a0380062ca7f55d84f4a8233dbf0a84f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60

Leasing Is Good Business presentation to Rating Agencies September 24, 2003

Leasing Is Good Business • Industry Overview: – 2002 SIA – Piper Jaffrey Report • Current Real Time Performance Metrics • Large Company Performance / Values and Consolidation • Funding Experiences • CP Conduits and Securitization Experiences • Current Industry Performance Issues

Industry Overview: • 2002 ELA SIA • Piper Jaffrey Report

Highlights from ELA Survey of Industry Activity
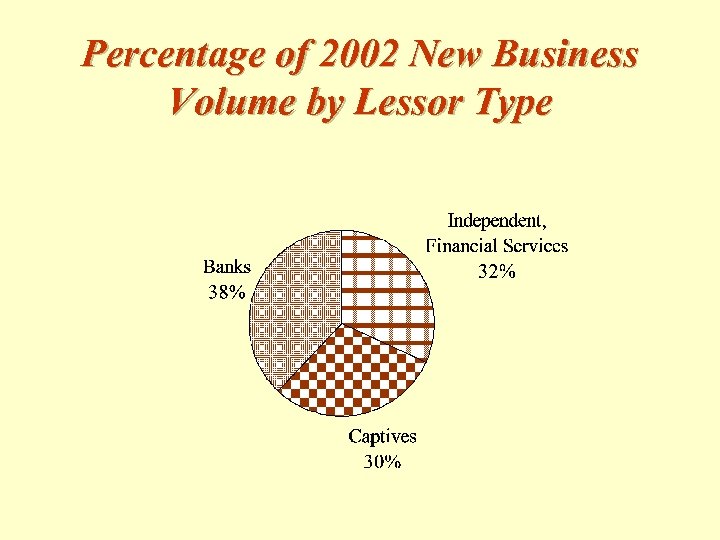
Percentage of 2002 New Business Volume by Lessor Type
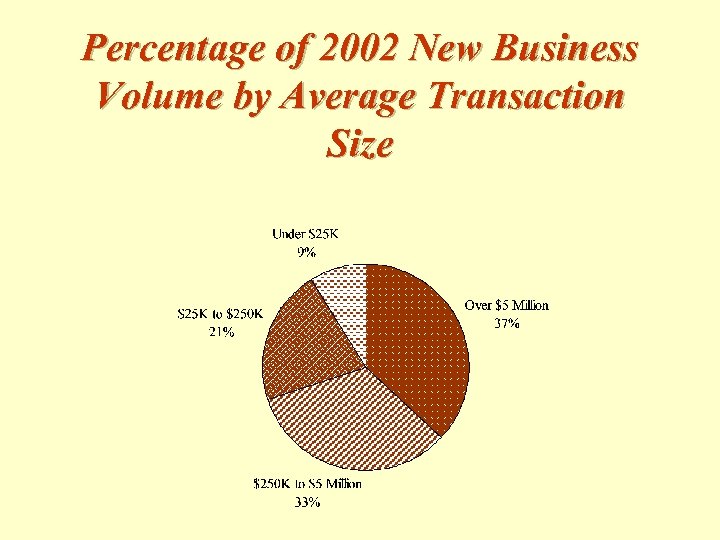
Percentage of 2002 New Business Volume by Average Transaction Size
