63c4e4546a245cac1c44b3642075f592.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Learning Objectives Welcome to class of Export Import Practices Dr. Satyendra Singh Professor, Marketing and International Business University of Winnipeg Canada s. singh@uwinnipeg. ca http: //abem. uwinnipeg. ca www. abem. ca/conference

Learning Objectives: § Explain why firms export and problem areas of exporting § Identify the sources of export counseling and support § Discuss the meaning of the various terms of sale § Identify some sources of export financing § Describe the activities of a foreign freight forwarder § Understand the kinds of export documents required § Identify import sources

Why Export? • Reasons to export – To serve markets where the firm has no or limited production facilities – To satisfy a host government’s requirement that the local subsidiary have exports – To remain price-competitive in the home market – To test foreign markets and foreign competition inexpensively

Reasons to export? – To offset domestic market’s cyclical sales – To achieve additional sales – To extend a product’s life cycle – To respond strategically to foreign competitors – To achieve the success the firm’s management has seen others achieve – To improve the efficiency of manufacturing equipment

Reasons not to Export • Two major reasons – Preoccupation with the vast American market – Reluctance to become involved in a new, unknown and therefore risky operation • Not active in international markets due to – Lack of knowledge • Locating foreign markets • Payment and financing procedures • Export procedures

Sources of Export Counseling • Trade Information Center (TIC) – The federal government has to set this up as a first stop for information – Visit http: //www. edc. ca • International Trade Administration (ITA) – Offers a wide range of export promotion activities that include • Market Access and Compliance (MAC) • Trade Development • U. S. and Foreign Commercial Services (US&FCS)

Sources of Export Counseling • Small Business Administration (SBA) – The office of International Trade of the SBA works through • • Small Business Administration offices Score Program Small Business Development Centers for International Business Education and Research (CIBERs)

Show and Sell • Trade events to facilitate international trade – U. S. pavilions – Trade missions – Product literature center – Reverse trade missions

Export Marketing Plan • Essentially same as domestic marketing plan • Specific about – Markets to be developed – Marketing strategy for serving them – Tactics to make the strategy operational

Terms of Sale… • INCOTERMS – Universal trade terminology developed by the International Chamber of Commerce – Ex-Works • Risk passes at factory door • US equivalent: FOB (free on board)

Terms of Sale – FAS • Free alongside ship, port of call – CIF • Cost, insurance, freight, foreign port – CFR • cost and freight, foreign port – DAF • Delivered at frontier

Payment Procedures… • Payment terms offered by exporters to foreign buyers – Cash in advance • When credit standing of the buyer unknown or uncertain – Open account • When sale is made on open account – Seller assumes payment risk – Offered to reliable customers in economically stable countries

Payment Procedures… – Consignment • Goods shipped to buyer; payment made when sold • Payment risk assumed by seller – Letter of credit (L/C) • Document issued by buyer’s bank – Promise to pay seller specified amount when bank has received documents stipulated in letter of credit

