - in 1920 the 18 th Amendment was ratified, which introduced the ‘dry law’ – a complete prohibition to produce and consume alcohol in the US; - ‘moonshine’ – home-made alcohol; - a ‘speakeasy’ – an illegal place during the Prohibition years where people could find drinks; - in 1920 women in all US states finally gained the right to vote; - after the Great War American women were encouraged to drop their jobs and return to the housekeeping
 ‘Post-war’ US: race issues - NAACP – National Association for Advancement of Colored. People; - NAACP was formed in 1909 and worked to improve the blacks’ living and fought for their rights; - Ku Klux Klan revived after the Great War, about 3 to 8 million people joined it against the blacks, Catholics, immigrants, and Jews; - Marcus Garvey; - the Harlem Renaissance – a cultural movement in Manhattan; - in 1921 the Emergency Quota Act was passed that curtailed the levels of immigration: Northern Europeans were preferred, the Asians were denied entrance completely Claude Mc. Kay Langston Hughes Zora. Neale Hurston
‘Post-war’ US: race issues - NAACP – National Association for Advancement of Colored. People; - NAACP was formed in 1909 and worked to improve the blacks’ living and fought for their rights; - Ku Klux Klan revived after the Great War, about 3 to 8 million people joined it against the blacks, Catholics, immigrants, and Jews; - Marcus Garvey; - the Harlem Renaissance – a cultural movement in Manhattan; - in 1921 the Emergency Quota Act was passed that curtailed the levels of immigration: Northern Europeans were preferred, the Asians were denied entrance completely Claude Mc. Kay Langston Hughes Zora. Neale Hurston
 ‘The Roaring Twenties’ flappers a jazz-band at a bootlegger’s Al Capone - mass production made goods cheap and affordable to all; - life conditions improved with cheap electricity, cars, and public works); - salaries rose by 25%; - by 1929 the US population reached 122 million; - the level of unemployment didn't exceed 5%; - Hollywood was on the rise as many European actors left the post-war Europe in the hope of a better life in the US; - the Prohibition of alcohol led to much bootlegging, smuggling, and, eventually, to the appearance of mafia
‘The Roaring Twenties’ flappers a jazz-band at a bootlegger’s Al Capone - mass production made goods cheap and affordable to all; - life conditions improved with cheap electricity, cars, and public works); - salaries rose by 25%; - by 1929 the US population reached 122 million; - the level of unemployment didn't exceed 5%; - Hollywood was on the rise as many European actors left the post-war Europe in the hope of a better life in the US; - the Prohibition of alcohol led to much bootlegging, smuggling, and, eventually, to the appearance of mafia
 The Great Depression (1929 -1933) - in 1926, recession began in the US; - in 1929 the Wall Street Crash led to multiple bankruptcies; - during the Great Depression the US industrial production fell 50% and exports 70%; - unemployment reached 23%; - marches and demonstrations; - Hoover persuaded employers to keep wages, increased spending on building roads, bridges and public buildings, but he refused to introduce federal unemployment relief Herbert Hoover 31 st US President (1929 -1933)
The Great Depression (1929 -1933) - in 1926, recession began in the US; - in 1929 the Wall Street Crash led to multiple bankruptcies; - during the Great Depression the US industrial production fell 50% and exports 70%; - unemployment reached 23%; - marches and demonstrations; - Hoover persuaded employers to keep wages, increased spending on building roads, bridges and public buildings, but he refused to introduce federal unemployment relief Herbert Hoover 31 st US President (1929 -1933)
 The Great Depression (1929 -1933) - the ‘New Deal’ policy - laws that regulated the economy; - by 1938 the unemployment fell to 17. 4%; - the Fair Labor Standards Act established a minimum wage and maximum work hours. Franklin Roosevelt 32 nd US President (1933 -1945)
The Great Depression (1929 -1933) - the ‘New Deal’ policy - laws that regulated the economy; - by 1938 the unemployment fell to 17. 4%; - the Fair Labor Standards Act established a minimum wage and maximum work hours. Franklin Roosevelt 32 nd US President (1933 -1945)
 American Prose Scott F. Fitzgerald The Great Gatsby Ernest Hemingway A Farewell to Arms William Faulkne Absalom! Absalom John Steinbeck The Grapes of Wrath Theodore Dreiser Sister Carrie Edith Wharton The Age of Innocence Sherwood Anderson Death in the Woods Upton Sinclair Oil! Sinclair Lewis Babbit
American Prose Scott F. Fitzgerald The Great Gatsby Ernest Hemingway A Farewell to Arms William Faulkne Absalom! Absalom John Steinbeck The Grapes of Wrath Theodore Dreiser Sister Carrie Edith Wharton The Age of Innocence Sherwood Anderson Death in the Woods Upton Sinclair Oil! Sinclair Lewis Babbit
 American Poetry and Theatre Ezra Pound Hugh Selwyn. Mauberley Robert Frost North of Boston Eugene O’Neil Mourning Becomes Electra
American Poetry and Theatre Ezra Pound Hugh Selwyn. Mauberley Robert Frost North of Boston Eugene O’Neil Mourning Becomes Electra
 American Art: Ashcan School Robert Henri Snow in New York Tam Gan Mary Agnes
American Art: Ashcan School Robert Henri Snow in New York Tam Gan Mary Agnes
 American Art: Precisionism Charles. Demuth Sail in Two Movements Trees and Barns, Bermuda Incense of a New Church
American Art: Precisionism Charles. Demuth Sail in Two Movements Trees and Barns, Bermuda Incense of a New Church
 American Art: Photo-Secession a photo portrait of Georgia O’Keeffe Alfred. Stieglitz Dirigible
American Art: Photo-Secession a photo portrait of Georgia O’Keeffe Alfred. Stieglitz Dirigible
 American Art: American Realism After the War – a Medal and Maybe a Job John Sloan Mc. Sorley’s. Bar Self-Portrait
American Art: American Realism After the War – a Medal and Maybe a Job John Sloan Mc. Sorley’s. Bar Self-Portrait
 American Art: the Southwest Ram’s Head White Hollyhock and Little Hills Georgia O’Keeffe Blue and Green Music #13 Special
American Art: the Southwest Ram’s Head White Hollyhock and Little Hills Georgia O’Keeffe Blue and Green Music #13 Special
 American Music Jazz Blues Edward ‘Duke’ Ellington Satin Doll Sophisticated Lady William Handy St Louis Blues Memphis Blues Louis Armstrong West End Blues Bessie Smith Tain’t. Nobody’s Business If I Do
American Music Jazz Blues Edward ‘Duke’ Ellington Satin Doll Sophisticated Lady William Handy St Louis Blues Memphis Blues Louis Armstrong West End Blues Bessie Smith Tain’t. Nobody’s Business If I Do
 American Cinema Clark Gable Cary Grant Bette Davis Jean Harlow Rudolph Valentino Fred Astaire Greta. Garbo Joan Crawford
American Cinema Clark Gable Cary Grant Bette Davis Jean Harlow Rudolph Valentino Fred Astaire Greta. Garbo Joan Crawford
 American Animation Walt Disney
American Animation Walt Disney


