a24c210d04c26f5cdebc0a215072ac8b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali LECTURE 1 Office Management Tool - II INTRODUCTION TO DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali The database environment • To be able to function, an organisation needs information, e. g. – list of books in a library, – customer details in a retail business, – specifications of cars and their components for a car manufacturer • Information may be defined as data represented in a meaningful form. • Same data shown in different ways will provide different information to different viewers Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • A major requirement of any computer system is to store and retrieve data in a way that is meaningful to the end user – – so the core of any Information System is data, which is to be transformed into information through data modelling. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali Definitions • Data: – Meaningful facts, text, graphics, images, sound, video segments. • Database: – An organized collection of logically related data. • Information: – Data processed to be useful in decision making. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • Metadata: – Data that describes the properties or characteristics of other data. – Does not include sample data – Allows database designers and users to understand the meaning of the data Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali What is Databases? • Often abbreviated DB. • A database is a collection of related information. • A database is a collection of information that is organized so that it can easily be accessed, managed, and updated. – For example, a phone book is a database of names, addresses and phone numbers. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • A collection of information organized in such a way that a computer program can quickly select desired pieces of data. • You can think of a database as an electronic filing system Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

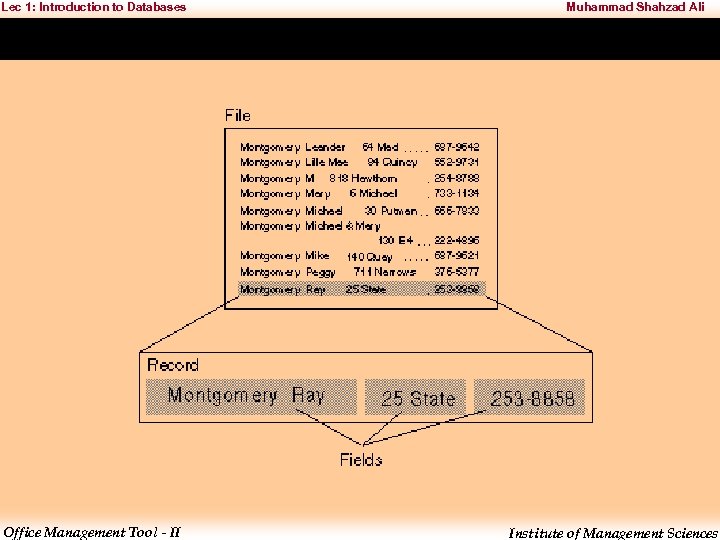
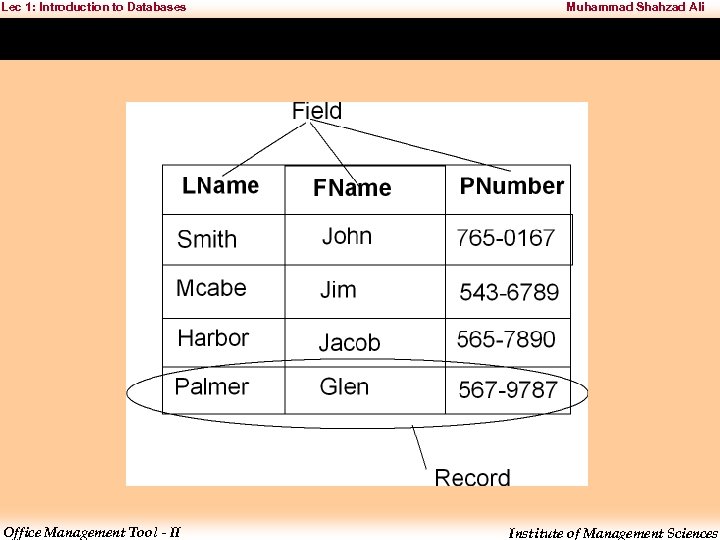
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • Traditional databases are organized by fields, records, and files. • A field is a single piece of information; – a record is one complete set of fields; and – a file is a collection of records. – For example, a telephone book is similar to a file. – It contains a list of records, each of which consists of three fields: name, address, and telephone number. