c66941e0fddc4b83fc9e42b7e3764a4d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Learning Outcomes • Mahasiswa akan dapat menjelaskan pengertian atrian, system antrian, struktur dan analisis pola kedatangan pada sistem antrian. Bina Nusantara
Learning Outcomes • Mahasiswa akan dapat menjelaskan pengertian atrian, system antrian, struktur dan analisis pola kedatangan pada sistem antrian. Bina Nusantara
 Outline Materi: • • • Bina Nusantara Pengertian Antrian Sistem Antrian Struktur dasar model antrian Bentuk-bentuk model antrian Analisis pola kedatangan Contoh. .
Outline Materi: • • • Bina Nusantara Pengertian Antrian Sistem Antrian Struktur dasar model antrian Bentuk-bentuk model antrian Analisis pola kedatangan Contoh. .
 Pengertian • Istilah “antrian” atau disiplin “garis tunggu” atau “waiting lines” menunjukan pada kondisi dimana kedatangan dipilih untuk dilayani. Prosedur yang umum diguna-kan adalah kedatangan menempati garis tunggu atas dasar yang : “datang pertama dilayani pertama” (FCFS), walaupun beberapa prioritas dapat mengubah pola pelayanan ini, namum analisis ini tidak mempertimbangkan kemungkinan itu. Bina Nusantara
Pengertian • Istilah “antrian” atau disiplin “garis tunggu” atau “waiting lines” menunjukan pada kondisi dimana kedatangan dipilih untuk dilayani. Prosedur yang umum diguna-kan adalah kedatangan menempati garis tunggu atas dasar yang : “datang pertama dilayani pertama” (FCFS), walaupun beberapa prioritas dapat mengubah pola pelayanan ini, namum analisis ini tidak mempertimbangkan kemungkinan itu. Bina Nusantara
 Waiting Lines • First studied by A. K. Erlang in 1913. – Analyzed telephone facilities. • Body of knowledge called queuing theory. – Queue is another name for waiting line. • Decision problem: – Balance cost of providing good service with cost of customers waiting. Bina Nusantara
Waiting Lines • First studied by A. K. Erlang in 1913. – Analyzed telephone facilities. • Body of knowledge called queuing theory. – Queue is another name for waiting line. • Decision problem: – Balance cost of providing good service with cost of customers waiting. Bina Nusantara
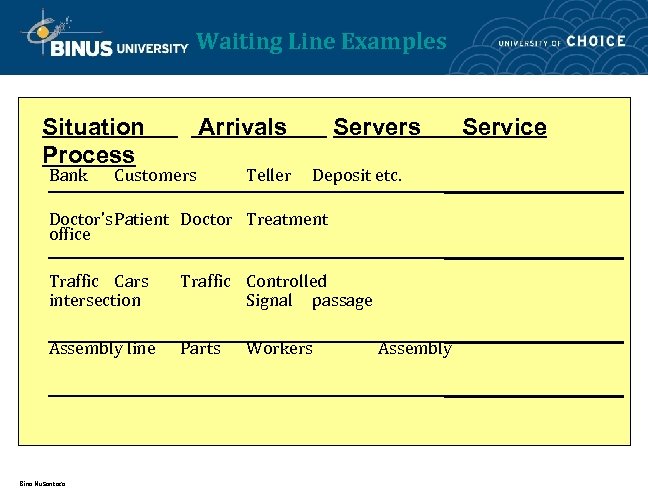 Waiting Line Examples Situation Process Bank Arrivals Customers Teller Servers Deposit etc. Doctor’s. Patient Doctor Treatment office Traffic Cars intersection Traffic Controlled Signal passage Assembly line Parts Bina Nusantara Workers Assembly Service
Waiting Line Examples Situation Process Bank Arrivals Customers Teller Servers Deposit etc. Doctor’s. Patient Doctor Treatment office Traffic Cars intersection Traffic Controlled Signal passage Assembly line Parts Bina Nusantara Workers Assembly Service
