ef5bc8320b1df3c93840b604e2226010.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 Learning to Detect Malicious URLs Justin Ma, Lawrence Saul, Stefan Savage, Geoff Voelker Computer Science & Engineering UC San Diego Presentation for Google May 5, 2010
Learning to Detect Malicious URLs Justin Ma, Lawrence Saul, Stefan Savage, Geoff Voelker Computer Science & Engineering UC San Diego Presentation for Google May 5, 2010
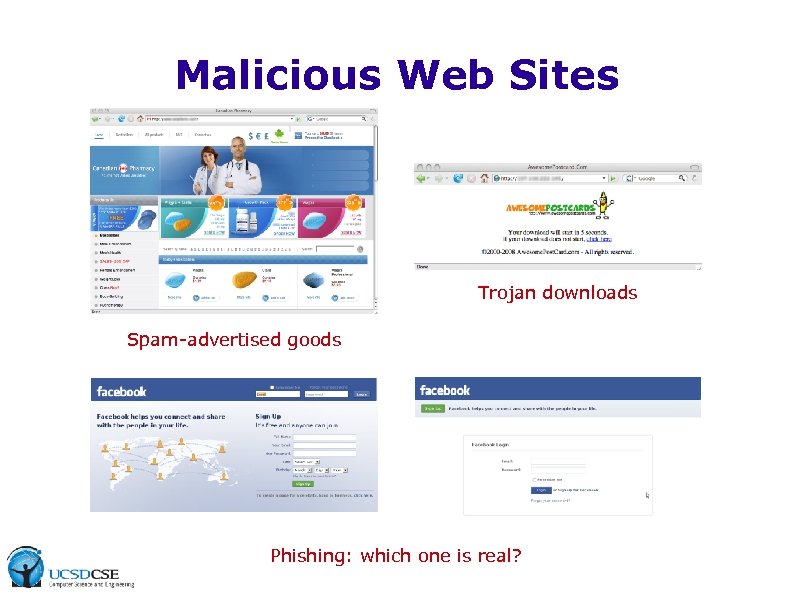 Malicious Web Sites Trojan downloads Spam-advertised goods Phishing: which one is real?
Malicious Web Sites Trojan downloads Spam-advertised goods Phishing: which one is real?
 Visiting Malicious Web Sites URL = Uniform Resource Locator • Safe URL? • Malicious download? http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll • Spam-advertised site? http: //fblight. com • Phishing site? http: //mail. ru http: //www. cs. ucsd. edu/~jtma/ Predict what is safe without committing to risky actions 3
Visiting Malicious Web Sites URL = Uniform Resource Locator • Safe URL? • Malicious download? http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll • Spam-advertised site? http: //fblight. com • Phishing site? http: //mail. ru http: //www. cs. ucsd. edu/~jtma/ Predict what is safe without committing to risky actions 3
 Problem in a Nutshell URL features to identify malicious Web sites No context, no content Different classes of URLs Benign, spam, phishing, exploits, scams. . . For now, distinguish benign vs. malicious facebook. com fblight. com 4
Problem in a Nutshell URL features to identify malicious Web sites No context, no content Different classes of URLs Benign, spam, phishing, exploits, scams. . . For now, distinguish benign vs. malicious facebook. com fblight. com 4
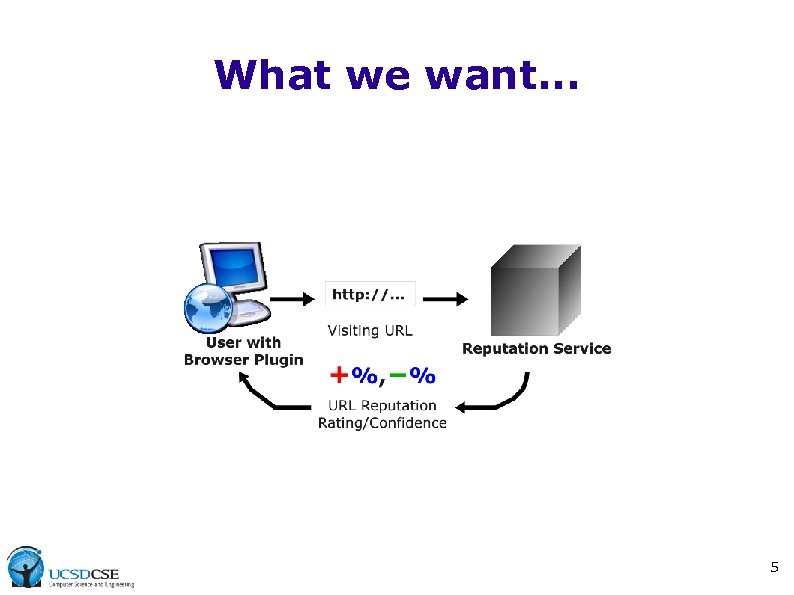 What we want. . . 5
What we want. . . 5
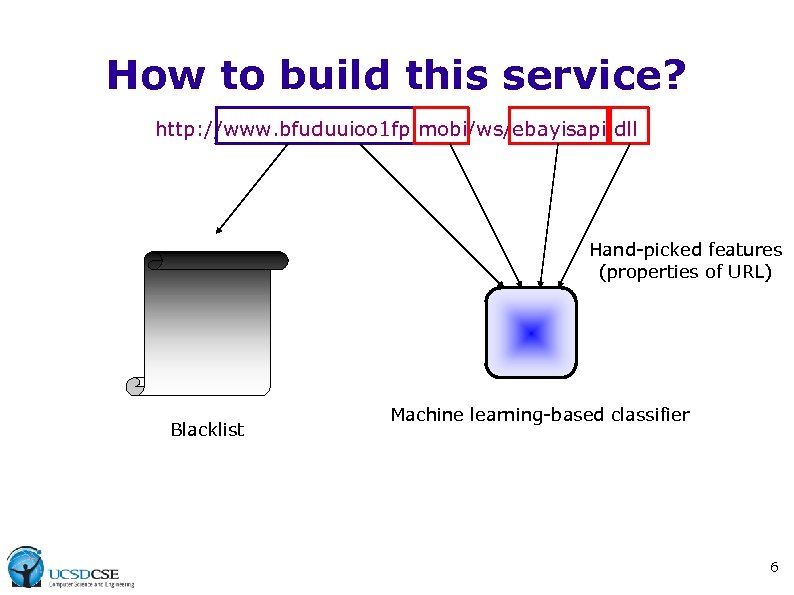 How to build this service? http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll Hand-picked features (properties of URL) Blacklist Machine learning-based classifier 6
How to build this service? http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll Hand-picked features (properties of URL) Blacklist Machine learning-based classifier 6
 State of the Practice Current approaches Blacklists [SORBS, URIBL, SURBL, Spamhaus, Site. Advisor, WOT, Iron. Port, Web. Sense] Learning on hand-tuned features [Kan & Thi '05, Garera et al. '07, CANTINA, Guan et al. '09] Limitations Cannot learn from newest examples quickly Cannot quickly adapt to newest features Arms race: fast feedback cycle is critical More automated approach? 7
State of the Practice Current approaches Blacklists [SORBS, URIBL, SURBL, Spamhaus, Site. Advisor, WOT, Iron. Port, Web. Sense] Learning on hand-tuned features [Kan & Thi '05, Garera et al. '07, CANTINA, Guan et al. '09] Limitations Cannot learn from newest examples quickly Cannot quickly adapt to newest features Arms race: fast feedback cycle is critical More automated approach? 7
