 Lec 27: Refrigeration 1
Lec 27: Refrigeration 1
 • For next time: – Class projects due Wednesday, December 3, 2003. • Outline: – Refrigeration cycle – Idealized cycle devices – Example • Important points: – Distinguish between heat pumps and refrigerators – Know what devices make up the refrigeration cycle. 2
• For next time: – Class projects due Wednesday, December 3, 2003. • Outline: – Refrigeration cycle – Idealized cycle devices – Example • Important points: – Distinguish between heat pumps and refrigerators – Know what devices make up the refrigeration cycle. 2
 Refrigeration affects many areas of your life • The obvious: – Refrigerator/Freezers allow food preservation – Air conditioning makes Texas inhabitable between July 4 and mid-September • Refrigerated fishing boats allow preservation of catch • Refrigerated trucks are used to ship fruits/meats • Refrigeration makes possible medical procedures that call for lowering body 3 temperatures
Refrigeration affects many areas of your life • The obvious: – Refrigerator/Freezers allow food preservation – Air conditioning makes Texas inhabitable between July 4 and mid-September • Refrigerated fishing boats allow preservation of catch • Refrigerated trucks are used to ship fruits/meats • Refrigeration makes possible medical procedures that call for lowering body 3 temperatures
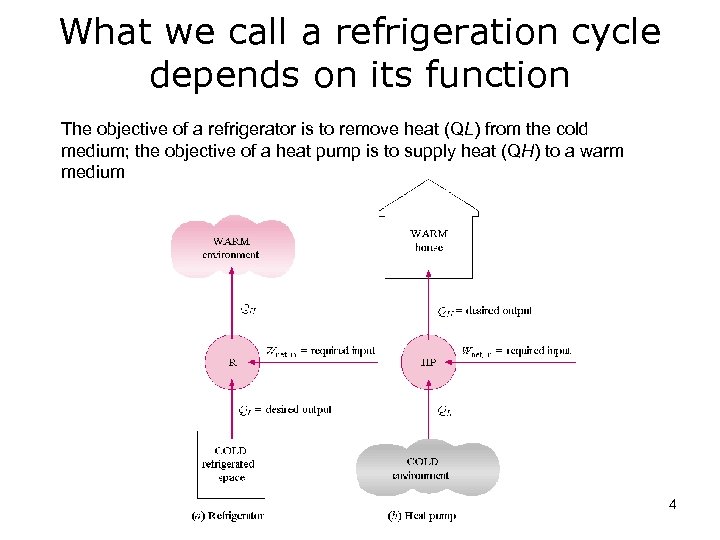 What we call a refrigeration cycle depends on its function The objective of a refrigerator is to remove heat (QL) from the cold medium; the objective of a heat pump is to supply heat (QH) to a warm medium 4
What we call a refrigeration cycle depends on its function The objective of a refrigerator is to remove heat (QL) from the cold medium; the objective of a heat pump is to supply heat (QH) to a warm medium 4
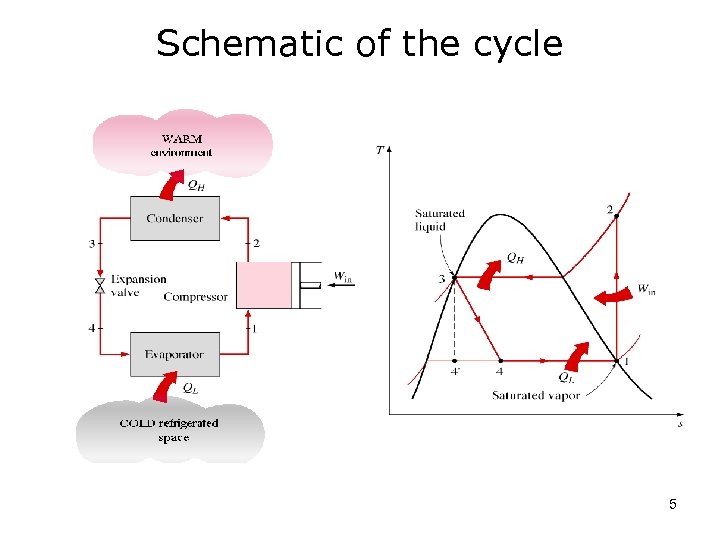 Schematic of the cycle 5
Schematic of the cycle 5
 Four processes in cycle • Isentropic compression (1 to 2) • Constant pressure condensation (2 to 3) • Isenhalpic expansion (3 to 4) • Constant pressure evaporation (4 to 1) 6
Four processes in cycle • Isentropic compression (1 to 2) • Constant pressure condensation (2 to 3) • Isenhalpic expansion (3 to 4) • Constant pressure evaporation (4 to 1) 6
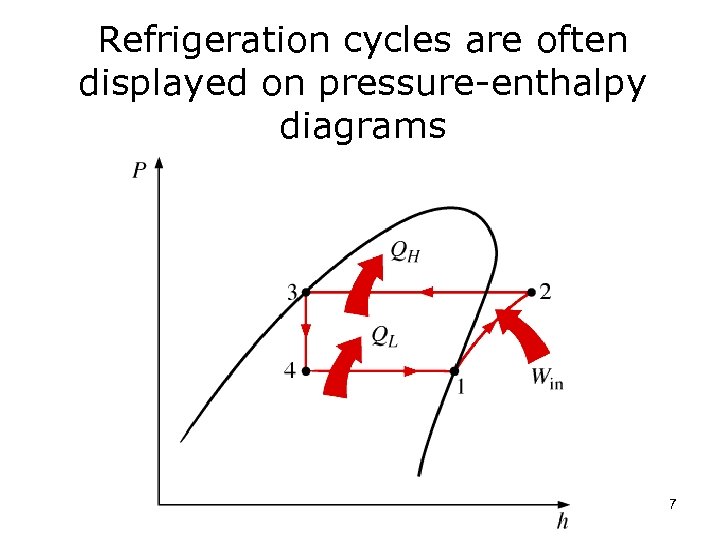 Refrigeration cycles are often displayed on pressure-enthalpy diagrams 7
Refrigeration cycles are often displayed on pressure-enthalpy diagrams 7
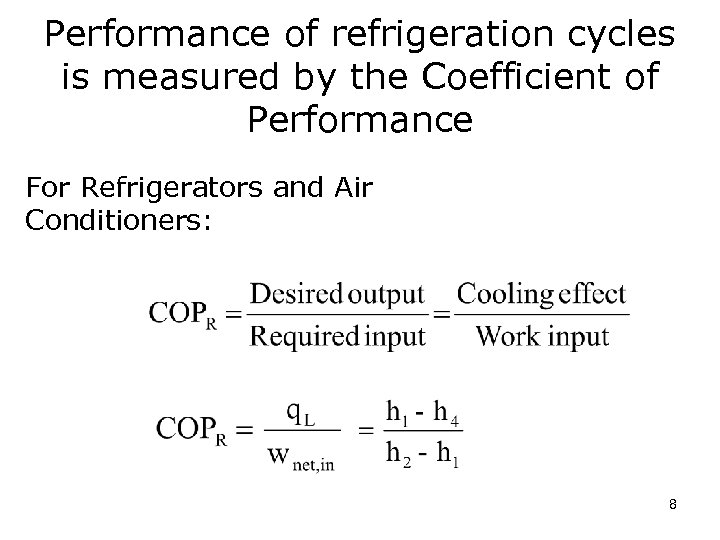 Performance of refrigeration cycles is measured by the Coefficient of Performance For Refrigerators and Air Conditioners: 8
Performance of refrigeration cycles is measured by the Coefficient of Performance For Refrigerators and Air Conditioners: 8
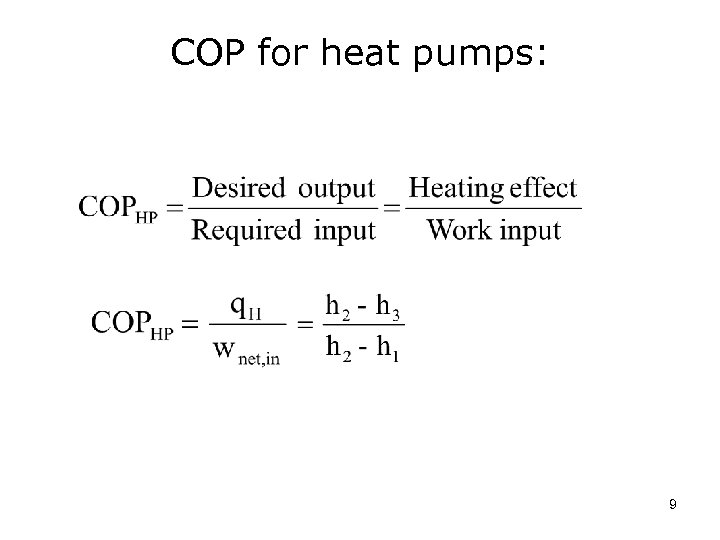 COP for heat pumps: 9
COP for heat pumps: 9