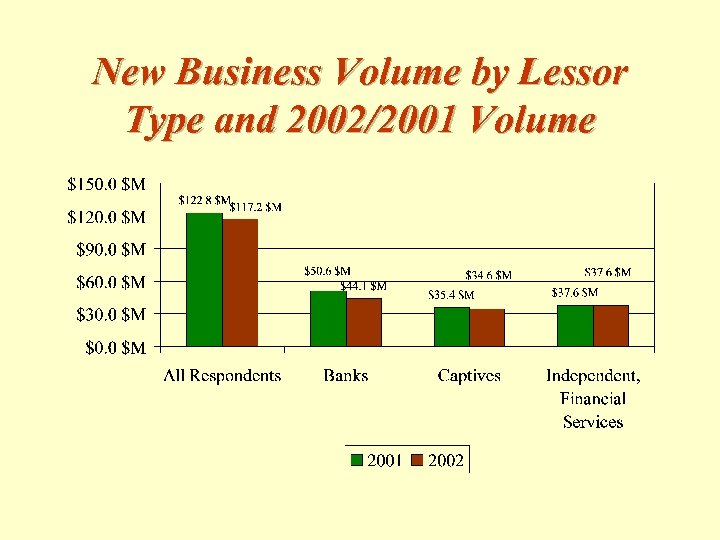
New Business Volume by Lessor Type and 2002/2001 Volume
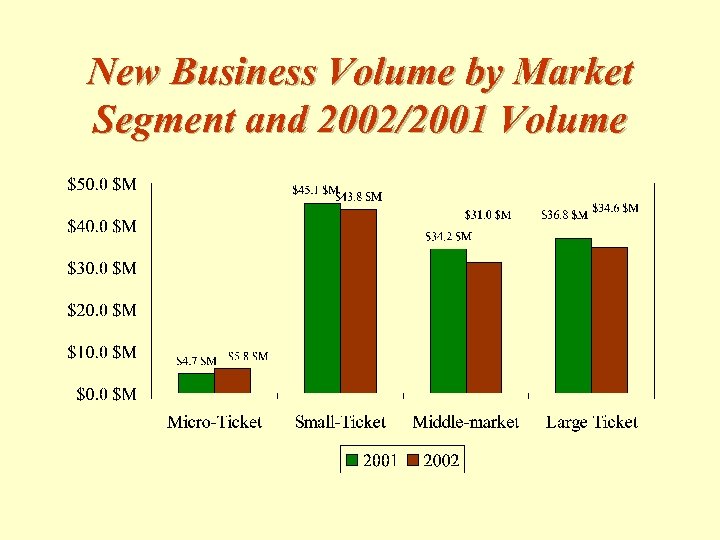
New Business Volume by Market Segment and 2002/2001 Volume
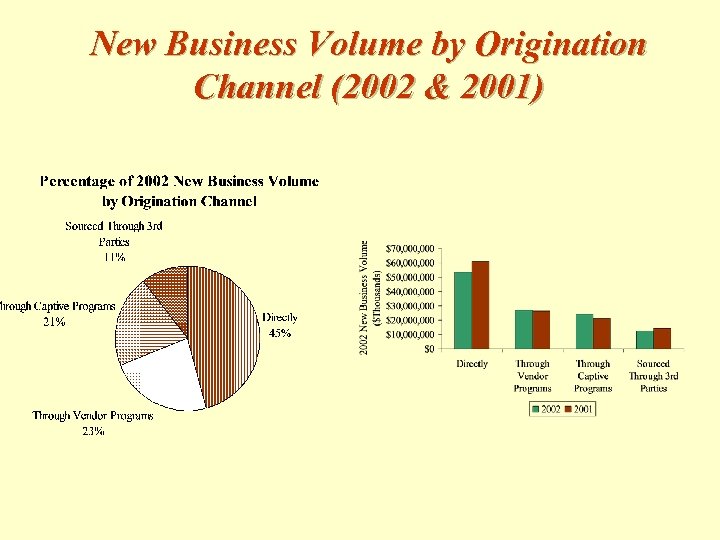
New Business Volume by Origination Channel (2002 & 2001)
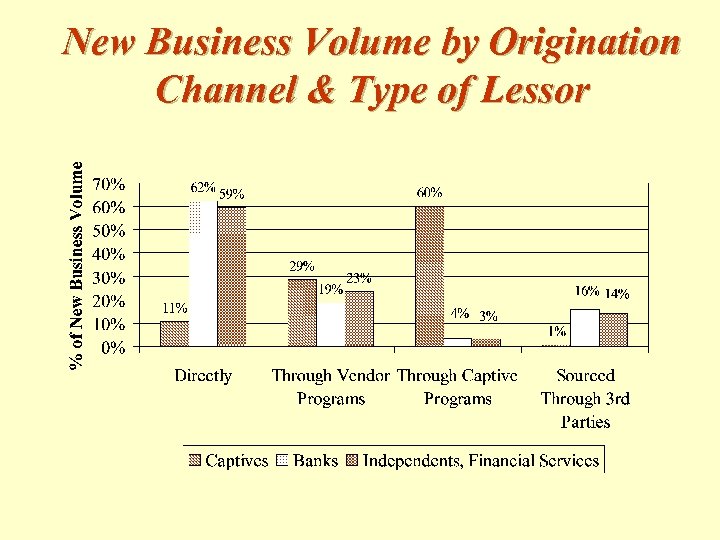
New Business Volume by Origination Channel & Type of Lessor
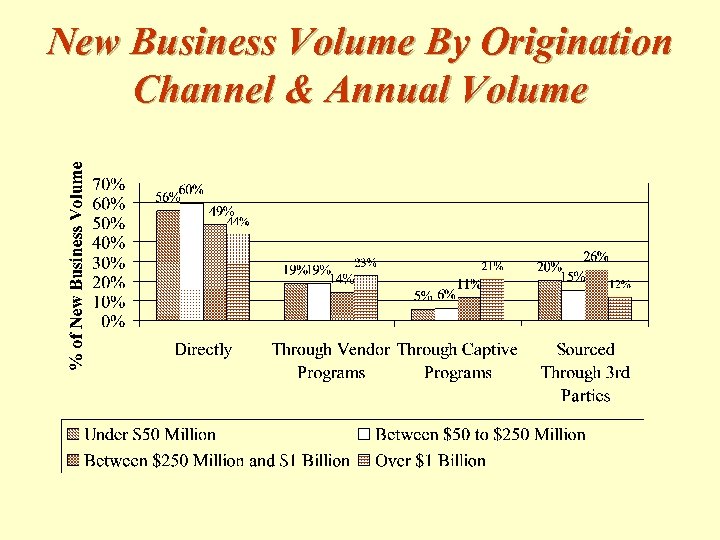
New Business Volume By Origination Channel & Annual Volume
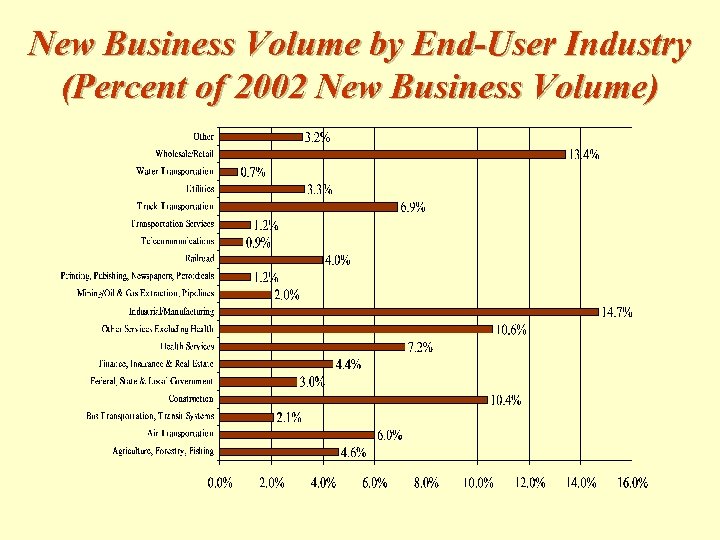
New Business Volume by End-User Industry (Percent of 2002 New Business Volume)
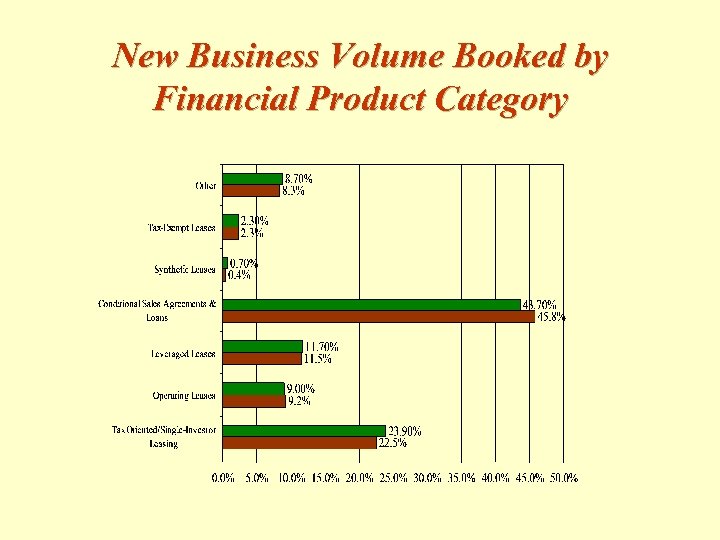
New Business Volume Booked by Financial Product Category