 Waiting Line Components • Arrivals: Customers (people, machines, calls, etc. ) that demand service. • Service System: Includes waiting line and servers. • Waiting Line (Queue): Arrivals waiting for a free server. • Servers: People or machines that provide service to the arrivals. Bina Nusantara
Waiting Line Components • Arrivals: Customers (people, machines, calls, etc. ) that demand service. • Service System: Includes waiting line and servers. • Waiting Line (Queue): Arrivals waiting for a free server. • Servers: People or machines that provide service to the arrivals. Bina Nusantara
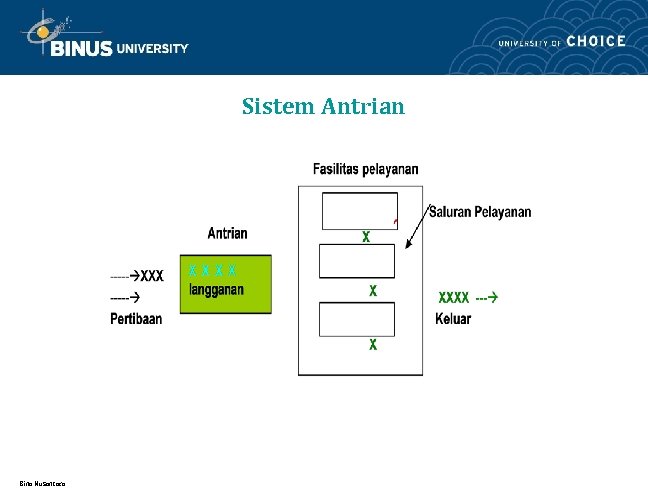 Sistem Antrian Bina Nusantara
Sistem Antrian Bina Nusantara
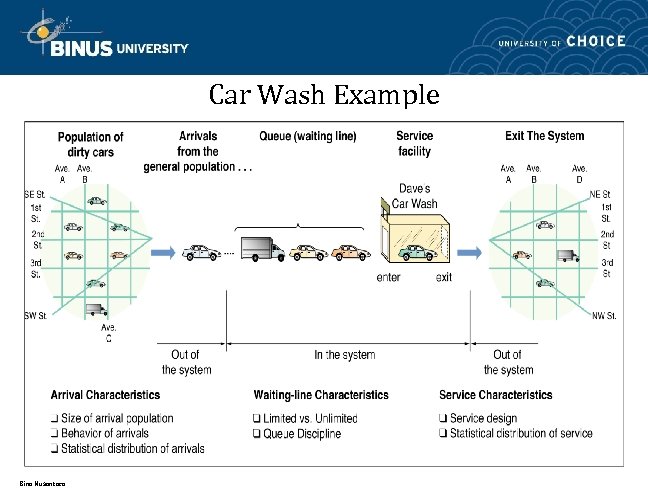 Car Wash Example Bina Nusantara
Car Wash Example Bina Nusantara
 Waiting Line Terminology • Queue: Waiting line. • Arrival: 1 person, machine, part, etc. that arrives and demands service. • Queue discipline: Rules for determining the order that arrivals receive service. • Channels: Parallel servers. • Phases: Sequential stages in service. Bina Nusantara
Waiting Line Terminology • Queue: Waiting line. • Arrival: 1 person, machine, part, etc. that arrives and demands service. • Queue discipline: Rules for determining the order that arrivals receive service. • Channels: Parallel servers. • Phases: Sequential stages in service. Bina Nusantara
 Input Characteristics • Input source (population) size. – Infinite: Number in service does not affect probability of a new arrival. • A very large population can be treated as infinite. – Finite: Number in service affects probability of a new arrival. • Example: Population = 10 aircraft that may need repair. • Arrival pattern. – Random: Use Poisson probability distribution. – Non-random: Appointments. Bina Nusantara
Input Characteristics • Input source (population) size. – Infinite: Number in service does not affect probability of a new arrival. • A very large population can be treated as infinite. – Finite: Number in service affects probability of a new arrival. • Example: Population = 10 aircraft that may need repair. • Arrival pattern. – Random: Use Poisson probability distribution. – Non-random: Appointments. Bina Nusantara
 Poisson Distribution • Number of events that occur in an interval of time. – Example: Number of customers that arrive each half-hour. • Discrete distribution with mean = – Example: Mean arrival rate = 5/hour. – Probability: • Bina Nusantara Time between arrivals has a negative exponential distribution.
Poisson Distribution • Number of events that occur in an interval of time. – Example: Number of customers that arrive each half-hour. • Discrete distribution with mean = – Example: Mean arrival rate = 5/hour. – Probability: • Bina Nusantara Time between arrivals has a negative exponential distribution.