 Contributions URL classification system Used by large Web mail providers Practical large-scale machine learning in computer security Large feature sets + online learning Related work: Whittaker, Ryner, Nazif, “Large-Scale Automatic Classification of Phishing Pages” (NDSS'10) 8
Contributions URL classification system Used by large Web mail providers Practical large-scale machine learning in computer security Large feature sets + online learning Related work: Whittaker, Ryner, Nazif, “Large-Scale Automatic Classification of Phishing Pages” (NDSS'10) 8
 Today's Talk Problem Moving Beyond Blacklists Large-Scale Online Learning Conclusion 9
Today's Talk Problem Moving Beyond Blacklists Large-Scale Online Learning Conclusion 9
 Today's Talk Problem Moving Beyond Blacklists Large-Scale Online Learning Conclusion 10
Today's Talk Problem Moving Beyond Blacklists Large-Scale Online Learning Conclusion 10
![Moving Beyond Blacklists [Ma, Saul, Savage, Voelker (KDD 2009)] Preliminary study: Do our features Moving Beyond Blacklists [Ma, Saul, Savage, Voelker (KDD 2009)] Preliminary study: Do our features](https://present5.com/presentation/ef5bc8320b1df3c93840b604e2226010/image-11.jpg) Moving Beyond Blacklists [Ma, Saul, Savage, Voelker (KDD 2009)] Preliminary study: Do our features work? Batch algorithms for now 104 examples and features Outline System overview Features ← focus of this segment Experimental results 11
Moving Beyond Blacklists [Ma, Saul, Savage, Voelker (KDD 2009)] Preliminary study: Do our features work? Batch algorithms for now 104 examples and features Outline System overview Features ← focus of this segment Experimental results 11
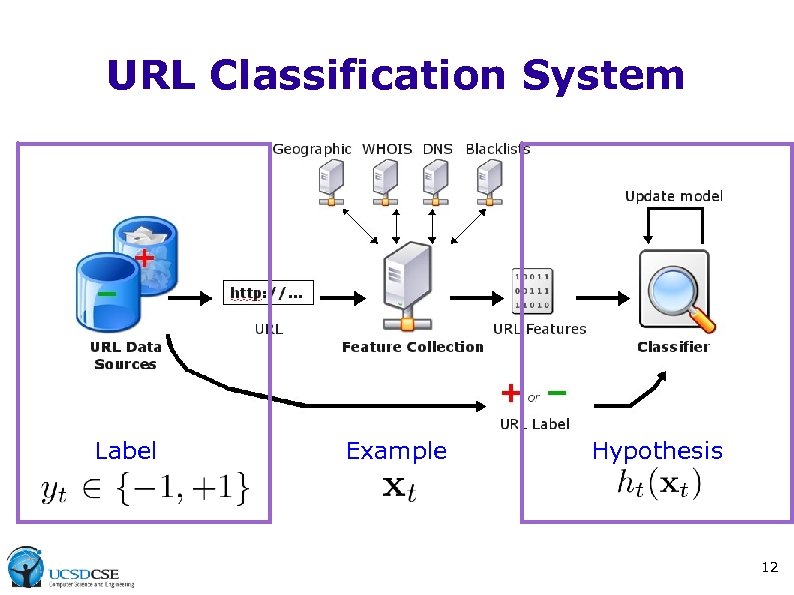 URL Classification System Label Example Hypothesis 12
URL Classification System Label Example Hypothesis 12
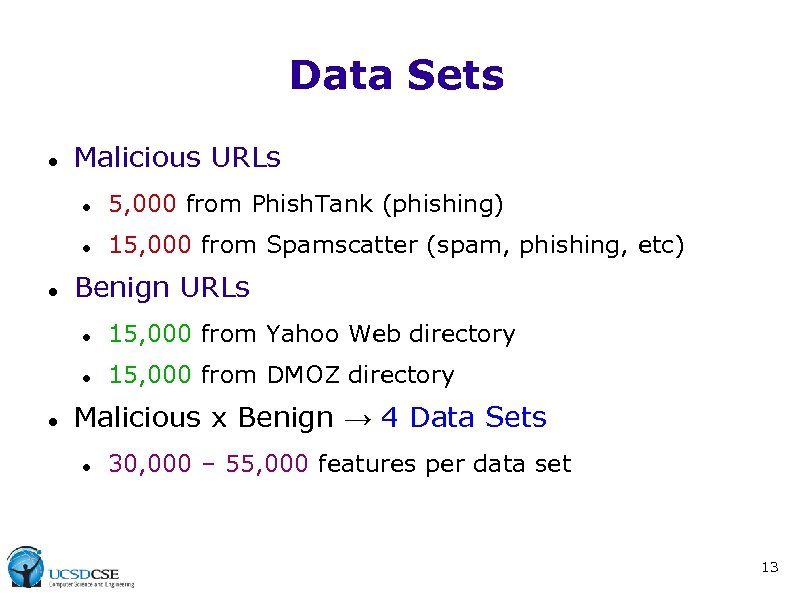 Data Sets Malicious URLs 5, 000 from Phish. Tank (phishing) 15, 000 from Spamscatter (spam, phishing, etc) Benign URLs 15, 000 from Yahoo Web directory 15, 000 from DMOZ directory Malicious x Benign → 4 Data Sets 30, 000 – 55, 000 features per data set 13
Data Sets Malicious URLs 5, 000 from Phish. Tank (phishing) 15, 000 from Spamscatter (spam, phishing, etc) Benign URLs 15, 000 from Yahoo Web directory 15, 000 from DMOZ directory Malicious x Benign → 4 Data Sets 30, 000 – 55, 000 features per data set 13
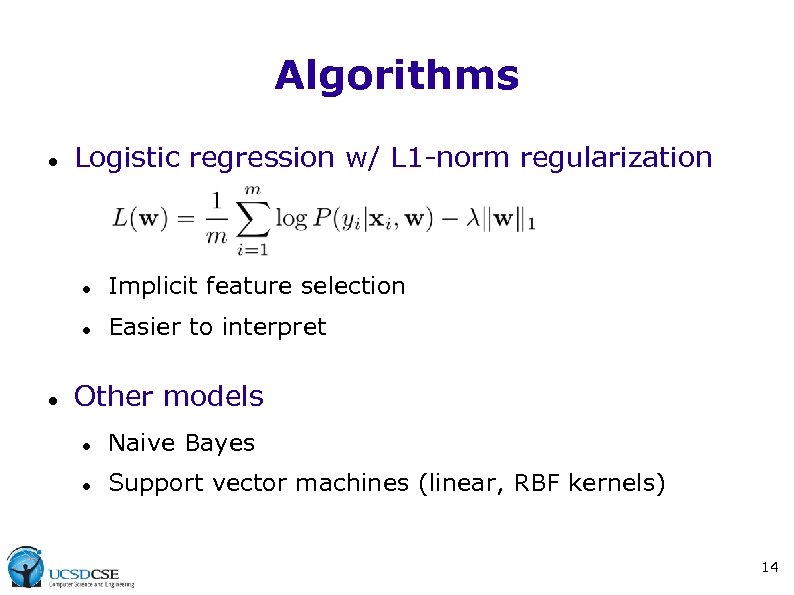 Algorithms Logistic regression w/ L 1 -norm regularization Implicit feature selection Easier to interpret Other models Naive Bayes Support vector machines (linear, RBF kernels) 14
Algorithms Logistic regression w/ L 1 -norm regularization Implicit feature selection Easier to interpret Other models Naive Bayes Support vector machines (linear, RBF kernels) 14
 Features Example 15
Features Example 15