COMPANY PERFORMANCE
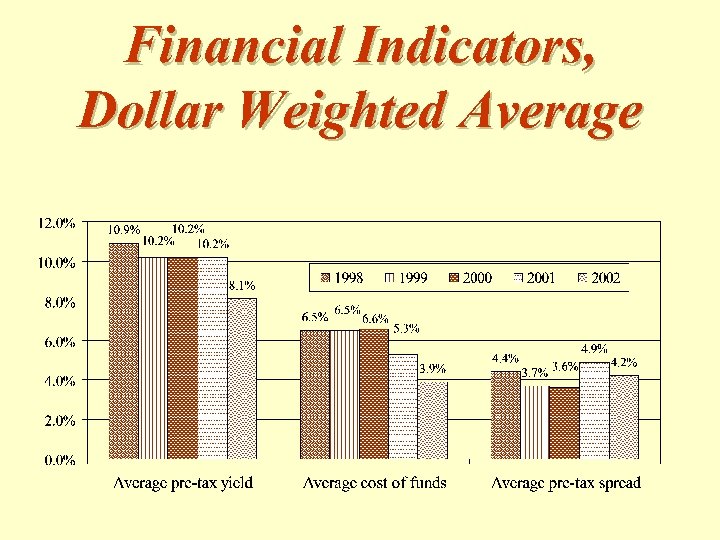
Financial Indicators, Dollar Weighted Average
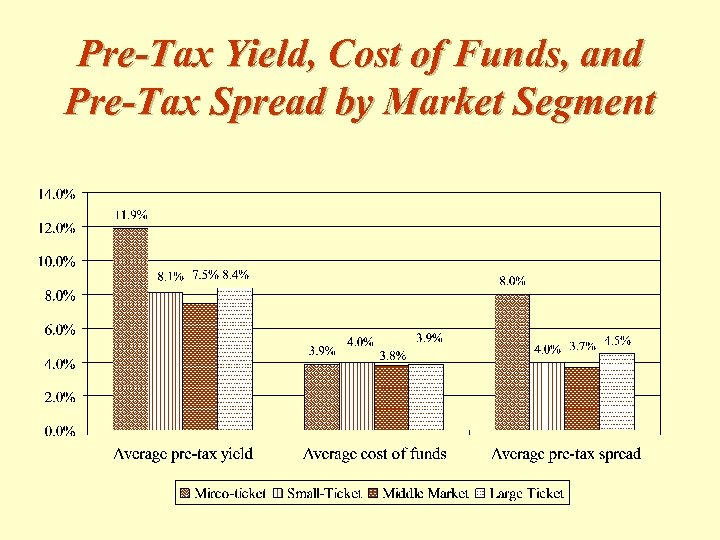
Pre-Tax Yield, Cost of Funds, and Pre-Tax Spread by Market Segment

