68359bb8f9e159c340865f98b1ceb27a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 180
 Learning Outcomes LOs Dr. Gregory J. Maffet NCAAA Consultant Dr. Naser M. Sarhan NCAAA Consultant KFUPM 29 -30 January 2014
Learning Outcomes LOs Dr. Gregory J. Maffet NCAAA Consultant Dr. Naser M. Sarhan NCAAA Consultant KFUPM 29 -30 January 2014
 Workshop’s Learning Outcomes (LOs) Attendees at the end of this workshop will be able to: 1. Comprehend the nature and role of Program and Comprehend Course learning outcomes in instruction. 2. Align an understanding relationships between Teaching Methods, Assessments Methods and LOs, 3. Write learning outcomes using the correct format Write
Workshop’s Learning Outcomes (LOs) Attendees at the end of this workshop will be able to: 1. Comprehend the nature and role of Program and Comprehend Course learning outcomes in instruction. 2. Align an understanding relationships between Teaching Methods, Assessments Methods and LOs, 3. Write learning outcomes using the correct format Write
 Workshop’s LOs 4. Summarize the role of learning outcomes in Summarize instruction and assessment. • Why we are writing learning outcomes? • The role of learning outcomes in assessment? (including Rubrics and KPIs) 5. Use the five domains of learning specified in Use National Qualification Framework; including the selection of verbs that map to measurable instructional objectives, learning outcomes and assessment.
Workshop’s LOs 4. Summarize the role of learning outcomes in Summarize instruction and assessment. • Why we are writing learning outcomes? • The role of learning outcomes in assessment? (including Rubrics and KPIs) 5. Use the five domains of learning specified in Use National Qualification Framework; including the selection of verbs that map to measurable instructional objectives, learning outcomes and assessment.
 Workshop’s Los 6. Construct learning outcomes from learning Construct objectives, in order to develop learning outcomes for Programs and Courses. 7. Mapping learning outcomes Mapping
Workshop’s Los 6. Construct learning outcomes from learning Construct objectives, in order to develop learning outcomes for Programs and Courses. 7. Mapping learning outcomes Mapping
 1 st Day Sessions First session • KPIs for Profile Data, NCAAA KPIs • Introduction to Learning Outcomes (LOs) Second session • Importance & Benefits of • General Guidelines LOs • Recommendations and • Where do LOs come from? Suggestions • Characteristics of LOs • The difference between Learning Outcomes • and Learning Objectives Third Session • LO Process and Levels • NQF Learning Domains and LO – Verbs
1 st Day Sessions First session • KPIs for Profile Data, NCAAA KPIs • Introduction to Learning Outcomes (LOs) Second session • Importance & Benefits of • General Guidelines LOs • Recommendations and • Where do LOs come from? Suggestions • Characteristics of LOs • The difference between Learning Outcomes • and Learning Objectives Third Session • LO Process and Levels • NQF Learning Domains and LO – Verbs
 Example from your SSRP – Profile, p. 12 3. Key Performance Indicators The following KPI’s are adopted to monitor the achievement in accomplishing the Program objectives. 1. Graduation with a GPA acceptable by Industry 2. satisfaction at alumni/employer surveys 3. To build up an instrument park, corresponding to most world class universities 4. Field training of students must be continuously updated with latest techniques. 5. Industry-standard computer modeling and interpretation packages must be included in the curriculum 6. Average time for procuring equipment and instruments.
Example from your SSRP – Profile, p. 12 3. Key Performance Indicators The following KPI’s are adopted to monitor the achievement in accomplishing the Program objectives. 1. Graduation with a GPA acceptable by Industry 2. satisfaction at alumni/employer surveys 3. To build up an instrument park, corresponding to most world class universities 4. Field training of students must be continuously updated with latest techniques. 5. Industry-standard computer modeling and interpretation packages must be included in the curriculum 6. Average time for procuring equipment and instruments.
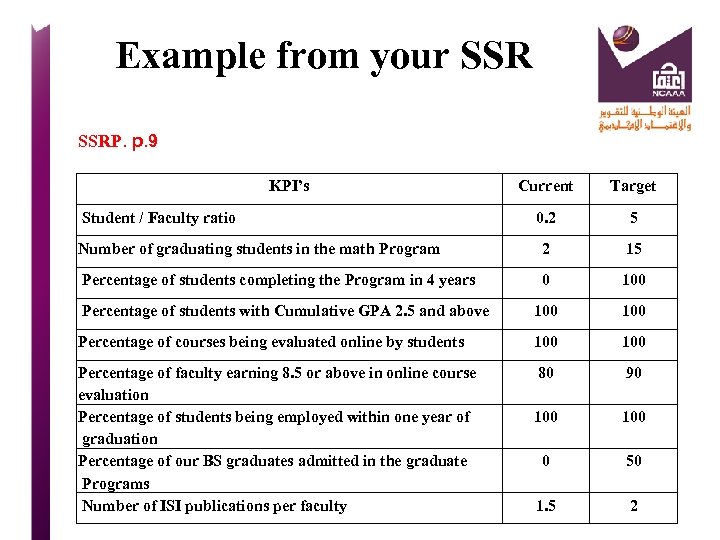 Example from your SSRP. p. 9 KPI’s Current Target 0. 2 5 Number of graduating students in the math Program 2 15 Percentage of students completing the Program in 4 years 0 100 Percentage of students with Cumulative GPA 2. 5 and above 100 Percentage of courses being evaluated online by students 100 Percentage of faculty earning 8. 5 or above in online course evaluation Percentage of students being employed within one year of graduation Percentage of our BS graduates admitted in the graduate Programs Number of ISI publications per faculty 80 90 100 0 50 1. 5 2 Student / Faculty ratio
Example from your SSRP. p. 9 KPI’s Current Target 0. 2 5 Number of graduating students in the math Program 2 15 Percentage of students completing the Program in 4 years 0 100 Percentage of students with Cumulative GPA 2. 5 and above 100 Percentage of courses being evaluated online by students 100 Percentage of faculty earning 8. 5 or above in online course evaluation Percentage of students being employed within one year of graduation Percentage of our BS graduates admitted in the graduate Programs Number of ISI publications per faculty 80 90 100 0 50 1. 5 2 Student / Faculty ratio
 Example from your SSRP – Standard 4, p. 36 The learning outcomes taken together become the overall strategy for the degree plan. The department is currently looking into the possibility of setting a standard end-of. Program examination (exit exam) that will assess specific learning outcomes. Verification of learning outcomes in the form of feedback from potential employers from work placement SSRP – Standard 3, p. 34 Periodically, feedback is sought from alumni and employers. In many occasions, the feedback is used for Program quality improvement almost immediately. The grades of graduating students are reviewed as a way to measure performance.
Example from your SSRP – Standard 4, p. 36 The learning outcomes taken together become the overall strategy for the degree plan. The department is currently looking into the possibility of setting a standard end-of. Program examination (exit exam) that will assess specific learning outcomes. Verification of learning outcomes in the form of feedback from potential employers from work placement SSRP – Standard 3, p. 34 Periodically, feedback is sought from alumni and employers. In many occasions, the feedback is used for Program quality improvement almost immediately. The grades of graduating students are reviewed as a way to measure performance.
 Example from your SSR • The assessment of Program outcomes is done on continuous basis. SSRP, p. 22 • Since the Program outcomes are intrinsically related to Program objectives, achievement of Program outcomes is an essential prerequisite of student qualification at graduation. . . Level of achievement of the Program outcomes is periodically measured to examine the extent to which they are met. SSRP, p. 24
Example from your SSR • The assessment of Program outcomes is done on continuous basis. SSRP, p. 22 • Since the Program outcomes are intrinsically related to Program objectives, achievement of Program outcomes is an essential prerequisite of student qualification at graduation. . . Level of achievement of the Program outcomes is periodically measured to examine the extent to which they are met. SSRP, p. 24
 Example from your SSR The intended student learning outcomes are periodically evaluated through various means like public presentations, exams, assignments, projects, etc. Appropriate Program evaluation mechanisms including graduating student surveys, employment outcome data, employer feedback and subsequent performance of graduates are used to provide evidence about the usefulness of intended learning outcomes and the extent to which they are achieved. SSRP – Standard 4. , p. 38
Example from your SSR The intended student learning outcomes are periodically evaluated through various means like public presentations, exams, assignments, projects, etc. Appropriate Program evaluation mechanisms including graduating student surveys, employment outcome data, employer feedback and subsequent performance of graduates are used to provide evidence about the usefulness of intended learning outcomes and the extent to which they are achieved. SSRP – Standard 4. , p. 38
 Example from your SSR • Students learning outcomes are evaluated based on HW, quizzes, and exams, and in some cases reports and presentations, are used to measure the student learning outcomes. SSRP, p. 31 • Faculty members make sure that students are tested in a manner that allows them to assess the extent to which learning outcomes are met. They maintain a check on their testing procedures. SSRP, p. 35.
Example from your SSR • Students learning outcomes are evaluated based on HW, quizzes, and exams, and in some cases reports and presentations, are used to measure the student learning outcomes. SSRP, p. 31 • Faculty members make sure that students are tested in a manner that allows them to assess the extent to which learning outcomes are met. They maintain a check on their testing procedures. SSRP, p. 35.
 KPIs for Profile Data, NCAAA KPIs
KPIs for Profile Data, NCAAA KPIs
 Key Performance Indicators: Why? Performance of a higher education institution & its Programs is complex (teaching, research, community…) KPIs summarize performance in key areas scientifically, rationally, and meaningfully for different stakeholders: 1. Faculty & Staff 2. Students 3. External agencies (NCAAA, employers, …) NCAAA
Key Performance Indicators: Why? Performance of a higher education institution & its Programs is complex (teaching, research, community…) KPIs summarize performance in key areas scientifically, rationally, and meaningfully for different stakeholders: 1. Faculty & Staff 2. Students 3. External agencies (NCAAA, employers, …) NCAAA
 What are KPIs? ? ? … KPIs = Key Performance Indicators …a measure of performance or achievement …a Key Success Indicator (KSI) …a measure of results and efficiency results Quantifiable performance measures used to define success and measure progress toward the achievement of goals. (maybe qualitative via rubrics)
What are KPIs? ? ? … KPIs = Key Performance Indicators …a measure of performance or achievement …a Key Success Indicator (KSI) …a measure of results and efficiency results Quantifiable performance measures used to define success and measure progress toward the achievement of goals. (maybe qualitative via rubrics)
 KPI KEY is fundamentally important to gain advantage; a make-or-break component for success. Performance when outcomes can be clearly outcomes measured, quantified, and easily influenced by influenced the institution or Program. Indicator provides leading information on future performance. (ie. , when the gas gauge is on “E” then the leading information tells us that the car’s future performance will be to stop; so the action plan is to get gas immediately)
KPI KEY is fundamentally important to gain advantage; a make-or-break component for success. Performance when outcomes can be clearly outcomes measured, quantified, and easily influenced by influenced the institution or Program. Indicator provides leading information on future performance. (ie. , when the gas gauge is on “E” then the leading information tells us that the car’s future performance will be to stop; so the action plan is to get gas immediately)
 NCAAA Learning & Teaching KPIs 5. Ratio of students to teaching staff (Based on full time equivalents) 6. Students overall rating on the quality of their courses. (Average rating of students on a five point scale on overall evaluation of courses. ) 7. Proportion of teaching staff with verified doctoral qualifications. 8. Percentage of students entering Programs who successfully complete first year. 9. Proportion of students entering undergraduate Programs who complete those Programs in minimum time. 10. Proportion of students entering post graduate Programs who complete those Programs in specified time. 11. Proportion of graduates from undergraduate Programs who within six months of graduation are: employed, enrolled in further study, not seeking employment or further study
NCAAA Learning & Teaching KPIs 5. Ratio of students to teaching staff (Based on full time equivalents) 6. Students overall rating on the quality of their courses. (Average rating of students on a five point scale on overall evaluation of courses. ) 7. Proportion of teaching staff with verified doctoral qualifications. 8. Percentage of students entering Programs who successfully complete first year. 9. Proportion of students entering undergraduate Programs who complete those Programs in minimum time. 10. Proportion of students entering post graduate Programs who complete those Programs in specified time. 11. Proportion of graduates from undergraduate Programs who within six months of graduation are: employed, enrolled in further study, not seeking employment or further study
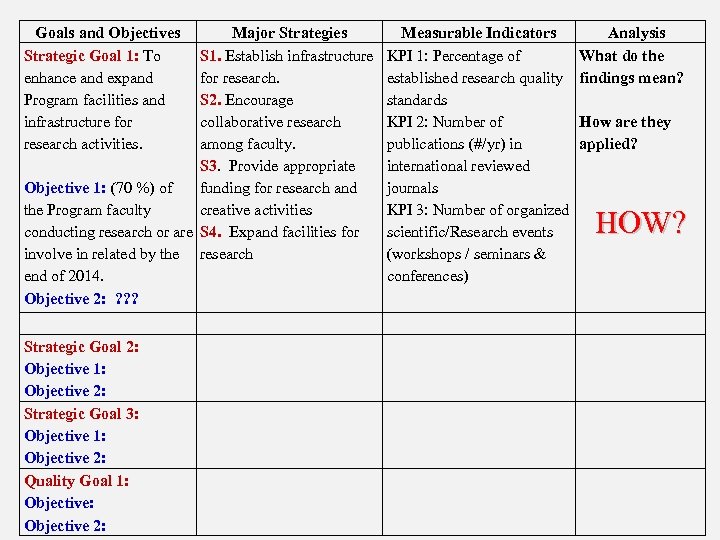 Goals and Objectives Strategic Goal 1: To enhance and expand Program facilities and infrastructure for research activities. Major Strategies S 1. Establish infrastructure for research. S 2. Encourage collaborative research among faculty. S 3. Provide appropriate Objective 1: (70 %) of funding for research and the Program faculty creative activities conducting research or are S 4. Expand facilities for involve in related by the research end of 2014. Objective 2: ? ? ? Strategic Goal 2: Objective 1: Objective 2: Strategic Goal 3: Objective 1: Objective 2: Quality Goal 1: Objective 2: Measurable Indicators KPI 1: Percentage of established research quality standards KPI 2: Number of publications (#/yr) in international reviewed journals KPI 3: Number of organized scientific/Research events (workshops / seminars & conferences) Analysis What do the findings mean? How are they applied? HOW?
Goals and Objectives Strategic Goal 1: To enhance and expand Program facilities and infrastructure for research activities. Major Strategies S 1. Establish infrastructure for research. S 2. Encourage collaborative research among faculty. S 3. Provide appropriate Objective 1: (70 %) of funding for research and the Program faculty creative activities conducting research or are S 4. Expand facilities for involve in related by the research end of 2014. Objective 2: ? ? ? Strategic Goal 2: Objective 1: Objective 2: Strategic Goal 3: Objective 1: Objective 2: Quality Goal 1: Objective 2: Measurable Indicators KPI 1: Percentage of established research quality standards KPI 2: Number of publications (#/yr) in international reviewed journals KPI 3: Number of organized scientific/Research events (workshops / seminars & conferences) Analysis What do the findings mean? How are they applied? HOW?
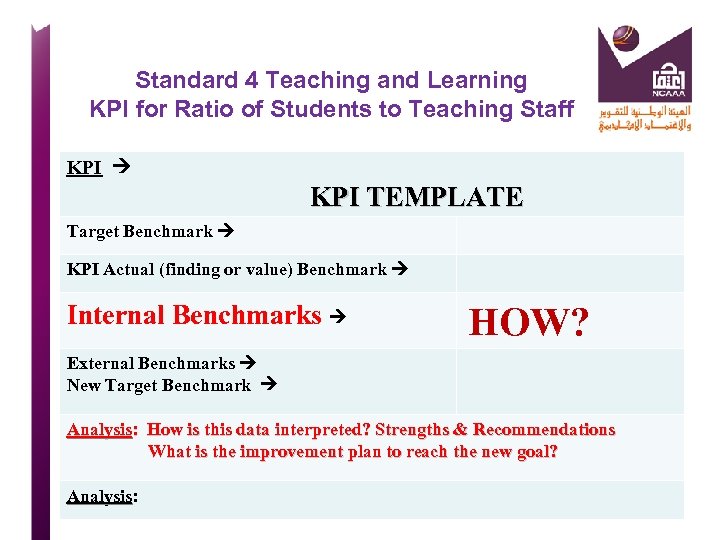 Standard 4 Teaching and Learning KPI for Ratio of Students to Teaching Staff KPI KPI TEMPLATE Target Benchmark KPI Actual (finding or value) Benchmark Internal Benchmarks HOW? External Benchmarks New Target Benchmark Analysis: How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal? Analysis:
Standard 4 Teaching and Learning KPI for Ratio of Students to Teaching Staff KPI KPI TEMPLATE Target Benchmark KPI Actual (finding or value) Benchmark Internal Benchmarks HOW? External Benchmarks New Target Benchmark Analysis: How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal? Analysis:
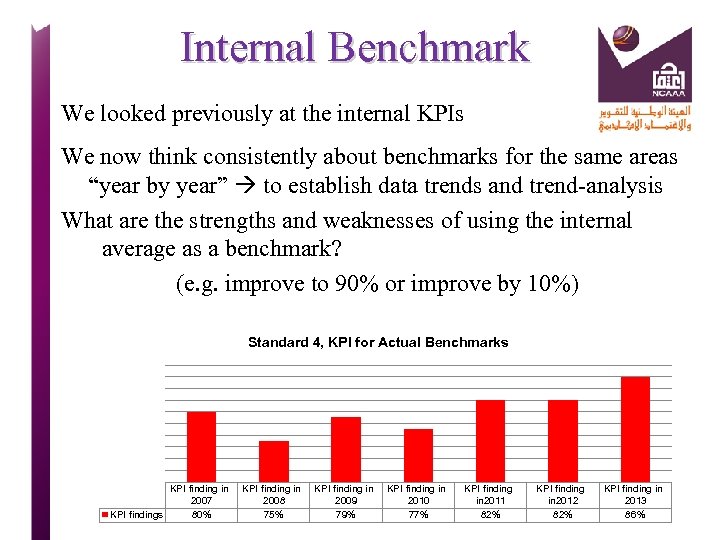 Internal Benchmark We looked previously at the internal KPIs We now think consistently about benchmarks for the same areas “year by year” to establish data trends and trend-analysis What are the strengths and weaknesses of using the internal average as a benchmark? (e. g. improve to 90% or improve by 10%) Standard 4, KPI for Actual Benchmarks KPI finding in 2007 KPI findings 80% KPI finding in 2008 75% KPI finding in 2009 79% KPI finding in 2010 77% KPI finding in 2011 82% KPI finding in 2012 82% KPI finding in 2013 86%
Internal Benchmark We looked previously at the internal KPIs We now think consistently about benchmarks for the same areas “year by year” to establish data trends and trend-analysis What are the strengths and weaknesses of using the internal average as a benchmark? (e. g. improve to 90% or improve by 10%) Standard 4, KPI for Actual Benchmarks KPI finding in 2007 KPI findings 80% KPI finding in 2008 75% KPI finding in 2009 79% KPI finding in 2010 77% KPI finding in 2011 82% KPI finding in 2012 82% KPI finding in 2013 86%
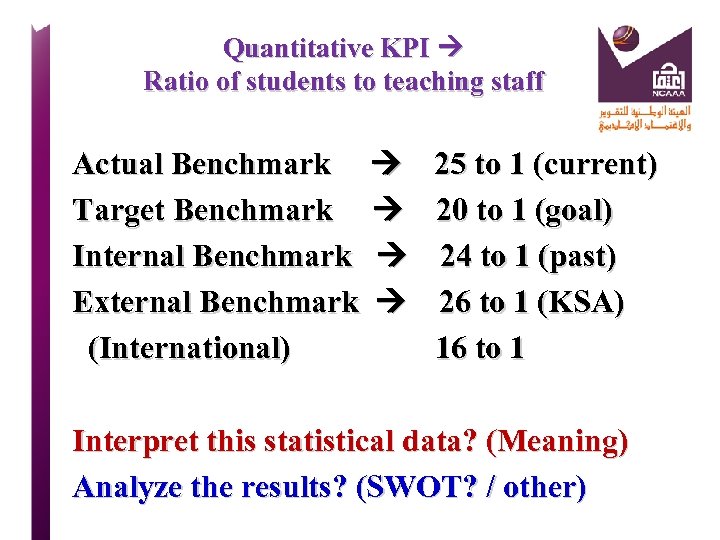
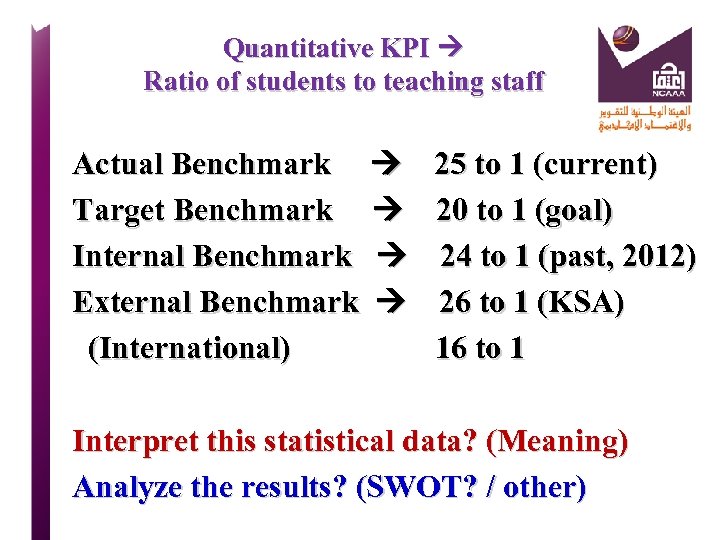 Quantitative KPI Ratio of students to teaching staff Actual Benchmark 25 to 1 (current) Target Benchmark 20 to 1 (goal) Internal Benchmark 24 to 1 (past, 2012) External Benchmark 26 to 1 (KSA) (International) 16 to 1 Interpret this statistical data? (Meaning) Analyze the results? (SWOT? / other)
Quantitative KPI Ratio of students to teaching staff Actual Benchmark 25 to 1 (current) Target Benchmark 20 to 1 (goal) Internal Benchmark 24 to 1 (past, 2012) External Benchmark 26 to 1 (KSA) (International) 16 to 1 Interpret this statistical data? (Meaning) Analyze the results? (SWOT? / other)
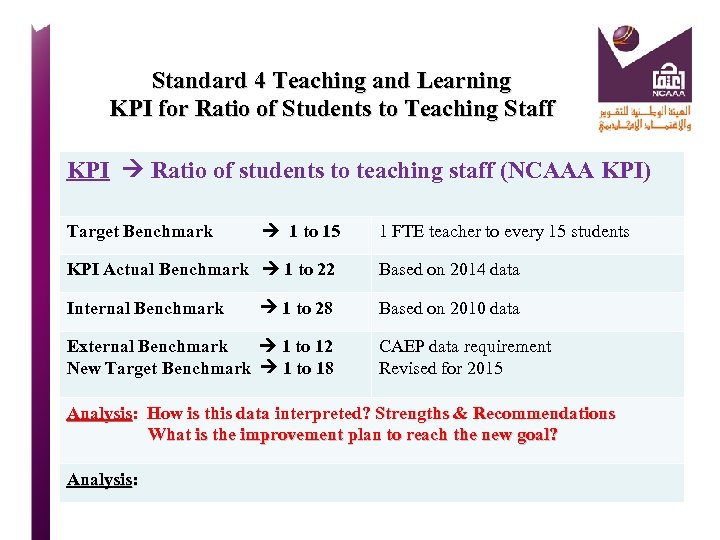 Standard 4 Teaching and Learning KPI for Ratio of Students to Teaching Staff KPI Ratio of students to teaching staff (NCAAA KPI) Target Benchmark 1 to 15 1 FTE teacher to every 15 students KPI Actual Benchmark 1 to 22 Based on 2014 data Internal Benchmark 1 to 28 Based on 2010 data External Benchmark 1 to 12 CAEP data requirement New Target Benchmark 1 to 18 Revised for 2015 Analysis: How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal? Analysis:
Standard 4 Teaching and Learning KPI for Ratio of Students to Teaching Staff KPI Ratio of students to teaching staff (NCAAA KPI) Target Benchmark 1 to 15 1 FTE teacher to every 15 students KPI Actual Benchmark 1 to 22 Based on 2014 data Internal Benchmark 1 to 28 Based on 2010 data External Benchmark 1 to 12 CAEP data requirement New Target Benchmark 1 to 18 Revised for 2015 Analysis: How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal? Analysis:
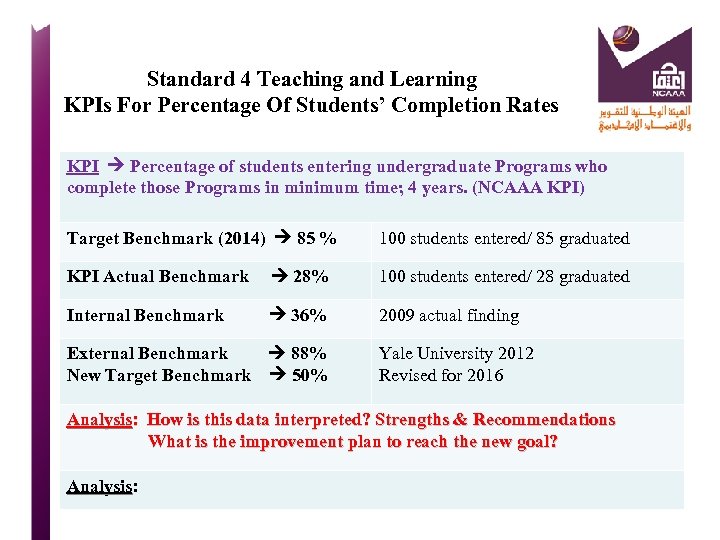 Standard 4 Teaching and Learning KPIs For Percentage Of Students’ Completion Rates KPI Percentage of students entering undergraduate Programs who complete those Programs in minimum time; 4 years. (NCAAA KPI) Target Benchmark (2014) 85 % 100 students entered/ 85 graduated KPI Actual Benchmark 28% 100 students entered/ 28 graduated Internal Benchmark 36% 2009 actual finding External Benchmark 88% Yale University 2012 New Target Benchmark 50% Revised for 2016 Analysis: How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal? Analysis:
Standard 4 Teaching and Learning KPIs For Percentage Of Students’ Completion Rates KPI Percentage of students entering undergraduate Programs who complete those Programs in minimum time; 4 years. (NCAAA KPI) Target Benchmark (2014) 85 % 100 students entered/ 85 graduated KPI Actual Benchmark 28% 100 students entered/ 28 graduated Internal Benchmark 36% 2009 actual finding External Benchmark 88% Yale University 2012 New Target Benchmark 50% Revised for 2016 Analysis: How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal? Analysis:
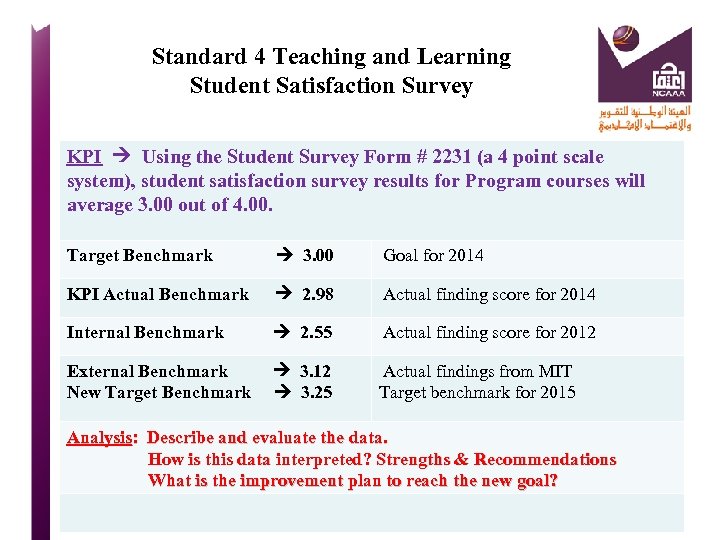 Standard 4 Teaching and Learning Student Satisfaction Survey KPI Using the Student Survey Form # 2231 (a 4 point scale system), student satisfaction survey results for Program courses will average 3. 00 out of 4. 00. Target Benchmark 3. 00 Goal for 2014 KPI Actual Benchmark 2. 98 Actual finding score for 2014 Internal Benchmark 2. 55 Actual finding score for 2012 External Benchmark 3. 12 Actual findings from MIT New Target Benchmark 3. 25 Target benchmark for 2015 Analysis: Describe and evaluate the data. How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal?
