aee5855040a27922423d9b775b2842c4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Learning Source Descriptions for Data Integration An. Hai Doan Pedro Domingos Alon Levy Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington
Learning Source Descriptions for Data Integration An. Hai Doan Pedro Domingos Alon Levy Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington
 Overview l Problem definition – schema matching l Solution – multi-strategy learning l Prototype system – LSD (Learning Source Descriptions) Experiments l Related work l Summary & future work l 2
Overview l Problem definition – schema matching l Solution – multi-strategy learning l Prototype system – LSD (Learning Source Descriptions) Experiments l Related work l Summary & future work l 2
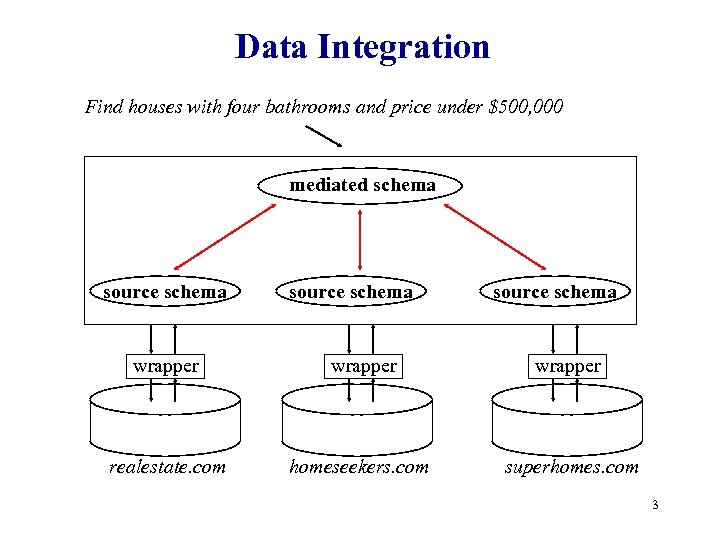 Data Integration Find houses with four bathrooms and price under $500, 000 mediated schema source schema wrapper realestate. com homeseekers. com superhomes. com 3
Data Integration Find houses with four bathrooms and price under $500, 000 mediated schema source schema wrapper realestate. com homeseekers. com superhomes. com 3
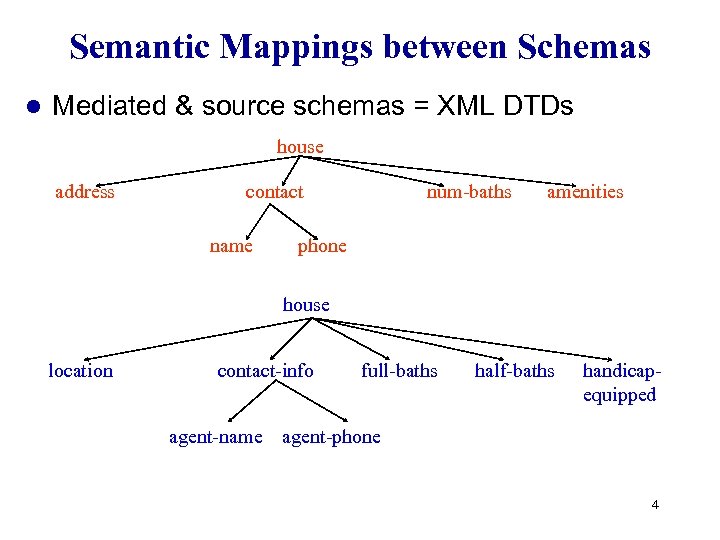 Semantic Mappings between Schemas l Mediated & source schemas = XML DTDs house address contact name num-baths amenities phone house location contact-info agent-name full-baths half-baths handicapequipped agent-phone 4
Semantic Mappings between Schemas l Mediated & source schemas = XML DTDs house address contact name num-baths amenities phone house location contact-info agent-name full-baths half-baths handicapequipped agent-phone 4
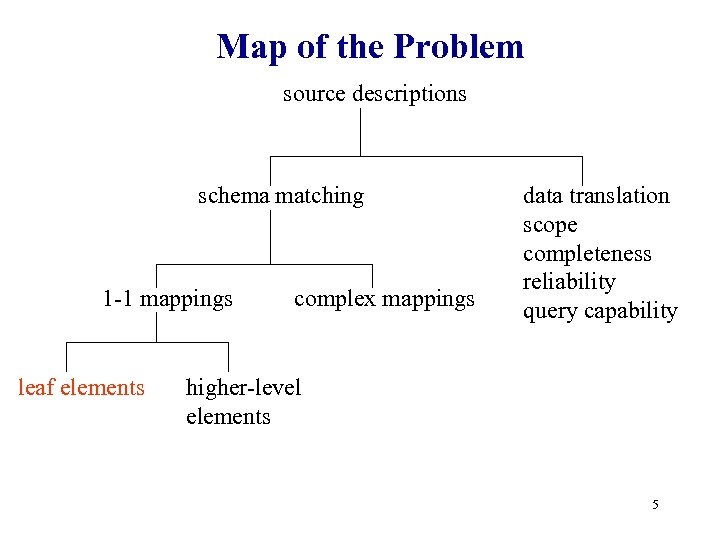 Map of the Problem source descriptions schema matching 1 -1 mappings leaf elements complex mappings data translation scope completeness reliability query capability higher-level elements 5
Map of the Problem source descriptions schema matching 1 -1 mappings leaf elements complex mappings data translation scope completeness reliability query capability higher-level elements 5