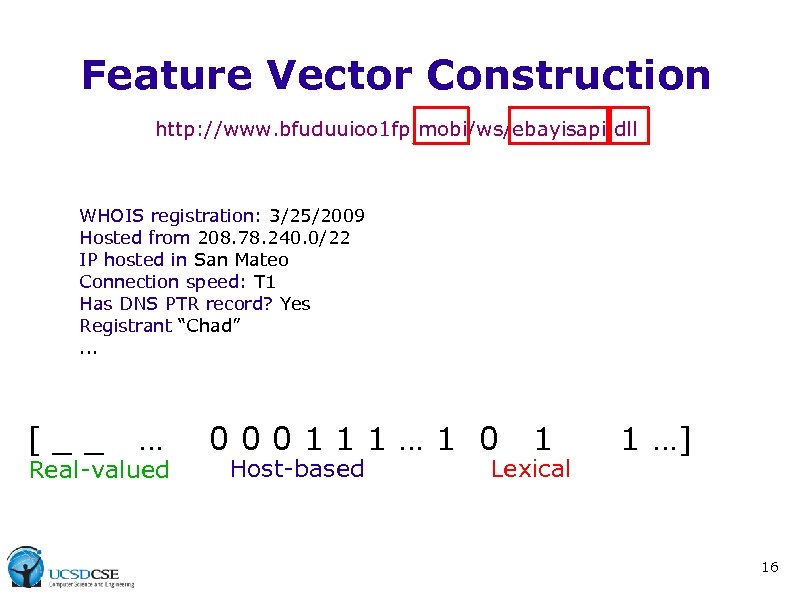 Feature Vector Construction http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll WHOIS registration: 3/25/2009 Hosted from 208. 78. 240. 0/22 IP hosted in San Mateo Connection speed: T 1 Has DNS PTR record? Yes Registrant “Chad”. . . [__ … Real-valued 000111… 1 0 Host-based 1 Lexical 1 …] 16
Feature Vector Construction http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll WHOIS registration: 3/25/2009 Hosted from 208. 78. 240. 0/22 IP hosted in San Mateo Connection speed: T 1 Has DNS PTR record? Yes Registrant “Chad”. . . [__ … Real-valued 000111… 1 0 Host-based 1 Lexical 1 …] 16
 Features to consider? 1)Blacklists 2)Simple heuristics 3)Domain name registration 4)Host properties 5)Lexical 17
Features to consider? 1)Blacklists 2)Simple heuristics 3)Domain name registration 4)Host properties 5)Lexical 17
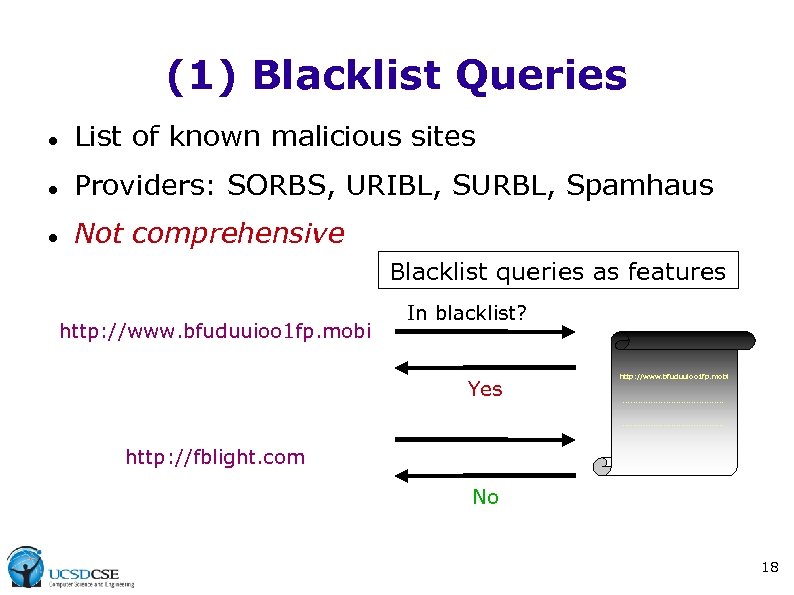 (1) Blacklist Queries List of known malicious sites Providers: SORBS, URIBL, SURBL, Spamhaus Not comprehensive Blacklist queries as features http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi In blacklist? Yes http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi. . . . . http: //fblight. com No 18
(1) Blacklist Queries List of known malicious sites Providers: SORBS, URIBL, SURBL, Spamhaus Not comprehensive Blacklist queries as features http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi In blacklist? Yes http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi. . . . . http: //fblight. com No 18
![(2) Manually-Selected Features [Fette et al. , 2007][Zhang et al. , 2007][Bergholz et al. (2) Manually-Selected Features [Fette et al. , 2007][Zhang et al. , 2007][Bergholz et al.](https://present5.com/presentation/ef5bc8320b1df3c93840b604e2226010/image-19.jpg) (2) Manually-Selected Features [Fette et al. , 2007][Zhang et al. , 2007][Bergholz et al. , 2008] Considered by previous studies IP address in hostname? Number of dots in URL WHOIS (domain name) registration date http: //72. 23. 5. 122/www. bankofamerica. com/ http: //www. bankofamerica. com. qytrpbcw. stopgap. cn/ stopgap. cn registered 2 May 2010 19
(2) Manually-Selected Features [Fette et al. , 2007][Zhang et al. , 2007][Bergholz et al. , 2008] Considered by previous studies IP address in hostname? Number of dots in URL WHOIS (domain name) registration date http: //72. 23. 5. 122/www. bankofamerica. com/ http: //www. bankofamerica. com. qytrpbcw. stopgap. cn/ stopgap. cn registered 2 May 2010 19
 (3) WHOIS Features Domain name registration Date of registration, update, expiration Registrant: Who registered domain? Registrar: Who manages registration? http: //yammeringyellowtail. com http: //angryalbacore. com http: //sleazysalmon. com http: //mangymackerel. com Registered on 4 May 2010 By Spam. Media 20