Standard 4 Teaching and Learning Student Satisfaction Survey KPI Using the Student Survey Form # 2231 (a 4 point scale system), student satisfaction survey results for Program courses will average 3. 00 out of 4. 00. Target Benchmark 3. 00 Goal for 2014 KPI Actual Benchmark 2. 98 Actual finding score for 2014 Internal Benchmark 2. 55 Actual finding score for 2012 External Benchmark 3. 12 Actual findings from MIT New Target Benchmark 3. 25 Target benchmark for 2015 Analysis: Describe and evaluate the data. How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal?
 Standard 4 Teaching and Learning Faculty Satisfaction Survey KPI Target Benchmark KPI Finding Benchmark Internal Benchmark External Benchmark New Target Benchmark Complete KPI Template Analysis: Describe and evaluate the data. How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal?
Standard 4 Teaching and Learning Faculty Satisfaction Survey KPI Target Benchmark KPI Finding Benchmark Internal Benchmark External Benchmark New Target Benchmark Complete KPI Template Analysis: Describe and evaluate the data. How is this data interpreted? Strengths & Recommendations What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal?
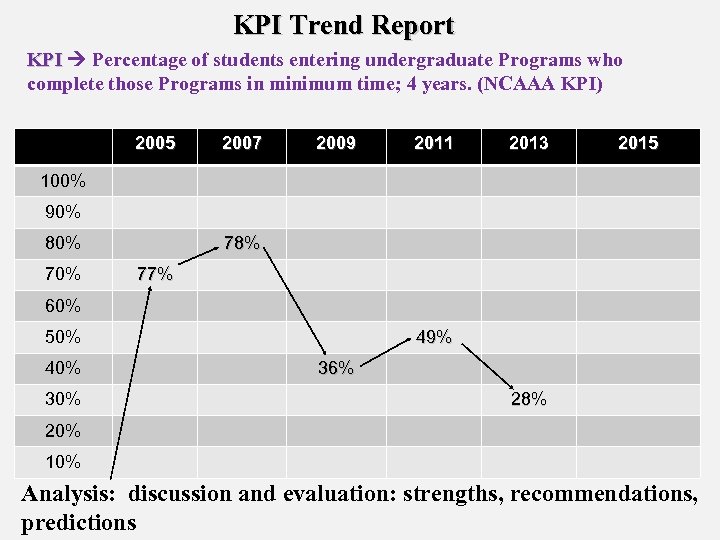 KPI Trend Report KPI Percentage of students entering undergraduate Programs who KPI complete those Programs in minimum time; 4 years. (NCAAA KPI) 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 100% 90% 80% 78% 77% 60% 50% 40% 30% 49% 36% 28% 20% 10% Analysis: discussion and evaluation: strengths, recommendations, predictions
KPI Trend Report KPI Percentage of students entering undergraduate Programs who KPI complete those Programs in minimum time; 4 years. (NCAAA KPI) 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 100% 90% 80% 78% 77% 60% 50% 40% 30% 49% 36% 28% 20% 10% Analysis: discussion and evaluation: strengths, recommendations, predictions
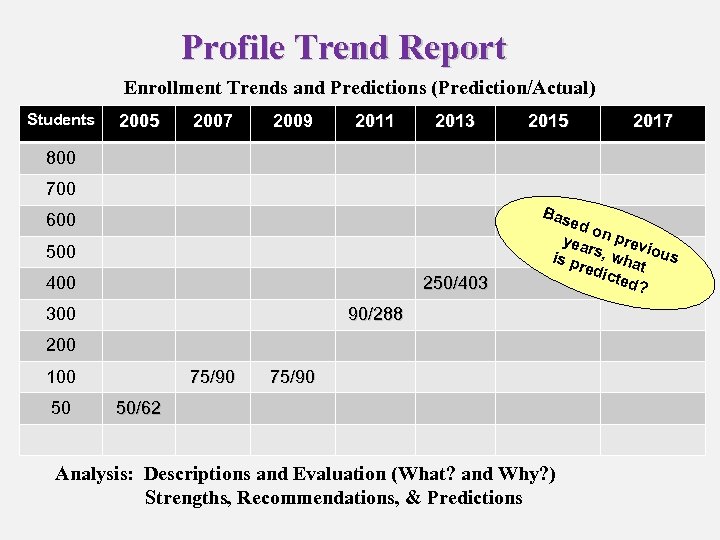 Profile Trend Report Enrollment Trends and Predictions (Prediction/Actual) Students 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 2017 800 700 Bas 600 500 400 250/403 300 ed o yea n prev i r is p s, wha ous red icte t d? 90/288 200 100 50 75/90 50/62 Analysis: Descriptions and Evaluation (What? and Why? ) Strengths, Recommendations, & Predictions
Profile Trend Report Enrollment Trends and Predictions (Prediction/Actual) Students 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 2017 800 700 Bas 600 500 400 250/403 300 ed o yea n prev i r is p s, wha ous red icte t d? 90/288 200 100 50 75/90 50/62 Analysis: Descriptions and Evaluation (What? and Why? ) Strengths, Recommendations, & Predictions
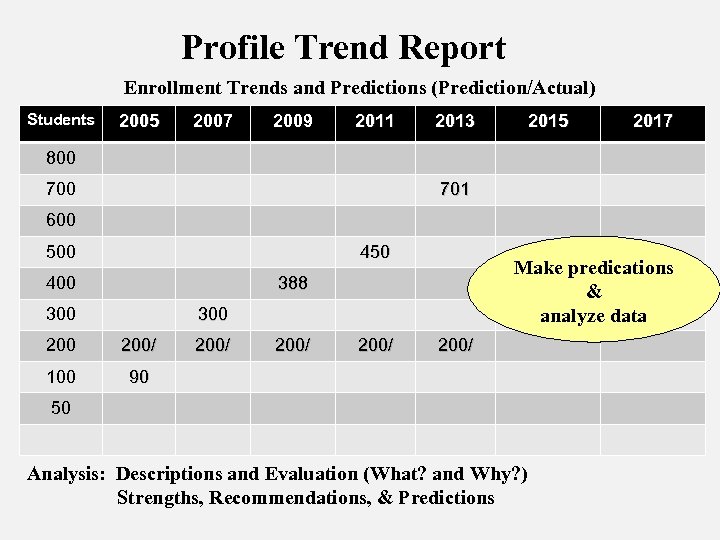 Profile Trend Report Enrollment Trends and Predictions (Prediction/Actual) Students 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 2017 800 701 600 500 450 400 Make predications & analyze data 388 300 200/ 100 200/ 90 50 Analysis: Descriptions and Evaluation (What? and Why? ) Strengths, Recommendations, & Predictions
Profile Trend Report Enrollment Trends and Predictions (Prediction/Actual) Students 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 2017 800 701 600 500 450 400 Make predications & analyze data 388 300 200/ 100 200/ 90 50 Analysis: Descriptions and Evaluation (What? and Why? ) Strengths, Recommendations, & Predictions
 Quantitative KPI Ratio of students to teaching staff Actual Benchmark 25 to 1 (current) Target Benchmark 20 to 1 (goal) Internal Benchmark 24 to 1 (past) External Benchmark 26 to 1 (KSA) (International) 16 to 1 Interpret this statistical data? (Meaning) Analyze the results? (SWOT? / other)
Quantitative KPI Ratio of students to teaching staff Actual Benchmark 25 to 1 (current) Target Benchmark 20 to 1 (goal) Internal Benchmark 24 to 1 (past) External Benchmark 26 to 1 (KSA) (International) 16 to 1 Interpret this statistical data? (Meaning) Analyze the results? (SWOT? / other)
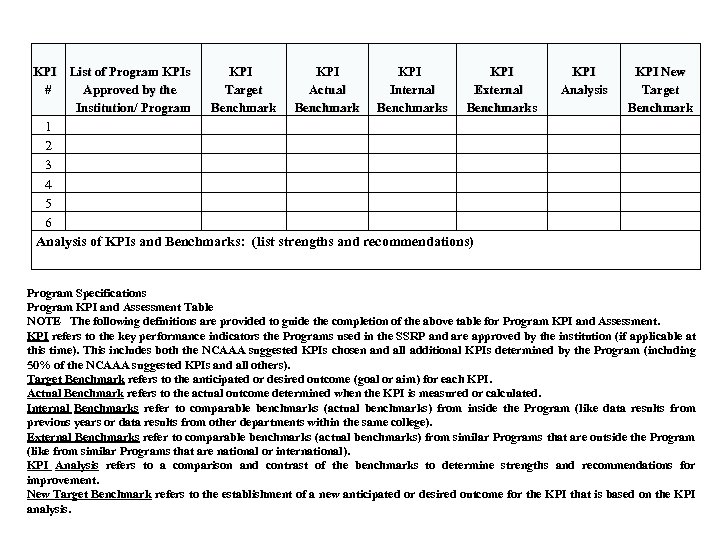 KPI List of Program KPIs # Approved by the Institution/ Program KPI Target Benchmark KPI Actual Benchmark KPI Internal Benchmarks KPI External Benchmarks KPI Analysis KPI New Target Benchmark 1 2 3 4 5 6 Analysis of KPIs and Benchmarks: (list strengths and recommendations) Program Specifications Program KPI and Assessment Table NOTE The following definitions are provided to guide the completion of the above table for Program KPI and Assessment. KPI refers to the key performance indicators the Programs used in the SSRP and are approved by the institution (if applicable at this time). This includes both the NCAAA suggested KPIs chosen and all additional KPIs determined by the Program (including 50% of the NCAAA suggested KPIs and all others). Target Benchmark refers to the anticipated or desired outcome (goal or aim) for each KPI. Actual Benchmark refers to the actual outcome determined when the KPI is measured or calculated. Internal Benchmarks refer to comparable benchmarks (actual benchmarks) from inside the Program (like data results from previous years or data results from other departments within the same college). External Benchmarks refer to comparable benchmarks (actual benchmarks) from similar Programs that are outside the Program (like from similar Programs that are national or international). KPI Analysis refers to a comparison and contrast of the benchmarks to determine strengths and recommendations for improvement. New Target Benchmark refers to the establishment of a new anticipated or desired outcome for the KPI that is based on the KPI analysis.
KPI List of Program KPIs # Approved by the Institution/ Program KPI Target Benchmark KPI Actual Benchmark KPI Internal Benchmarks KPI External Benchmarks KPI Analysis KPI New Target Benchmark 1 2 3 4 5 6 Analysis of KPIs and Benchmarks: (list strengths and recommendations) Program Specifications Program KPI and Assessment Table NOTE The following definitions are provided to guide the completion of the above table for Program KPI and Assessment. KPI refers to the key performance indicators the Programs used in the SSRP and are approved by the institution (if applicable at this time). This includes both the NCAAA suggested KPIs chosen and all additional KPIs determined by the Program (including 50% of the NCAAA suggested KPIs and all others). Target Benchmark refers to the anticipated or desired outcome (goal or aim) for each KPI. Actual Benchmark refers to the actual outcome determined when the KPI is measured or calculated. Internal Benchmarks refer to comparable benchmarks (actual benchmarks) from inside the Program (like data results from previous years or data results from other departments within the same college). External Benchmarks refer to comparable benchmarks (actual benchmarks) from similar Programs that are outside the Program (like from similar Programs that are national or international). KPI Analysis refers to a comparison and contrast of the benchmarks to determine strengths and recommendations for improvement. New Target Benchmark refers to the establishment of a new anticipated or desired outcome for the KPI that is based on the KPI analysis.
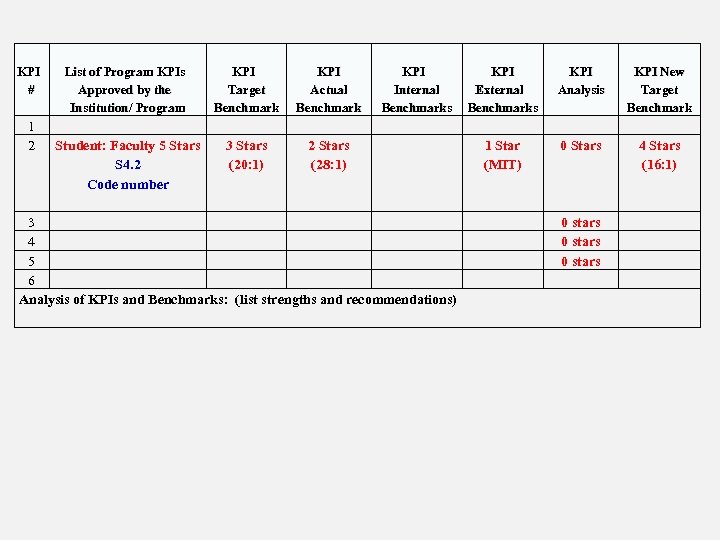 KPI # 1 2 List of Program KPIs Approved by the Institution/ Program KPI Target Benchmark KPI Actual Benchmark Student: Faculty 5 Stars S 4. 2 Code number 3 Stars (20: 1) KPI Internal Benchmarks 2 Stars (28: 1) 3 4 5 6 Analysis of KPIs and Benchmarks: (list strengths and recommendations) KPI External Benchmarks KPI Analysis KPI New Target Benchmark 1 Star (MIT) 0 Stars 4 Stars (16: 1) 0 stars
KPI # 1 2 List of Program KPIs Approved by the Institution/ Program KPI Target Benchmark KPI Actual Benchmark Student: Faculty 5 Stars S 4. 2 Code number 3 Stars (20: 1) KPI Internal Benchmarks 2 Stars (28: 1) 3 4 5 6 Analysis of KPIs and Benchmarks: (list strengths and recommendations) KPI External Benchmarks KPI Analysis KPI New Target Benchmark 1 Star (MIT) 0 Stars 4 Stars (16: 1) 0 stars
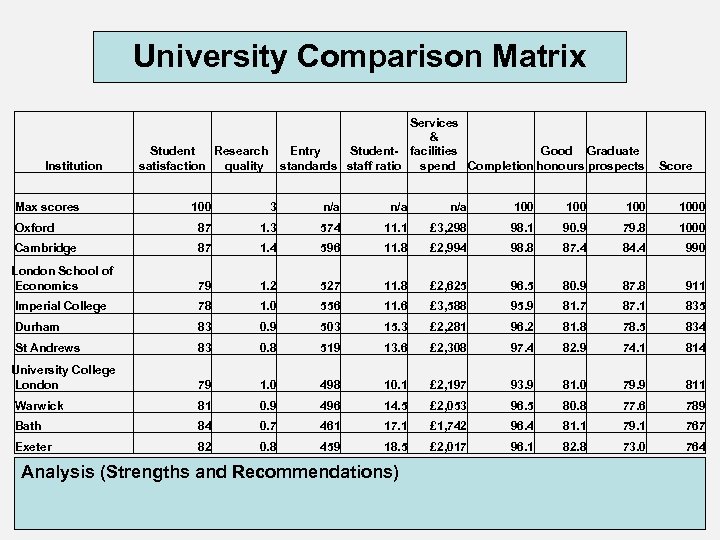 University Comparison Matrix Institution Max scores Services & Entry Student- facilities Good Graduate standards staff ratio spend Completion honours prospects Student Research satisfaction quality Score 100 3 n/a n/a 100 1000 Oxford 87 1. 3 574 11. 1 £ 3, 298 98. 1 90. 9 79. 8 1000 Cambridge 87 1. 4 596 11. 8 £ 2, 994 98. 8 87. 4 84. 4 990 London School of Economics 79 1. 2 527 11. 8 £ 2, 625 96. 5 80. 9 87. 8 911 Imperial College 78 1. 0 556 11. 6 £ 3, 588 95. 9 81. 7 87. 1 835 Durham 83 0. 9 503 15. 3 £ 2, 281 96. 2 81. 8 78. 5 834 St Andrews 83 0. 8 519 13. 6 £ 2, 308 97. 4 82. 9 74. 1 814 University College London 79 1. 0 498 10. 1 £ 2, 197 93. 9 81. 0 79. 9 811 Warwick 81 0. 9 496 14. 5 £ 2, 053 96. 5 80. 8 77. 6 789 Bath 84 0. 7 461 17. 1 £ 1, 742 96. 4 81. 1 79. 1 767 Exeter 82 0. 8 459 18. 5 £ 2, 017 96. 1 82. 8 73. 0 764 Analysis (Strengths and Recommendations)
University Comparison Matrix Institution Max scores Services & Entry Student- facilities Good Graduate standards staff ratio spend Completion honours prospects Student Research satisfaction quality Score 100 3 n/a n/a 100 1000 Oxford 87 1. 3 574 11. 1 £ 3, 298 98. 1 90. 9 79. 8 1000 Cambridge 87 1. 4 596 11. 8 £ 2, 994 98. 8 87. 4 84. 4 990 London School of Economics 79 1. 2 527 11. 8 £ 2, 625 96. 5 80. 9 87. 8 911 Imperial College 78 1. 0 556 11. 6 £ 3, 588 95. 9 81. 7 87. 1 835 Durham 83 0. 9 503 15. 3 £ 2, 281 96. 2 81. 8 78. 5 834 St Andrews 83 0. 8 519 13. 6 £ 2, 308 97. 4 82. 9 74. 1 814 University College London 79 1. 0 498 10. 1 £ 2, 197 93. 9 81. 0 79. 9 811 Warwick 81 0. 9 496 14. 5 £ 2, 053 96. 5 80. 8 77. 6 789 Bath 84 0. 7 461 17. 1 £ 1, 742 96. 4 81. 1 79. 1 767 Exeter 82 0. 8 459 18. 5 £ 2, 017 96. 1 82. 8 73. 0 764 Analysis (Strengths and Recommendations)
 Introduction • The Design phase of a typical curriculum The Design phase development process (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation) is largely concerned with developing clearning objectives and learning outcomes. • It is important to recognize during this phase that to recognize there is a direct relationship between objectives, learning outcomes, teaching strategy / methods & students assessments (Rubrics – KPIs with benchmarking and analysis).
