8893df857f8de2a66256126e11bef004.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Learning, Recognizing, and Assisting with Activities Tom Dietterich Oregon State University
Learning, Recognizing, and Assisting with Activities Tom Dietterich Oregon State University
 Assumptions • Goal: Integrated, autonomous, and useful AI systems – Must collaborate well with people • Must recognize and understand human goals, attentional state, costs of coordination, etc.
Assumptions • Goal: Integrated, autonomous, and useful AI systems – Must collaborate well with people • Must recognize and understand human goals, attentional state, costs of coordination, etc.
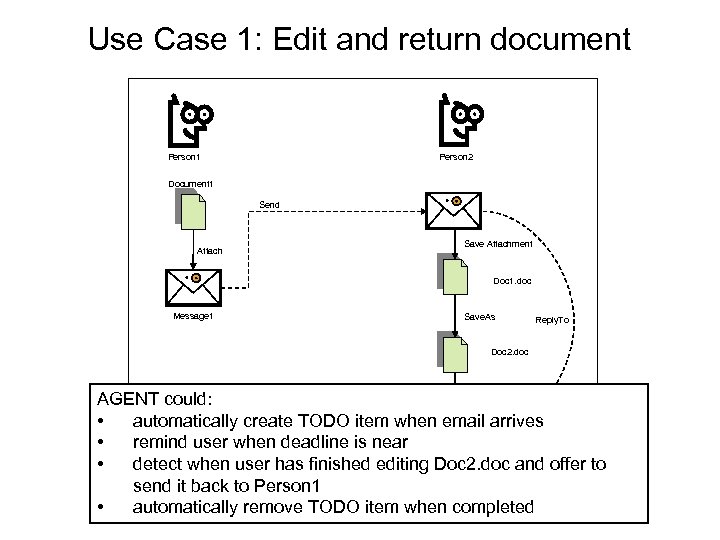 Use Case 1: Edit and return document Person 2 Person 1 Document 1 Send Attach Save Attachment Doc 1. doc Message 1 Save. As Reply. To Doc 2. doc Attach AGENT could: • automatically create TODO item when email arrives Send • remind user when deadline is near • detect when user has finished editing Doc 2. doc and offer to send it back to Person 1 • automatically remove TODO item when completed
Use Case 1: Edit and return document Person 2 Person 1 Document 1 Send Attach Save Attachment Doc 1. doc Message 1 Save. As Reply. To Doc 2. doc Attach AGENT could: • automatically create TODO item when email arrives Send • remind user when deadline is near • detect when user has finished editing Doc 2. doc and offer to send it back to Person 1 • automatically remove TODO item when completed
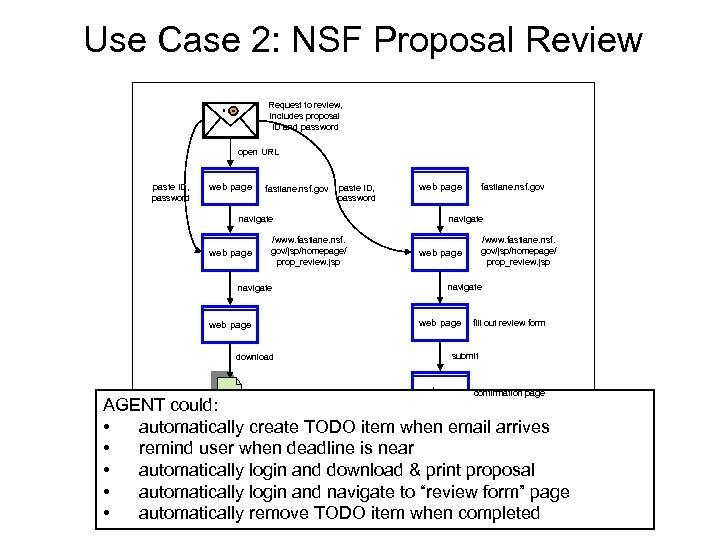 Use Case 2: NSF Proposal Review Request to review, includes proposal ID and password open URL paste ID, password web page fastlane. nsf. gov paste ID, password navigate web page /www. fastlane. nsf. gov/jsp/homepage/ prop_review. jsp navigate web page navigate download service/nsf/proposal. pdf /www. fastlane. nsf. gov/jsp/homepage/ prop_review. jsp web page navigate web page fastlane. nsf. gov fill out review form submit web page confirmation page AGENT could: logout print • automatically create TODO item when email arrives • remind user when deadline is near web page • automatically login and download & print proposal • automatically login and navigate to “review form” page • automatically remove TODO item when completed
Use Case 2: NSF Proposal Review Request to review, includes proposal ID and password open URL paste ID, password web page fastlane. nsf. gov paste ID, password navigate web page /www. fastlane. nsf. gov/jsp/homepage/ prop_review. jsp navigate web page navigate download service/nsf/proposal. pdf /www. fastlane. nsf. gov/jsp/homepage/ prop_review. jsp web page navigate web page fastlane. nsf. gov fill out review form submit web page confirmation page AGENT could: logout print • automatically create TODO item when email arrives • remind user when deadline is near web page • automatically login and download & print proposal • automatically login and navigate to “review form” page • automatically remove TODO item when completed