(3) WHOIS Features Domain name registration Date of registration, update, expiration Registrant: Who registered domain? Registrar: Who manages registration? http: //yammeringyellowtail. com http: //angryalbacore. com http: //sleazysalmon. com http: //mangymackerel. com Registered on 4 May 2010 By Spam. Media 20
 (4) Host-Based Features Blacklisted? (SORBS, URIBL, SURBL, Spamhaus) Bad Parts of the Internet WHOIS: registrar, registrant, dates IP address: Which ASes/IP prefixes? DNS: TTL? PTR record exists/resolves? Geography-related: Locale? Connection speed? facebook. com 69. 63. 176. 0/20 fblight. com 75. 102. 60. 0/22 21
(4) Host-Based Features Blacklisted? (SORBS, URIBL, SURBL, Spamhaus) Bad Parts of the Internet WHOIS: registrar, registrant, dates IP address: Which ASes/IP prefixes? DNS: TTL? PTR record exists/resolves? Geography-related: Locale? Connection speed? facebook. com 69. 63. 176. 0/20 fblight. com 75. 102. 60. 0/22 21
![(5) Lexical Features [Kolari et al. , 2006] Tokens in URL hostname + path (5) Lexical Features [Kolari et al. , 2006] Tokens in URL hostname + path](https://present5.com/presentation/ef5bc8320b1df3c93840b604e2226010/image-22.jpg) (5) Lexical Features [Kolari et al. , 2006] Tokens in URL hostname + path Length of URL Number of dots http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll 22
(5) Lexical Features [Kolari et al. , 2006] Tokens in URL hostname + path Length of URL Number of dots http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll 22
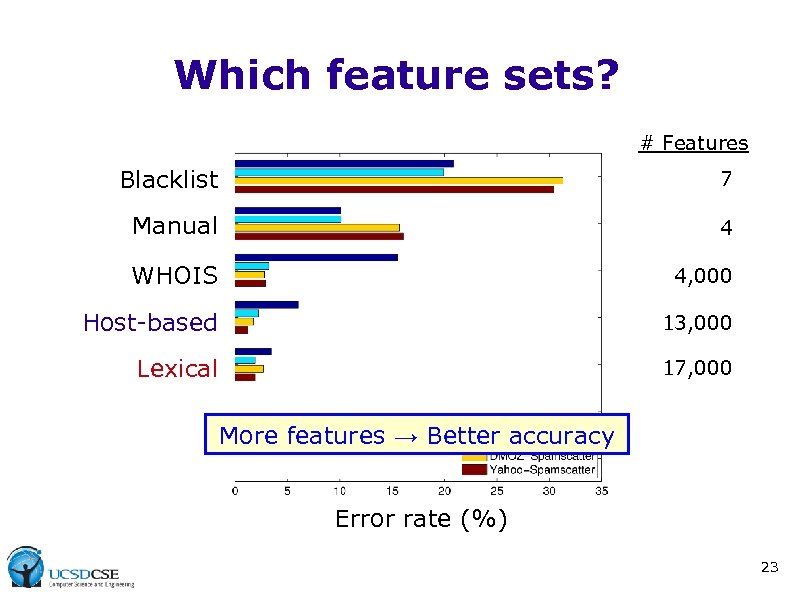 Which feature sets? # Features Blacklist 7 Manual 4 WHOIS 4, 000 Host-based 13, 000 Lexical 17, 000 More features → Better accuracy Error rate (%) 23
Which feature sets? # Features Blacklist 7 Manual 4 WHOIS 4, 000 Host-based 13, 000 Lexical 17, 000 More features → Better accuracy Error rate (%) 23
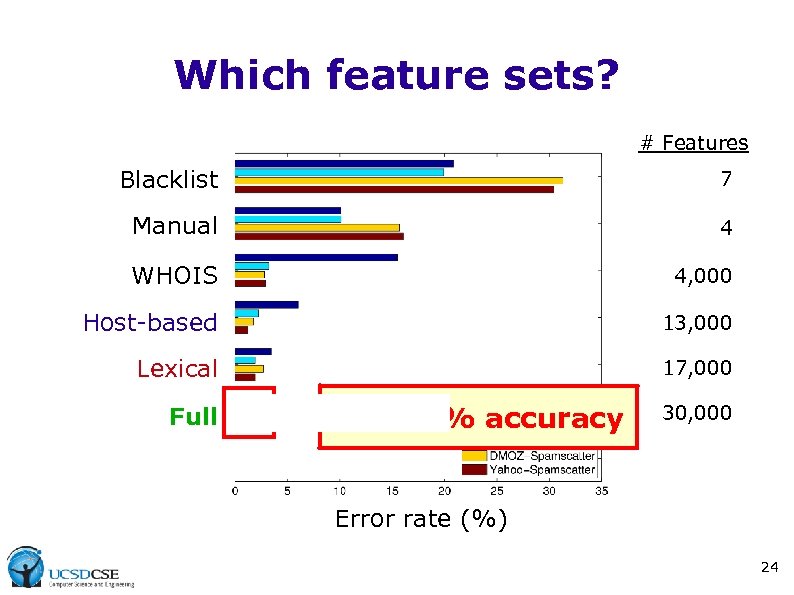 Which feature sets? # Features Blacklist 7 Manual 4 WHOIS 4, 000 Host-based 13, 000 Lexical 17, 000 Full 96— 99% accuracy 30, 000 Error rate (%) 24
Which feature sets? # Features Blacklist 7 Manual 4 WHOIS 4, 000 Host-based 13, 000 Lexical 17, 000 Full 96— 99% accuracy 30, 000 Error rate (%) 24
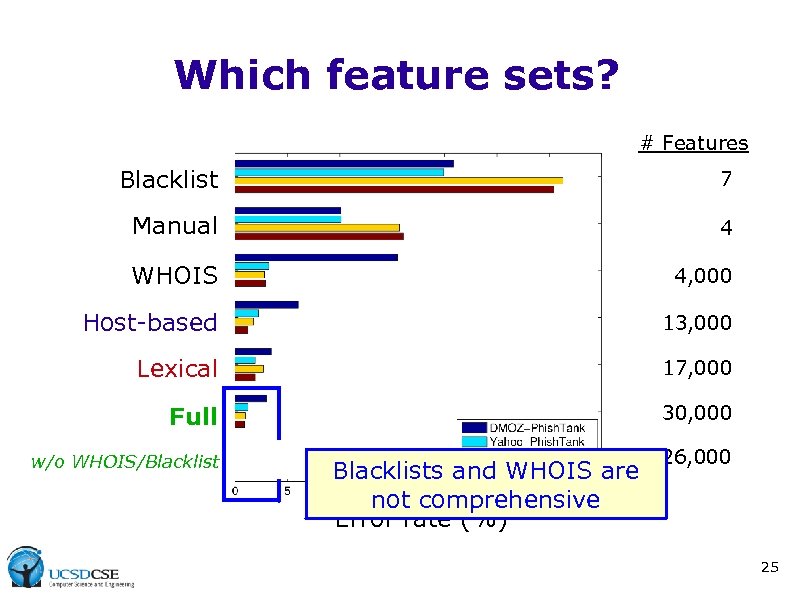 Which feature sets? # Features Blacklist 7 Manual 4 WHOIS 4, 000 Host-based 13, 000 Lexical 17, 000 Full 30, 000 w/o WHOIS/Blacklist 26, 000 Blacklists and WHOIS are not comprehensive Error rate (%) 25
Which feature sets? # Features Blacklist 7 Manual 4 WHOIS 4, 000 Host-based 13, 000 Lexical 17, 000 Full 30, 000 w/o WHOIS/Blacklist 26, 000 Blacklists and WHOIS are not comprehensive Error rate (%) 25
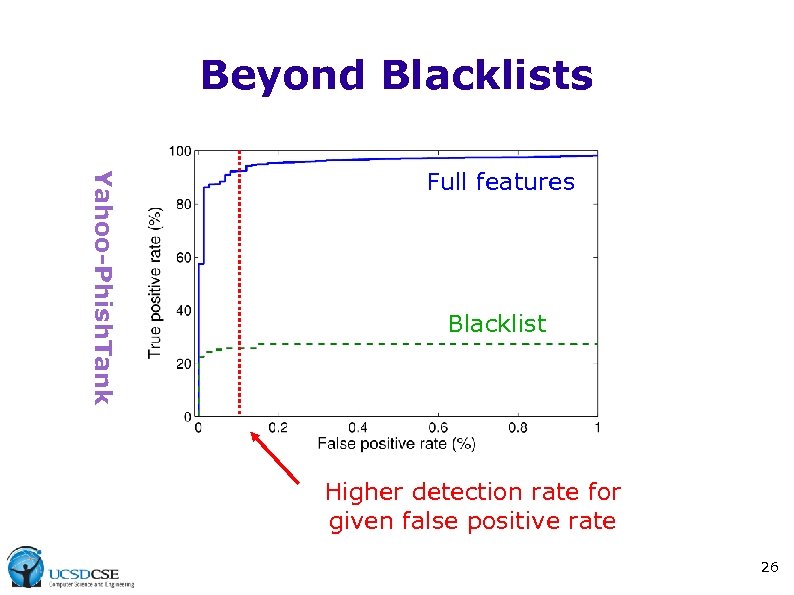 Beyond Blacklists Yahoo-Phish. Tank Full features Blacklist Higher detection rate for given false positive rate 26
Beyond Blacklists Yahoo-Phish. Tank Full features Blacklist Higher detection rate for given false positive rate 26
 Summary Detect malicious URLs with high accuracy Diverse feature set helps: 99% w/ 30, 000+ features Only using URL Model analysis (more in KDD'09 paper) What about scalable and adaptive malicious URL detection system? 27