Pre-Tax Yield, Cost of Funds & Pre. Tax Spread, Dollar Weighted Average
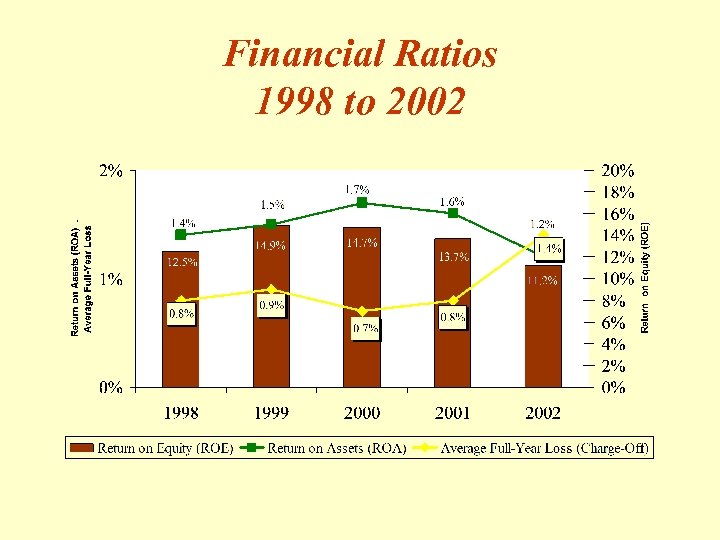
Financial Ratios 1998 to 2002
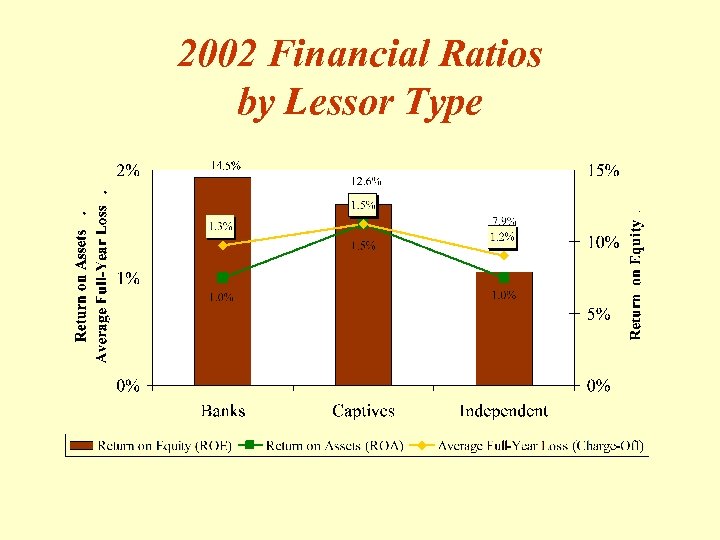
2002 Financial Ratios by Lessor Type

2002 Financial Ratios by Market Segment
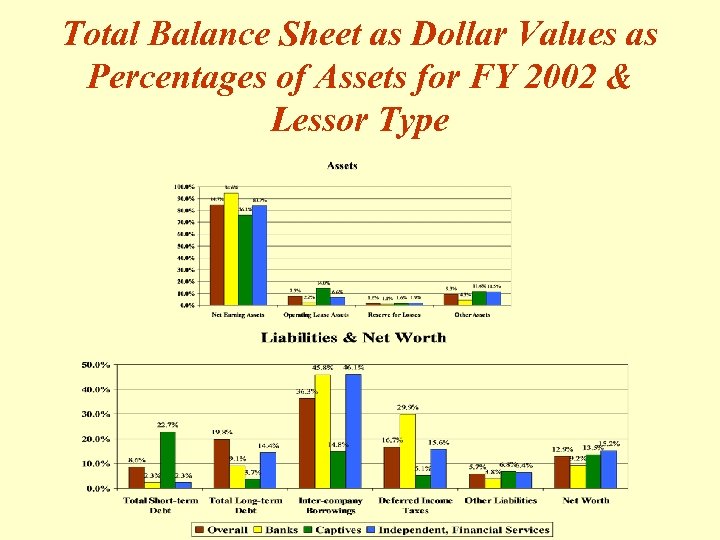
Total Balance Sheet as Dollar Values as Percentages of Assets for FY 2002 & Lessor Type
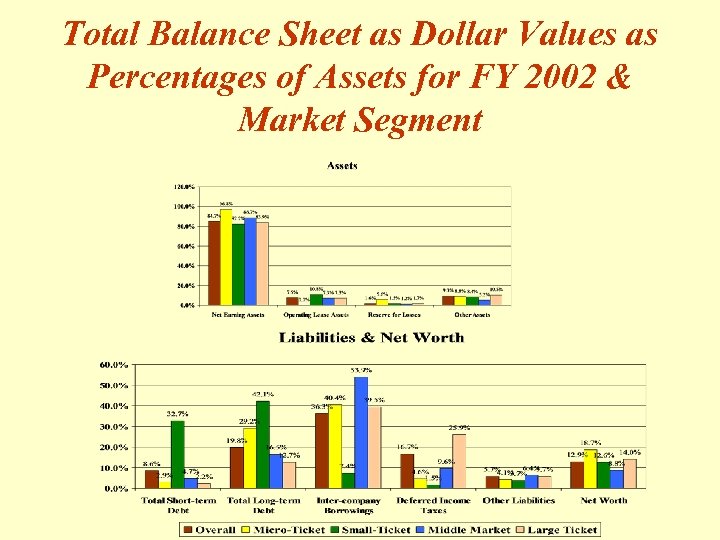
Total Balance Sheet as Dollar Values as Percentages of Assets for FY 2002 & Market Segment