Introduction • The Design phase of a typical curriculum The Design phase development process (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation) is largely concerned with developing clearning objectives and learning outcomes. • It is important to recognize during this phase that to recognize there is a direct relationship between objectives, learning outcomes, teaching strategy / methods & students assessments (Rubrics – KPIs with benchmarking and analysis).
 Theory Into Practice 5 Questions for Instructional Design 1. What do you want the student to be able to do? (Outcome) 2. What does the student need to know in order to do this well? (Curriculum) 3. What activity will facilitate the learning? (Pedagogy—learning & teaching) 4. How will the student demonstrate the learning? (Assessment) 5. How will the teacher know the student has done this well? (Criteria)
Theory Into Practice 5 Questions for Instructional Design 1. What do you want the student to be able to do? (Outcome) 2. What does the student need to know in order to do this well? (Curriculum) 3. What activity will facilitate the learning? (Pedagogy—learning & teaching) 4. How will the student demonstrate the learning? (Assessment) 5. How will the teacher know the student has done this well? (Criteria)
 Learning Outcome are: • Learning outcomes: describe what learners are supposed to know, understand, or are able to do know understand are able to do at the end of the Program or course. • LOs are based upon: • the needs of the learner (individual & personal). • the needs of society (mission statements). • what the learner should know about a particular subject in order to perform successfully (career perform and personal lifestyle).
Learning Outcome are: • Learning outcomes: describe what learners are supposed to know, understand, or are able to do know understand are able to do at the end of the Program or course. • LOs are based upon: • the needs of the learner (individual & personal). • the needs of society (mission statements). • what the learner should know about a particular subject in order to perform successfully (career perform and personal lifestyle).
 LOs are: • What a STUDENT should learn as a result of a What period of specified and supported study. • The ACHIEVEMENTS of the learner rather The then the intentions of the teacher. then the • Focus is directly on Student Performance.
LOs are: • What a STUDENT should learn as a result of a What period of specified and supported study. • The ACHIEVEMENTS of the learner rather The then the intentions of the teacher. then the • Focus is directly on Student Performance.
 LOs are: Formal statements that articulate • What students know and are able to do after instruction • Why students need to do this -- relevancy
LOs are: Formal statements that articulate • What students know and are able to do after instruction • Why students need to do this -- relevancy
 LOs are: Are concerned with the learning of the student: learning STUDENT… PERFORMANCE and ACHIEVEMENT PERFORMANCE Ø What the student CAN DO Ø What the student KNOWS AND CAN DO Ø What the student UNDERSTANDS OR Ø COMPREHENDS and CAN DO Must be measurable or observable
LOs are: Are concerned with the learning of the student: learning STUDENT… PERFORMANCE and ACHIEVEMENT PERFORMANCE Ø What the student CAN DO Ø What the student KNOWS AND CAN DO Ø What the student UNDERSTANDS OR Ø COMPREHENDS and CAN DO Must be measurable or observable
 Objectives vs. LOs • The distinction between learning outcomes and learning objectives is not universally recognized. • Many instructors may find that the term “learning outcomes” describes what they have already understood by the term “learning objectives. ” What is the difference?
Objectives vs. LOs • The distinction between learning outcomes and learning objectives is not universally recognized. • Many instructors may find that the term “learning outcomes” describes what they have already understood by the term “learning objectives. ” What is the difference?
 For NCAAA the difference between course LOs and objectives… • Learning objectives are statements of what the are teacher intends for the students to learn and are generally part of a teacher-centered approach [are Mission, traditional, teacher or content driven]. • Learning outcomes are statements of what the are student will KNOW and be able to DO or demonstrate as a result of their learning and are part of a student-centered approach.
For NCAAA the difference between course LOs and objectives… • Learning objectives are statements of what the are teacher intends for the students to learn and are generally part of a teacher-centered approach [are Mission, traditional, teacher or content driven]. • Learning outcomes are statements of what the are student will KNOW and be able to DO or demonstrate as a result of their learning and are part of a student-centered approach.
 Objectives vs. LOs • Learning objectives, for example, may outline the objectives material the INSTRUCTOR intends to cover in the INSTRUCTOR course / Program or the disciplinary questions the class will address. Known as IN-PUTS. • By contrast, learning outcomes focus on what the STUDENTS know, comprehend and realistically are STUDENTS able to do… [skill performance] by the end of an assignment, activity, class, or course [achievement]. Known as OUT-PUTS.
Objectives vs. LOs • Learning objectives, for example, may outline the objectives material the INSTRUCTOR intends to cover in the INSTRUCTOR course / Program or the disciplinary questions the class will address. Known as IN-PUTS. • By contrast, learning outcomes focus on what the STUDENTS know, comprehend and realistically are STUDENTS able to do… [skill performance] by the end of an assignment, activity, class, or course [achievement]. Known as OUT-PUTS.
 Objectives vs. LOs • learning outcomes, mean focusing on the application and integration of the course content from the perspective of the student. • learning outcomes can more explicitly and directly address expectations for student learning.
Objectives vs. LOs • learning outcomes, mean focusing on the application and integration of the course content from the perspective of the student. • learning outcomes can more explicitly and directly address expectations for student learning.
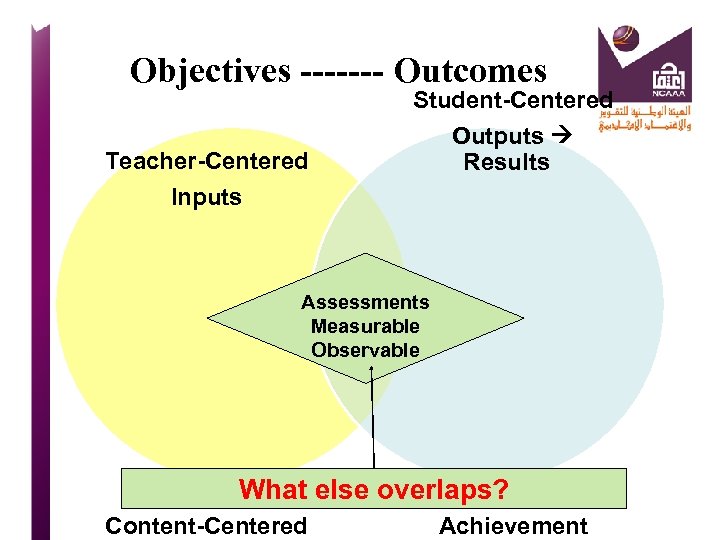 Objectives ------- Outcomes Teacher-Centered Inputs Student-Centered Outputs Results Assessments Measurable Observable Performance & What else overlaps? Content-Centered Achievement
Objectives ------- Outcomes Teacher-Centered Inputs Student-Centered Outputs Results Assessments Measurable Observable Performance & What else overlaps? Content-Centered Achievement
 Writing Objectives & LOs Writing Learning objectives can be written as teacher or curriculum centered content or they can be rewritten as student-centered learning outcomes The teacher will. . . OR will the student will…. Both learning objectives and outcomes must be measurable or observable. One assessment is for teaching and another assessment is for a student’s learning.
Writing Objectives & LOs Writing Learning objectives can be written as teacher or curriculum centered content or they can be rewritten as student-centered learning outcomes The teacher will. . . OR will the student will…. Both learning objectives and outcomes must be measurable or observable. One assessment is for teaching and another assessment is for a student’s learning.
 Examples • Example of a Learning Objective: Students will be taught the basic principles of database searching. [teacher will teach basic principles … ] • Example of a Learning Outcome: Students will be able to apply the principles of database searching in a review of literature. [student will KNOW and APPLY…]
Examples • Example of a Learning Objective: Students will be taught the basic principles of database searching. [teacher will teach basic principles … ] • Example of a Learning Outcome: Students will be able to apply the principles of database searching in a review of literature. [student will KNOW and APPLY…]
 Objectives or Outcomes? Which Dentist do you want working on your teeth? Dentist Student A: The teacher will instruct the student to know how to successfully drill cavities and repair teeth… Student B: The student earns 100% on the exam for drilling cavities and repairing teeth…. Student C: The student knows how and successfully drills out cavities and repairs teeth… Student D: The teacher successfully taught the student to drill out cavities and repair teeth.
Objectives or Outcomes? Which Dentist do you want working on your teeth? Dentist Student A: The teacher will instruct the student to know how to successfully drill cavities and repair teeth… Student B: The student earns 100% on the exam for drilling cavities and repairing teeth…. Student C: The student knows how and successfully drills out cavities and repairs teeth… Student D: The teacher successfully taught the student to drill out cavities and repair teeth.
 Objectives or Outcomes? Which Pharmacist do you want filling your meds? Pharmacist Student A: The teacher will instruct the students to know how to successfully fill medical prescriptions… Student B: The student earns 100% on the exam for filling medical prescriptions…. Student C: The student knows how and successfully fills medical prescriptions… Student D: The teacher successfully taught the student to fill medical prescriptions….
Objectives or Outcomes? Which Pharmacist do you want filling your meds? Pharmacist Student A: The teacher will instruct the students to know how to successfully fill medical prescriptions… Student B: The student earns 100% on the exam for filling medical prescriptions…. Student C: The student knows how and successfully fills medical prescriptions… Student D: The teacher successfully taught the student to fill medical prescriptions….
 Exercise • Please work as group in writing three learning objectives for your Program. • Now, re-write these objectives as LOs • Be prepared to share them and analyze the difference – they will be collected in order to be used latter.
Exercise • Please work as group in writing three learning objectives for your Program. • Now, re-write these objectives as LOs • Be prepared to share them and analyze the difference – they will be collected in order to be used latter.
 NCAAA 10 Minute Break Session 2 Importance & Benefits of LOs Where do LOs come from? Characteristics of LOs LO Process and Levels NQF Learning Domains & LO – Verbs
NCAAA 10 Minute Break Session 2 Importance & Benefits of LOs Where do LOs come from? Characteristics of LOs LO Process and Levels NQF Learning Domains & LO – Verbs
 The Importance of LOs 1. LOs build evidence for accountability, accountability accreditation, and for continuous improvement. § Show evidence of how well students learn. Show evidence § Use evidence for continuous improvement and Use evidence strategic plans.
The Importance of LOs 1. LOs build evidence for accountability, accountability accreditation, and for continuous improvement. § Show evidence of how well students learn. Show evidence § Use evidence for continuous improvement and Use evidence strategic plans.
 The Importance of LOs 2. Know what you are doing… 3. Know why you are doing it… 4. Know what students are learning as a result; (key for assessment). 5. Make improvement changes based on results (research based improvements)
The Importance of LOs 2. Know what you are doing… 3. Know why you are doing it… 4. Know what students are learning as a result; (key for assessment). 5. Make improvement changes based on results (research based improvements)
 The Importance of LOs Shifting from: • Teachers teaching…. to students learning • Teaching effectiveness…. to learning results
The Importance of LOs Shifting from: • Teachers teaching…. to students learning • Teaching effectiveness…. to learning results
 Course learning outcomes serve the following purposes… • To inform students of what is expected of them. • To guide the teacher in his/her approach to delivery of content and assessment that focuses on what the student will be able to do as a result of the learning. • To influence the domain and level of learning required of the delivery and assessment. • To fulfill the requirements of one or more Program outcomes.
Course learning outcomes serve the following purposes… • To inform students of what is expected of them. • To guide the teacher in his/her approach to delivery of content and assessment that focuses on what the student will be able to do as a result of the learning. • To influence the domain and level of learning required of the delivery and assessment. • To fulfill the requirements of one or more Program outcomes.
 Learning Outcomes help… 1. Select learning content objectives and skills content (What to teach? Teaching content priorities? ) 2. Development of instructional strategies that align with specific learning outcomes. 3. Develop and select instructional and Program materials that align with specific learning outcomes. 4. Construct evaluation instruments for assessing student performance based on the learning. outcomes. 5. Improve overall Program and as a faculty.
Learning Outcomes help… 1. Select learning content objectives and skills content (What to teach? Teaching content priorities? ) 2. Development of instructional strategies that align with specific learning outcomes. 3. Develop and select instructional and Program materials that align with specific learning outcomes. 4. Construct evaluation instruments for assessing student performance based on the learning. outcomes. 5. Improve overall Program and as a faculty.
 Benefits of Learning Outcomes 1. Learning outcomes measure & characterize the values that an institution, Program, or course have values articulated for student development & performance. 2. A set of student learning outcomes define what students will know and be able to do when they have completed any degree, regardless of his/her major.
Benefits of Learning Outcomes 1. Learning outcomes measure & characterize the values that an institution, Program, or course have values articulated for student development & performance. 2. A set of student learning outcomes define what students will know and be able to do when they have completed any degree, regardless of his/her major.
 Benefits for Learning Outcomes 3. Student learning outcomes will help guide faculty across the university to develop curricula, plan courses, determine financial needs, design syllabi, construct learning activities, and assess student learning. 4. LOs provide a framework for learners and framework advisers in order to discuss the goals of the curriculum and the personal career goals for individual students.
Benefits for Learning Outcomes 3. Student learning outcomes will help guide faculty across the university to develop curricula, plan courses, determine financial needs, design syllabi, construct learning activities, and assess student learning. 4. LOs provide a framework for learners and framework advisers in order to discuss the goals of the curriculum and the personal career goals for individual students.
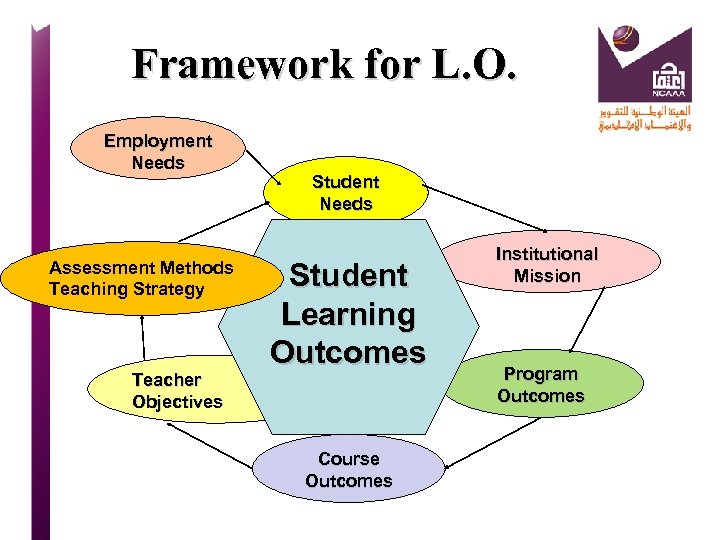 Framework for L. O. Employment Needs Assessment Methods Teaching Strategy Teacher Objectives Student Needs Student Learning Outcomes Course Outcomes Institutional Mission Program Outcomes
Framework for L. O. Employment Needs Assessment Methods Teaching Strategy Teacher Objectives Student Needs Student Learning Outcomes Course Outcomes Institutional Mission Program Outcomes
 Benefit: OBE “Outcome-Based Education” • Outcome-based education is a method of teaching that focuses on what students know and can actually do after they are taught. • All curriculum and teaching decisions are made based on how best to facilitate the desired outcome. • The desired outcome is selected first and the curriculum is created to support the intended outcome. • This leads to a planning process in reverse of traditional educational planning.
Benefit: OBE “Outcome-Based Education” • Outcome-based education is a method of teaching that focuses on what students know and can actually do after they are taught. • All curriculum and teaching decisions are made based on how best to facilitate the desired outcome. • The desired outcome is selected first and the curriculum is created to support the intended outcome. • This leads to a planning process in reverse of traditional educational planning.
 Where do L. O. come from? Learning Outcomes flows out from…… …the Mission Statement What must students do to demonstrate that the Institution and Program Mission Statements are accomplished?
Where do L. O. come from? Learning Outcomes flows out from…… …the Mission Statement What must students do to demonstrate that the Institution and Program Mission Statements are accomplished?
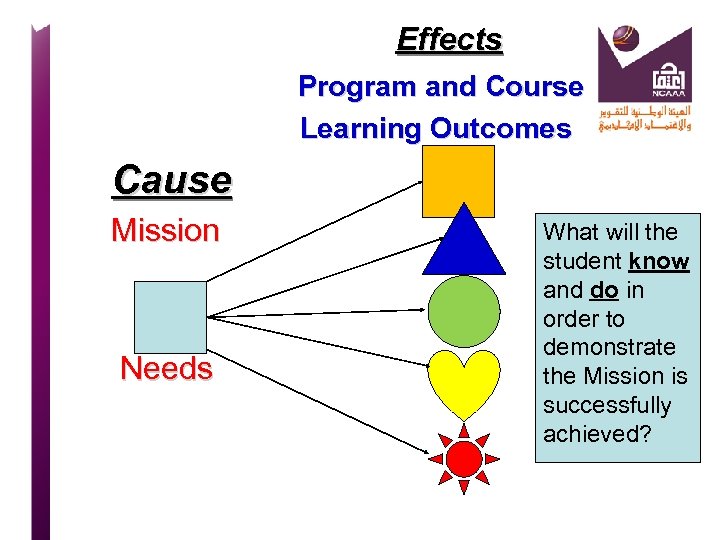 Effects Program and Course Learning Outcomes Cause Mission Needs What will the student know and do in order to demonstrate the Mission is successfully achieved?
Effects Program and Course Learning Outcomes Cause Mission Needs What will the student know and do in order to demonstrate the Mission is successfully achieved?
 Where do L. O. come from? In addition to Knowledge & Cognitive Skills Domains, Learning Outcomes flows out from…… …student needs assessment … and employers needs (cause and effect chart)
Where do L. O. come from? In addition to Knowledge & Cognitive Skills Domains, Learning Outcomes flows out from…… …student needs assessment … and employers needs (cause and effect chart)
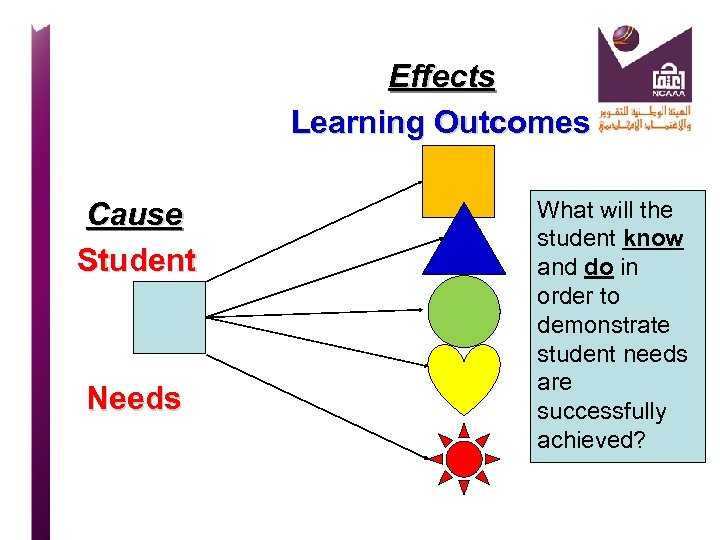 Effects Learning Outcomes Cause Student Needs What will the student know and do in order to demonstrate student needs are successfully achieved?
Effects Learning Outcomes Cause Student Needs What will the student know and do in order to demonstrate student needs are successfully achieved?
 Characteristics of a Graduate Are: Holders of a bachelor degree in any Program should have demonstrated: 1. Knowledge of a comprehensive, coherent and systematic body of Knowledge knowledge in a field of inquiry; 2. The ability to investigate complex problems and develop creative solutions ability with limited guidance; 3. The ability to use appropriate statistical techniques in the analysis and ability resolution of complex issues, and select and use the most appropriate mechanisms for communicating the results to a variety of audiences; 4. Capacity to provide leadership and willingness to cooperate fully with others in joint projects and initiatives; 5. In the case of a professional Program the full range of knowledge and skill required for effective practice in the profession concerned. required for effective practice Are these LOs?
Characteristics of a Graduate Are: Holders of a bachelor degree in any Program should have demonstrated: 1. Knowledge of a comprehensive, coherent and systematic body of Knowledge knowledge in a field of inquiry; 2. The ability to investigate complex problems and develop creative solutions ability with limited guidance; 3. The ability to use appropriate statistical techniques in the analysis and ability resolution of complex issues, and select and use the most appropriate mechanisms for communicating the results to a variety of audiences; 4. Capacity to provide leadership and willingness to cooperate fully with others in joint projects and initiatives; 5. In the case of a professional Program the full range of knowledge and skill required for effective practice in the profession concerned. required for effective practice Are these LOs?