Summary Detect malicious URLs with high accuracy Diverse feature set helps: 99% w/ 30, 000+ features Only using URL Model analysis (more in KDD'09 paper) What about scalable and adaptive malicious URL detection system? 27
 Today's Talk Problem Moving Beyond Blacklists Large-Scale Online Learning Conclusion 28
Today's Talk Problem Moving Beyond Blacklists Large-Scale Online Learning Conclusion 28
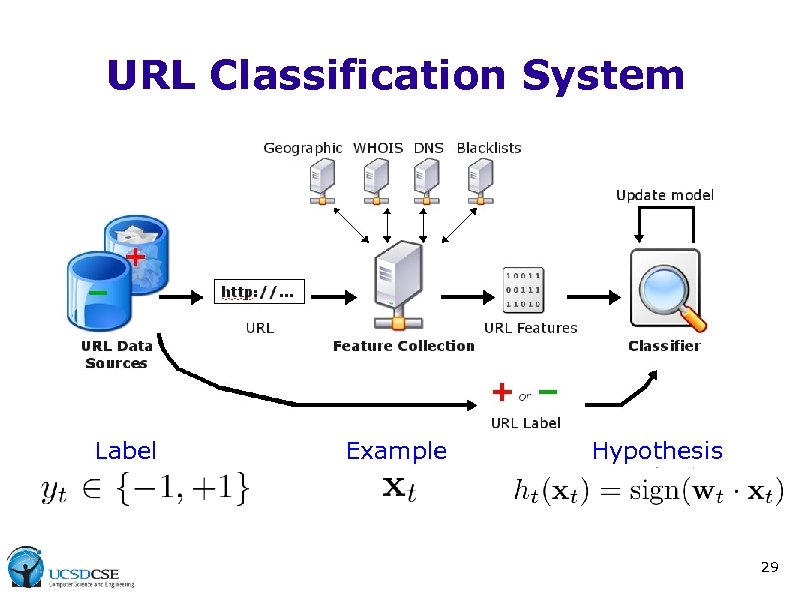 URL Classification System Label Example Hypothesis 29
URL Classification System Label Example Hypothesis 29
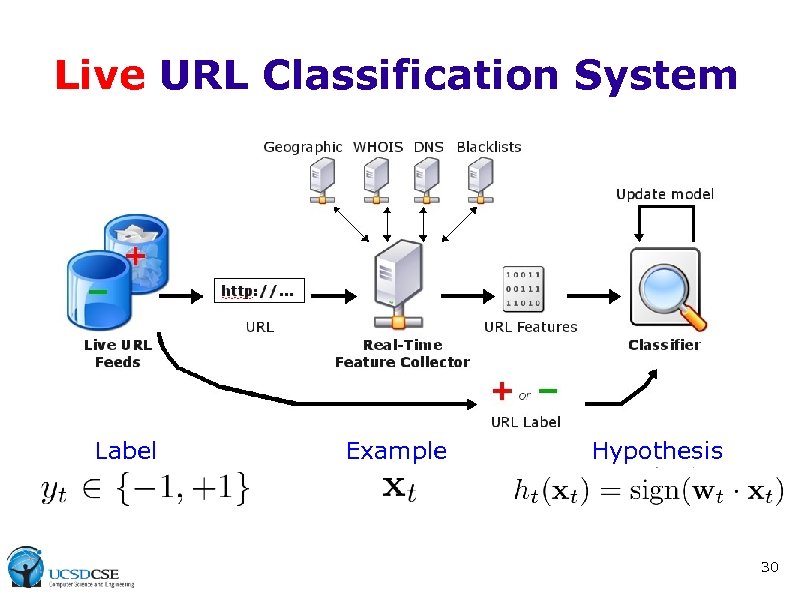 Live URL Classification System Label Example Hypothesis 30
Live URL Classification System Label Example Hypothesis 30
![Large-Scale Online Learning [Ma, Saul, Savage, Voelker (ICML 2009)] How do we scale to Large-Scale Online Learning [Ma, Saul, Savage, Voelker (ICML 2009)] How do we scale to](https://present5.com/presentation/ef5bc8320b1df3c93840b604e2226010/image-31.jpg) Large-Scale Online Learning [Ma, Saul, Savage, Voelker (ICML 2009)] How do we scale to live, large-scale data? Outline Live training feed Challenges: scale and non-stationarity Need for large, fresh training sets Online learning 31
Large-Scale Online Learning [Ma, Saul, Savage, Voelker (ICML 2009)] How do we scale to live, large-scale data? Outline Live training feed Challenges: scale and non-stationarity Need for large, fresh training sets Online learning 31
 Live Training Feed Malicious URLs (spamming and phishing) 6, 000— 7, 500 per day from Web mail provider Benign URLs From Yahoo Web directory Total of 20, 000 URLs per day Collected Jan – May, 2009 120 days More than two million examples 32
Live Training Feed Malicious URLs (spamming and phishing) 6, 000— 7, 500 per day from Web mail provider Benign URLs From Yahoo Web directory Total of 20, 000 URLs per day Collected Jan – May, 2009 120 days More than two million examples 32
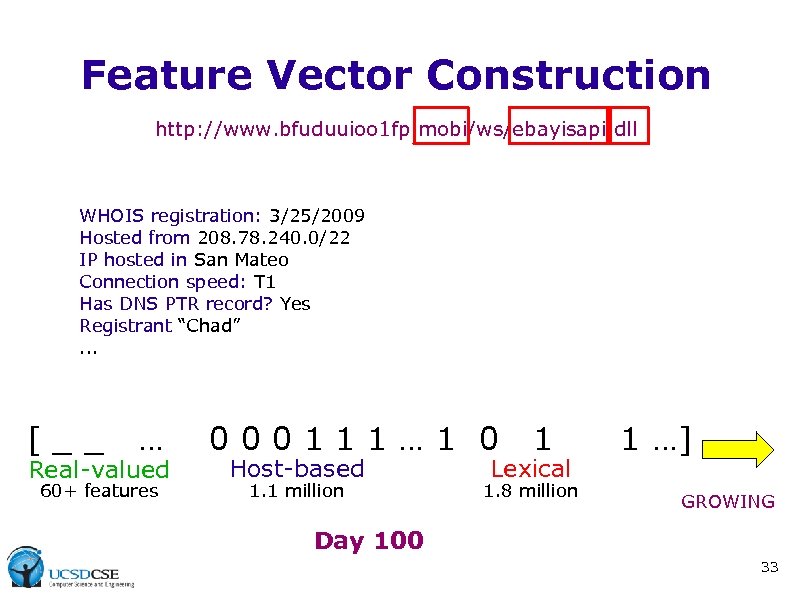 Feature Vector Construction http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll WHOIS registration: 3/25/2009 Hosted from 208. 78. 240. 0/22 IP hosted in San Mateo Connection speed: T 1 Has DNS PTR record? Yes Registrant “Chad”. . . [__ … Real-valued 60+ features 000111… 1 0 Host-based 1. 1 million 1 Lexical 1. 8 million 1 …] GROWING Day 100 33
Feature Vector Construction http: //www. bfuduuioo 1 fp. mobi/ws/ebayisapi. dll WHOIS registration: 3/25/2009 Hosted from 208. 78. 240. 0/22 IP hosted in San Mateo Connection speed: T 1 Has DNS PTR record? Yes Registrant “Chad”. . . [__ … Real-valued 60+ features 000111… 1 0 Host-based 1. 1 million 1 Lexical 1. 8 million 1 …] GROWING Day 100 33
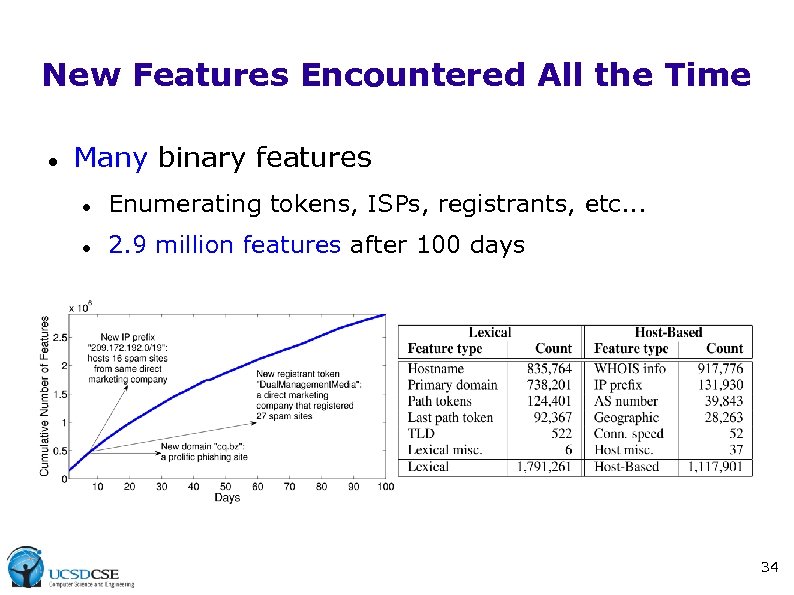 New Features Encountered All the Time Many binary features Enumerating tokens, ISPs, registrants, etc. . . 2. 9 million features after 100 days 34