Piper Jaffrey Commercial Finance Market Dynamics

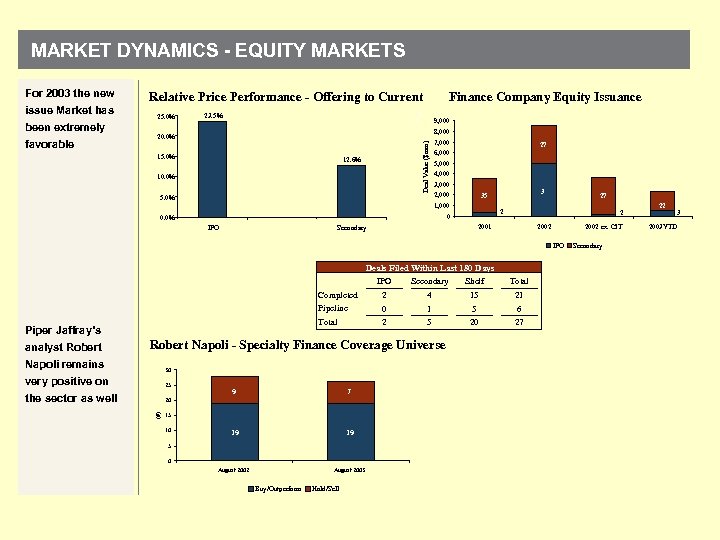
MARKET DYNAMICS - EQUITY MARKETS For 2003 the new Relative Price Performance - Offering to Current issue Market has 2 favorable 25. 0% 23. 5% 9, 000 7 8, 000 20. 0% 15. 0% Deal Value ($mm) been extremely Finance Company Equity Issuance 12. 6% 10. 0% 5. 0% 7, 000 6, 000 27 5, 000 4, 000 3, 000 2, 000 1, 000 IPO 2 2001 Secondary 27 2 0 0. 0% 3 35 2002 ex. CIT IPO Deals Filed Within Last 180 Days IPO Shelf Total ____ Secondary ________ Completed 2 4 15 21 Pipeline 0 1 5 6 ________ Total Piper Jaffray’s analyst Robert 2 5 Robert Napoli - Specialty Finance Coverage Universe 30 very positive on 25 the sector as well 20 (#) Napoli remains 9 7 19 19 August 2002 August 2003 15 10 5 0 Buy/Outperform Hold/Sell 20 27 Secondary 22 2003 YTD 3








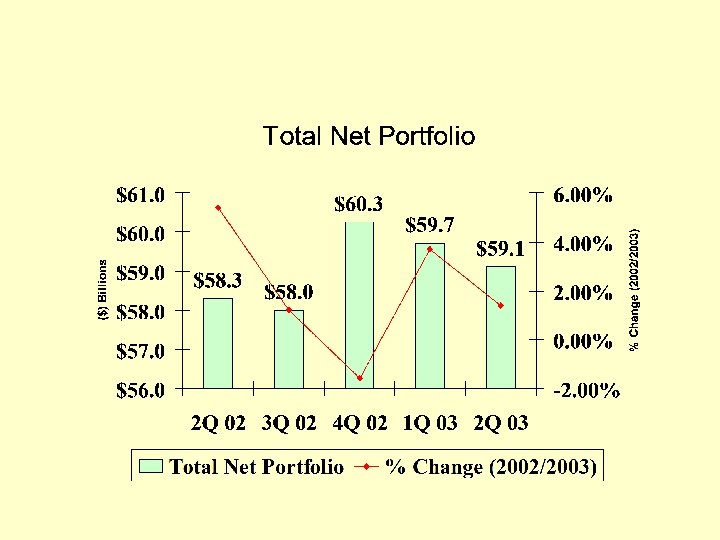
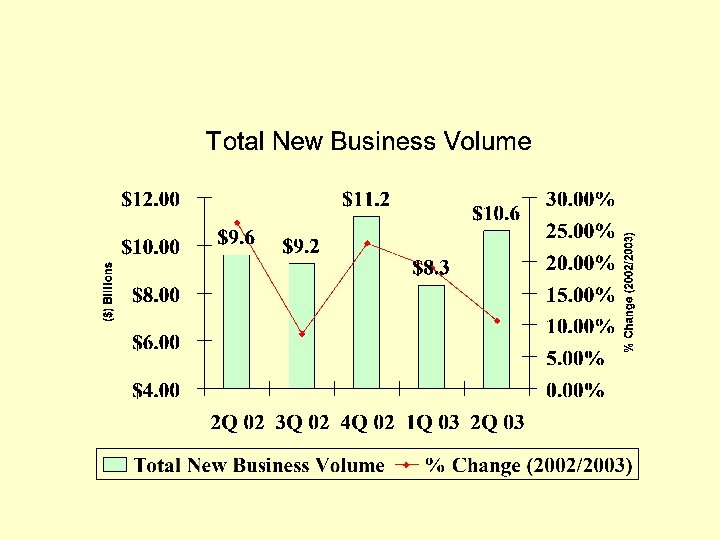
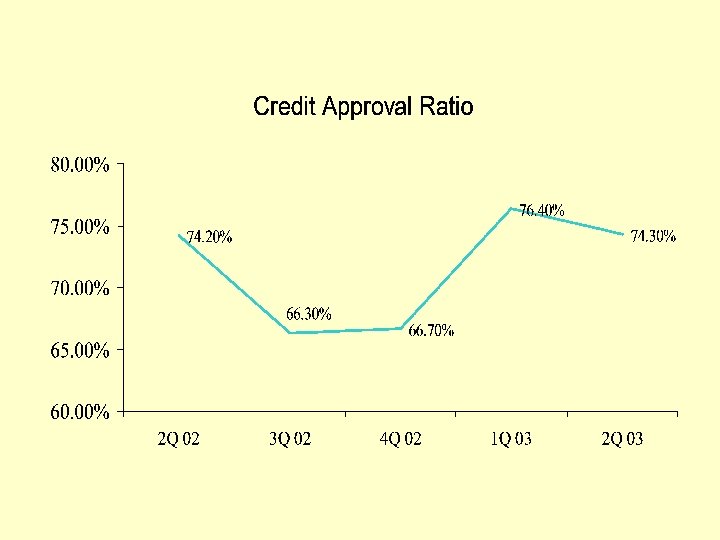
Current Real Time Performance Metrics