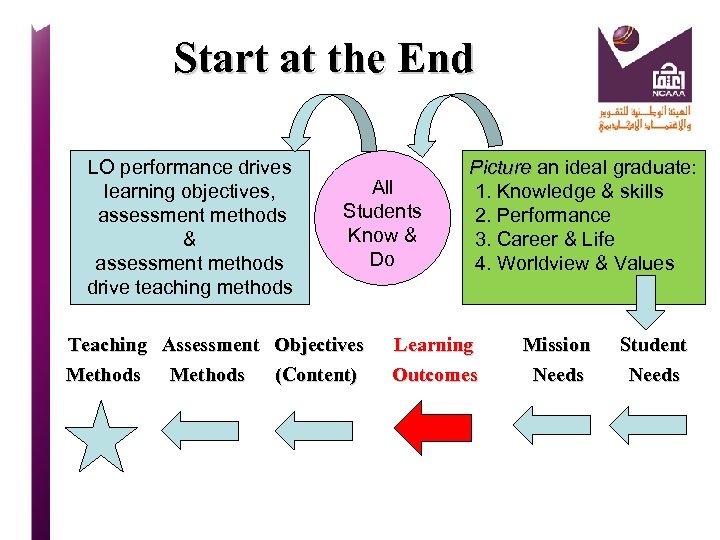 Start at the End LO performance drives Picture an ideal graduate: Picture learning objectives, assessment methods & assessment methods drive teaching methods All Students Know & Do 1. Knowledge & skills 2. Performance 3. Career & Life 4. Worldview & Values Teaching Assessment Objectives Learning Mission Student Methods (Content) Outcomes Needs
Start at the End LO performance drives Picture an ideal graduate: Picture learning objectives, assessment methods & assessment methods drive teaching methods All Students Know & Do 1. Knowledge & skills 2. Performance 3. Career & Life 4. Worldview & Values Teaching Assessment Objectives Learning Mission Student Methods (Content) Outcomes Needs
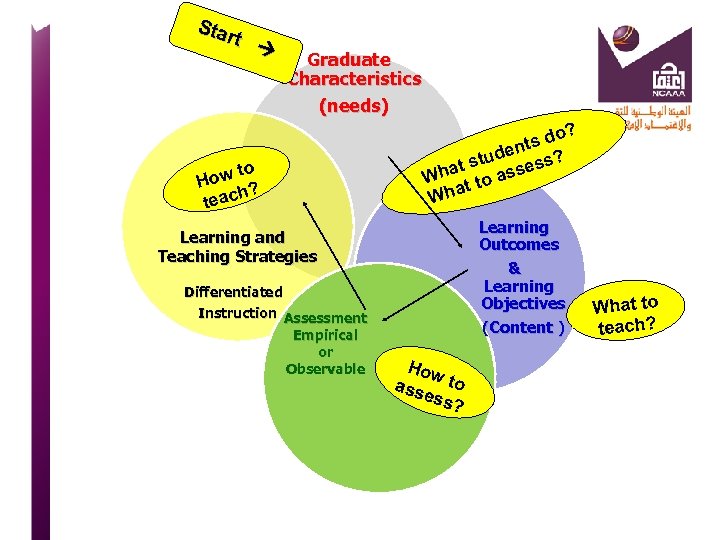 Sta rt Graduate Characteristics (needs) o? ts d n tude ess? ts Wha t to ass Wha o ow t H ? each t Learning Outcomes & Learning Objectives (Content ) Learning and Teaching Strategies Differentiated Instruction Assessment Empirical or Observable How ass to ess ? What to teach?
Sta rt Graduate Characteristics (needs) o? ts d n tude ess? ts Wha t to ass Wha o ow t H ? each t Learning Outcomes & Learning Objectives (Content ) Learning and Teaching Strategies Differentiated Instruction Assessment Empirical or Observable How ass to ess ? What to teach?
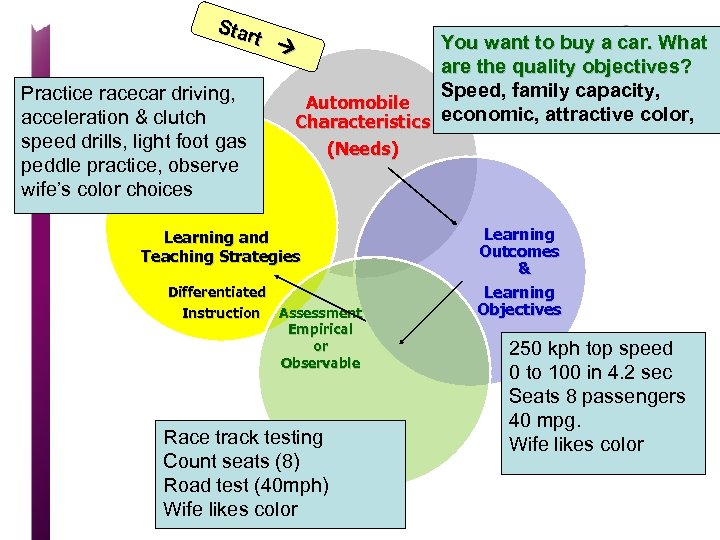 Star t Practice racecar driving, acceleration & clutch speed drills, light foot gas peddle practice, observe wife’s color choices You want to buy a car. What are the quality objectives? Speed, family capacity, Automobile Characteristics economic, attractive color, (Needs) Learning and Teaching Strategies Differentiated Instruction Assessment Empirical or Observable Race track testing Count seats (8) Road test (40 mph) Wife likes color Learning Outcomes & Learning Objectives 250 kph top speed 0 to 100 in 4. 2 sec Seats 8 passengers 40 mpg. Wife likes color
Star t Practice racecar driving, acceleration & clutch speed drills, light foot gas peddle practice, observe wife’s color choices You want to buy a car. What are the quality objectives? Speed, family capacity, Automobile Characteristics economic, attractive color, (Needs) Learning and Teaching Strategies Differentiated Instruction Assessment Empirical or Observable Race track testing Count seats (8) Road test (40 mph) Wife likes color Learning Outcomes & Learning Objectives 250 kph top speed 0 to 100 in 4. 2 sec Seats 8 passengers 40 mpg. Wife likes color
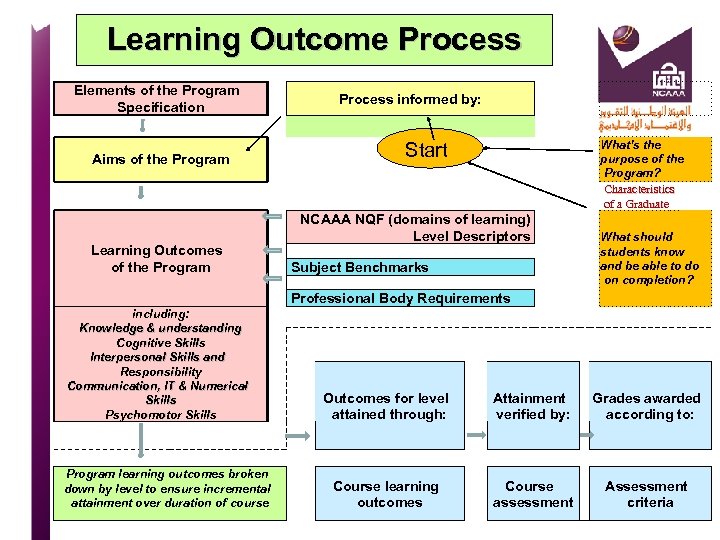 Learning Outcome Process Elements of the Program Specification Aims of the Program Learning Outcomes of the Program Process informed by: What’s the purpose of the Program? Characteristics of a Graduate Start NCAAA NQF (domains of learning) Level Descriptors Subject Benchmarks What should students know and be able to do on completion? Professional Body Requirements including: Knowledge & understanding Cognitive Skills Interpersonal Skills and Responsibility Communication, IT & Numerical Skills Psychomotor Skills Program learning outcomes broken down by level to ensure incremental attainment over duration of course Outcomes for level attained through: Attainment verified by: Grades awarded according to: Course learning outcomes Course assessment Assessment criteria
Learning Outcome Process Elements of the Program Specification Aims of the Program Learning Outcomes of the Program Process informed by: What’s the purpose of the Program? Characteristics of a Graduate Start NCAAA NQF (domains of learning) Level Descriptors Subject Benchmarks What should students know and be able to do on completion? Professional Body Requirements including: Knowledge & understanding Cognitive Skills Interpersonal Skills and Responsibility Communication, IT & Numerical Skills Psychomotor Skills Program learning outcomes broken down by level to ensure incremental attainment over duration of course Outcomes for level attained through: Attainment verified by: Grades awarded according to: Course learning outcomes Course assessment Assessment criteria
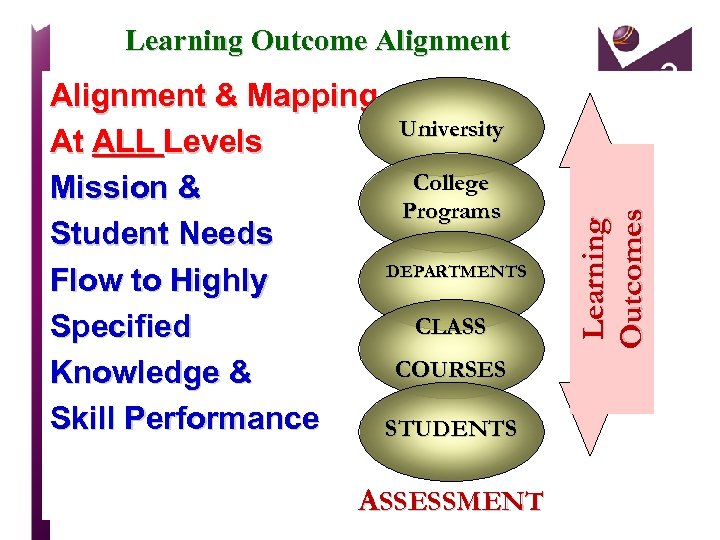 Alignment & Mapping University At ALL Levels College Mission & Programs Student Needs DEPARTMENTS Flow to Highly CLASS Specified COURSES Knowledge & Skill Performance STUDENTS ASSESSMENT Learning Outcomes Learning Outcome Alignment
Alignment & Mapping University At ALL Levels College Mission & Programs Student Needs DEPARTMENTS Flow to Highly CLASS Specified COURSES Knowledge & Skill Performance STUDENTS ASSESSMENT Learning Outcomes Learning Outcome Alignment
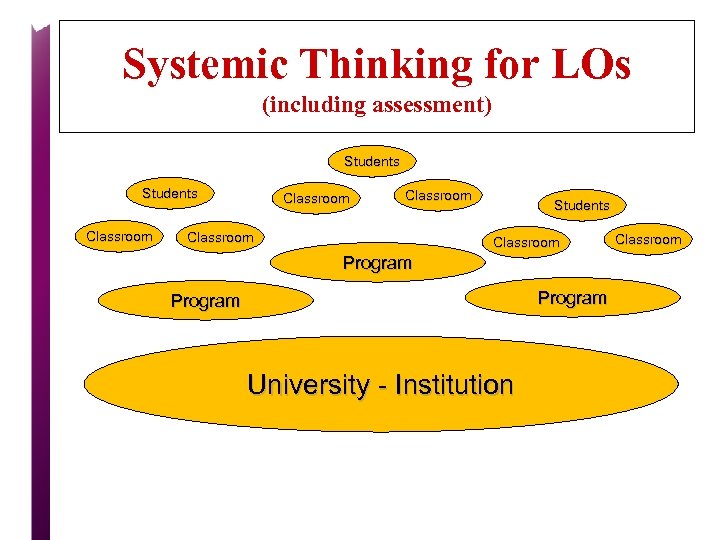 Systemic Thinking for LOs (including assessment) Students Classroom Students Classroom Program University - Institution Classroom
Systemic Thinking for LOs (including assessment) Students Classroom Students Classroom Program University - Institution Classroom
 (including assessment) LOs Quality System fo
(including assessment) LOs Quality System fo
 NQF Level Descriptors • Level descriptors are generic statements describing the characteristics and context of learning expected at each level (year). level • These help guide faculty expectations of students and they are designed to ensure equivalence and consistency of standards across subject areas. • They are set out in the University’s Academic Regulations and Policies and are based on those recommended by the National Qualification Framework (NQF). Framework
NQF Level Descriptors • Level descriptors are generic statements describing the characteristics and context of learning expected at each level (year). level • These help guide faculty expectations of students and they are designed to ensure equivalence and consistency of standards across subject areas. • They are set out in the University’s Academic Regulations and Policies and are based on those recommended by the National Qualification Framework (NQF). Framework
 RPR Quotes The Panel also examined a number of student projects for a number of courses. While some of the topics were appropriate …. the work presented often falls below what would be expected at this level Some projects were essentially descriptions that did not involve any analysis or practical activity. Others, which or practical activity. involve practical work, were written up without any material that demonstrated the design and implementation demonstrated of the systems described. The Panel feels that many of the projects do not meet the CLOs (course learning outcomes).
RPR Quotes The Panel also examined a number of student projects for a number of courses. While some of the topics were appropriate …. the work presented often falls below what would be expected at this level Some projects were essentially descriptions that did not involve any analysis or practical activity. Others, which or practical activity. involve practical work, were written up without any material that demonstrated the design and implementation demonstrated of the systems described. The Panel feels that many of the projects do not meet the CLOs (course learning outcomes).
 Characteristics of Good Learning Outcomes 1. Measurable or Observable Measurable 2. Clear to the student & instructor Clear 3. Integrated, developmental, and transferable Integrated 4. Use discipline-specific competencies or standards as a basis, not an end basis 5. Similar scope & scale 6. “In order to. . ” do …. . gets to the purpose, uniqueness, and real world application of learning and teaching. 7. Use a variety of learning domains
Characteristics of Good Learning Outcomes 1. Measurable or Observable Measurable 2. Clear to the student & instructor Clear 3. Integrated, developmental, and transferable Integrated 4. Use discipline-specific competencies or standards as a basis, not an end basis 5. Similar scope & scale 6. “In order to. . ” do …. . gets to the purpose, uniqueness, and real world application of learning and teaching. 7. Use a variety of learning domains
 Good LOs are… ü Usually written in the future tense ü Identify important learning requirements ü Are achievable ü Use clear language easily understandable to student When writing outcomes, it may be useful to use the following expression: “At the end of this Program or course the student should be able to……. ” Then follow with a verb. Useful verbs are: ? ? ?
Good LOs are… ü Usually written in the future tense ü Identify important learning requirements ü Are achievable ü Use clear language easily understandable to student When writing outcomes, it may be useful to use the following expression: “At the end of this Program or course the student should be able to……. ” Then follow with a verb. Useful verbs are: ? ? ?
 Suggested Verbs Establish Provide Tabulate Schedule Audit Align Construct List Compile Demonstrate Draft Prepare Write Update Articulate Collect Generate Produce Document Develop Helpful? Need much more!!
Suggested Verbs Establish Provide Tabulate Schedule Audit Align Construct List Compile Demonstrate Draft Prepare Write Update Articulate Collect Generate Produce Document Develop Helpful? Need much more!!
 Verbs Not To Use Consider Maintain Continue Ensure Understand Strengthen Encourage Maximize Reflect Review Enlarge Examine Explore Deepen Better? Yes… BUT!! Some of these verbs can be used if tied to specific actions or quantification
Verbs Not To Use Consider Maintain Continue Ensure Understand Strengthen Encourage Maximize Reflect Review Enlarge Examine Explore Deepen Better? Yes… BUT!! Some of these verbs can be used if tied to specific actions or quantification
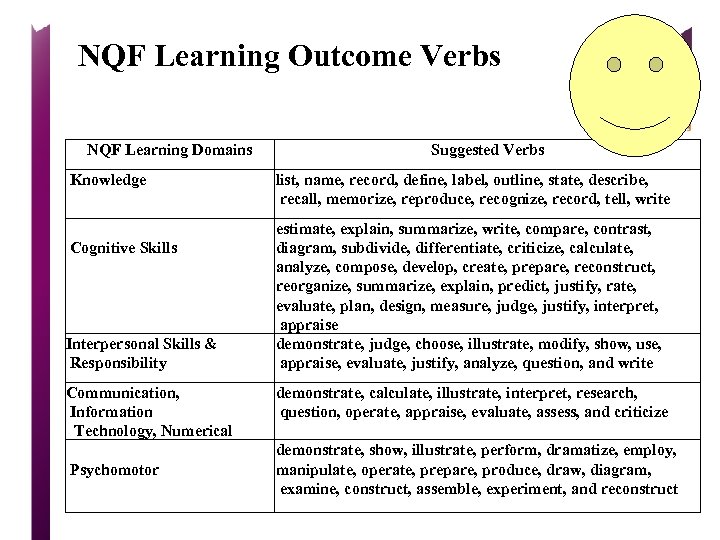 NQF Learning Outcome Verbs NQF Learning Domains Knowledge Cognitive Skills Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility Communication, Information Technology, Numerical Psychomotor Suggested Verbs list, name, record, define, label, outline, state, describe, recall, memorize, reproduce, recognize, record, tell, write estimate, explain, summarize, write, compare, contrast, diagram, subdivide, differentiate, criticize, calculate, analyze, compose, develop, create, prepare, reconstruct, reorganize, summarize, explain, predict, justify, rate, evaluate, plan, design, measure, judge, justify, interpret, appraise demonstrate, judge, choose, illustrate, modify, show, use, appraise, evaluate, justify, analyze, question, and write demonstrate, calculate, illustrate, interpret, research, question, operate, appraise, evaluate, assess, and criticize demonstrate, show, illustrate, perform, dramatize, employ, manipulate, operate, prepare, produce, draw, diagram, examine, construct, assemble, experiment, and reconstruct
NQF Learning Outcome Verbs NQF Learning Domains Knowledge Cognitive Skills Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility Communication, Information Technology, Numerical Psychomotor Suggested Verbs list, name, record, define, label, outline, state, describe, recall, memorize, reproduce, recognize, record, tell, write estimate, explain, summarize, write, compare, contrast, diagram, subdivide, differentiate, criticize, calculate, analyze, compose, develop, create, prepare, reconstruct, reorganize, summarize, explain, predict, justify, rate, evaluate, plan, design, measure, judge, justify, interpret, appraise demonstrate, judge, choose, illustrate, modify, show, use, appraise, evaluate, justify, analyze, question, and write demonstrate, calculate, illustrate, interpret, research, question, operate, appraise, evaluate, assess, and criticize demonstrate, show, illustrate, perform, dramatize, employ, manipulate, operate, prepare, produce, draw, diagram, examine, construct, assemble, experiment, and reconstruct
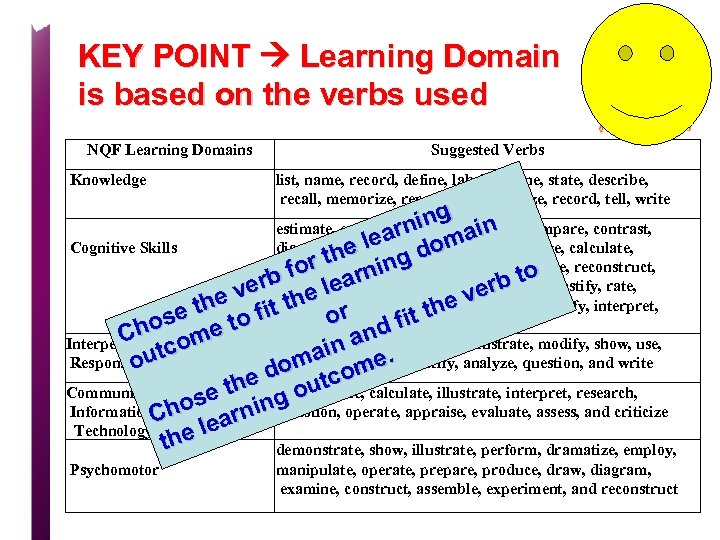 KEY POINT Learning Domain is based on the verbs used NQF Learning Domains Knowledge Suggested Verbs list, name, record, define, label, outline, state, describe, recall, memorize, reproduce, recognize, record, tell, write g estimate, explain, summarize, write, compare, contrast, rnin main lea do Cognitive Skills diagram, subdivide, differentiate, criticize, calculate, e r th ning analyze, compose, develop, create, prepare, reconstruct, b fo lear r reorganize, summarize, explain, predict, justify, rate, b to ver e ve tevaluate, plan, design, measure, judge, justify, interpret, he e th to fi appraise r t th o d fi hos me n C Interpersonal Skills & demonstrate, judge, choose, illustrate, modify, show, use, o na. c i Responsibility appraise, evaluate, justify, analyze, question, and write ma me out o m d tco he demonstrate, calculate, illustrate, interpret, research, u Communication, se t ing o Information. Cho arn question, operate, appraise, evaluate, assess, and criticize le Technology, Numerical he t demonstrate, show, illustrate, perform, dramatize, employ, Psychomotor manipulate, operate, prepare, produce, draw, diagram, examine, construct, assemble, experiment, and reconstruct
KEY POINT Learning Domain is based on the verbs used NQF Learning Domains Knowledge Suggested Verbs list, name, record, define, label, outline, state, describe, recall, memorize, reproduce, recognize, record, tell, write g estimate, explain, summarize, write, compare, contrast, rnin main lea do Cognitive Skills diagram, subdivide, differentiate, criticize, calculate, e r th ning analyze, compose, develop, create, prepare, reconstruct, b fo lear r reorganize, summarize, explain, predict, justify, rate, b to ver e ve tevaluate, plan, design, measure, judge, justify, interpret, he e th to fi appraise r t th o d fi hos me n C Interpersonal Skills & demonstrate, judge, choose, illustrate, modify, show, use, o na. c i Responsibility appraise, evaluate, justify, analyze, question, and write ma me out o m d tco he demonstrate, calculate, illustrate, interpret, research, u Communication, se t ing o Information. Cho arn question, operate, appraise, evaluate, assess, and criticize le Technology, Numerical he t demonstrate, show, illustrate, perform, dramatize, employ, Psychomotor manipulate, operate, prepare, produce, draw, diagram, examine, construct, assemble, experiment, and reconstruct
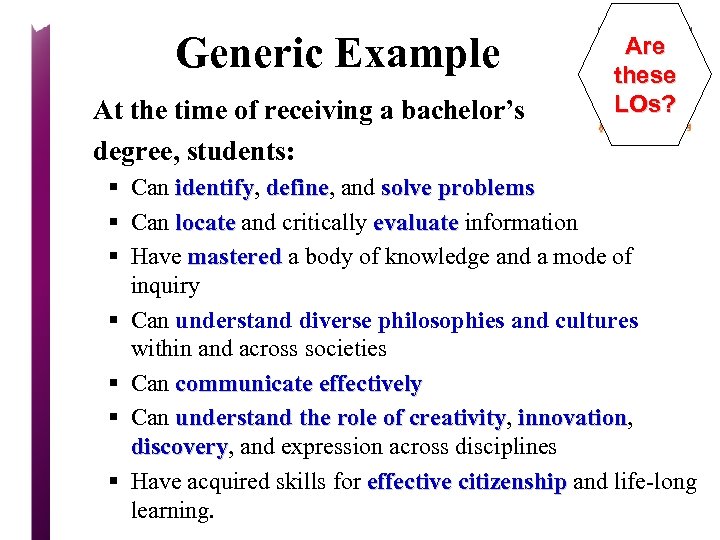 Generic Example At the time of receiving a bachelor’s degree, students: Are these LOs? § Can identify, define, and solve problems identify define § Can locate and critically evaluate information locate evaluate § Have mastered a body of knowledge and a mode of mastered inquiry § Can understand diverse philosophies and cultures within and across societies § Can communicate effectively § Can understand the role of creativity, innovation, understand the role of creativity innovation discovery, and expression across disciplines discovery § Have acquired skills for effective citizenship and life-long effective citizenship learning.
Generic Example At the time of receiving a bachelor’s degree, students: Are these LOs? § Can identify, define, and solve problems identify define § Can locate and critically evaluate information locate evaluate § Have mastered a body of knowledge and a mode of mastered inquiry § Can understand diverse philosophies and cultures within and across societies § Can communicate effectively § Can understand the role of creativity, innovation, understand the role of creativity innovation discovery, and expression across disciplines discovery § Have acquired skills for effective citizenship and life-long effective citizenship learning.