New Features Encountered All the Time Many binary features Enumerating tokens, ISPs, registrants, etc. . . 2. 9 million features after 100 days 34
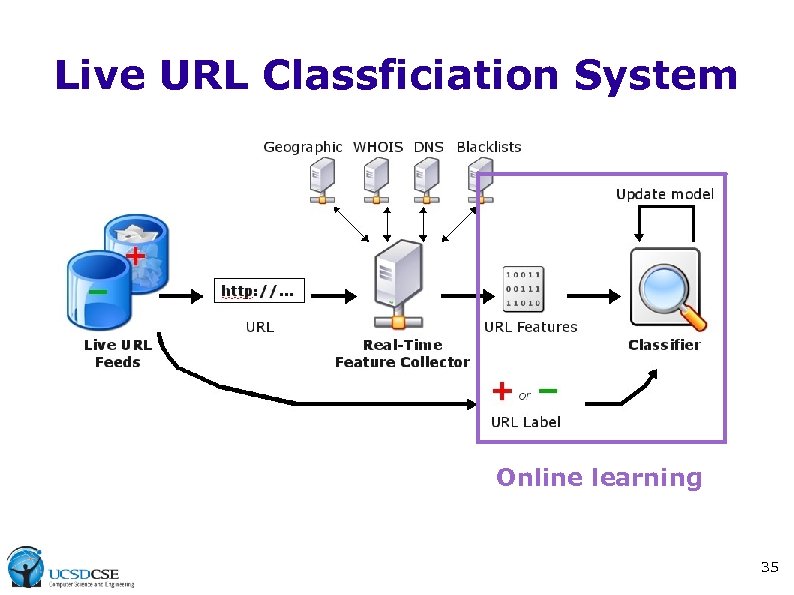 Live URL Classficiation System Online learning 35
Live URL Classficiation System Online learning 35
 Practical Challenges of ML in Systems Industrial concerns Scale: millions of examples, features Non-stationarity: examples change over time (arms race w/ criminals) Pivotal decision: batch or online? 36
Practical Challenges of ML in Systems Industrial concerns Scale: millions of examples, features Non-stationarity: examples change over time (arms race w/ criminals) Pivotal decision: batch or online? 36
 Batch vs. Online Learning Batch/offline learning SVM, logistic regression, decision trees, etc Online learning Perceptron-style algorithms Online learning addresses scale Single pass over data and non-stationarity Multiple passes over data No incremental updates Potentially high memory and processing overhead Incremental updates Low memory and processing overhead 37
Batch vs. Online Learning Batch/offline learning SVM, logistic regression, decision trees, etc Online learning Perceptron-style algorithms Online learning addresses scale Single pass over data and non-stationarity Multiple passes over data No incremental updates Potentially high memory and processing overhead Incremental updates Low memory and processing overhead 37
 Evaluations Online learning for URL reputation Need for large, fresh training sets Comparing online algorithms Continuous retraining Growing feature vector 38
Evaluations Online learning for URL reputation Need for large, fresh training sets Comparing online algorithms Continuous retraining Growing feature vector 38
 Need lots of fresh training data? SVM trained once SVM retrained daily Fresh data helps 39
Need lots of fresh training data? SVM trained once SVM retrained daily Fresh data helps 39
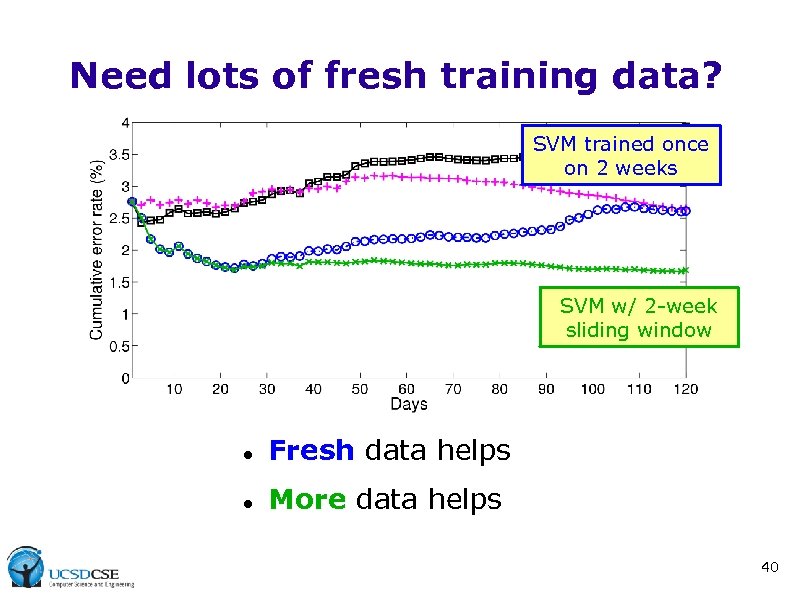 Need lots of fresh training data? SVM trained once on 2 weeks SVM w/ 2 -week sliding window Fresh data helps More data helps 40
Need lots of fresh training data? SVM trained once on 2 weeks SVM w/ 2 -week sliding window Fresh data helps More data helps 40
 Which online algorithm? Perceptron Stochastic Gradient Descent for Logistic Regression Confidence-Weighted Learning 41
Which online algorithm? Perceptron Stochastic Gradient Descent for Logistic Regression Confidence-Weighted Learning 41
![Perceptron [Rosenblatt, 1958] Convergence result: + radius Number of mistakes ≤ margin + + Perceptron [Rosenblatt, 1958] Convergence result: + radius Number of mistakes ≤ margin + +](https://present5.com/presentation/ef5bc8320b1df3c93840b604e2226010/image-42.jpg) Perceptron [Rosenblatt, 1958] Convergence result: + radius Number of mistakes ≤ margin + + − − + − Update on each mistake: 42