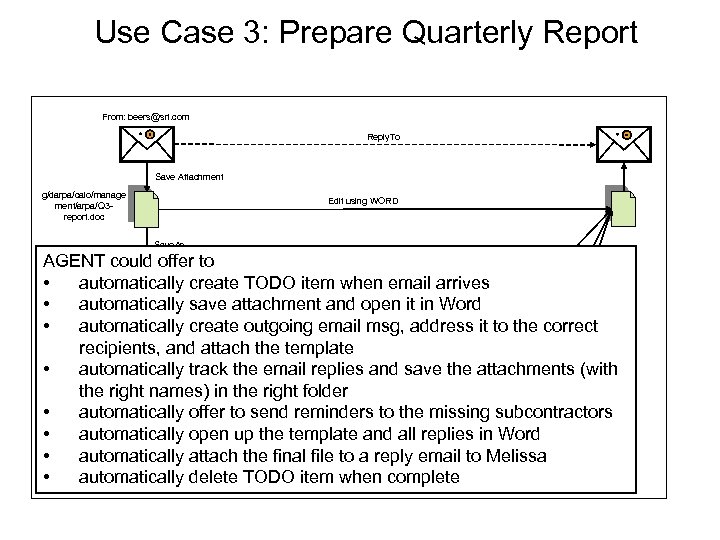 Use Case 3: Prepare Quarterly Report From: beers@sri. com Reply. To Save Attachment Attach g/darpa/calo/manage ment/arpa/Q 3 report. doc Edit using WORD Save. As Chin AGENT could offer to Save Attachment: Q 3 -report-chin. doc • automatically create TODO item when email arrives Paste • automatically save attachment and open it in Word Attach • automatically create outgoing email msg, address it to the correct Williams Save Attachment: recipients, and attach the template Q 3 -report-williams. doc Send • automatically track the email replies and save the attachments (with the right names) in the right folder Sanchez • automatically offer to send reminders to the missing subcontractors Save Attachment: Q 3 -report-sanchez. doc Send • automatically open up the template and all replies in Word • automatically attach the final file to a reply email to Melissa reminder • automatically delete TODO item when complete g/darpa/calo/manage ment/arpa/Q 3 -reporttemplate. doc
Use Case 3: Prepare Quarterly Report From: beers@sri. com Reply. To Save Attachment Attach g/darpa/calo/manage ment/arpa/Q 3 report. doc Edit using WORD Save. As Chin AGENT could offer to Save Attachment: Q 3 -report-chin. doc • automatically create TODO item when email arrives Paste • automatically save attachment and open it in Word Attach • automatically create outgoing email msg, address it to the correct Williams Save Attachment: recipients, and attach the template Q 3 -report-williams. doc Send • automatically track the email replies and save the attachments (with the right names) in the right folder Sanchez • automatically offer to send reminders to the missing subcontractors Save Attachment: Q 3 -report-sanchez. doc Send • automatically open up the template and all replies in Word • automatically attach the final file to a reply email to Melissa reminder • automatically delete TODO item when complete g/darpa/calo/manage ment/arpa/Q 3 -reporttemplate. doc
 Research Challenges • • Representing Workflows Learning Workflows Recognizing Workflows Deciding (Learning) When and How to Help
Research Challenges • • Representing Workflows Learning Workflows Recognizing Workflows Deciding (Learning) When and How to Help
 Representing Workflows • For what purpose: – execution: • sequence of actions (possibly with conditionals and iteration) – recognition: • partially-ordered sequence of actions (with conditionals and iteration) • capture additional features to aid recognition (e. g. , email speech acts) – learning: • need action models to detect unobserved steps and understand goals – assistance • need action models to understand goals • Workflow steps: – informational inputs (file name, file, URL) – action (click Download) – action models (creates file on disk with file name; contents = contents of URL file)