Payment Procedures • Letter of credit • Confirmed L/C – Correspondent bank in seller’s country agrees to honor issuing bank’s L/C • Irrevocable L/C – Once the seller has accepted L/C, buyer cannot alter or cancel it without seller’s consent
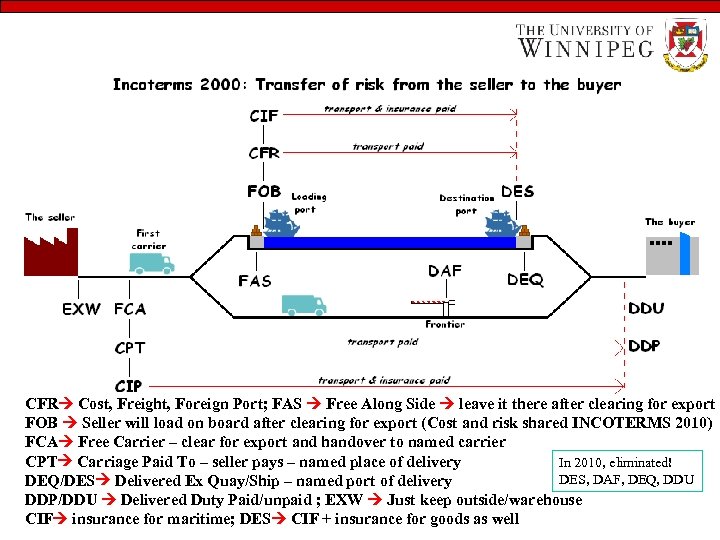
CFR Cost, Freight, Foreign Port; FAS Free Along Side leave it there after clearing for export FOB Seller will load on board after clearing for export (Cost and risk shared INCOTERMS 2010) FCA Free Carrier – clear for export and handover to named carrier CPT Carriage Paid To – seller pays – named place of delivery In 2010, eliminated! DES, DAF, DEQ, DDU DEQ/DES Delivered Ex Quay/Ship – named port of delivery DDP/DDU Delivered Duty Paid/unpaid ; EXW Just keep outside/warehouse CIF insurance for maritime; DES CIF + insurance for goods as well
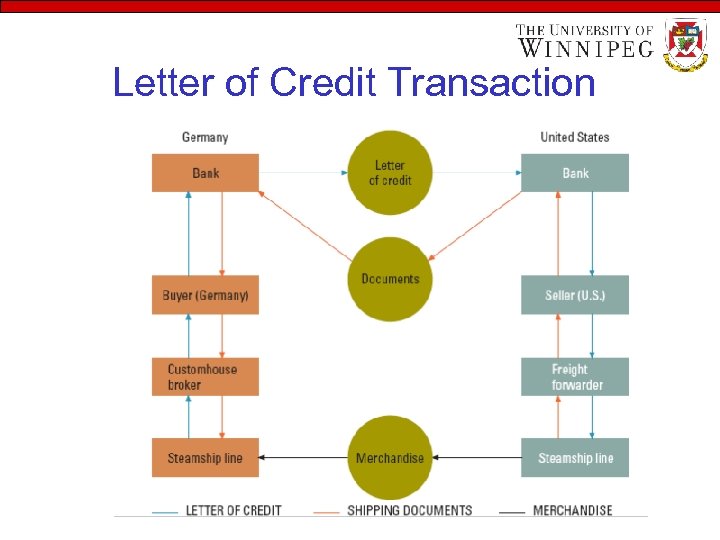
Letter of Credit Transaction

Documents • Air Waybill – A bill of lading issued by an air carrier • Pro Forma Invoice – Exporter’s formal quotation: description of the merchandise, price, delivery time, method of shipment, ports of exit and entry, and terms of sale

Export Financing… • Private Source – Commercial Banks – Banker’s acceptance • Time draft with maturity of less than 270 days that has been accepted by the bank on which the draft was drawn, thus becoming the accepting bank’s obligation; may be bought and sold at a discount in the financial markets like other commercial paper – Factoring • Discounting an account receivable without recourse

Export Financing… – Forfeiting • Purchasing without recourse an account receivable whose credit terms are longer than the 90 to 180 days usual in factoring; unlike factoring, political and transfer risks are borne by the forfeiter

Export Financing • Public Sources – Export-Import Bank (Ex-Imbank) • Principal government agency that aids American exporters by means of loans, guarantees, and insurance programs – Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) • U. S. government corporation that offers American investors in developing countries insurance against expropriation, currency inconvertibility, and damages from wars and revolutions

Other Public Incentives • Foreign Trade Zone – Duty-free area designed to facilitate trade by reducing the effect of customs restrictions • Free Trade Zone – An area designated by the government as outside its customs territory • Customs drawback – Rebate on customs duties