Perceptron [Rosenblatt, 1958] Convergence result: + radius Number of mistakes ≤ margin + + − − + − Update on each mistake: 42
![Logistic Regression with SGD [Bottou, 1998] Log likelihood: For every example: where Proportional 43 Logistic Regression with SGD [Bottou, 1998] Log likelihood: For every example: where Proportional 43](https://present5.com/presentation/ef5bc8320b1df3c93840b604e2226010/image-43.jpg) Logistic Regression with SGD [Bottou, 1998] Log likelihood: For every example: where Proportional 43
Logistic Regression with SGD [Bottou, 1998] Log likelihood: For every example: where Proportional 43
![Confidence-Weighted Learning [Dredze et al. , 2008] [Crammer et al. , 2009] Maintain Gaussian Confidence-Weighted Learning [Dredze et al. , 2008] [Crammer et al. , 2009] Maintain Gaussian](https://present5.com/presentation/ef5bc8320b1df3c93840b604e2226010/image-44.jpg) Confidence-Weighted Learning [Dredze et al. , 2008] [Crammer et al. , 2009] Maintain Gaussian distribution over weight vector: Constrained problem: Closed-form update: Diagonal covariance matrix for evals Update features at different rates 44
Confidence-Weighted Learning [Dredze et al. , 2008] [Crammer et al. , 2009] Maintain Gaussian distribution over weight vector: Constrained problem: Closed-form update: Diagonal covariance matrix for evals Update features at different rates 44
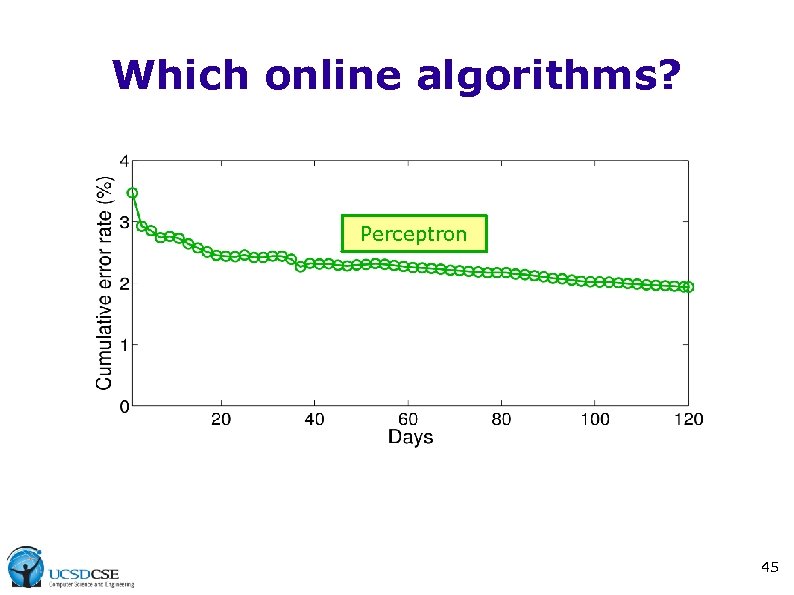 Which online algorithms? Perceptron 45
Which online algorithms? Perceptron 45
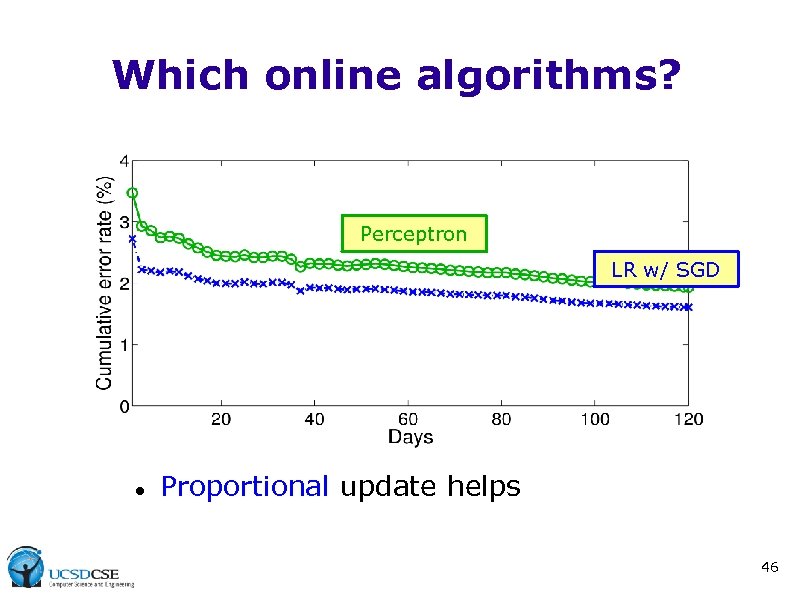 Which online algorithms? Perceptron LR w/ SGD Proportional update helps 46
Which online algorithms? Perceptron LR w/ SGD Proportional update helps 46
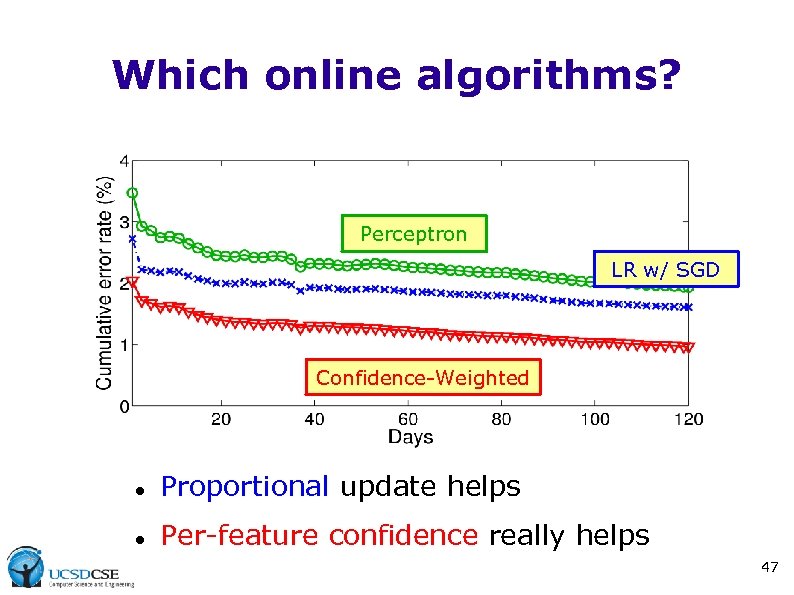 Which online algorithms? Perceptron LR w/ SGD Confidence-Weighted Proportional update helps Per-feature confidence really helps 47
Which online algorithms? Perceptron LR w/ SGD Confidence-Weighted Proportional update helps Per-feature confidence really helps 47
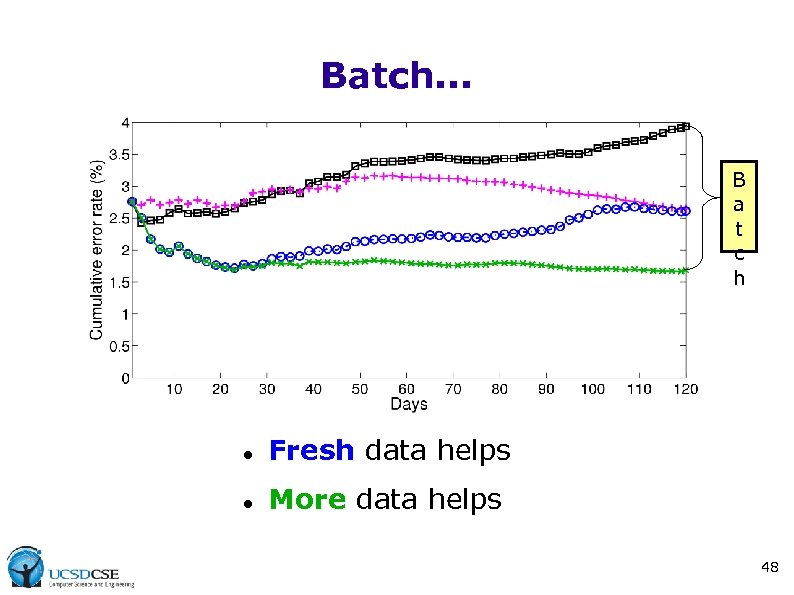 Batch. . . B a t c h Fresh data helps More data helps 48
Batch. . . B a t c h Fresh data helps More data helps 48
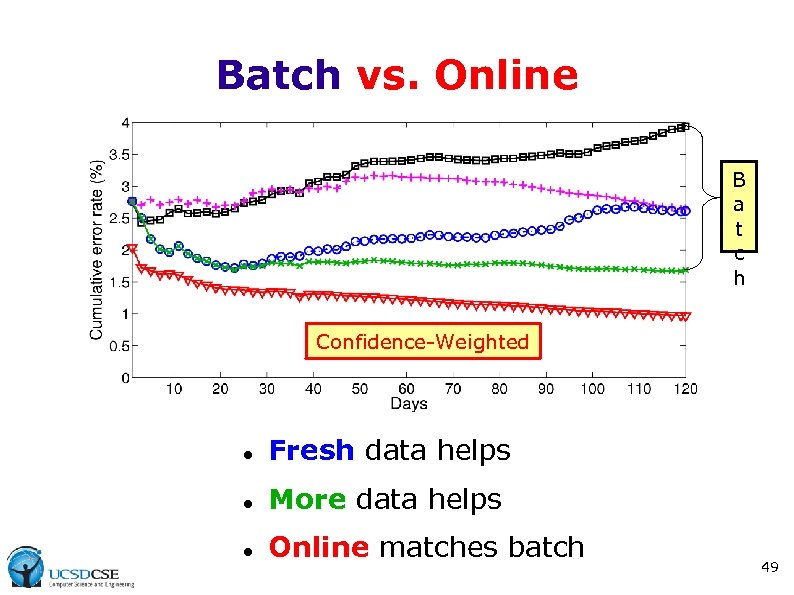 Batch vs. Online B a t c h Confidence-Weighted Fresh data helps More data helps Online matches batch 49
Batch vs. Online B a t c h Confidence-Weighted Fresh data helps More data helps Online matches batch 49
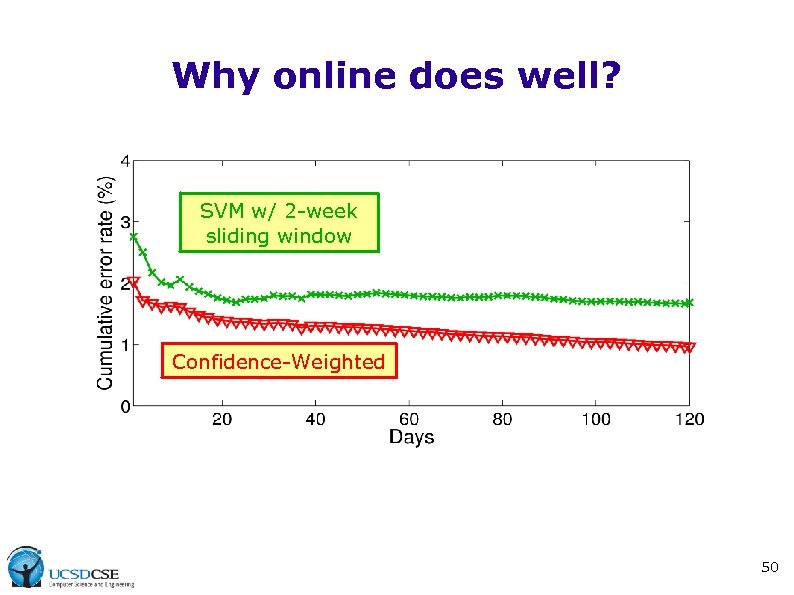 Why online does well? SVM w/ 2 -week sliding window Confidence-Weighted 50
Why online does well? SVM w/ 2 -week sliding window Confidence-Weighted 50
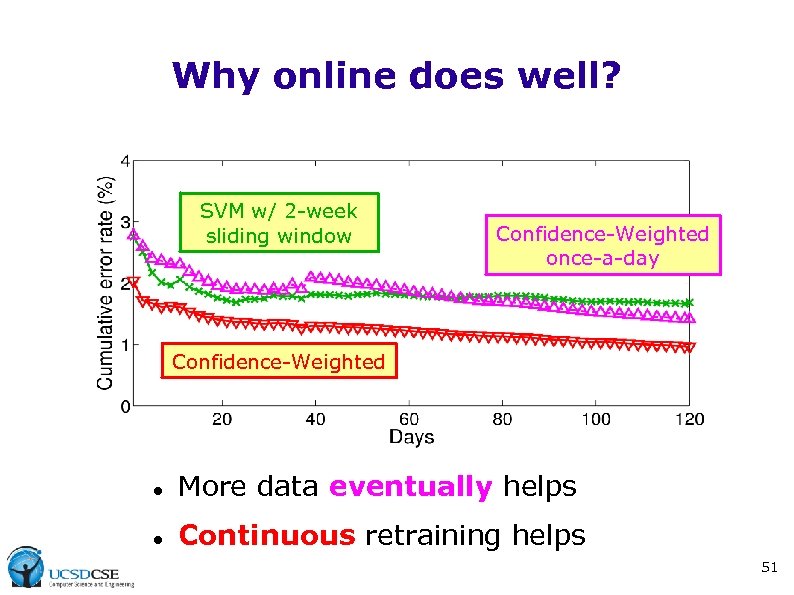 Why online does well? SVM w/ 2 -week sliding window Confidence-Weighted once-a-day Confidence-Weighted More data eventually helps Continuous retraining helps 51
Why online does well? SVM w/ 2 -week sliding window Confidence-Weighted once-a-day Confidence-Weighted More data eventually helps Continuous retraining helps 51