 Example of Program LOs e lyz a An is th At the time of receiving a BSN Degree, students: § Can identify, define, and solve problems; § Can locate and critically evaluate information; § Have mastered a body of knowledge and a mode of inquiry; § Can understand diverse philosophies and cultures within and across societies; § Can communicate effectively; § Can understand the role of creativity, innovation, discovery, and expression across disciplines; and § Have acquired skills for effective citizenship and life-long learning. What is the major problem with this list? ?
Example of Program LOs e lyz a An is th At the time of receiving a BSN Degree, students: § Can identify, define, and solve problems; § Can locate and critically evaluate information; § Have mastered a body of knowledge and a mode of inquiry; § Can understand diverse philosophies and cultures within and across societies; § Can communicate effectively; § Can understand the role of creativity, innovation, discovery, and expression across disciplines; and § Have acquired skills for effective citizenship and life-long learning. What is the major problem with this list? ?
 Specific Program LOs (Dentistry Examples) 1. 2. Graduates should demonstrate sound knowledge of the following areas as they relate to the practice of dentistry (includes a list of over 20 specific dentistry content areas). Graduates must have the ability to apply their knowledge and understanding of relevant principles and theories in carrying out the following types of responsibilities (e. g. problem recognition for disease identification and diagnosis, problem solving in dental care, critical thinking of dental research, patient investigation—biopsy techniques, radiography, treatment plans). Write 3 specific Program LOs for your Program by using the generic Program LOs shown on the previous slide. (present to group using flip chart + Analyze)
Specific Program LOs (Dentistry Examples) 1. 2. Graduates should demonstrate sound knowledge of the following areas as they relate to the practice of dentistry (includes a list of over 20 specific dentistry content areas). Graduates must have the ability to apply their knowledge and understanding of relevant principles and theories in carrying out the following types of responsibilities (e. g. problem recognition for disease identification and diagnosis, problem solving in dental care, critical thinking of dental research, patient investigation—biopsy techniques, radiography, treatment plans). Write 3 specific Program LOs for your Program by using the generic Program LOs shown on the previous slide. (present to group using flip chart + Analyze)
 30 Minute Break Prayer
30 Minute Break Prayer
 NCAAA Session 3 General Guidelines Recommendations & Suggestions NQF Learning Domains & LOs Writing LOs
NCAAA Session 3 General Guidelines Recommendations & Suggestions NQF Learning Domains & LOs Writing LOs
 Difference between course learning outcomes & Program learning outcomes? LOs at Program level are broad for all students in the Program. Course LOs are content or skill specific: Describing what the student will be able to do. They determine: 1. Content, 2. Delivery and 3. Assessment of each course, and, along with other courses, meet the Program outcomes.
Difference between course learning outcomes & Program learning outcomes? LOs at Program level are broad for all students in the Program. Course LOs are content or skill specific: Describing what the student will be able to do. They determine: 1. Content, 2. Delivery and 3. Assessment of each course, and, along with other courses, meet the Program outcomes.
 Example: Program Learning Outcome Ø Upon successful completion of the Program…. a student will be able to critically evaluate problems and alternative solutions in a wide variety of business and organizational contexts in different socio-cultural and political environments. How is this clear? Measurable? Observable? What NQF domain of learning? How will you assess this?
Example: Program Learning Outcome Ø Upon successful completion of the Program…. a student will be able to critically evaluate problems and alternative solutions in a wide variety of business and organizational contexts in different socio-cultural and political environments. How is this clear? Measurable? Observable? What NQF domain of learning? How will you assess this?
 Example: Course Learning Outcome Ø On successful completion of the course students… students will be able to discuss 7 different ways how will be able to discuss 7 different ways information technology can be used to help business organizations to succeed in their objectives. How is this clear? Measurable? Observable? What NQF domain of learning? How will you assess this?
Example: Course Learning Outcome Ø On successful completion of the course students… students will be able to discuss 7 different ways how will be able to discuss 7 different ways information technology can be used to help business organizations to succeed in their objectives. How is this clear? Measurable? Observable? What NQF domain of learning? How will you assess this?
 Well written L. O. are…. Use a verb that indicates what the learner is expected to be able to do at the end of the period of learning; measurable or observable. Word(s) that indicate on what or with what the learner is acting. If the outcome is about skills then the word(s) may describe the way the skill is performed or the tool to be used. Word(s) that indicate the nature (in context or in terms of standard) of the performance required as evidence that the learning was achieved.
Well written L. O. are…. Use a verb that indicates what the learner is expected to be able to do at the end of the period of learning; measurable or observable. Word(s) that indicate on what or with what the learner is acting. If the outcome is about skills then the word(s) may describe the way the skill is performed or the tool to be used. Word(s) that indicate the nature (in context or in terms of standard) of the performance required as evidence that the learning was achieved.
 Learning Outcome Magar’s 3 Parts for Successful LOs 1. A measurable verb 2. The important condition (if any) under which the performance is to occur and 3. The criterion of acceptable performance. When Magar’s 3 parts of a LO are used correctly a LO may also be a KPI
Learning Outcome Magar’s 3 Parts for Successful LOs 1. A measurable verb 2. The important condition (if any) under which the performance is to occur and 3. The criterion of acceptable performance. When Magar’s 3 parts of a LO are used correctly a LO may also be a KPI
 Student needs Learning outcomes Student needs example: “Student needs to learn how to fish in the ocean to survive on the island. ” What are some learning outcomes that fit this student’s needs? 1. (Knowledge)__________________ 2. (Cognitive)__________________ 3. (Skill) ____________________________________
Student needs Learning outcomes Student needs example: “Student needs to learn how to fish in the ocean to survive on the island. ” What are some learning outcomes that fit this student’s needs? 1. (Knowledge)__________________ 2. (Cognitive)__________________ 3. (Skill) ____________________________________
 Write a Learning Outcome (whole group activity 1/2) We’re taking a friend desert camping for the first time. What does a graduate of desert camping school need to know or what skills are required? Like, “What to do if a sand storm comes up? ” 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________
Write a Learning Outcome (whole group activity 1/2) We’re taking a friend desert camping for the first time. What does a graduate of desert camping school need to know or what skills are required? Like, “What to do if a sand storm comes up? ” 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________
 Re-write as Learning Outcomes Using Megar’s 3 Parts (whole group activity 2/2) 1. What to do if a sand storm comes up? 2. What to do if he runs out of water? 3. He needs compass reading and mapping skills? Re-write the content objectives as LOs. 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________ How do the LOs utilize Magar’s 3 Parts?
Re-write as Learning Outcomes Using Megar’s 3 Parts (whole group activity 2/2) 1. What to do if a sand storm comes up? 2. What to do if he runs out of water? 3. He needs compass reading and mapping skills? Re-write the content objectives as LOs. 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________ How do the LOs utilize Magar’s 3 Parts?
 Recommendations & Suggestions 1. Aim for between four and eight learning outcomes for each course, and up to twenty-five for an entire Program. 2. Start Program outcomes with the phrase: “A successful learner from this Program will be able to …. . ” 3. Start course outcomes with the phrase: “On successful completion of the course, you will be able to …. . ”
Recommendations & Suggestions 1. Aim for between four and eight learning outcomes for each course, and up to twenty-five for an entire Program. 2. Start Program outcomes with the phrase: “A successful learner from this Program will be able to …. . ” 3. Start course outcomes with the phrase: “On successful completion of the course, you will be able to …. . ”
 Recommendations & Suggestions 4. These phrases lead to action verbs so that students are able to demonstrate that they have learned or achieved the outcome. 5. “to demonstrate” leads to objective assessment or objective evaluation or measurement of student performance and achievements. 6. Use one verb per learning outcome, and keep the sentence structure simple. 7. Avoid unnecessary language; if absolutely necessary, use more than one sentence to ensure clarity.
Recommendations & Suggestions 4. These phrases lead to action verbs so that students are able to demonstrate that they have learned or achieved the outcome. 5. “to demonstrate” leads to objective assessment or objective evaluation or measurement of student performance and achievements. 6. Use one verb per learning outcome, and keep the sentence structure simple. 7. Avoid unnecessary language; if absolutely necessary, use more than one sentence to ensure clarity.
 Recommendations & Suggestions 8. Verbs relating to knowledge outcomes – ‘know, ’ ‘understand, ’ ‘appreciate’ – tend to be vague, or to focus on the process students have gone through (e. g. understand research [process]) rather than the process final outcome of that process (e. g. create & list [do] do strategies appropriate to the research topic). 9. Use action verbs, such as: ‘solve, ’ ‘write, ’ ‘evaluate, ’ ‘analyse’ to indicate how students can demonstrate acquisition of that knowledge.
Recommendations & Suggestions 8. Verbs relating to knowledge outcomes – ‘know, ’ ‘understand, ’ ‘appreciate’ – tend to be vague, or to focus on the process students have gone through (e. g. understand research [process]) rather than the process final outcome of that process (e. g. create & list [do] do strategies appropriate to the research topic). 9. Use action verbs, such as: ‘solve, ’ ‘write, ’ ‘evaluate, ’ ‘analyse’ to indicate how students can demonstrate acquisition of that knowledge.
 National Qualification Framework The principal elements in the NQF are: • Levels: numbered and linked to qualification titles to describe the increasing intellectual demand complexity of learning expected as students progress to higher academic awards. • Credits Points: allocated to describe the amount of work or volume of learning expected for an academic award or units or other components of a Program. • Domains of Learning: The broad categories of types of learning outcomes that a Program is intended to develop.
National Qualification Framework The principal elements in the NQF are: • Levels: numbered and linked to qualification titles to describe the increasing intellectual demand complexity of learning expected as students progress to higher academic awards. • Credits Points: allocated to describe the amount of work or volume of learning expected for an academic award or units or other components of a Program. • Domains of Learning: The broad categories of types of learning outcomes that a Program is intended to develop.
 NQF Domains of Learning Outcomes are aligned with the five domains of learning provided in the NQF. Domains of learning apply to both Program and Course learning outcomes Always keep in mind both Program & Course L. O. s
NQF Domains of Learning Outcomes are aligned with the five domains of learning provided in the NQF. Domains of learning apply to both Program and Course learning outcomes Always keep in mind both Program & Course L. O. s
 Five Learning Domains: NQF 1. 2. 3. 4. Knowledge Cognitive skills Interpersonal skills and responsibility Communication, information technology and numerical skills 5. Psychomotor skills NCAAA Use with Program, Course, and Field Experience Specifications templates.
Five Learning Domains: NQF 1. 2. 3. 4. Knowledge Cognitive skills Interpersonal skills and responsibility Communication, information technology and numerical skills 5. Psychomotor skills NCAAA Use with Program, Course, and Field Experience Specifications templates.
 1. Knowledge: the ability to recall, understand, and Knowledge present information, including: • Knowledge of specific facts and details facts • Knowledge of concepts, principles and theories • Answers may be memorized or closely paraphrased from assigned material. • Knowledge of procedures; steps in a process. • VERBS Define, list, name, recall basic information
1. Knowledge: the ability to recall, understand, and Knowledge present information, including: • Knowledge of specific facts and details facts • Knowledge of concepts, principles and theories • Answers may be memorized or closely paraphrased from assigned material. • Knowledge of procedures; steps in a process. • VERBS Define, list, name, recall basic information
 2. Cognitive Skills Cognitive skills: the ability to…. • Apply conceptual understanding of concepts, principles, and theories, • Apply procedures involved in critical thinking and creative problem solving, both when asked to do so, and when faced with unanticipated new situations, • Investigate issues and problems in a field of study using a range of sources and draw valid conclusions. • Ability to comprehend the meaning of material. • Answers must be in the student’s own words while still using terminology appropriate to the course material. • VERBS Explain, summarize, distinguish between, restate
2. Cognitive Skills Cognitive skills: the ability to…. • Apply conceptual understanding of concepts, principles, and theories, • Apply procedures involved in critical thinking and creative problem solving, both when asked to do so, and when faced with unanticipated new situations, • Investigate issues and problems in a field of study using a range of sources and draw valid conclusions. • Ability to comprehend the meaning of material. • Answers must be in the student’s own words while still using terminology appropriate to the course material. • VERBS Explain, summarize, distinguish between, restate
 3. Interpersonal Skills and Responsibility Including the ability to: • Take responsibility for their own learning and continuing personal and professional development, • Work effectively in groups and exercise leadership when appropriate, • Act responsibly in personal and professional relationships, • Act ethically and consistently with high moral standards in personal and public forums.
3. Interpersonal Skills and Responsibility Including the ability to: • Take responsibility for their own learning and continuing personal and professional development, • Work effectively in groups and exercise leadership when appropriate, • Act responsibly in personal and professional relationships, • Act ethically and consistently with high moral standards in personal and public forums.
 4. Communication, Information Technology and Numerical Skills Including the ability to: • Communicate effectively in oral and written effectively form, • Use information and communications Use technology, and • Use basic mathematical and statistical mathematical techniques.
4. Communication, Information Technology and Numerical Skills Including the ability to: • Communicate effectively in oral and written effectively form, • Use information and communications Use technology, and • Use basic mathematical and statistical mathematical techniques.
 5. Psychomotor Skills Psychomotor skills: manual dexterity • Extremely important in some fields of study. For example, very high levels of psychomotor skills are required for a surgeon, an artist, or a musician. • Psychomotor skills apply only to certain fields, and their nature varies widely.
5. Psychomotor Skills Psychomotor skills: manual dexterity • Extremely important in some fields of study. For example, very high levels of psychomotor skills are required for a surgeon, an artist, or a musician. • Psychomotor skills apply only to certain fields, and their nature varies widely.
 Example 1 Poor Learning Outcome: • Students will name three types of rock in order to differentiate among the three (knowledge domain for cognitive skill). skill Good Learning Outcome: • Students will compare and contrast the characteristics of the three types of rocks in order to differentiate among the three.
Example 1 Poor Learning Outcome: • Students will name three types of rock in order to differentiate among the three (knowledge domain for cognitive skill). skill Good Learning Outcome: • Students will compare and contrast the characteristics of the three types of rocks in order to differentiate among the three.
 Student needs LOs (small groups) 1. Identify a student need for your specialized course (center circle). 2. List 5 learning outcomes that are directly based on this need (connecting circles). 3. Explain how each LO meets Magar’s 3 part requirements (connecting lines). Bubble Map - 2
Student needs LOs (small groups) 1. Identify a student need for your specialized course (center circle). 2. List 5 learning outcomes that are directly based on this need (connecting circles). 3. Explain how each LO meets Magar’s 3 part requirements (connecting lines). Bubble Map - 2
 2 nd Day Sessions First Session Review Key Components Second Session Intro LO Attitudes Relationships between LO Qualitative Teaching Methods and Assessment Rubrics Assessments Methods and LOs LO Quantitative KPIs Assessment of Learning Outcomes Mapping Third Session Addressing Common Problems Associated with Writing LOs & Assessment
2 nd Day Sessions First Session Review Key Components Second Session Intro LO Attitudes Relationships between LO Qualitative Teaching Methods and Assessment Rubrics Assessments Methods and LOs LO Quantitative KPIs Assessment of Learning Outcomes Mapping Third Session Addressing Common Problems Associated with Writing LOs & Assessment
 LO Review 1. What is the difference between a learning objective and learning outcome? 2. Where do LOs come from? 3. How are LOs used or applied (benefits)? 4. What are the characteristics of a good LO? 5. What kind of verbs are required for LOs? 6. What are the 3 parts to Megar’s LOs?
LO Review 1. What is the difference between a learning objective and learning outcome? 2. Where do LOs come from? 3. How are LOs used or applied (benefits)? 4. What are the characteristics of a good LO? 5. What kind of verbs are required for LOs? 6. What are the 3 parts to Megar’s LOs?
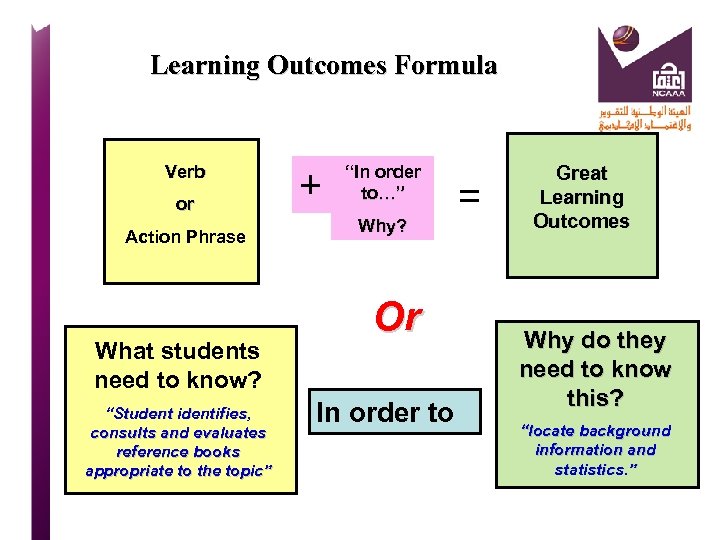 Learning Outcomes Formula Verb or Action Phrase What students need to know? “Student identifies, consults and evaluates reference books appropriate to the topic” + “In order to…” Why? Or In order to = Great Learning Outcomes Why do they need to know this? “locate background information and statistics. ”
Learning Outcomes Formula Verb or Action Phrase What students need to know? “Student identifies, consults and evaluates reference books appropriate to the topic” + “In order to…” Why? Or In order to = Great Learning Outcomes Why do they need to know this? “locate background information and statistics. ”
 Writing Learning Outcomes • Learning outcomes should specify the minimum acceptable standard for a student to be successful (pass a course) “threshold level”. • This means that it is important to express learning outcomes in terms of the essential learning for a course, so there should be a small number of learning outcomes which are of central importance, not a large number of superficial outcomes.
Writing Learning Outcomes • Learning outcomes should specify the minimum acceptable standard for a student to be successful (pass a course) “threshold level”. • This means that it is important to express learning outcomes in terms of the essential learning for a course, so there should be a small number of learning outcomes which are of central importance, not a large number of superficial outcomes.
 Review: A good L. O. is…. ü Active it describes what students can do ü Attractive students want to achieve it ü Comprehensible students know exactly what it means ü Appropriate to the student’s current goals and career plans ü Attainable most students will meet it, with appropriate effort ü MEASURABLE essential for assessment
Review: A good L. O. is…. ü Active it describes what students can do ü Attractive students want to achieve it ü Comprehensible students know exactly what it means ü Appropriate to the student’s current goals and career plans ü Attainable most students will meet it, with appropriate effort ü MEASURABLE essential for assessment
 Things to avoid… Avoid learning outcomes which are too broad in scope, such as broad in scope ‘Recall the fundamental concepts of Structural, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering. ’ Avoid learning outcomes which are too narrow in scope, such as scope ‘State the six categories in Bloom’s Taxonomy. ’ Avoid overloading your course with too much ‘content’; knowledge ’; and understanding outcomes emphasize what your students will be able to comprehend and explain, but this isn’t as important as being comprehend explain able to use the information through: application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation
Things to avoid… Avoid learning outcomes which are too broad in scope, such as broad in scope ‘Recall the fundamental concepts of Structural, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering. ’ Avoid learning outcomes which are too narrow in scope, such as scope ‘State the six categories in Bloom’s Taxonomy. ’ Avoid overloading your course with too much ‘content’; knowledge ’; and understanding outcomes emphasize what your students will be able to comprehend and explain, but this isn’t as important as being comprehend explain able to use the information through: application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation
 LOs & Quality of Teaching NCAAA Standard 4, paragraph 4. 6 • Teaching must be of high quality with appropriate strategies used for different appropriate categories of learning outcomes and student learning styles. • Differentiated Instruction
LOs & Quality of Teaching NCAAA Standard 4, paragraph 4. 6 • Teaching must be of high quality with appropriate strategies used for different appropriate categories of learning outcomes and student learning styles. • Differentiated Instruction
 LO Alignment LOs determine student assessment… LOs … student assessment determines … BOTH… teaching strategy and teaching methods. Together they form a FAMILY
LO Alignment LOs determine student assessment… LOs … student assessment determines … BOTH… teaching strategy and teaching methods. Together they form a FAMILY
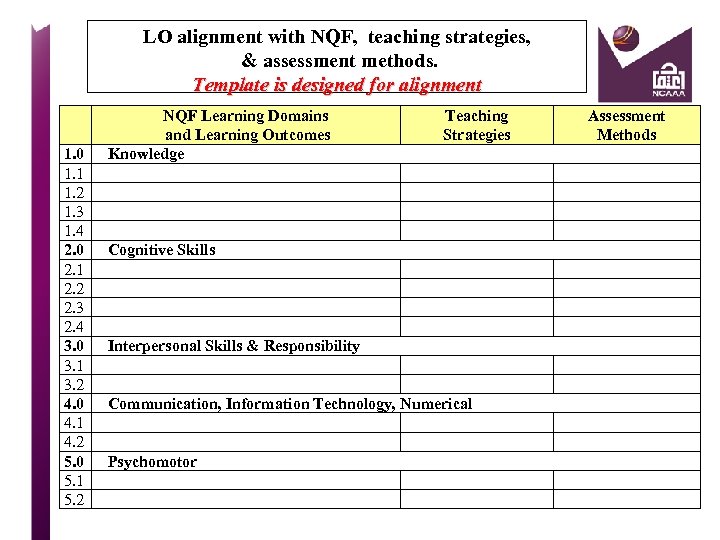 LO alignment with NQF, teaching strategies, & assessment methods. Template is designed for alignment NQF Learning Domains Teaching and Learning Outcomes Strategies 1. 0 Knowledge 1. 1 1. 2 1. 3 1. 4 2. 0 Cognitive Skills 2. 1 2. 2 2. 3 2. 4 3. 0 Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility 3. 1 3. 2 4. 0 Communication, Information Technology, Numerical 4. 1 4. 2 5. 0 Psychomotor 5. 1 5. 2 Assessment Methods
LO alignment with NQF, teaching strategies, & assessment methods. Template is designed for alignment NQF Learning Domains Teaching and Learning Outcomes Strategies 1. 0 Knowledge 1. 1 1. 2 1. 3 1. 4 2. 0 Cognitive Skills 2. 1 2. 2 2. 3 2. 4 3. 0 Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility 3. 1 3. 2 4. 0 Communication, Information Technology, Numerical 4. 1 4. 2 5. 0 Psychomotor 5. 1 5. 2 Assessment Methods
 RPR Quote The Panel examined the Course Specifications for a significant number of courses. It had some concerns about the level of the assessment instruments (Tools) that were used in the delivery of some of the courses, the coverage of learning outcomes that these assessment instruments addressed, and the soundness of the assessment.
RPR Quote The Panel examined the Course Specifications for a significant number of courses. It had some concerns about the level of the assessment instruments (Tools) that were used in the delivery of some of the courses, the coverage of learning outcomes that these assessment instruments addressed, and the soundness of the assessment.