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Office Management Tool - II Muhammad Shahzad Ali Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Office Management Tool - II Muhammad Shahzad Ali Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali Database Management System (DBMS) • To access information from a database, you need a database management system (DBMS). • This is a collection of programs that enables you to enter, organize, and select data in a database. OR • A Database Management System (DBMS) is a software tool that facilitates creating, maintaining, and manipulating an information database. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • DMBS is a collection of programs that enables you to store, modify, and extract information from a database. • There are many different types of DBMSs, ranging from small systems that run on personal computers to huge systems that run on mainframes. • The following are examples of database applications: – computerized library systems – automated teller machines – flight reservation systems Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • Requests for information from a database are made in the form of a query. • In fact, most of today's database systems are referred to as a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS), because of their ability to store related data across multiple tables. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) • A relational database management system (RDBMS) is a database management system (DBMS) that is based on the relational model as introduced by E. F. Codd. • Most popular databases currently in use are based on the relational database model. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • A short definition of an RDBMS is: – a DBMS in which data is stored in tables and the relationships among the data are also stored in tables. – The data can be accessed or reassembled in many different ways without having to change the table forms. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) • A relational database management system (RDBMS) is a program that lets you create, update, and administer a relational database. • Relational Database Management System a type of database management system (DBMS) that stores data in the form of related tables. • An important feature of relational systems is that a single database can be spread across several tables. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • Some of the more popular relational database management systems include: – Microsoft Access – Filemaker – Microsoft SQL Server – My. SQL – Oracle Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali What is Record? • In the context of a relational database, a row—also called a record or tuple—represents a single, structured data item in a table. • In simple terms, a database table can be thought of as consisting of rows and columns or fields. • Each row in a table represents a set of related data, and every row in the table has the same structure. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
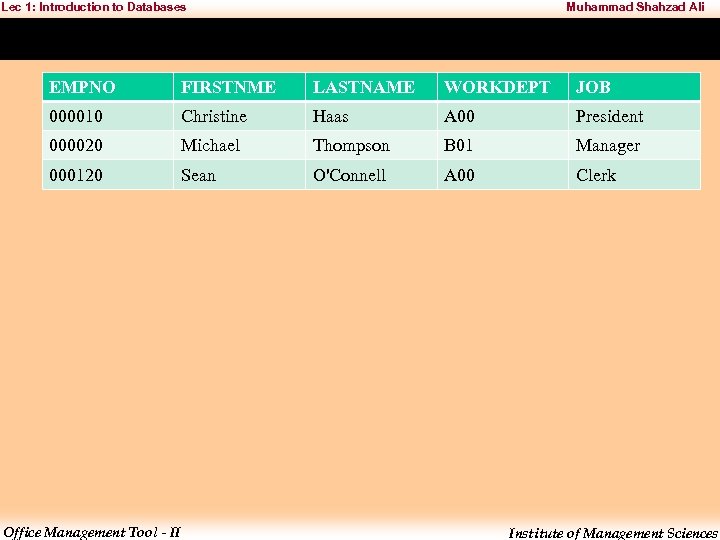
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali EMPNO FIRSTNME LASTNAME WORKDEPT JOB 000010 Christine Haas A 00 President 000020 Michael Thompson B 01 Manager 000120 Sean O'Connell A 00 Clerk Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali What is Entity? • The first step in developing a database design is to identify the types of data to be stored in database tables. • A database includes information about the entities in an organization or business, and their relationships to each other. • In a relational database, entities are represented as tables. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
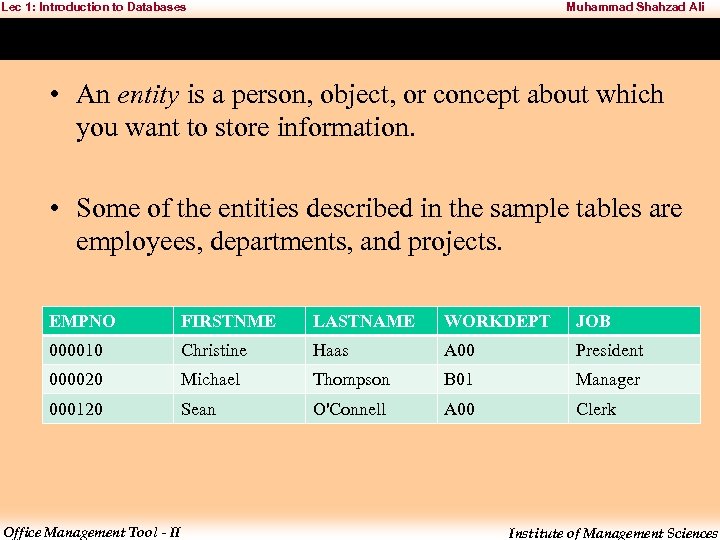
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • An entity is a person, object, or concept about which you want to store information. • Some of the entities described in the sample tables are employees, departments, and projects. EMPNO FIRSTNME LASTNAME WORKDEPT JOB 000010 Christine Haas A 00 President 000020 Michael Thompson B 01 Manager 000120 Sean O'Connell A 00 Clerk Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
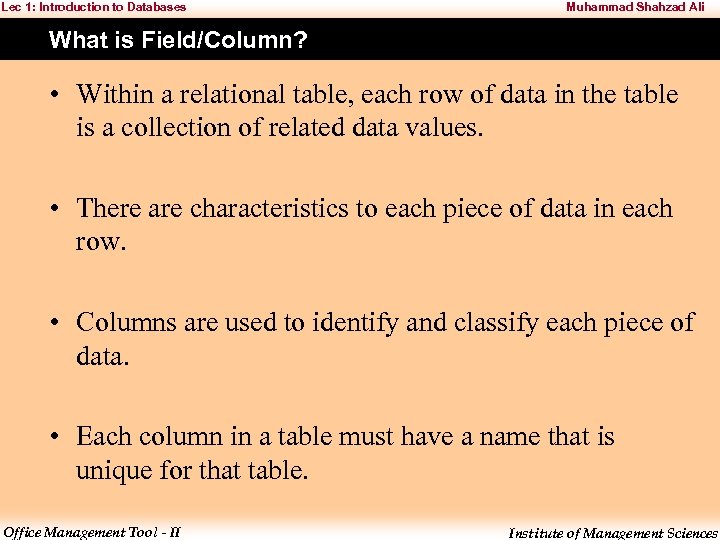
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali What is Field/Column? • Within a relational table, each row of data in the table is a collection of related data values. • There are characteristics to each piece of data in each row. • Columns are used to identify and classify each piece of data. • Each column in a table must have a name that is unique for that table. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • The data type and length specify the type of data and the maximum length that are valid for the column. • Data types may be chosen from those provided by the database manager or you may choose to create your own user-defined types. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali Database Applications • Banking: all transactions • Airlines: reservations, schedules • Universities: registration, grades • Sales: customers, products, purchases • Online retailers: order tracking, customized recommendations • Manufacturing: production, inventory, orders, supply chain • Human resources: employee records, salaries, tax deductions Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali Data Manipulation Language (DML) • Language for accessing and manipulating the data. • DML also known as query language. • Structured Query Language (SQL) is the most widely used query language. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
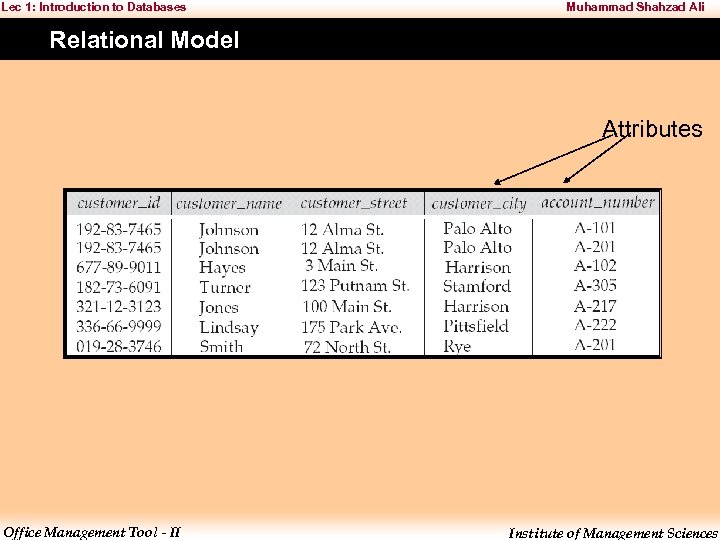
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali Relational Model Attributes Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
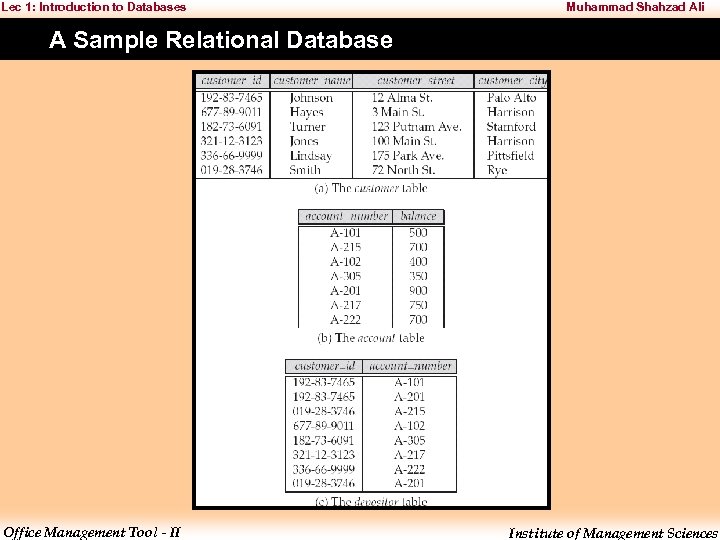
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali A Sample Relational Database Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
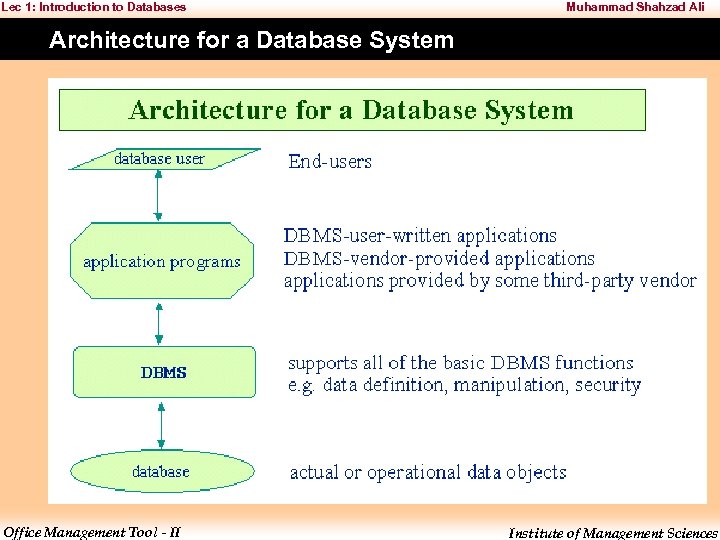
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali Architecture for a Database System Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
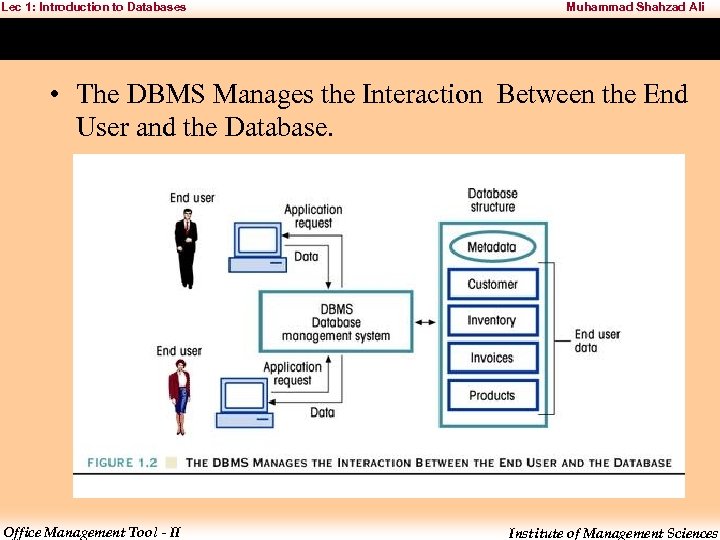
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • The DBMS Manages the Interaction Between the End User and the Database. Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali The Database System Components • Hardware – Computer – Peripherals • Software – Operating systems software – DBMS software – Applications programs and utilities software Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • People – Systems administrators – Database administrators (DBAs) – Database designers – Systems analysts and programmers – End users Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • Procedures – Instructions and rules that govern the design and use of the database system • Data – Collection of facts stored in the database Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali Types of Database Systems • Number of Users – Single-user • Desktop database – Multiuser • Workgroup database • Enterprise database Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences

Lec 1: Introduction to Databases Muhammad Shahzad Ali • Location – Centralized – Distributed • Use – Transactional (Production) – Decision support – Data warehouse Office Management Tool - II Institute of Management Sciences
a24c210d04c26f5cdebc0a215072ac8b.ppt