Representing Workflows • For what purpose: – execution: • sequence of actions (possibly with conditionals and iteration) – recognition: • partially-ordered sequence of actions (with conditionals and iteration) • capture additional features to aid recognition (e. g. , email speech acts) – learning: • need action models to detect unobserved steps and understand goals – assistance • need action models to understand goals • Workflow steps: – informational inputs (file name, file, URL) – action (click Download) – action models (creates file on disk with file name; contents = contents of URL file)
 Representing Workflows comment. On. Document : mail. Arrived(Email. RID, Requester, Speech. Act, Deadline, [Attachment 1]), outlook. Open(Email. RID), attachment. Save(Email. RID, Attachment 1, File. RID), word. Edit. Document(File. RID, Edited. File. RID), outlook. Open(Email. RID), outlook. Compose. Reply(New. Email. RID, Email. RID), outlook. Send. Reply(New. Email. RID, Requester, Speech. Act 2, [Attachment 2]), outlook. Attachment. Info(New. Email. RID, Edited. File. RID, Attachment 2). word. Edit. Document(File. RID, Final. RID) : word. Open(File. RID), finish. Edit(File. RID, Final. RID). // simply close the file and return it finish. Edit(File. RID, File. RID) : word. Close(File. RID). // close the file, then later re-open it and continue finish. Edit(File. RID, Final. RID) : word. Close(File. RID), word. Open(File. RID), finish. Edit(File. RID, Final. RID). // perform a Save. As and then continue finish. Edit(File. RID, Final. RID) : word. Save. As(File. RID, New. File. RID), finish. Edit(New. File. RID, Final. RID).
Representing Workflows comment. On. Document : mail. Arrived(Email. RID, Requester, Speech. Act, Deadline, [Attachment 1]), outlook. Open(Email. RID), attachment. Save(Email. RID, Attachment 1, File. RID), word. Edit. Document(File. RID, Edited. File. RID), outlook. Open(Email. RID), outlook. Compose. Reply(New. Email. RID, Email. RID), outlook. Send. Reply(New. Email. RID, Requester, Speech. Act 2, [Attachment 2]), outlook. Attachment. Info(New. Email. RID, Edited. File. RID, Attachment 2). word. Edit. Document(File. RID, Final. RID) : word. Open(File. RID), finish. Edit(File. RID, Final. RID). // simply close the file and return it finish. Edit(File. RID, File. RID) : word. Close(File. RID). // close the file, then later re-open it and continue finish. Edit(File. RID, Final. RID) : word. Close(File. RID), word. Open(File. RID), finish. Edit(File. RID, Final. RID). // perform a Save. As and then continue finish. Edit(File. RID, Final. RID) : word. Save. As(File. RID, New. File. RID), finish. Edit(New. File. RID, Final. RID).