 Current State of Affairs l Largely done by hand – labor intensive & error prone – key bottleneck in building applications l Will only be exacerbated – data sharing & XML become pervasive – proliferation of DTDs – translation of legacy data l Need automatic approaches to scale up! 6
Current State of Affairs l Largely done by hand – labor intensive & error prone – key bottleneck in building applications l Will only be exacerbated – data sharing & XML become pervasive – proliferation of DTDs – translation of legacy data l Need automatic approaches to scale up! 6
 Our Approach Use machine learning to match schemas l Basic idea l 1. create training data – manually map a set of sources to mediated schema 2. train system on training data – learns from – – – name of schema elements format of values frequency of words & symbols characteristics of value distribution proximity, position, structure, . . . 3. system proposes mappings for subsequent sources 7
Our Approach Use machine learning to match schemas l Basic idea l 1. create training data – manually map a set of sources to mediated schema 2. train system on training data – learns from – – – name of schema elements format of values frequency of words & symbols characteristics of value distribution proximity, position, structure, . . . 3. system proposes mappings for subsequent sources 7
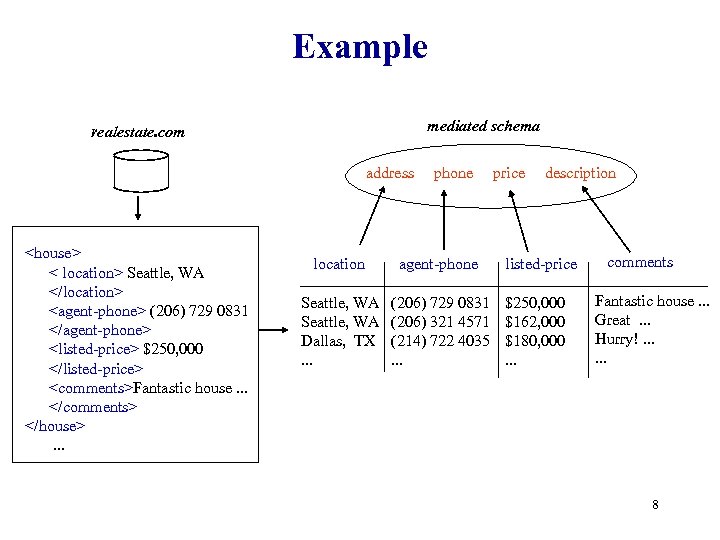 Example mediated schema realestate. com address
Example mediated schema realestate. com address
 Multi-Strategy Learning l Use a set of base learners – each exploits certain types of information l Match schema elements of a new source – apply the learners – combine their predictions using a meta-learner l Meta-learner – measures base learner accuracy on training data – weighs each learner based on its accuracy 9
Multi-Strategy Learning l Use a set of base learners – each exploits certain types of information l Match schema elements of a new source – apply the learners – combine their predictions using a meta-learner l Meta-learner – measures base learner accuracy on training data – weighs each learner based on its accuracy 9