ELA’s 2 nd Quarter 2003 Performance Indicator Report (PIR) (A Trend analysis based on surveys conducted by the ELA)
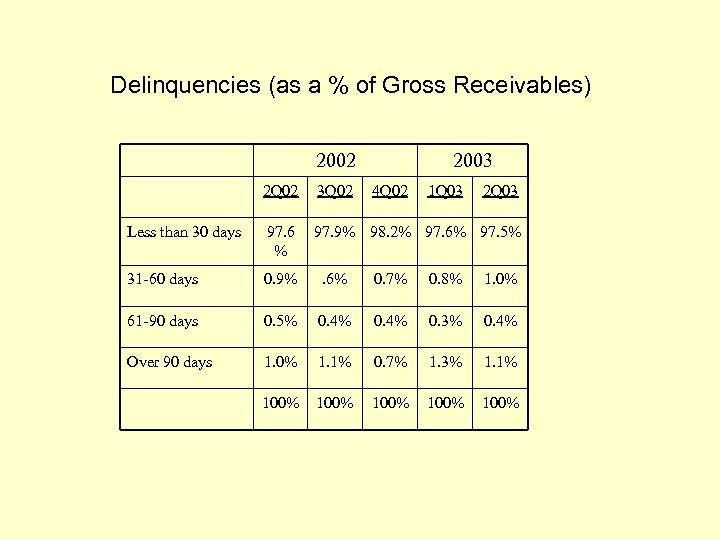
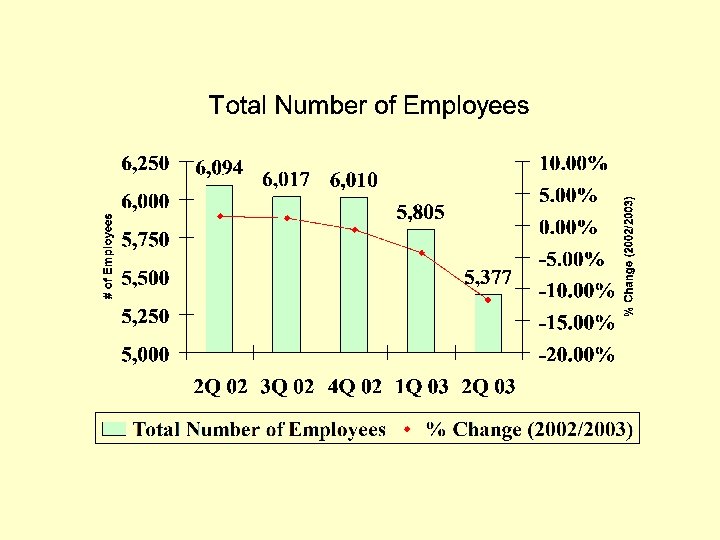
Delinquencies (as a % of Gross Receivables) 2002 2003 2 Q 02 3 Q 02 4 Q 02 1 Q 03 2 Q 03 Less than 30 days 97. 6 % 97. 9% 98. 2% 97. 6% 97. 5% 31 -60 days 0. 9% . 6% 0. 7% 0. 8% 1. 0% 61 -90 days 0. 5% 0. 4% 0. 3% 0. 4% Over 90 days 1. 0% 1. 1% 0. 7% 1. 3% 1. 1% 100% 100%