 Teaching Methods and LOs 1. Focus is on learning outcomes in debates on teaching strategies or methods in higher education 2. “Teaching methods” are not an end in themselves, methods not they are a means to an end student performance end 3. They are the vehicle(s) teachers use to lead vehicle(s) students towards particular learning outcomes. 4. Evaluate teaching methods against the learning outcomes that we are seeking for our students to know and demonstrate.
Teaching Methods and LOs 1. Focus is on learning outcomes in debates on teaching strategies or methods in higher education 2. “Teaching methods” are not an end in themselves, methods not they are a means to an end student performance end 3. They are the vehicle(s) teachers use to lead vehicle(s) students towards particular learning outcomes. 4. Evaluate teaching methods against the learning outcomes that we are seeking for our students to know and demonstrate.
 Teaching Methods and LOs 5. First step in operationalizing it is to clarify the First step learning outcomes at which we are aiming (measurable or observable). measurable observable 6. Second step involves developing a contingency approach (differentiated instruction) to the choice instruction of teaching methods; whereby there is “fitness for purpose” (alignment of each LO with teaching strategy-methods).
Teaching Methods and LOs 5. First step in operationalizing it is to clarify the First step learning outcomes at which we are aiming (measurable or observable). measurable observable 6. Second step involves developing a contingency approach (differentiated instruction) to the choice instruction of teaching methods; whereby there is “fitness for purpose” (alignment of each LO with teaching strategy-methods).
 Teaching Methods & LOs 7. When selecting any teaching and learning method it is important to ensure that the method will enable the students to achieve method will enable the students achieve and demonstrate what are intended as learning demonstrate outcomes. 8. There are different kinds of methods available (differentiated instruction): instruction 1. effective in building up subject knowledge 2. contribution to developing generic skills
Teaching Methods & LOs 7. When selecting any teaching and learning method it is important to ensure that the method will enable the students to achieve method will enable the students achieve and demonstrate what are intended as learning demonstrate outcomes. 8. There are different kinds of methods available (differentiated instruction): instruction 1. effective in building up subject knowledge 2. contribution to developing generic skills
 Teaching Methods Mapping Courses Codes Teaching Methods Lecture Small Groups Discussion Project Activity Debate Research Lab Guest Expert Demonstration 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108
Teaching Methods Mapping Courses Codes Teaching Methods Lecture Small Groups Discussion Project Activity Debate Research Lab Guest Expert Demonstration 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108
 LO Alignment Student needs to learn how to fish in the ocean to survive on the island. Learning outcomes that fit this need? 1. Student is able to catch one fish per day. 2. Student catches fish by demonstrating 3 different fishing methods. What assessment methods will align with them? ___________________ What teaching methods will the teacher use to enable students to successfully demonstrate LO achievement? ____________
LO Alignment Student needs to learn how to fish in the ocean to survive on the island. Learning outcomes that fit this need? 1. Student is able to catch one fish per day. 2. Student catches fish by demonstrating 3 different fishing methods. What assessment methods will align with them? ___________________ What teaching methods will the teacher use to enable students to successfully demonstrate LO achievement? ____________
 RPR Quotes The course CS 320 Programming Languages: Concepts and Paradigms covers procedural, object-oriented, functional and logic paradigms. However, the assessment instruments covered only procedural Programming. [incomplete assessment] Some were incomplete, lacking for example some assessment incomplete instruments. For example a course portfolio for CS 371 Web Development contained only one of the three quizzes. In course specifications for CS 330 Introduction to Operating Systems, only the final examination was provided. Some course specifications are inconsistent.
RPR Quotes The course CS 320 Programming Languages: Concepts and Paradigms covers procedural, object-oriented, functional and logic paradigms. However, the assessment instruments covered only procedural Programming. [incomplete assessment] Some were incomplete, lacking for example some assessment incomplete instruments. For example a course portfolio for CS 371 Web Development contained only one of the three quizzes. In course specifications for CS 330 Introduction to Operating Systems, only the final examination was provided. Some course specifications are inconsistent.
 LO Alignment (small groups) 1. Put one of your course LOs in the center circle. 2. Indentify LO student assessments that will determine the level of student performance in the 5 outer circles. 3. List teaching methods that align with the LO and the student assessment on the lines attached to the outer circles. (bubble map 2)
LO Alignment (small groups) 1. Put one of your course LOs in the center circle. 2. Indentify LO student assessments that will determine the level of student performance in the 5 outer circles. 3. List teaching methods that align with the LO and the student assessment on the lines attached to the outer circles. (bubble map 2)
 Learning OUTCOMES …. are “performance of knowledge, skills, and attitudes embedded within them. ” Attitudes may include ethics. Attitudes? ? ?
Learning OUTCOMES …. are “performance of knowledge, skills, and attitudes embedded within them. ” Attitudes may include ethics. Attitudes? ? ?
 ATTITUDES Why do we teach ATTITUDES? ATTITUDES What are the ATTITUDES that student performance outcomes expect? How do you teach attitudes? How to assess attitudes?
ATTITUDES Why do we teach ATTITUDES? ATTITUDES What are the ATTITUDES that student performance outcomes expect? How do you teach attitudes? How to assess attitudes?
 Quantitative Assessments Qualitative Assessments
Quantitative Assessments Qualitative Assessments
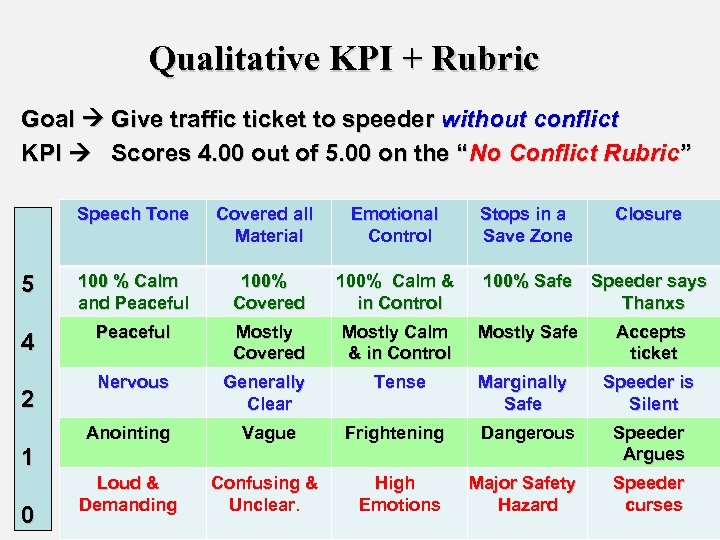 Qualitative KPI + Rubric Goal Give traffic ticket to speeder without conflict KPI Scores 4. 00 out of 5. 00 on the “No Conflict Rubric” Speech Tone Covered all Material Emotional Control 5 100 % Calm and Peaceful 100% Covered 100% Calm & in Control 4 Peaceful Mostly Covered Mostly Calm & in Control Mostly Safe Accepts ticket Nervous Generally Clear Tense Marginally Safe Speeder is Silent Anointing Vague Frightening Dangerous Speeder Argues Loud & Demanding Confusing & Unclear. High Emotions Major Safety Hazard Speeder curses 2 Stops in a Save Zone 100% Safe Speeder says Thanxs 1 0 Closure
Qualitative KPI + Rubric Goal Give traffic ticket to speeder without conflict KPI Scores 4. 00 out of 5. 00 on the “No Conflict Rubric” Speech Tone Covered all Material Emotional Control 5 100 % Calm and Peaceful 100% Covered 100% Calm & in Control 4 Peaceful Mostly Covered Mostly Calm & in Control Mostly Safe Accepts ticket Nervous Generally Clear Tense Marginally Safe Speeder is Silent Anointing Vague Frightening Dangerous Speeder Argues Loud & Demanding Confusing & Unclear. High Emotions Major Safety Hazard Speeder curses 2 Stops in a Save Zone 100% Safe Speeder says Thanxs 1 0 Closure
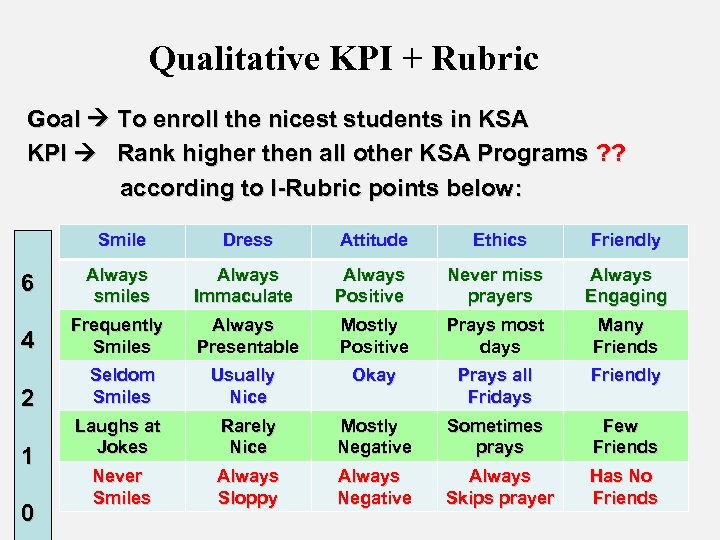 Qualitative KPI + Rubric Goal To enroll the nicest students in KSA KPI Rank higher then all other KSA Programs ? ? according to I-Rubric points below: Smile Dress Attitude Ethics Friendly 6 Always smiles Always Immaculate Always Positive Never miss prayers Always Engaging 4 Frequently Smiles Always Presentable Mostly Positive Prays most days Many Friends 2 Seldom Smiles Usually Nice Okay Prays all Fridays Friendly Laughs at Jokes Rarely Nice Mostly Negative Sometimes prays Few Friends Never Smiles Always Sloppy Always Negative Always Skips prayer Has No Friends 1 0
Qualitative KPI + Rubric Goal To enroll the nicest students in KSA KPI Rank higher then all other KSA Programs ? ? according to I-Rubric points below: Smile Dress Attitude Ethics Friendly 6 Always smiles Always Immaculate Always Positive Never miss prayers Always Engaging 4 Frequently Smiles Always Presentable Mostly Positive Prays most days Many Friends 2 Seldom Smiles Usually Nice Okay Prays all Fridays Friendly Laughs at Jokes Rarely Nice Mostly Negative Sometimes prays Few Friends Never Smiles Always Sloppy Always Negative Always Skips prayer Has No Friends 1 0
 Bubble Map + In the center circle write an attitude; a student need for a course or a Program. In the connected circles write learning outcomes you want performed. On the lines outside each learning outcome circle write how to teach and asess this attitude for each learning outcome
Bubble Map + In the center circle write an attitude; a student need for a course or a Program. In the connected circles write learning outcomes you want performed. On the lines outside each learning outcome circle write how to teach and asess this attitude for each learning outcome
 Session 5 Relationship between teaching methods and assessment methods…. with learning outcomes.
Session 5 Relationship between teaching methods and assessment methods…. with learning outcomes.
 Start at the End Teaching strategy and methods depend on the assessment methods utilized. The assessments utilized depends on the learning outcome VERB that guides the assessment process to validate student learning and direct teaching methods. Teaching Assessment Objectives Learning Mission Student Methods (Content) Outcomes Needs
Start at the End Teaching strategy and methods depend on the assessment methods utilized. The assessments utilized depends on the learning outcome VERB that guides the assessment process to validate student learning and direct teaching methods. Teaching Assessment Objectives Learning Mission Student Methods (Content) Outcomes Needs
 Key for Learning Outcomes Key is ASSESSMENT Learning outcomes must be…. measurable and meaningful to be assessed accurately. Who will know? Student? Faculty? How will I know? Evidence? What evidence is needed? Demonstration: statistical, observable, or quantifiable data… or rubrics?
Key for Learning Outcomes Key is ASSESSMENT Learning outcomes must be…. measurable and meaningful to be assessed accurately. Who will know? Student? Faculty? How will I know? Evidence? What evidence is needed? Demonstration: statistical, observable, or quantifiable data… or rubrics?
 NCAAA: L. O. + Assessment NCAAA Standard 4, paragraph 4. 4: Student assessment processes must be appropriate for the intended learning outcomes and effectively and fairly administered with independent verification of standards achieved.
NCAAA: L. O. + Assessment NCAAA Standard 4, paragraph 4. 4: Student assessment processes must be appropriate for the intended learning outcomes and effectively and fairly administered with independent verification of standards achieved.
 Assessment of Learning Outcomes 1. Indirect Assessment 2. Direct Assessment
Assessment of Learning Outcomes 1. Indirect Assessment 2. Direct Assessment
 Quality Assurance of Assessment of Learning Outcomes…. May be achieved: 1. By direct observation – inspection of assessment direct indicators with benchmarks with analysis; (imbedded KPIs with benchmarking for LOs or rubrics) 2. By indirect measurement– by examining the indirect specifications of assessment processes 3. By indirect feedback – from students, from indirect employers, from external examiner, from professional bodies (surveys).
Quality Assurance of Assessment of Learning Outcomes…. May be achieved: 1. By direct observation – inspection of assessment direct indicators with benchmarks with analysis; (imbedded KPIs with benchmarking for LOs or rubrics) 2. By indirect measurement– by examining the indirect specifications of assessment processes 3. By indirect feedback – from students, from indirect employers, from external examiner, from professional bodies (surveys).
 Align Assessment with LOs Assessments should provide instructors and students with evidence of how well the students have learned what is intend them to learn. What educators, practitioners, & students want students to learn and be able to do should guide the choice and design of the assessment. There are two major reasons for aligning assessments with LOs. First, alignment increases the probability that educators will provide students with the opportunities to learn and practice or demonstrate the knowledge and skills that are required. Second, when assessments and LOs are aligned, “good grades” are more likely to translate into “good learning” performance. When LOs and assessments are misaligned, many students will focus their efforts on activities that may lead to good grades on assessments, rather than focusing their efforts on learning what is important to do or achieve in the real world.
Align Assessment with LOs Assessments should provide instructors and students with evidence of how well the students have learned what is intend them to learn. What educators, practitioners, & students want students to learn and be able to do should guide the choice and design of the assessment. There are two major reasons for aligning assessments with LOs. First, alignment increases the probability that educators will provide students with the opportunities to learn and practice or demonstrate the knowledge and skills that are required. Second, when assessments and LOs are aligned, “good grades” are more likely to translate into “good learning” performance. When LOs and assessments are misaligned, many students will focus their efforts on activities that may lead to good grades on assessments, rather than focusing their efforts on learning what is important to do or achieve in the real world.
 LOs and Assessment Ø State clearly each outcome you are seeking: How would State clearly each outcome you are seeking: you recognize it? What does it look like? What precisely will the student be able to do or demonstrate? Ø Selecting and Implementing Assessment Methods § Not every LO can always be directly assessed; identify assessed those that you prize most highly and that can be meaningfully measured. § Select strategic methods or instruments for gathering evidence to show whether students have achieved the expected learning outcomes (for example; KPIs with multiple benchmarks or rubrics). multiple benchmarks or rubrics
LOs and Assessment Ø State clearly each outcome you are seeking: How would State clearly each outcome you are seeking: you recognize it? What does it look like? What precisely will the student be able to do or demonstrate? Ø Selecting and Implementing Assessment Methods § Not every LO can always be directly assessed; identify assessed those that you prize most highly and that can be meaningfully measured. § Select strategic methods or instruments for gathering evidence to show whether students have achieved the expected learning outcomes (for example; KPIs with multiple benchmarks or rubrics). multiple benchmarks or rubrics
 LOs and Assessment Using Evidence Gathered in Assessment: 1. Specify procedures for analyzing and interpreting the procedures evidence gathered in assessment. 2. Prior to scoring assessments, determine any performance expectations (target benchmarks—external and internal). expectations 3. What is the relationship between the findings (actual and relationship target benchmarks)? Are scores or performance demonstrations consistent, inconsistent, or at opposite ends of the spectrum? 4. Use the data to pinpoint the areas in your Program that are achieving Program goals and also areas of your Program that warrant change for improvement.
LOs and Assessment Using Evidence Gathered in Assessment: 1. Specify procedures for analyzing and interpreting the procedures evidence gathered in assessment. 2. Prior to scoring assessments, determine any performance expectations (target benchmarks—external and internal). expectations 3. What is the relationship between the findings (actual and relationship target benchmarks)? Are scores or performance demonstrations consistent, inconsistent, or at opposite ends of the spectrum? 4. Use the data to pinpoint the areas in your Program that are achieving Program goals and also areas of your Program that warrant change for improvement.
 LOs and Assessment The following table presents examples of the kinds of assessment activities that can be used to assess different types of learning outcomes, and the ways that we can analyze or measure performance to produce useful feedback for teaching and learning.
LOs and Assessment The following table presents examples of the kinds of assessment activities that can be used to assess different types of learning outcomes, and the ways that we can analyze or measure performance to produce useful feedback for teaching and learning.
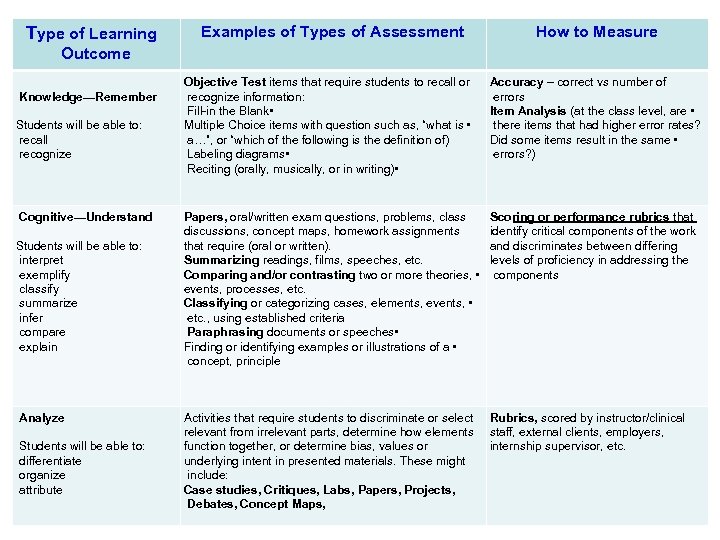 Type of Learning Examples of Types of Assessment How to Measure Outcome Knowledge—Remember Students will be able to: recall recognize Cognitive—Understand Students will be able to: interpret exemplify classify summarize infer compare explain Analyze Students will be able to: differentiate organize attribute Objective Test items that require students to recall or recognize information: Fill-in the Blank • Multiple Choice items with question such as, “what is • a…”, or “which of the following is the definition of) Labeling diagrams • Reciting (orally, musically, or in writing) • Accuracy – correct vs number of errors Item Analysis (at the class level, are • there items that had higher error rates? Did some items result in the same • errors? ) Papers, oral/written exam questions, problems, class discussions, concept maps, homework assignments that require (oral or written). Summarizing readings, films, speeches, etc. Comparing and/or contrasting two or more theories, • events, processes, etc. Classifying or categorizing cases, elements, events, • etc. , using established criteria Paraphrasing documents or speeches • Finding or identifying examples or illustrations of a • concept, principle Scoring or performance rubrics that identify critical components of the work and discriminates between differing levels of proficiency in addressing the components Activities that require students to discriminate or select relevant from irrelevant parts, determine how elements function together, or determine bias, values or underlying intent in presented materials. These might include: Case studies, Critiques, Labs, Papers, Projects, Debates, Concept Maps, Rubrics, scored by instructor/clinical staff, external clients, employers, internship supervisor, etc.
Type of Learning Examples of Types of Assessment How to Measure Outcome Knowledge—Remember Students will be able to: recall recognize Cognitive—Understand Students will be able to: interpret exemplify classify summarize infer compare explain Analyze Students will be able to: differentiate organize attribute Objective Test items that require students to recall or recognize information: Fill-in the Blank • Multiple Choice items with question such as, “what is • a…”, or “which of the following is the definition of) Labeling diagrams • Reciting (orally, musically, or in writing) • Accuracy – correct vs number of errors Item Analysis (at the class level, are • there items that had higher error rates? Did some items result in the same • errors? ) Papers, oral/written exam questions, problems, class discussions, concept maps, homework assignments that require (oral or written). Summarizing readings, films, speeches, etc. Comparing and/or contrasting two or more theories, • events, processes, etc. Classifying or categorizing cases, elements, events, • etc. , using established criteria Paraphrasing documents or speeches • Finding or identifying examples or illustrations of a • concept, principle Scoring or performance rubrics that identify critical components of the work and discriminates between differing levels of proficiency in addressing the components Activities that require students to discriminate or select relevant from irrelevant parts, determine how elements function together, or determine bias, values or underlying intent in presented materials. These might include: Case studies, Critiques, Labs, Papers, Projects, Debates, Concept Maps, Rubrics, scored by instructor/clinical staff, external clients, employers, internship supervisor, etc.
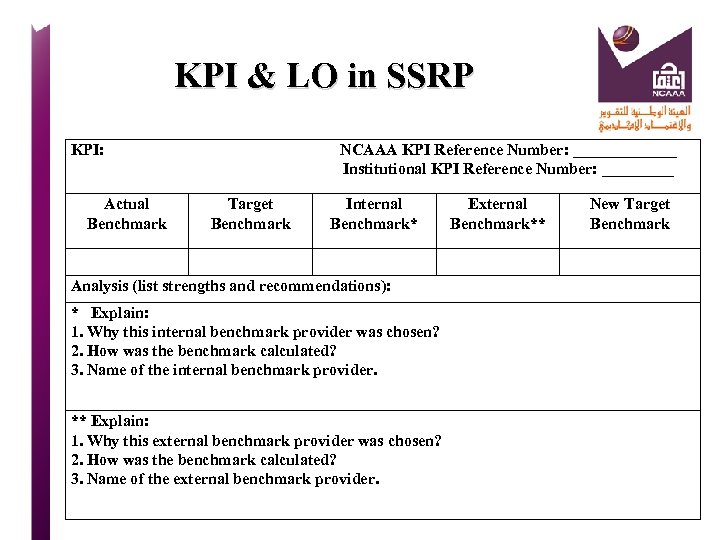 KPI & LO in SSRP KPI: NCAAA KPI Reference Number: _______ Institutional KPI Reference Number: _____ Actual Benchmark Target Benchmark Internal Benchmark* Analysis (list strengths and recommendations): * Explain: 1. Why this internal benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the internal benchmark provider. ** Explain: 1. Why this external benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the external benchmark provider. External Benchmark** New Target Benchmark
KPI & LO in SSRP KPI: NCAAA KPI Reference Number: _______ Institutional KPI Reference Number: _____ Actual Benchmark Target Benchmark Internal Benchmark* Analysis (list strengths and recommendations): * Explain: 1. Why this internal benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the internal benchmark provider. ** Explain: 1. Why this external benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the external benchmark provider. External Benchmark** New Target Benchmark
 General Example Objective To attract high-calibre students – defined as the top 25% in the national exams. Strategy Market Program to top 25% KPI and Outcome Data or Evidence Percentage of enrolled students from the top 25% Target Benchmark 40% of students enrolled next year to be in this high-calibre category
General Example Objective To attract high-calibre students – defined as the top 25% in the national exams. Strategy Market Program to top 25% KPI and Outcome Data or Evidence Percentage of enrolled students from the top 25% Target Benchmark 40% of students enrolled next year to be in this high-calibre category
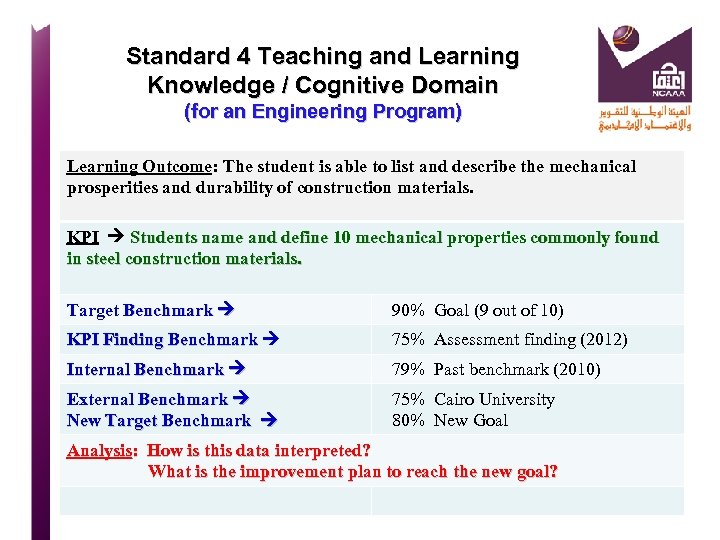 Standard 4 Teaching and Learning Knowledge / Cognitive Domain (for an Engineering Program) Learning Outcome: The student is able to list and describe the mechanical prosperities and durability of construction materials. KPI Students name and define 10 mechanical properties commonly found in steel construction materials. Target Benchmark 90% Goal (9 out of 10) KPI Finding Benchmark 75% Assessment finding (2012) Internal Benchmark 79% Past benchmark (2010) External Benchmark 75% Cairo University New Target Benchmark 80% New Goal Analysis: How is this data interpreted? What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal?