 Learners l Input – schema information: name, proximity, structure, . . . – data information: value, format, . . . l Output – prediction weighted by confidence score l Examples – Name matcher – agent-name => (name, 0. 7), (phone, 0. 3) – Frequency learner – “Seattle, WA” => (address, 0. 8), (name, 0. 2) – “Great location. . . ” => (description, 0. 9), (address, 0. 1) 10
Learners l Input – schema information: name, proximity, structure, . . . – data information: value, format, . . . l Output – prediction weighted by confidence score l Examples – Name matcher – agent-name => (name, 0. 7), (phone, 0. 3) – Frequency learner – “Seattle, WA” => (address, 0. 8), (name, 0. 2) – “Great location. . . ” => (description, 0. 9), (address, 0. 1) 10
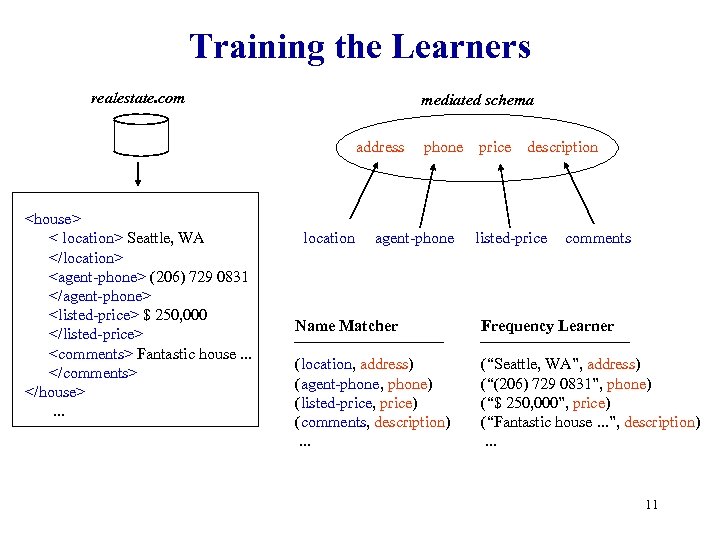 Training the Learners realestate. com mediated schema address
Training the Learners realestate. com mediated schema address
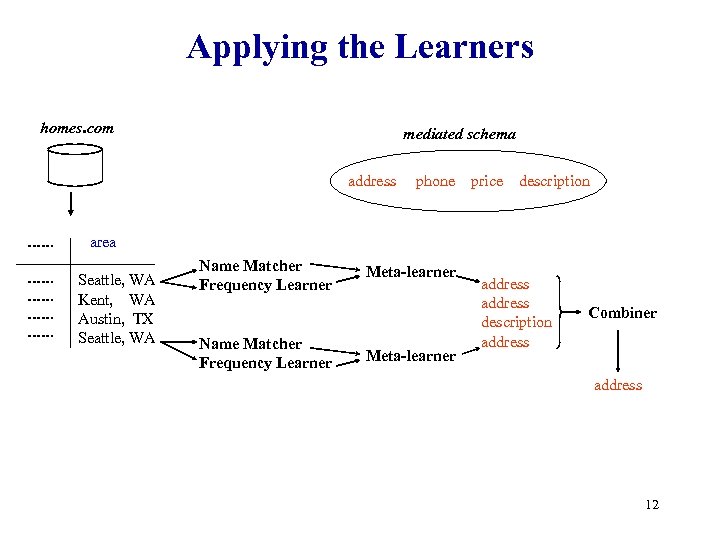 Applying the Learners homes. com mediated schema address phone price description area Seattle, WA Kent, WA Austin, TX Seattle, WA Name Matcher Frequency Learner Meta-learner address description address Combiner address 12
Applying the Learners homes. com mediated schema address phone price description area Seattle, WA Kent, WA Austin, TX Seattle, WA Name Matcher Frequency Learner Meta-learner address description address Combiner address 12
 The LSD System l Base learners/modules – – l name matcher Naive Bayesian learner Whirl nearest-neighbor classifier [Cohen&Hirsh-KDD 98] county-name recognizer Meta-learner – uses stacking [Ting&Witten 99, Wolpert 92] – uses training data to learn weights for base learners – combines predictions using confidence scores/weights 13
The LSD System l Base learners/modules – – l name matcher Naive Bayesian learner Whirl nearest-neighbor classifier [Cohen&Hirsh-KDD 98] county-name recognizer Meta-learner – uses stacking [Ting&Witten 99, Wolpert 92] – uses training data to learn weights for base learners – combines predictions using confidence scores/weights 13
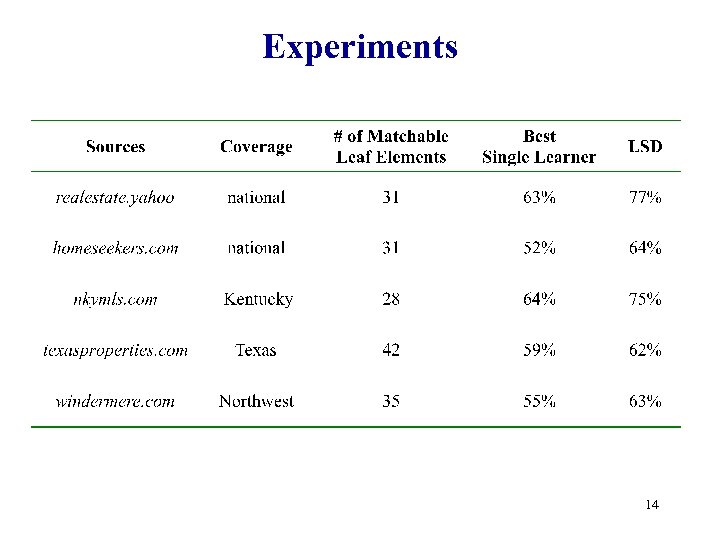 Experiments 14
Experiments 14