 Learning Workflows • Learning by Demonstration – LAPDOG: PBD system at SRI – Lau, et al. at IBM and before that UW – PLOW: Allen et al. Rochester • Learning by Observation (unsupervised) – Weld et al.
Learning Workflows • Learning by Demonstration – LAPDOG: PBD system at SRI – Lau, et al. at IBM and before that UW – PLOW: Allen et al. Rochester • Learning by Observation (unsupervised) – Weld et al.
 Recognizing Workflows • Challenges on the desktop – Multiple workflows interleaved – Multiple instances of the same workflow interleaved • reviewing multiple NSF proposals – Sharing across workflows • log in and navigate only once, then download multiple files – Unmodeled background events • IM, nytimes. com, weather. com, etc.
Recognizing Workflows • Challenges on the desktop – Multiple workflows interleaved – Multiple instances of the same workflow interleaved • reviewing multiple NSF proposals – Sharing across workflows • log in and navigate only once, then download multiple files – Unmodeled background events • IM, nytimes. com, weather. com, etc.
 Recognition Task • Given: – a set of workflow schemas – an observation sequence • Find: – all instances of those workflow schemas in the observation sequence – detect each instance as early as possible – report the current state of all active workflow schemas at each point in time • Metrics: – false positives, false negatives, timeliness
Recognition Task • Given: – a set of workflow schemas – an observation sequence • Find: – all instances of those workflow schemas in the observation sequence – detect each instance as early as possible – report the current state of all active workflow schemas at each point in time • Metrics: – false positives, false negatives, timeliness
 Assistance • What steps can the AGENT do? • What steps should the AGENT do? • How and when should the AGENT coordinate with the user? • Decision-theoretic collaboration – model the user’s intentions and attentional state – estimate the expected benefit of AGENT’s assistive plan (including coordination cost) – choose action that maximizes expected benefit
Assistance • What steps can the AGENT do? • What steps should the AGENT do? • How and when should the AGENT coordinate with the user? • Decision-theoretic collaboration – model the user’s intentions and attentional state – estimate the expected benefit of AGENT’s assistive plan (including coordination cost) – choose action that maximizes expected benefit
 Rich Intention Structures • Goal stack – traditional programming languages – hierarchical reinforcement learning formalisms – cognitive architectures: SOAR, ACT-R • Goal graph – ABL (Mateas) • The user’s TODO list is an intention structure – so is the Inbox for many people • Revised statement of our goal: – representation, learning, recognition, and assistance with rich intention structures
Rich Intention Structures • Goal stack – traditional programming languages – hierarchical reinforcement learning formalisms – cognitive architectures: SOAR, ACT-R • Goal graph – ABL (Mateas) • The user’s TODO list is an intention structure – so is the Inbox for many people • Revised statement of our goal: – representation, learning, recognition, and assistance with rich intention structures
 Related Topics • Argumentation and Persuasion – How do two agents exchange information in order to reach agreement? • Explanation-based Teaching and Learning – – – AGENT makes a mistake user says “Why did you do that? ” AGENT explains user corrects parts of the explanation etc. • Transfer Learning – How do I transfer to you something I’ve learned when • you have a different ontology • I can’t give you all of my training data (privacy, bandwidth)?
Related Topics • Argumentation and Persuasion – How do two agents exchange information in order to reach agreement? • Explanation-based Teaching and Learning – – – AGENT makes a mistake user says “Why did you do that? ” AGENT explains user corrects parts of the explanation etc. • Transfer Learning – How do I transfer to you something I’ve learned when • you have a different ontology • I can’t give you all of my training data (privacy, bandwidth)?
 Summary • Goal: AI AGENT that can help humans • Prerequisite: AGENT must understand what its user is doing
Summary • Goal: AI AGENT that can help humans • Prerequisite: AGENT must understand what its user is doing