Standard 4 Teaching and Learning Knowledge / Cognitive Domain (for an Engineering Program) Learning Outcome: The student is able to list and describe the mechanical prosperities and durability of construction materials. KPI Students name and define 10 mechanical properties commonly found in steel construction materials. Target Benchmark 90% Goal (9 out of 10) KPI Finding Benchmark 75% Assessment finding (2012) Internal Benchmark 79% Past benchmark (2010) External Benchmark 75% Cairo University New Target Benchmark 80% New Goal Analysis: How is this data interpreted? What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal?
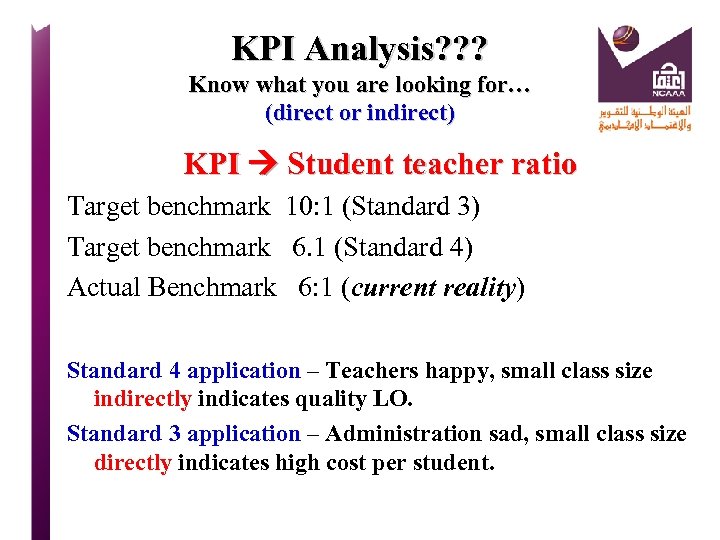 KPI Analysis? ? ? Know what you are looking for… (direct or indirect) KPI Student teacher ratio Target benchmark 10: 1 (Standard 3) Target benchmark 6. 1 (Standard 4) Actual Benchmark 6: 1 (current reality) Standard 4 application – Teachers happy, small class size indirectly indicates quality LO. Standard 3 application – Administration sad, small class size directly indicates high cost per student.
KPI Analysis? ? ? Know what you are looking for… (direct or indirect) KPI Student teacher ratio Target benchmark 10: 1 (Standard 3) Target benchmark 6. 1 (Standard 4) Actual Benchmark 6: 1 (current reality) Standard 4 application – Teachers happy, small class size indirectly indicates quality LO. Standard 3 application – Administration sad, small class size directly indicates high cost per student.
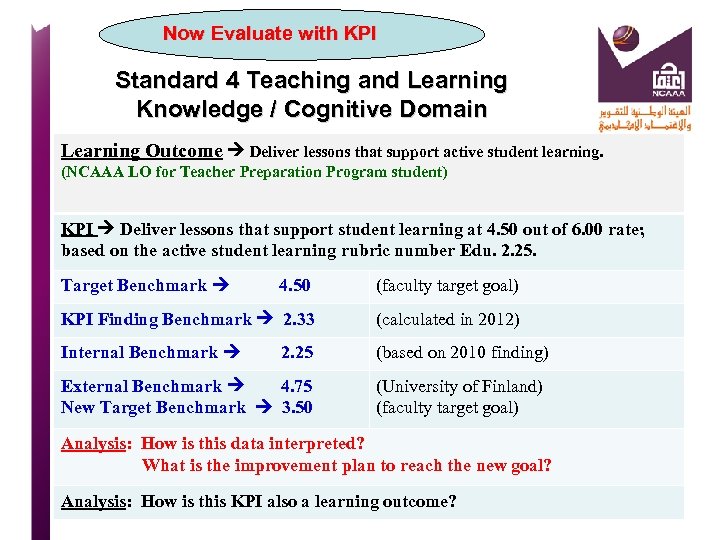 Now Evaluate with KPI Standard 4 Teaching and Learning Knowledge / Cognitive Domain Learning Outcome Deliver lessons that support active student learning. (NCAAA LO for Teacher Preparation Program student) KPI Deliver lessons that support student learning at 4. 50 out of 6. 00 rate; based on the active student learning rubric number Edu. 2. 25. Target Benchmark 4. 50 (faculty target goal) KPI Finding Benchmark 2. 33 (calculated in 2012) Internal Benchmark 2. 25 (based on 2010 finding) External Benchmark 4. 75 (University of Finland) New Target Benchmark 3. 50 (faculty target goal) Analysis: How is this data interpreted? What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal? Analysis: How is this KPI also a learning outcome?
Now Evaluate with KPI Standard 4 Teaching and Learning Knowledge / Cognitive Domain Learning Outcome Deliver lessons that support active student learning. (NCAAA LO for Teacher Preparation Program student) KPI Deliver lessons that support student learning at 4. 50 out of 6. 00 rate; based on the active student learning rubric number Edu. 2. 25. Target Benchmark 4. 50 (faculty target goal) KPI Finding Benchmark 2. 33 (calculated in 2012) Internal Benchmark 2. 25 (based on 2010 finding) External Benchmark 4. 75 (University of Finland) New Target Benchmark 3. 50 (faculty target goal) Analysis: How is this data interpreted? What is the improvement plan to reach the new goal? Analysis: How is this KPI also a learning outcome?
 Grading & Performance Rubrics What are Rubrics? A rubric is a scoring tool that explicitly represents the performance A rubric is a scoring tool expectations for an assignment or piece of work. A rubric divides the assigned work into component parts and provides clear descriptions of the characteristics of the work associated with each component, at varying levels of mastery. Rubrics can be used for a wide range of assignments: papers, Rubrics can be used projects, oral presentations, artistic performances, group projects, or qualitative assessments. Rubrics can be used as scoring or grading guides, to provide Rubrics can be used formative feedback to support and guide ongoing learning efforts, or both.
Grading & Performance Rubrics What are Rubrics? A rubric is a scoring tool that explicitly represents the performance A rubric is a scoring tool expectations for an assignment or piece of work. A rubric divides the assigned work into component parts and provides clear descriptions of the characteristics of the work associated with each component, at varying levels of mastery. Rubrics can be used for a wide range of assignments: papers, Rubrics can be used projects, oral presentations, artistic performances, group projects, or qualitative assessments. Rubrics can be used as scoring or grading guides, to provide Rubrics can be used formative feedback to support and guide ongoing learning efforts, or both.
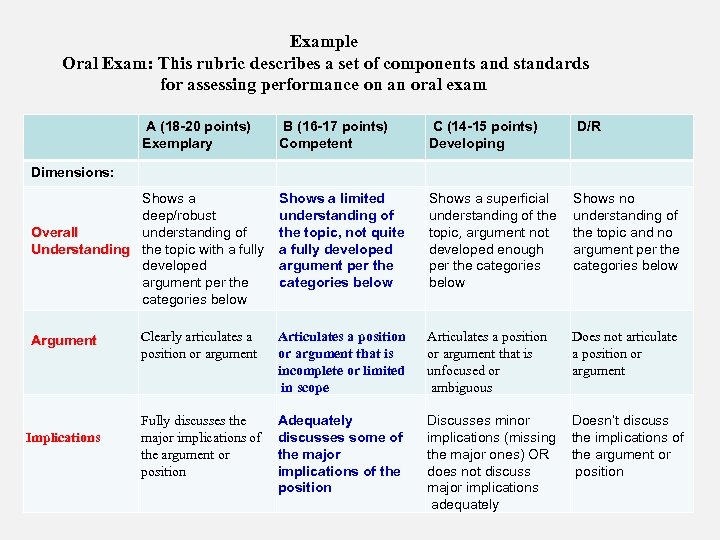 Example Oral Exam: This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing performance on an oral exam A (18 -20 points) Exemplary B (16 -17 points) Competent C (14 -15 points) Developing D/R Shows a limited understanding of the topic, not quite a fully developed argument per the categories below Shows a superficial understanding of the topic, argument not developed enough per the categories below Shows no understanding of the topic and no argument per the categories below Clearly articulates a position or argument Articulates a position or argument that is incomplete or limited in scope Articulates a position or argument that is unfocused or ambiguous Does not articulate a position or argument Fully discusses the major implications of the argument or position Adequately discusses some of the major implications of the position Discusses minor Doesn’t discuss implications (missing the implications of the major ones) OR the argument or does not discuss position major implications adequately Dimensions: Shows a deep/robust Overall understanding of Understanding the topic with a fully developed argument per the categories below Argument Implications
Example Oral Exam: This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing performance on an oral exam A (18 -20 points) Exemplary B (16 -17 points) Competent C (14 -15 points) Developing D/R Shows a limited understanding of the topic, not quite a fully developed argument per the categories below Shows a superficial understanding of the topic, argument not developed enough per the categories below Shows no understanding of the topic and no argument per the categories below Clearly articulates a position or argument Articulates a position or argument that is incomplete or limited in scope Articulates a position or argument that is unfocused or ambiguous Does not articulate a position or argument Fully discusses the major implications of the argument or position Adequately discusses some of the major implications of the position Discusses minor Doesn’t discuss implications (missing the implications of the major ones) OR the argument or does not discuss position major implications adequately Dimensions: Shows a deep/robust Overall understanding of Understanding the topic with a fully developed argument per the categories below Argument Implications
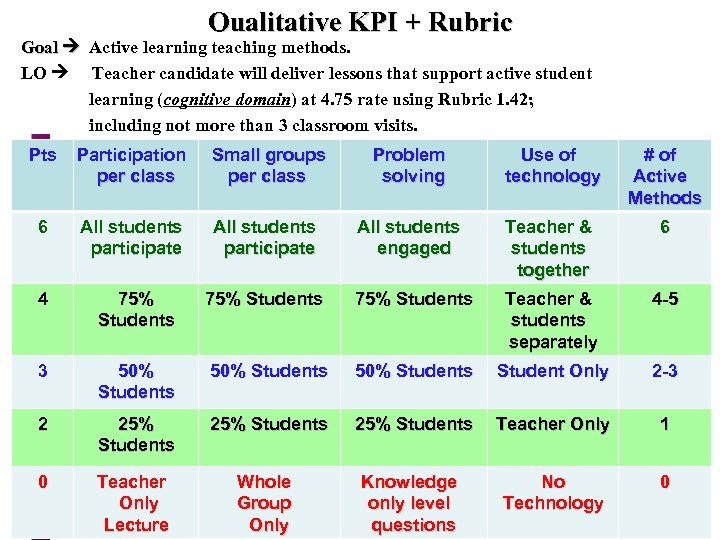 Qualitative KPI + Rubric Goal Active learning teaching methods. LO Teacher candidate will deliver lessons that support active student learning (cognitive domain) at 4. 75 rate using Rubric 1. 42; including not more than 3 classroom visits. Pts Participation Small groups Problem Use of per class solving technology # of Active Methods 6 All students participate All students engaged Teacher & students together 6 4 75% Students Teacher & students separately 4 -5 3 50% Students Student Only 2 -3 2 25% Students Teacher Only 1 0 Teacher Only Lecture Whole Group Only Knowledge only level questions No Technology 0
Qualitative KPI + Rubric Goal Active learning teaching methods. LO Teacher candidate will deliver lessons that support active student learning (cognitive domain) at 4. 75 rate using Rubric 1. 42; including not more than 3 classroom visits. Pts Participation Small groups Problem Use of per class solving technology # of Active Methods 6 All students participate All students engaged Teacher & students together 6 4 75% Students Teacher & students separately 4 -5 3 50% Students Student Only 2 -3 2 25% Students Teacher Only 1 0 Teacher Only Lecture Whole Group Only Knowledge only level questions No Technology 0
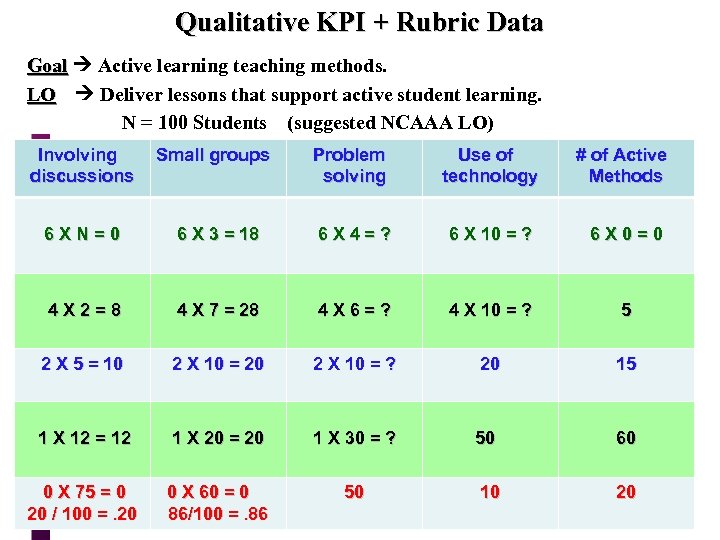 Qualitative KPI + Rubric Data Goal Active learning teaching methods. Goal LO Deliver lessons that support active student learning. LO N = 100 Students (suggested NCAAA LO) Involving discussions Small groups Problem solving Use of technology # of Active Methods 6 XN=0 6 X 3 = 18 6 X 4=? 6 X 10 = ? 6 X 0=0 4 X 2=8 4 X 7 = 28 4 X 6=? 4 X 10 = ? 5 2 X 5 = 10 2 X 10 = 20 2 X 10 = ? 20 15 1 X 12 = 12 1 X 20 = 20 1 X 30 = ? 50 60 0 X 75 = 0 20 / 100 =. 20 0 X 60 = 0 86/100 =. 86 50 10 20
Qualitative KPI + Rubric Data Goal Active learning teaching methods. Goal LO Deliver lessons that support active student learning. LO N = 100 Students (suggested NCAAA LO) Involving discussions Small groups Problem solving Use of technology # of Active Methods 6 XN=0 6 X 3 = 18 6 X 4=? 6 X 10 = ? 6 X 0=0 4 X 2=8 4 X 7 = 28 4 X 6=? 4 X 10 = ? 5 2 X 5 = 10 2 X 10 = 20 2 X 10 = ? 20 15 1 X 12 = 12 1 X 20 = 20 1 X 30 = ? 50 60 0 X 75 = 0 20 / 100 =. 20 0 X 60 = 0 86/100 =. 86 50 10 20
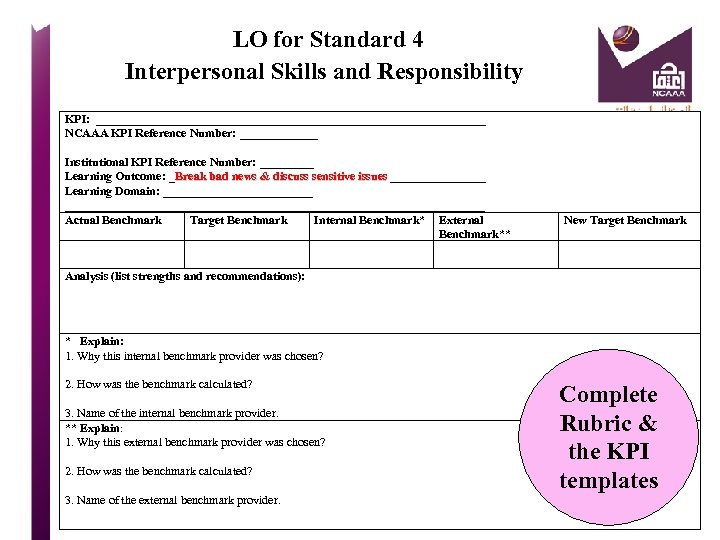 LO for Standard 4 Interpersonal Skills and Responsibility KPI: _________________________________ NCAAA KPI Reference Number: _______ Institutional KPI Reference Number: _____ Learning Outcome: _Break bad news & discuss sensitive issues ________ Learning Domain: ________________________________________________ Actual Benchmark Target Benchmark Internal Benchmark* External Benchmark** New Target Benchmark Analysis (list strengths and recommendations): * Explain: 1. Why this internal benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the internal benchmark provider. ** Explain: 1. Why this external benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the external benchmark provider. Complete Rubric & the KPI templates
LO for Standard 4 Interpersonal Skills and Responsibility KPI: _________________________________ NCAAA KPI Reference Number: _______ Institutional KPI Reference Number: _____ Learning Outcome: _Break bad news & discuss sensitive issues ________ Learning Domain: ________________________________________________ Actual Benchmark Target Benchmark Internal Benchmark* External Benchmark** New Target Benchmark Analysis (list strengths and recommendations): * Explain: 1. Why this internal benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the internal benchmark provider. ** Explain: 1. Why this external benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the external benchmark provider. Complete Rubric & the KPI templates
 Qualitative KPI + Rubric Goal KPI LO Pts 6 4 3 2 0
Qualitative KPI + Rubric Goal KPI LO Pts 6 4 3 2 0
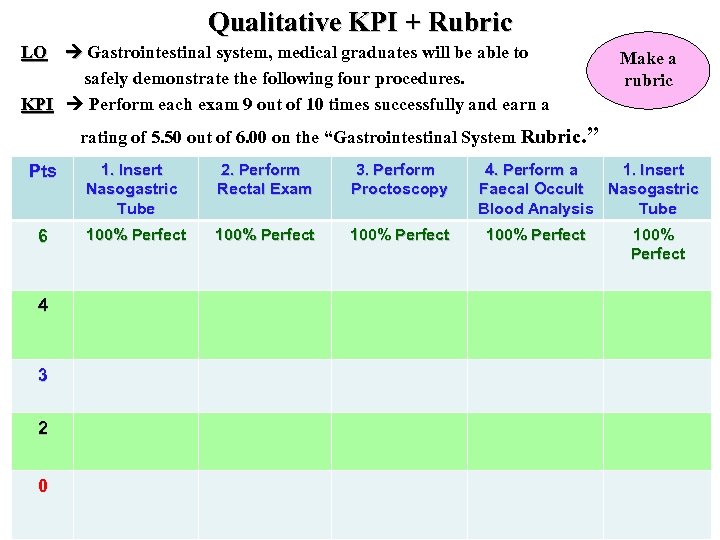 Qualitative KPI + Rubric LO Gastrointestinal system, medical graduates will be able to safely demonstrate the following four procedures. KPI Perform each exam 9 out of 10 times successfully and earn a KPI Make a rubric rating of 5. 50 out of 6. 00 on the “Gastrointestinal System Rubric. ” Pts 1. Insert Nasogastric Tube 2. Perform Rectal Exam 3. Perform Proctoscopy 6 100% Perfect 4 3 2 0 4. Perform a 1. Insert Faecal Occult Nasogastric Blood Analysis Tube 100% Perfect
Qualitative KPI + Rubric LO Gastrointestinal system, medical graduates will be able to safely demonstrate the following four procedures. KPI Perform each exam 9 out of 10 times successfully and earn a KPI Make a rubric rating of 5. 50 out of 6. 00 on the “Gastrointestinal System Rubric. ” Pts 1. Insert Nasogastric Tube 2. Perform Rectal Exam 3. Perform Proctoscopy 6 100% Perfect 4 3 2 0 4. Perform a 1. Insert Faecal Occult Nasogastric Blood Analysis Tube 100% Perfect
 Write KPI and LO for your Program. Write a KPI and LO for your course KPI: _________________________________ NCAAA KPI Reference Number: _______ Institutional KPI Reference Number: _____ Learning Outcome: _________ Learning Domain: ___________________________ Actual Benchmark Target Benchmark Internal Benchmark* External Benchmark** Analysis (list strengths and recommendations): * Explain: 1. Why this internal benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the internal benchmark provider. ** Explain: 1. Why this external benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the external benchmark provider. New Target Benchmark
Write KPI and LO for your Program. Write a KPI and LO for your course KPI: _________________________________ NCAAA KPI Reference Number: _______ Institutional KPI Reference Number: _____ Learning Outcome: _________ Learning Domain: ___________________________ Actual Benchmark Target Benchmark Internal Benchmark* External Benchmark** Analysis (list strengths and recommendations): * Explain: 1. Why this internal benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the internal benchmark provider. ** Explain: 1. Why this external benchmark provider was chosen? 2. How was the benchmark calculated? 3. Name of the external benchmark provider. New Target Benchmark
 Write a rubric for your Program or course LO Goal KPI LO Pts 6 4 3 2 0
Write a rubric for your Program or course LO Goal KPI LO Pts 6 4 3 2 0
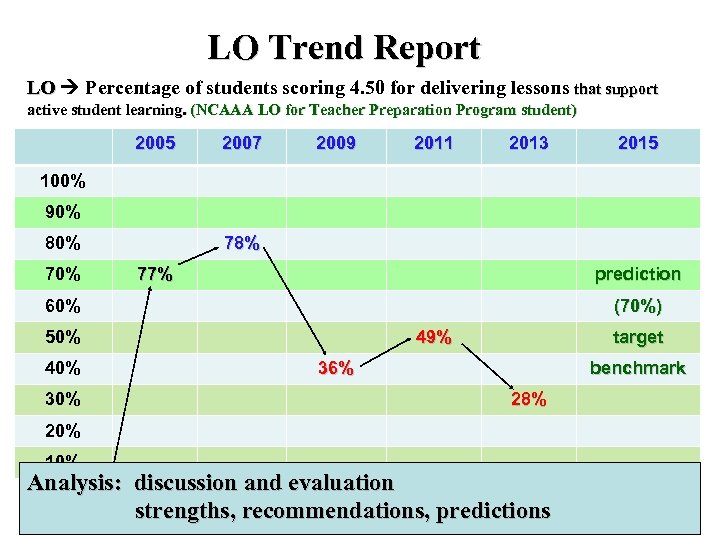 LO Trend Report LO Percentage of students scoring 4. 50 for delivering lessons that support LO active student learning. (NCAAA LO for Teacher Preparation Program student) 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 100% 90% 80% 78% 77% prediction 60% (70%) 50% 40% 30% 49% target 36% benchmark 28% 20% 10% Analysis: discussion and evaluation strengths, recommendations, predictions
LO Trend Report LO Percentage of students scoring 4. 50 for delivering lessons that support LO active student learning. (NCAAA LO for Teacher Preparation Program student) 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 100% 90% 80% 78% 77% prediction 60% (70%) 50% 40% 30% 49% target 36% benchmark 28% 20% 10% Analysis: discussion and evaluation strengths, recommendations, predictions
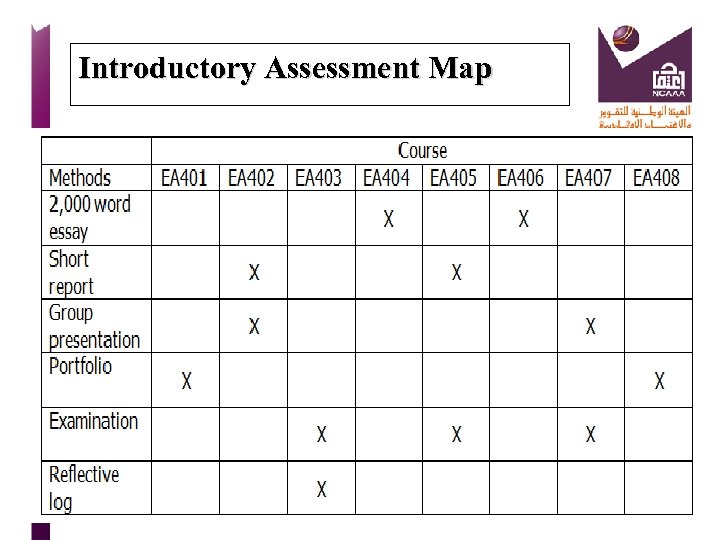 Introductory Assessment Map
Introductory Assessment Map
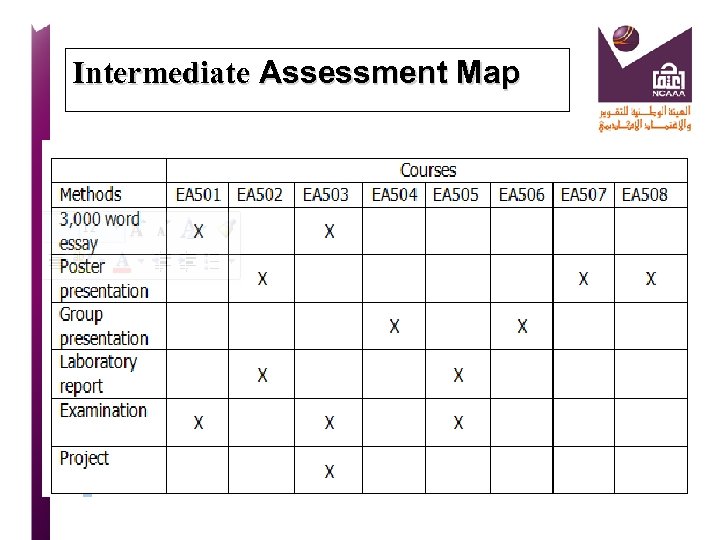 Intermediate Assessment Map
Intermediate Assessment Map
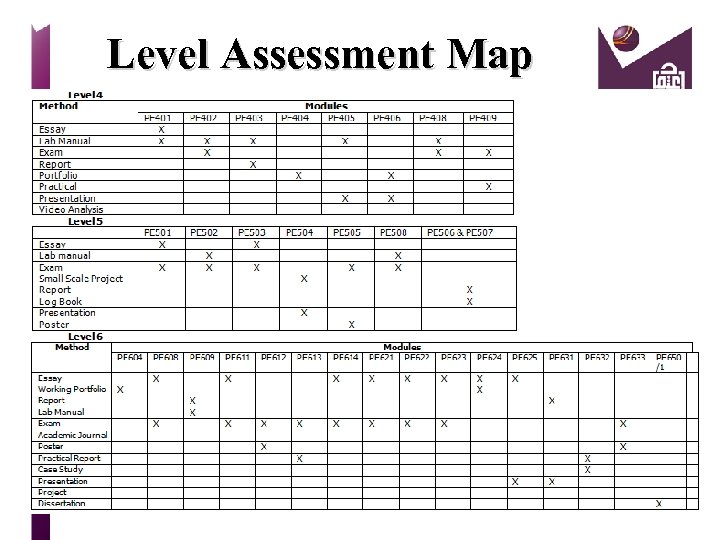 Level Assessment Map
Level Assessment Map
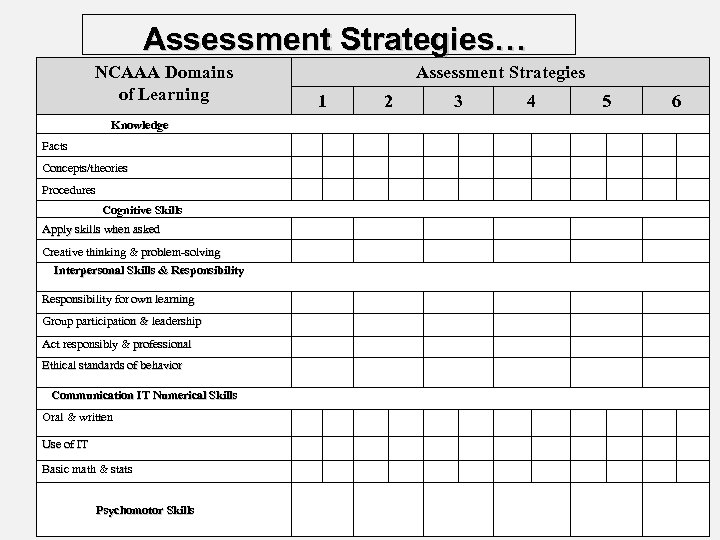 Assessment Strategies… NCAAA Domains of Learning Knowledge Facts Concepts/theories Procedures Cognitive Skills Apply skills when asked Creative thinking & problem-solving Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility for own learning Group participation & leadership Act responsibly & professional Ethical standards of behavior Communication IT Numerical Skills Oral & written Use of IT Basic math & stats Psychomotor Skills Assessment Strategies 1 2 3 4 5 6
Assessment Strategies… NCAAA Domains of Learning Knowledge Facts Concepts/theories Procedures Cognitive Skills Apply skills when asked Creative thinking & problem-solving Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility for own learning Group participation & leadership Act responsibly & professional Ethical standards of behavior Communication IT Numerical Skills Oral & written Use of IT Basic math & stats Psychomotor Skills Assessment Strategies 1 2 3 4 5 6
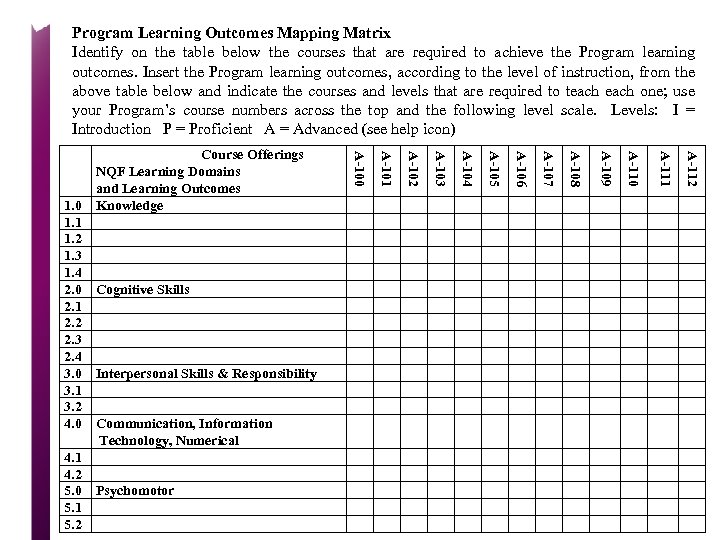 Program Learning Outcomes Mapping Matrix Identify on the table below the courses that are required to achieve the Program learning outcomes. Insert the Program learning outcomes, according to the level of instruction, from the above table below and indicate the courses and levels that are required to teach one; use your Program’s course numbers across the top and the following level scale. Levels: I = Introduction P = Proficient A = Advanced (see help icon) A-112 A-111 A-110 A-109 A-108 A-107 A-106 A-105 A-104 Psychomotor A-103 Communication, Information Technology, Numerical A-102 Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility A-101 4. 2 5. 0 5. 1 5. 2 Cognitive Skills A-100 1. 1 1. 2 1. 3 1. 4 2. 0 2. 1 2. 2 2. 3 2. 4 3. 0 3. 1 3. 2 4. 0 Course Offerings NQF Learning Domains and Learning Outcomes Knowledge