![Related Work l Rule-based approaches – TRANSCM [Milo&Zohar 98], ARTEMIS [Castano&Antonellis 99], [Palopoli et. Related Work l Rule-based approaches – TRANSCM [Milo&Zohar 98], ARTEMIS [Castano&Antonellis 99], [Palopoli et.](https://present5.com/presentation/aee5855040a27922423d9b775b2842c4/image-15.jpg) Related Work l Rule-based approaches – TRANSCM [Milo&Zohar 98], ARTEMIS [Castano&Antonellis 99], [Palopoli et. al. 98] – utilize only schema information l Learner-based approaches – SEMINT [Li&Clifton 94], ILA [Perkowitz&Etzioni 95] – employ a single learner, limited applicability l Multi-strategy learning in other domains – series of workshops [91, 93, 96, 98, 00] – [Freitag 98], Proverb [Keim et. al. 99] 15
Related Work l Rule-based approaches – TRANSCM [Milo&Zohar 98], ARTEMIS [Castano&Antonellis 99], [Palopoli et. al. 98] – utilize only schema information l Learner-based approaches – SEMINT [Li&Clifton 94], ILA [Perkowitz&Etzioni 95] – employ a single learner, limited applicability l Multi-strategy learning in other domains – series of workshops [91, 93, 96, 98, 00] – [Freitag 98], Proverb [Keim et. al. 99] 15
 Summary l Schema matching – automated by learning l Multi-strategy learning is essential – – l handles different types of data incorporates different types of domain knowledge easy to incorporate new learners alleviates effects of noise & dirty data Implemented LSD – promising results with initial experiments 16
Summary l Schema matching – automated by learning l Multi-strategy learning is essential – – l handles different types of data incorporates different types of domain knowledge easy to incorporate new learners alleviates effects of noise & dirty data Implemented LSD – promising results with initial experiments 16
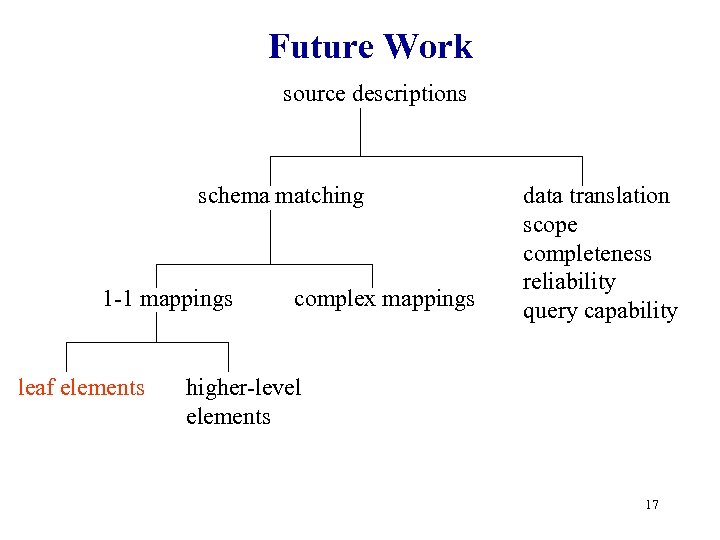 Future Work source descriptions schema matching 1 -1 mappings leaf elements complex mappings data translation scope completeness reliability query capability higher-level elements 17
Future Work source descriptions schema matching 1 -1 mappings leaf elements complex mappings data translation scope completeness reliability query capability higher-level elements 17