Leasing and Finance Company Dynamics 1
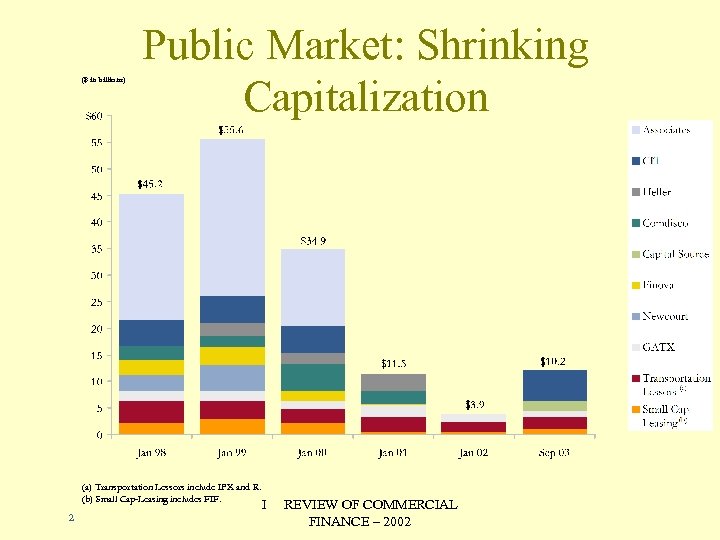
($ in billions) Public Market: Shrinking Capitalization (a) Transportation Lessors include IPX and R. (b) Small Cap-Leasing includes FIF. 2 I REVIEW OF COMMERCIAL FINANCE – 2002
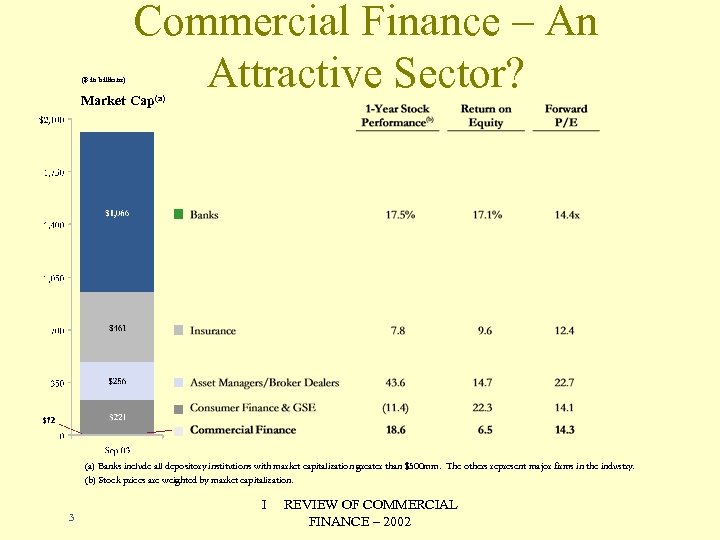
($ in billions) Commercial Finance – An Attractive Sector? Market Cap(a) Banks include all depository institutions with market capitalization greater than $500 mm. The others represent major firms in the industry. (b) Stock prices are weighted by market capitalization. 3 I REVIEW OF COMMERCIAL FINANCE – 2002
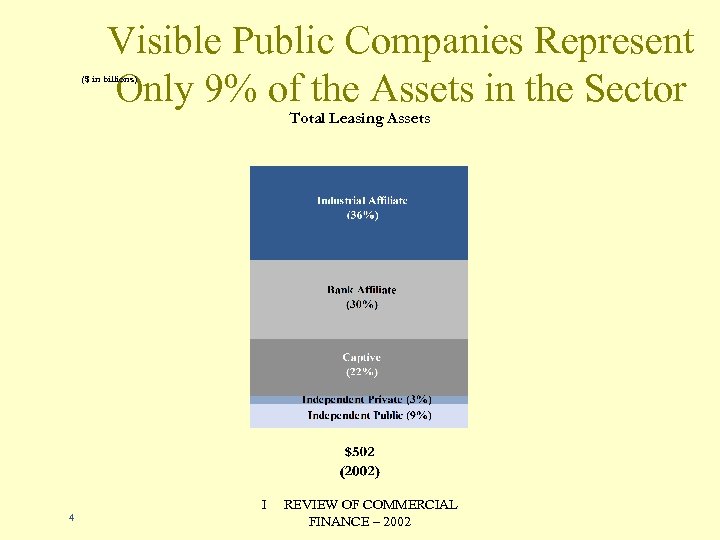
Visible Public Companies Represent Only 9% of the Assets in the Sector ($ in billions) Total Leasing Assets 4 I REVIEW OF COMMERCIAL FINANCE – 2002

$100+ Million Commercial Finance Transactions M&A Deal Volume (number of transactions in parentheses, $ in billions) Source: SNL Securities. Note: Commercial finance transactions with equity value greater than $100 million. 5 I REVIEW OF COMMERCIAL FINANCE – 2002
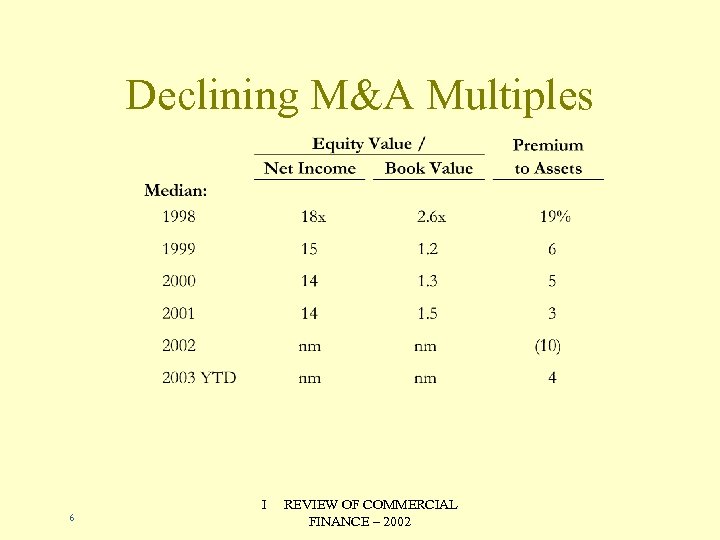
Declining M&A Multiples 6 I REVIEW OF COMMERCIAL FINANCE – 2002

Funding Experience: Debt Liquidity For Leasing Companies, Organization of Data and Current Topics revolving around Liquidity

Overview and Outline of an Information Book for Lenders and Investors • Provide the definitive framework for equipment leasing and finance companies making presentations to funding sources and investors. • Provide the definitive framework to funding sources and investors for understanding and comparing equipment leasing and finance companies. • Overview of all the Company operations, history of the company, management background, historical financial performance, historical portfolio performance and other background about the Company. • An outline of the book can be obtained from the ELA, by accessing the web page : www. elaonline. com A Guide for Effective Funding and Capital Market Presentations • Equipment Leasing and Finance Companies