 Waiting Line Characteristics • Line length: – Limited: Maximum number waiting is limited. • Example: Limited space for waiting. – Unlimited: No limit on number waiting. • Queue discipline: – FIFO (FCFS): First in, First out. (First come, first served). – Random: Select next arrival to serve at random from those waiting. – Priority: Give some arrivals priority for service. Bina Nusantara
Waiting Line Characteristics • Line length: – Limited: Maximum number waiting is limited. • Example: Limited space for waiting. – Unlimited: No limit on number waiting. • Queue discipline: – FIFO (FCFS): First in, First out. (First come, first served). – Random: Select next arrival to serve at random from those waiting. – Priority: Give some arrivals priority for service. Bina Nusantara
 Bentuk-bentuk Model Antrian • Single channel, single phase. – One server, one phase of service. • Single channel, multi-phase. – One server, multiple phases in service. • Multi-channel, single phase. – Multiple servers, one phase of service. • Multi-channel, multia-phase. – Multiple servers, multiple phases of service. Bina Nusantara
Bentuk-bentuk Model Antrian • Single channel, single phase. – One server, one phase of service. • Single channel, multi-phase. – One server, multiple phases in service. • Multi-channel, single phase. – Multiple servers, one phase of service. • Multi-channel, multia-phase. – Multiple servers, multiple phases of service. Bina Nusantara
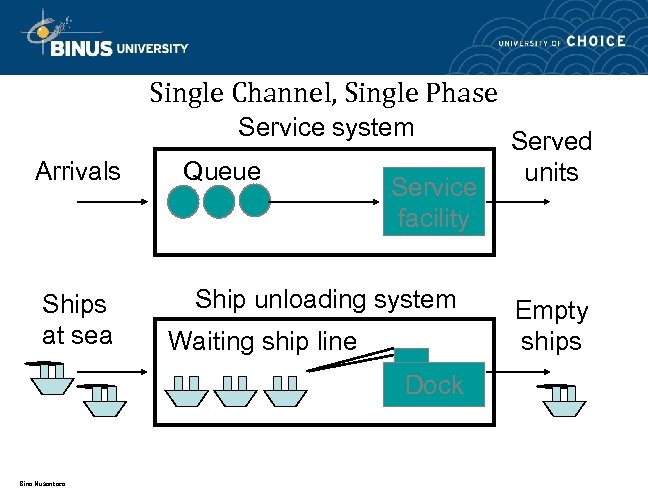 Single Channel, Single Phase Service system Arrivals Ships at sea Queue Service facility Ship unloading system Waiting ship line Dock Bina Nusantara Served units Empty ships
Single Channel, Single Phase Service system Arrivals Ships at sea Queue Service facility Ship unloading system Waiting ship line Dock Bina Nusantara Served units Empty ships
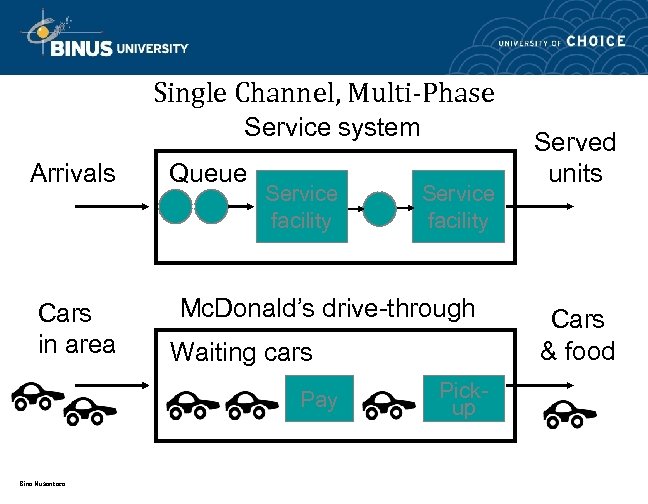 Single Channel, Multi-Phase Service system Arrivals Cars in area Queue Service facility Mc. Donald’s drive-through Waiting cars Pay Bina Nusantara Service facility Pickup Served units Cars & food
Single Channel, Multi-Phase Service system Arrivals Cars in area Queue Service facility Mc. Donald’s drive-through Waiting cars Pay Bina Nusantara Service facility Pickup Served units Cars & food
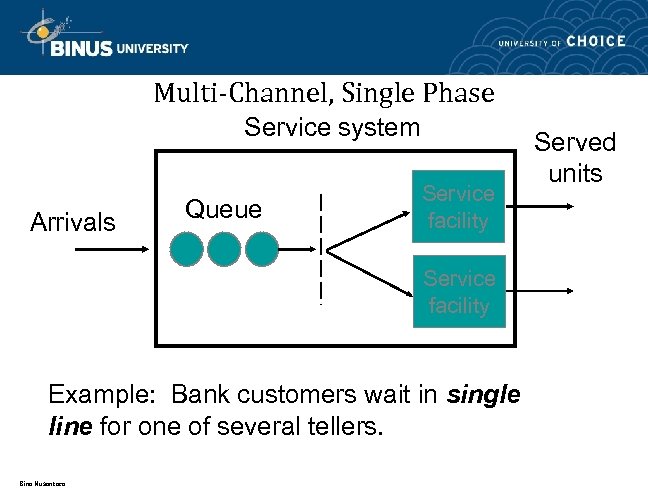 Multi-Channel, Single Phase Service system Arrivals Queue Service facility Example: Bank customers wait in single line for one of several tellers. Bina Nusantara Served units