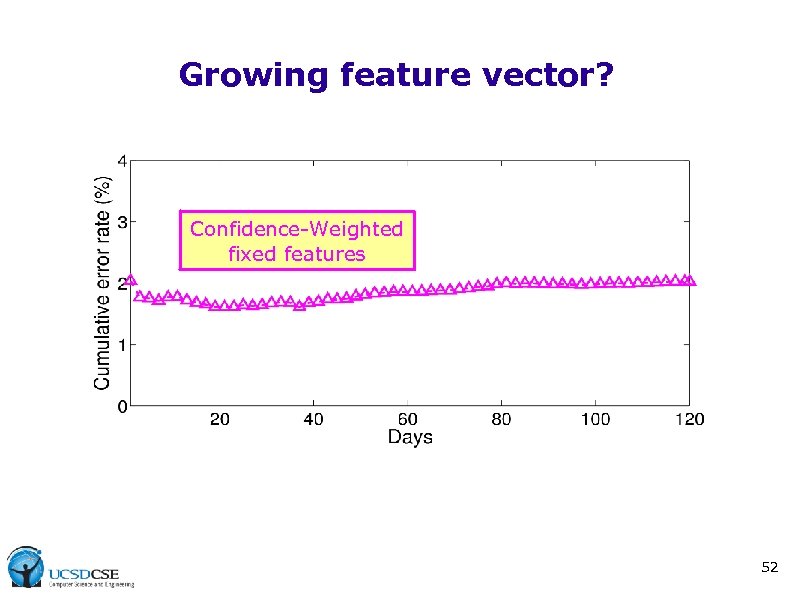 Growing feature vector? Confidence-Weighted fixed features 52
Growing feature vector? Confidence-Weighted fixed features 52
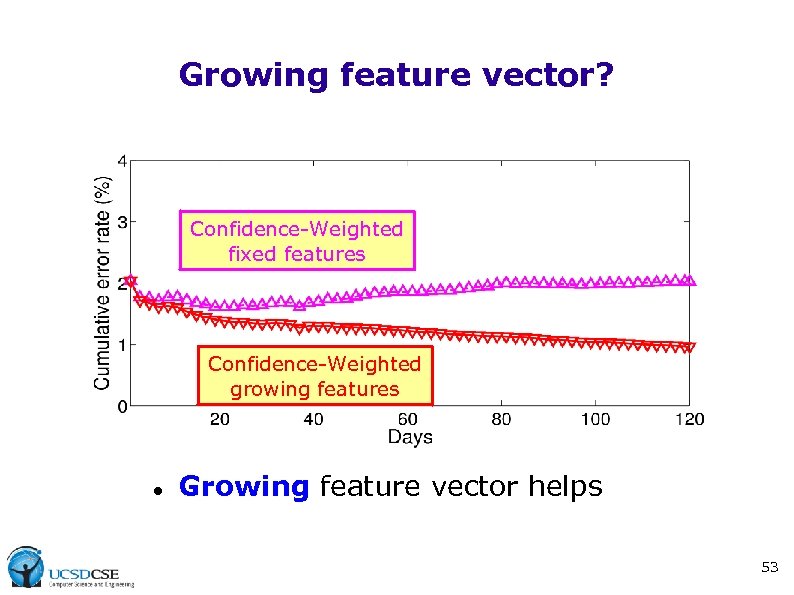 Growing feature vector? Confidence-Weighted fixed features Confidence-Weighted growing features Growing feature vector helps 53
Growing feature vector? Confidence-Weighted fixed features Confidence-Weighted growing features Growing feature vector helps 53
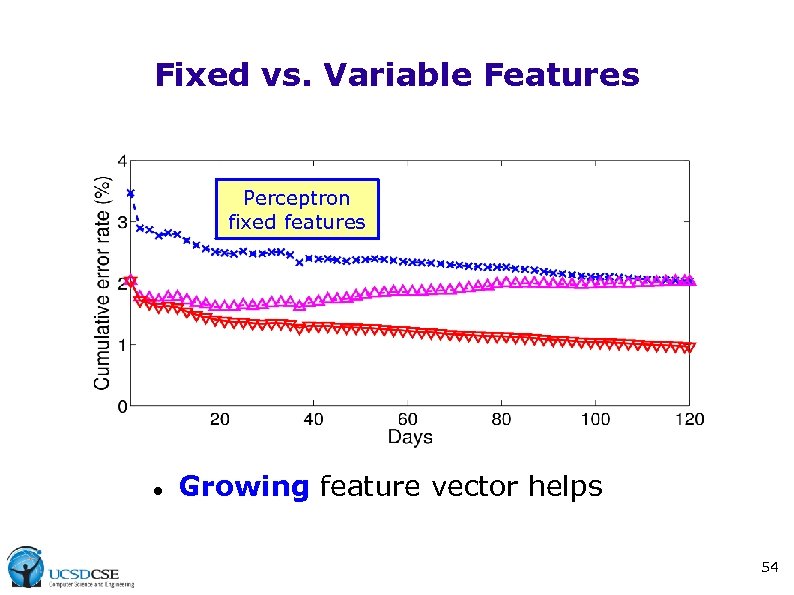 Fixed vs. Variable Features Perceptron fixed features Growing feature vector helps 54
Fixed vs. Variable Features Perceptron fixed features Growing feature vector helps 54
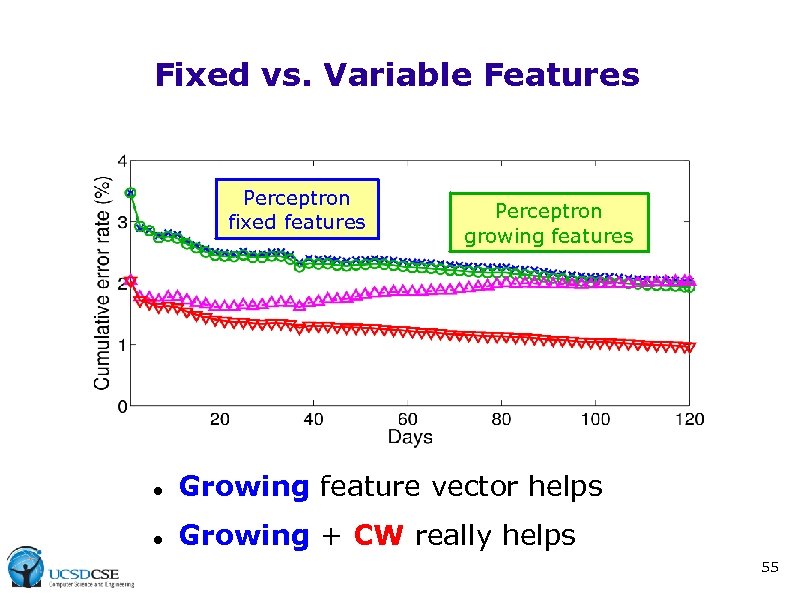 Fixed vs. Variable Features Perceptron fixed features Perceptron growing features Growing feature vector helps Growing + CW really helps 55
Fixed vs. Variable Features Perceptron fixed features Perceptron growing features Growing feature vector helps Growing + CW really helps 55
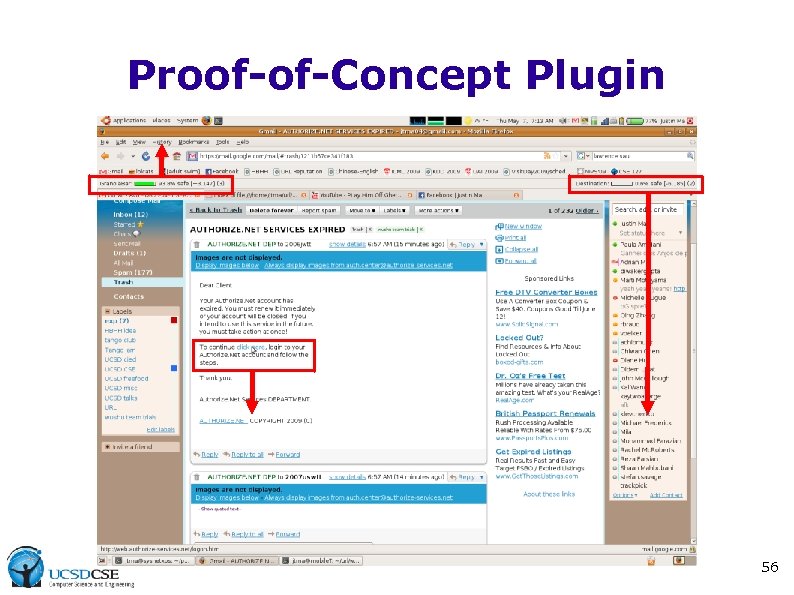 Proof-of-Concept Plugin 56
Proof-of-Concept Plugin 56
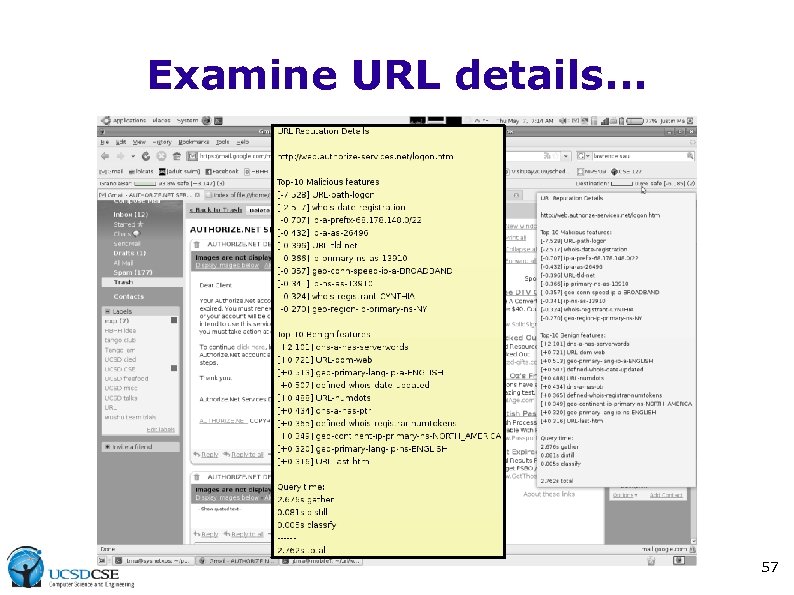 Examine URL details. . . 57
Examine URL details. . . 57
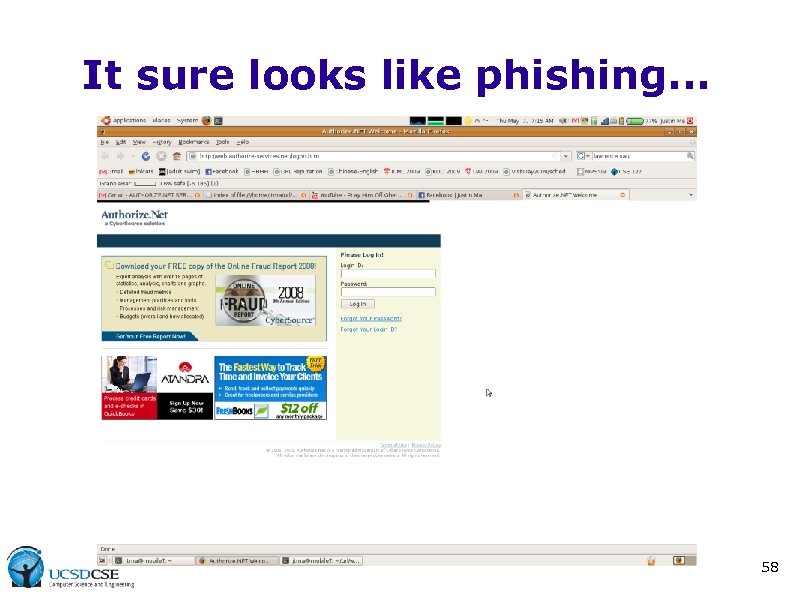 It sure looks like phishing. . . 58
It sure looks like phishing. . . 58
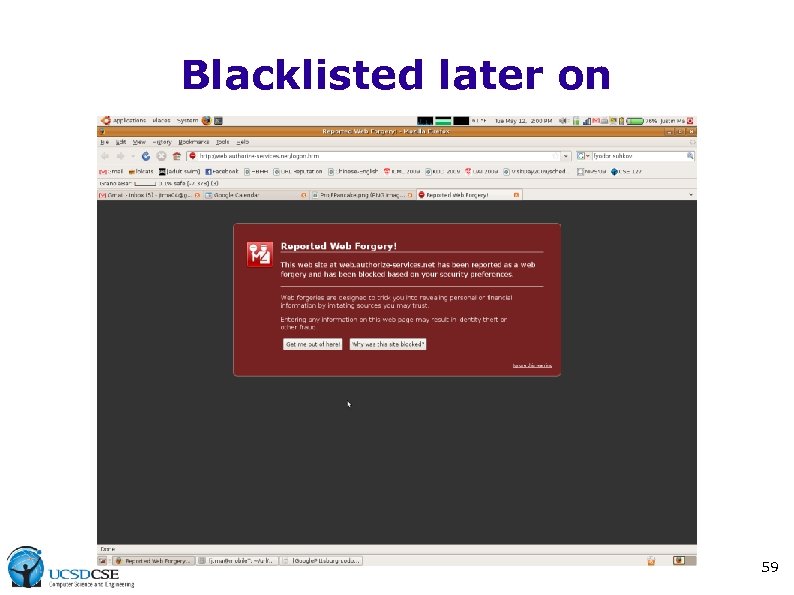 Blacklisted later on 59
Blacklisted later on 59
 Summary Detecting malicious URLs Relevant real-world problem Successful application of online learning What helps? Continuous retraining More, fresher data Growing feature vector Confidence-Weighted vs. Batch As accurate More adaptive Fewer resources 60
Summary Detecting malicious URLs Relevant real-world problem Successful application of online learning What helps? Continuous retraining More, fresher data Growing feature vector Confidence-Weighted vs. Batch As accurate More adaptive Fewer resources 60
 Today's Talk Problem Moving Beyond Blacklists Large-Scale Online Learning Conclusion 61
Today's Talk Problem Moving Beyond Blacklists Large-Scale Online Learning Conclusion 61
 Impact Public data set (UCI ML repo) Industrial impact Mail providers have adopted our approach for classifying URLs in email messages Project Info + Data Set http: //sysnet. ucsd. edu/projects/url/ 62
Impact Public data set (UCI ML repo) Industrial impact Mail providers have adopted our approach for classifying URLs in email messages Project Info + Data Set http: //sysnet. ucsd. edu/projects/url/ 62
 Final Thoughts: Systems + ML Systems: high-impact, large-scale applications ML: Methodical approaches Systems: Embrace real-world constraints ML: More than “plug-and-play” solutions Systems ↔ Machine Learning 63
Final Thoughts: Systems + ML Systems: high-impact, large-scale applications ML: Methodical approaches Systems: Embrace real-world constraints ML: More than “plug-and-play” solutions Systems ↔ Machine Learning 63