Required Information Sections of The Presentation to Investors, Rating Agencies, and other Interested Parties • • • Company Overview Management Marketing Financial Summary Existing Funding Strategy & Sources Credit Underwriting Policies & Procedures Documentation Procedures Billing & Collecting Policies & Procedures Asset Management Capabilities & Practices MIS Capabilities & Practices

Types of Financing For Lessors, Different Structures that Lessors Use • Commercial Paper Warehouse Facilities & Term Securitization: • Recourse Lines of Credit: Revolvers that are provided by local and regional banks that can be syndicated if the need arises. • Limited Recourse Revolving Lines of Credit: On Balance Sheet Treatment: example, facilities provided by Sovereign Bank, Alfa Insurance, Provident Bank are structured with the first losses (up to 20%) retained by the originator/lessor. These facilities can also be structured as a sale facility with servicing retained by the lessor. • Non-Recourse Term Portfolio Sales: Service Released, Gain on Sale Treatment. These facilities are used to de-leverage the balance sheet and provide the seller the present value income of the portfolio sold. • Subordinate note Financing: foreign and domestic banks provide term financing for both rated and un-rated debt for term securitization.

Commercial Paper Warehouse and Term Facilities fund a wide range of Assets including Leased Assets • Commercial Paper is a structured, rated method of providing a revolving credit facility. • These Facilities are very efficient, with large limits that provide bulk funding at interest rates that usually are significantly lower than other forms of bank financing. • Structures can vary, with a wide variety of assets funded using these kinds of facilities. • Pricing and credit facility size brings efficiency to the funding process. • One or two credit providers (co-purchase) allow for efficient management of the credit and renewal process. • Rating agency’s are familiar with the structures, thus allowing deeper access to term markets with different investors.

Recourse Lines of Credit provide short term liquidity • Lessors use local and regional banks to build portfolios that transition to CP facilities, Term Facilities, Limited Recourse Financings, and Non-Recourse Portfolio Sales. • Recourse Lines provide flexibility and the ability to expand through syndication among a number of banks. • Structures allow for various types of assets, including residuals, inventory and restructured assets to be financed. • Advance rates are generally higher than rated structured warehouse commercial paper facilities. • Local and Regional banks provide other financial services such as cash management, trust and collateral services that build lasting diverse funding relationships.

Limited Recourse Term Facilities (UNL) Ultimate Net Loss, provide sale or finance treatment • Many Lessors use these facilities to remove the assets from the balance sheet, usually footnoting the amount of recourse. • These facilities allow the originator/lessor to continue servicing. • The cost of setup and ongoing expenses are less than more traditional structured facilities. • This market serves smaller originators, that do not have access to the structured market place. • No commitment fees, but also not commitment to fund, thus providing no guarantee of future funding commitment. • Future recourse is limited, thus capping potential future losses. • These programs are usually structured as “perfect pay” with one payment due per month, on each funding. • Pricing and structures have become more aggressive as more lenders have entered the market over the last twelve to eighteen months.

Non-Recourse Term Loan Financings • This method of financing is used primarily by originators that need to diversify risk, rebalance a portfolio, or exit a business line. • The sale of a portfolio usually provides gain on sale treatment for financial statement purposes, and typically a cash gain. • No future recourse for credit losses. • No future servicing costs associated with servicing.

Current Critical Market Events Pertaining To Liquidity • Consolidation of Independent Finance Companies involved in Securitization • Bankruptcy of DVI and potential mis-representation. • Liquidity in the market/ Both Structured and Private markets (Senior and Subordinated). • New issuers / borrowers and the barriers to entry in obtaining debt. • Banks are interested in providing revolvers and other forms of credit to Leasing Companies. • Portfolio Buyers are also aggressively seeking new sources of leases. • Interest Rates have been increasing.

Treasury Note Rates for January 2002 through September 2003

Short-Term Interest Rates for January 2002 through September 2003

Since 1999, the Asset Securitization Group of DZ Bank has closed five equipment lease/loan transactions, three of which continue to be financed through Autobahn Funding Company, LLC, an asset backed commercial paper conduit.

Characteristics of Autobahn’s Leasing Company Clients - Independent, full service lessor (i. e sufficient infrastructure to perform originations, underwriting, funding, servicing and collections) - Generally in business five years or more · Serviced portfolio of $50 million or more · Consistent static pool loss history (typically four to ten years) · Diversified portfolio, generally small ticket sizes ($250, 000 or less) - Maintain $5 million or more in short-term revolving warehouse lines (used to accumulate leases prior to financing through CP conduit) - Tangible net worth and subordinated debt of $5 million plus

Characteristics of Autobahn’s Facilities for Leasing Companies Maximum facility amount: $50 - $200 million Committed facility, revolving for up to 5 years Overcollateralization of 3 times or more expected net osses Minimum targeted shadow rating of BBB/Baa 2 Interest rate risk mitigated through use of interest rate waps or caps Numerous individual lease eligibility criteria (e. g. elinquency status, transaction size, original term) Portfolio wide concentration limits (e. g. largest single bligor, geographic location, remaining term, lessee ndustry, equipment type)
a0380062ca7f55d84f4a8233dbf0a84f.ppt