Export Procedures • Foreign freight forwarders act as agents for exporters – Prepare documents – Book space – Offer advice about • • Markets Regulations Transportation Packing – Supply cargo insurance
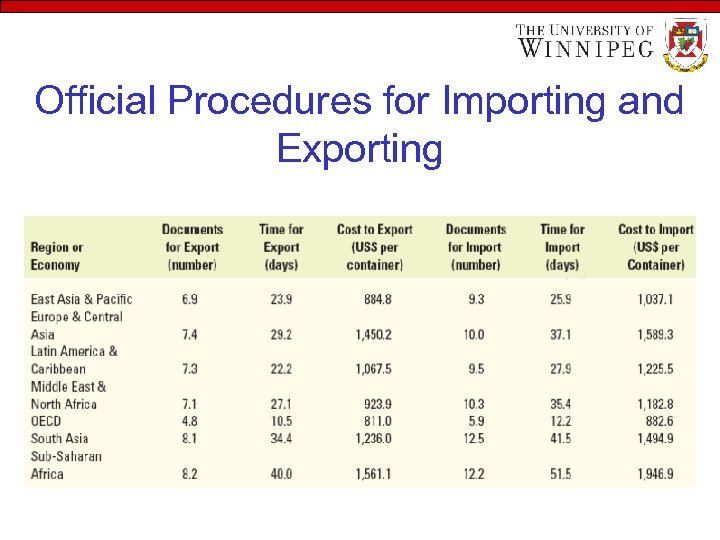
Official Procedures for Importing and Exporting

Shipping Documents… • Shipper’s Export Declaration – U. S. Department of Commerce form to control export shipments and record export statistics • Validated export license – Document issued by the U. S. government authorizing export of strategic commodity or shipment to unfriendly country • General Export License – Covers export commodities for which validated license not required; no formal application required

Shipping Documents • Export Bill of Lading – Contract of carriage between shipper and carrier: straight bill of lading is nonnegotiable; endorsed “to order” bill gives holder claim on merchandise • Insurance Certificate

Collection Documents • Commercial invoice • Include origin of goods, export packing marks, and clause stating goods will not be transshipped – Consular invoice • Purchased from the consul and prepared in local language – Certificate of origin • Issued by local Chamber of Commerce – Inspection certificate • Frequently required for grain, food, live animals

Export Shipments… § Containers § Reduce theft and handling costs § LASH (lighter aboard ship) § Barges for shallow inland waterways § RO-RO (roll on-roll off) § Can drive onto vessel § Air Freight § Can arrive in one day
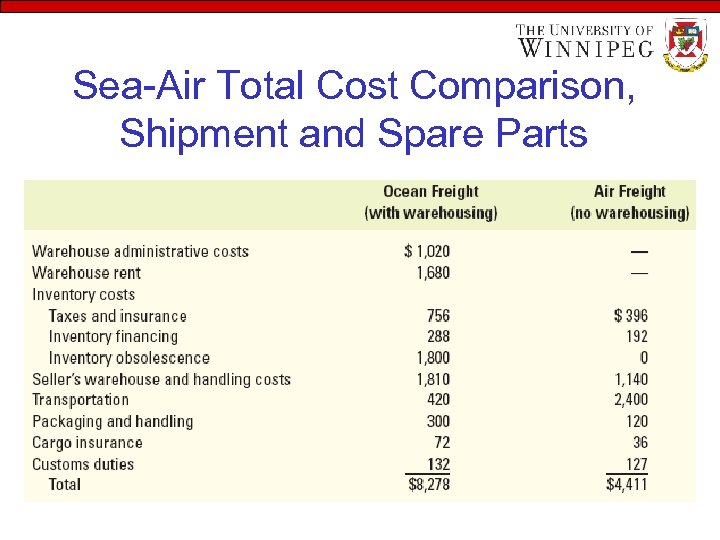
Sea-Air Total Cost Comparison, Shipment and Spare Parts

Air Freight • Total cost may decrease • Either the firm or the product may be airdependent • The market may be perishable • Competitive position may be strengthened

Importing • Ways to identify import sources – If similar imported products are already in the market, visit a retailer and examine the product label – If the product is not being imported, call the nearest consul or embassy of that country – Use the electronic bulletin boards of the World Trade Centers

Customhouse Broker • Independent business that handles import shipments • Acts as agent for importer – Customhouse broker brings goods through customs – May arrange transportation for goods after they leave customs – Need to know when imports are subject to import quotas and how much of the quota has been filled

Importing • Bonded warehouse – Area authorized by customs for storage of goods on which payment of import duties is deferred until goods are removed • Automated Commercial System (ACS) – Used to track, control, and process all commercial goods imported into U. S. • Import Duties – Importer must know how U. S. /Canada calculates import duties • The Harmonized Tariff Schedule of U. S. (HTSUSA) – American version of the Harmonized System used worldwide to classify imported products
63c4e4546a245cac1c44b3642075f592.ppt