Program Learning Outcomes Mapping Matrix Identify on the table below the courses that are required to achieve the Program learning outcomes. Insert the Program learning outcomes, according to the level of instruction, from the above table below and indicate the courses and levels that are required to teach one; use your Program’s course numbers across the top and the following level scale. Levels: I = Introduction P = Proficient A = Advanced (see help icon) A-112 A-111 A-110 A-109 A-108 A-107 A-106 A-105 A-104 Psychomotor A-103 Communication, Information Technology, Numerical A-102 Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility A-101 4. 2 5. 0 5. 1 5. 2 Cognitive Skills A-100 1. 1 1. 2 1. 3 1. 4 2. 0 2. 1 2. 2 2. 3 2. 4 3. 0 3. 1 3. 2 4. 0 Course Offerings NQF Learning Domains and Learning Outcomes Knowledge
 Session 6 Common Problems Associated with Writing Learning Outcomes
Session 6 Common Problems Associated with Writing Learning Outcomes
 Common Problems: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Language is too vague or too specific for course level Use of ambiguous words and phrases There are too many learning outcomes There are too many verbs in one learning outcome Overuse of the same verb Inappropriate cognitive level Use of progression Learning outcomes are not realistic Learning outcomes that are not, or cannot be, assessed
Common Problems: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Language is too vague or too specific for course level Use of ambiguous words and phrases There are too many learning outcomes There are too many verbs in one learning outcome Overuse of the same verb Inappropriate cognitive level Use of progression Learning outcomes are not realistic Learning outcomes that are not, or cannot be, assessed
 1. Language is too vague or too specific for course level • This is where learning outcomes are either written at a broad level more suitable for a Program or where the language is too prescriptive describing actions of a student that may be achievable at the end of a specific class rather than an entire course.
1. Language is too vague or too specific for course level • This is where learning outcomes are either written at a broad level more suitable for a Program or where the language is too prescriptive describing actions of a student that may be achievable at the end of a specific class rather than an entire course.
 Examples • Example of an outcome that is too broad: Students will be able to identify and demonstrate the dynamic nature of the environment in which marketing decisions are taken. • Example of an outcome that is too specific: Students will be able to outline the functions of marketing within a financial institution.
Examples • Example of an outcome that is too broad: Students will be able to identify and demonstrate the dynamic nature of the environment in which marketing decisions are taken. • Example of an outcome that is too specific: Students will be able to outline the functions of marketing within a financial institution.
 2. Ambiguous words and phrases • This refers to the use of vague terms like: know, understand, learn, be familiar with, be exposed to, be acquainted with, be aware of, appreciate, etc. • The main problem with using these verbs or phrases is that they are not universally understood so students or another teacher may interpret them differently. • Questions to consider are: how can you be sure that the students know or understand? and how can they demonstrate that they know or understand? demonstrate
2. Ambiguous words and phrases • This refers to the use of vague terms like: know, understand, learn, be familiar with, be exposed to, be acquainted with, be aware of, appreciate, etc. • The main problem with using these verbs or phrases is that they are not universally understood so students or another teacher may interpret them differently. • Questions to consider are: how can you be sure that the students know or understand? and how can they demonstrate that they know or understand? demonstrate
 Examples • Example of an outcome with ambiguous words: Students will be able to understand the function, structure and components of the musculoskeletal system. • Suggested alternative: Students will be able to explain the function, structure and components of the musculoskeletal system.
Examples • Example of an outcome with ambiguous words: Students will be able to understand the function, structure and components of the musculoskeletal system. • Suggested alternative: Students will be able to explain the function, structure and components of the musculoskeletal system.
 3. Too many learning outcomes • It is recommended at course level to have between four and six learning outcomes. Tips: • If you have too many outcomes you may want to consider whether some of the learning outcomes could be combined (and assessed via a rubric). • You may decide that a particular outcome is more relevant to a specific class than the entire course in which case you may wish to remove it. • Use your assessment and what it is measuring to prompt you.
3. Too many learning outcomes • It is recommended at course level to have between four and six learning outcomes. Tips: • If you have too many outcomes you may want to consider whether some of the learning outcomes could be combined (and assessed via a rubric). • You may decide that a particular outcome is more relevant to a specific class than the entire course in which case you may wish to remove it. • Use your assessment and what it is measuring to prompt you.
 4. Too many verbs in one learning outcome • Too many action verbs in one learning outcome can be confusing as it may not be clear which action is the most important for the student to be required to demonstrate. • In the example: consider if the focus for this outcome is on whether students can work in groups or whether they can apply basic principles and how this outcome is, or should be, assessed.
4. Too many verbs in one learning outcome • Too many action verbs in one learning outcome can be confusing as it may not be clear which action is the most important for the student to be required to demonstrate. • In the example: consider if the focus for this outcome is on whether students can work in groups or whether they can apply basic principles and how this outcome is, or should be, assessed.
 Example • Example of outcome with too many verbs: Students will have worked in small groups and considered the application of basic principles to different industrial processes. • There may be instances, where two verbs are codependent and consequently relevant to one learning outcome as seen in the example below: § Students will be able to recognize and solve problems recognize and solve relating to the basic concepts of chemical reactions.
Example • Example of outcome with too many verbs: Students will have worked in small groups and considered the application of basic principles to different industrial processes. • There may be instances, where two verbs are codependent and consequently relevant to one learning outcome as seen in the example below: § Students will be able to recognize and solve problems recognize and solve relating to the basic concepts of chemical reactions.
 5. Overuse of the same verb • In some cases, particularly when finding an alternative for ambiguous words/phrases such as know, understand or be familiar with, there can be a tendency to find a solution for one learning outcome and repeat it for others. • In some disciplines such as math there may be a need for repetitive use of words such as ‘solve’ or solve ‘calculate’ where there is no alternative required or calculate possible.
5. Overuse of the same verb • In some cases, particularly when finding an alternative for ambiguous words/phrases such as know, understand or be familiar with, there can be a tendency to find a solution for one learning outcome and repeat it for others. • In some disciplines such as math there may be a need for repetitive use of words such as ‘solve’ or solve ‘calculate’ where there is no alternative required or calculate possible.
 6. Inappropriate cognitive level • This is where there is an over use of verbs that require students to demonstrate knowledge where they may also be required to demonstrate a deeper learning such as analysis, synthesis and evaluation. • Choose the verb based on the relevant domain of learning.
6. Inappropriate cognitive level • This is where there is an over use of verbs that require students to demonstrate knowledge where they may also be required to demonstrate a deeper learning such as analysis, synthesis and evaluation. • Choose the verb based on the relevant domain of learning.
 7. Use of progression in learning outcomes • This is where a learning outcome refers to improvement in learning or other phrases that imply progression (series, sequence, succession, string, chain, evolution, development). • Progression is difficult to measure as the student would need to demonstrate levels of learning at varying points of time. It may be best to remove the reference to progression.
7. Use of progression in learning outcomes • This is where a learning outcome refers to improvement in learning or other phrases that imply progression (series, sequence, succession, string, chain, evolution, development). • Progression is difficult to measure as the student would need to demonstrate levels of learning at varying points of time. It may be best to remove the reference to progression.
 Example • Example of progression in a learning outcome: Students will have an increased proficiency in presentation skills. • Suggested Alternative: Students will be able to demonstrate a proficiency in presentation skills.
Example • Example of progression in a learning outcome: Students will have an increased proficiency in presentation skills. • Suggested Alternative: Students will be able to demonstrate a proficiency in presentation skills.
 8. Learning outcomes that are not practical • This is where learning outcomes are not realizable due to constraints of time and/or resources. • For example a learning outcome might demand an assessment load too great for the students or for the teacher.
8. Learning outcomes that are not practical • This is where learning outcomes are not realizable due to constraints of time and/or resources. • For example a learning outcome might demand an assessment load too great for the students or for the teacher.
 9. Outcomes that are not, or cannot, be assessed • As the traditional faculty-centered approach involved writing objectives from the point of view of what the lecturer intended to deliver. • Some learning outcomes can address the delivery of content only and are not covered anywhere in the assessment of the course.
9. Outcomes that are not, or cannot, be assessed • As the traditional faculty-centered approach involved writing objectives from the point of view of what the lecturer intended to deliver. • Some learning outcomes can address the delivery of content only and are not covered anywhere in the assessment of the course.
 Useful Tips • Check that each learning outcome is addressed in some way by assessment. • Check that all elements of the assessment have been included in the set of learning outcomes.
Useful Tips • Check that each learning outcome is addressed in some way by assessment. • Check that all elements of the assessment have been included in the set of learning outcomes.
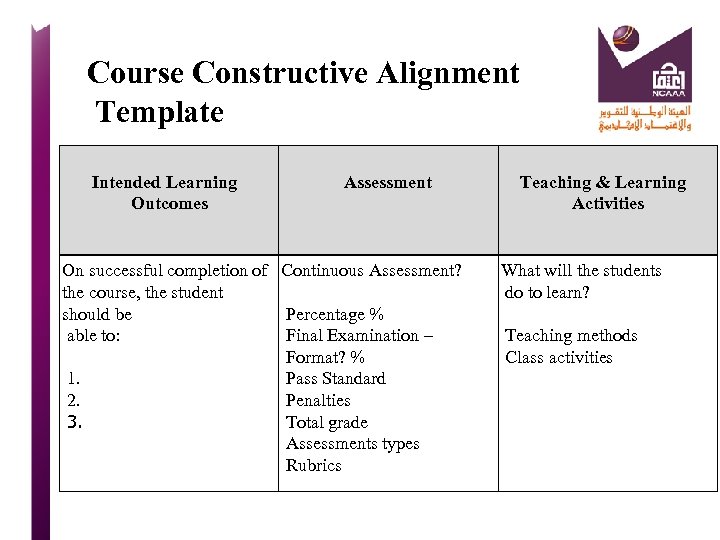 Course Constructive Alignment Template Intended Learning Outcomes Assessment On successful completion of Continuous Assessment? the course, the student should be Percentage % able to: Final Examination – Format? % 1. Pass Standard 2. Penalties Total grade 3. Assessments types Rubrics Teaching & Learning Activities What will the students do to learn? Teaching methods Class activities
Course Constructive Alignment Template Intended Learning Outcomes Assessment On successful completion of Continuous Assessment? the course, the student should be Percentage % able to: Final Examination – Format? % 1. Pass Standard 2. Penalties Total grade 3. Assessments types Rubrics Teaching & Learning Activities What will the students do to learn? Teaching methods Class activities
 Exercise Example 1: § To increase the student’s ability to visually identify white cells on a differential. § The student will identify correctly all white cells on a differential. Example 2: § The student will gain knowledge of automated chemistry tests. § The student will state the principle for each automated chemistry test listed
Exercise Example 1: § To increase the student’s ability to visually identify white cells on a differential. § The student will identify correctly all white cells on a differential. Example 2: § The student will gain knowledge of automated chemistry tests. § The student will state the principle for each automated chemistry test listed
 Exercise Example 3: § The student will be familiar with red blood cell maturation in the bone marrow. § The student will diagram the maturation of red blood cells. Example 4: § The student will understand the interpretation of hemoglobin electrophoresis patterns. § Given several electrophoresis scans, the student will correctly diagnose each normal or abnormal pattern.
Exercise Example 3: § The student will be familiar with red blood cell maturation in the bone marrow. § The student will diagram the maturation of red blood cells. Example 4: § The student will understand the interpretation of hemoglobin electrophoresis patterns. § Given several electrophoresis scans, the student will correctly diagnose each normal or abnormal pattern.
 Exercise Please identify which learning domain the following ILOs are related to: Lecture LOs (Hemolytic Anemias) • After attending the lecture, reading the assignment, and performing the tests in the laboratory, the student will: 1. Define the term hemolytic anemia. 2. Classify the major hemolytic anemias by their intrinsic or extrinsic causes.
Exercise Please identify which learning domain the following ILOs are related to: Lecture LOs (Hemolytic Anemias) • After attending the lecture, reading the assignment, and performing the tests in the laboratory, the student will: 1. Define the term hemolytic anemia. 2. Classify the major hemolytic anemias by their intrinsic or extrinsic causes.
 Exercise 3. Summarize each disease discussed in lecture including distinguishing characteristics, clinical manifestations, laboratory findings, pathology, and treatment. 4. For each disease discussed in lecture, determine the appropriate tests to resolve the problem. Include the principle and mechanism of each test in the evaluation. 5. Given a set of laboratory data and patient history, correctly diagnose the disease.
Exercise 3. Summarize each disease discussed in lecture including distinguishing characteristics, clinical manifestations, laboratory findings, pathology, and treatment. 4. For each disease discussed in lecture, determine the appropriate tests to resolve the problem. Include the principle and mechanism of each test in the evaluation. 5. Given a set of laboratory data and patient history, correctly diagnose the disease.
 One more Exercise Please read the listed LOs and identify what common problems are associated with each one and re–write it.
One more Exercise Please read the listed LOs and identify what common problems are associated with each one and re–write it.
 Conclusion Thank you for your time and reflections Dr. Gregory J. Maffet Dr. Nasser M. Sarhan
Conclusion Thank you for your time and reflections Dr. Gregory J. Maffet Dr. Nasser M. Sarhan