Multi-Channel, Single Phase Service system Arrivals Queue Service facility Example: Bank customers wait in single line for one of several tellers. Bina Nusantara Served units
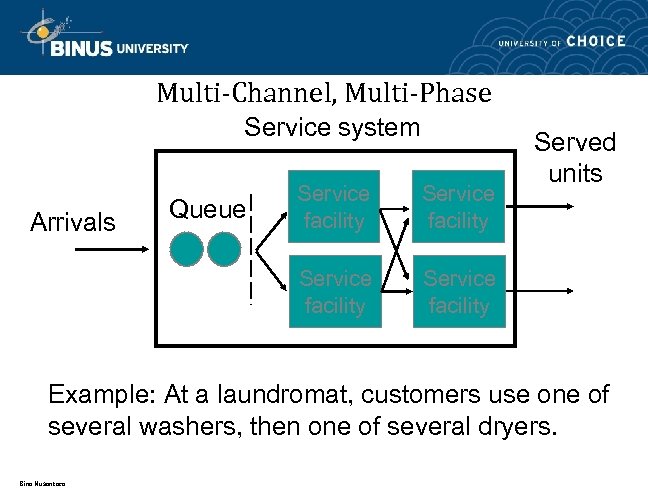 Multi-Channel, Multi-Phase Service system Queue Service facility Arrivals Service facility Served units Service facility Example: At a laundromat, customers use one of several washers, then one of several dryers. Bina Nusantara
Multi-Channel, Multi-Phase Service system Queue Service facility Arrivals Service facility Served units Service facility Example: At a laundromat, customers use one of several washers, then one of several dryers. Bina Nusantara
 Analisis Pola Pelayanan • Random: Use Negative exponential probability distribution. – Mean service rate = • 6 customers/hr. – Mean service time = 1/ • 1/6 hour = 10 minutes. • Bina Nusantara Non-random: May be constant. – Example: Automated car wash.
Analisis Pola Pelayanan • Random: Use Negative exponential probability distribution. – Mean service rate = • 6 customers/hr. – Mean service time = 1/ • 1/6 hour = 10 minutes. • Bina Nusantara Non-random: May be constant. – Example: Automated car wash.
 Assumptions in the Basic Model • Customer population is homogeneous and infinite. • Queue capacity is infinite. • Customers are well behaved (no balking or reneging). • Arrivals are served FCFS (FIFO). • Poisson arrivals. – The time between arrivals follows a negative exponential distribution • Service times are described by the negative exponential distribution. Bina Nusantara
Assumptions in the Basic Model • Customer population is homogeneous and infinite. • Queue capacity is infinite. • Customers are well behaved (no balking or reneging). • Arrivals are served FCFS (FIFO). • Poisson arrivals. – The time between arrivals follows a negative exponential distribution • Service times are described by the negative exponential distribution. Bina Nusantara
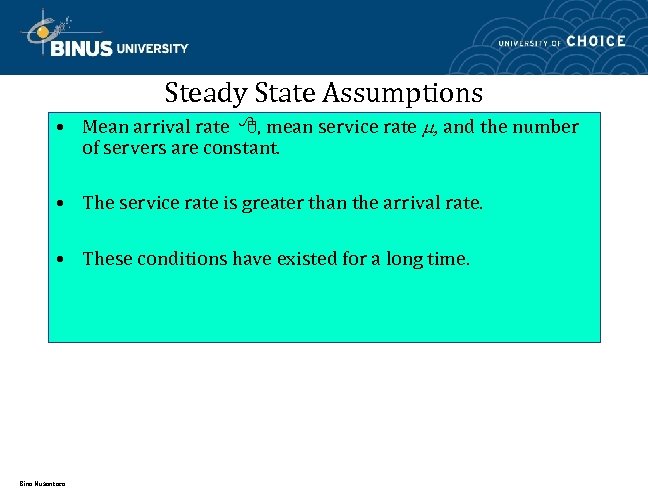 Steady State Assumptions • Mean arrival rate , mean service rate , and the number of servers are constant. • The service rate is greater than the arrival rate. • These conditions have existed for a long time. Bina Nusantara
Steady State Assumptions • Mean arrival rate , mean service rate , and the number of servers are constant. • The service rate is greater than the arrival rate. • These conditions have existed for a long time. Bina Nusantara
 Bina Nusantara
Bina Nusantara