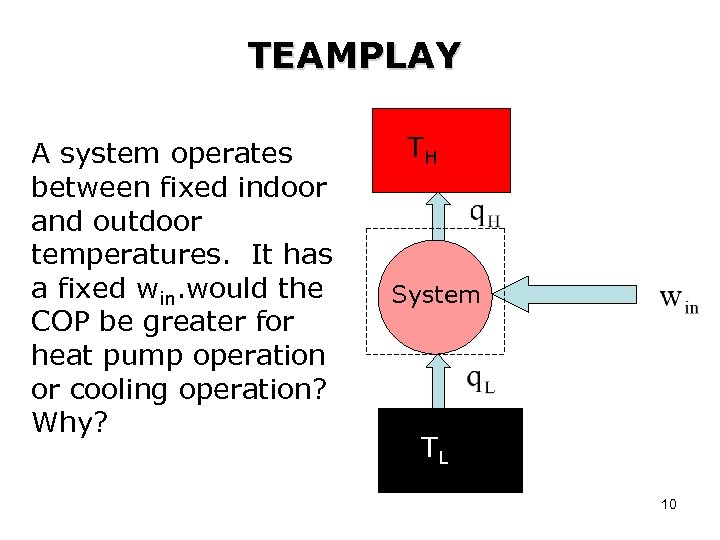 TEAMPLAY A system operates between fixed indoor and outdoor temperatures. It has a fixed win. would the COP be greater for heat pump operation or cooling operation? Why? TH System T TLL 10
TEAMPLAY A system operates between fixed indoor and outdoor temperatures. It has a fixed win. would the COP be greater for heat pump operation or cooling operation? Why? TH System T TLL 10
 TEAMPLAY • Show that the performance of a heat pump and a refrigerator are related by the expression COPHP = COPR + 1. 11
TEAMPLAY • Show that the performance of a heat pump and a refrigerator are related by the expression COPHP = COPR + 1. 11
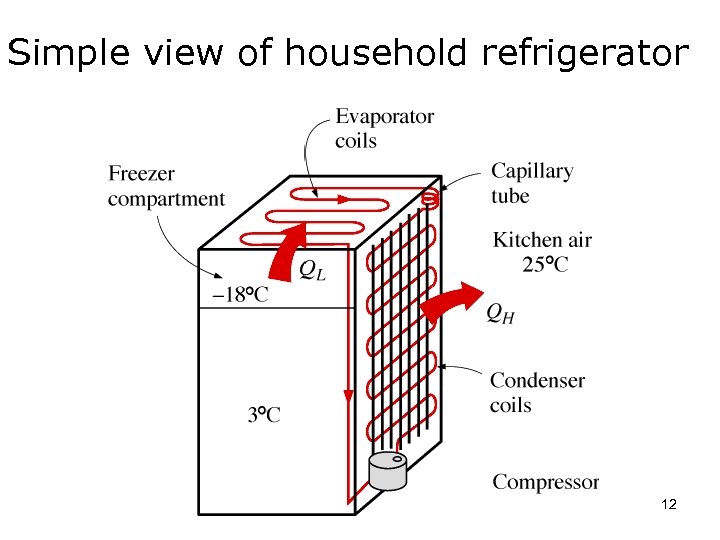 Simple view of household refrigerator 12
Simple view of household refrigerator 12
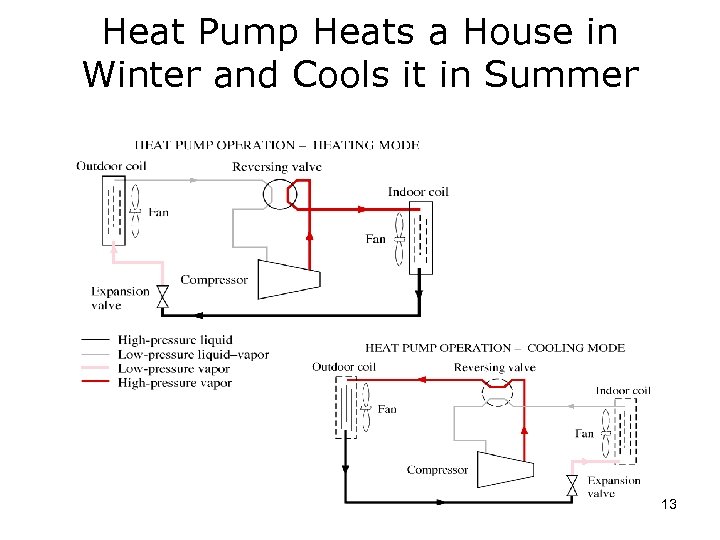 Heat Pump Heats a House in Winter and Cools it in Summer 13
Heat Pump Heats a House in Winter and Cools it in Summer 13
 TEAMPLAY Work Problem 8 -130 14
TEAMPLAY Work Problem 8 -130 14
 TEAMPLAY If the evaporating pressure were reduced to 0. 10 MPa in the previous problem, how would the following be affected (up, down, remain the same): • Evaporating Temperature? • Cooling capacity? • Work input to the compressor? Explain why. 15
TEAMPLAY If the evaporating pressure were reduced to 0. 10 MPa in the previous problem, how would the following be affected (up, down, remain the same): • Evaporating Temperature? • Cooling capacity? • Work input to the compressor? Explain why. 15