6894a9520ee53e9b1345b5e93eae45e9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

• Learning Objective: – Today I will be able to identify what changes demand by identifying ways I have contributed to demand. • Agenda: 1. 2. 3. 4. Learning Objective Lecture: Ch. 4. 3 Changes in Demand Vocabulary Exit Slip 1
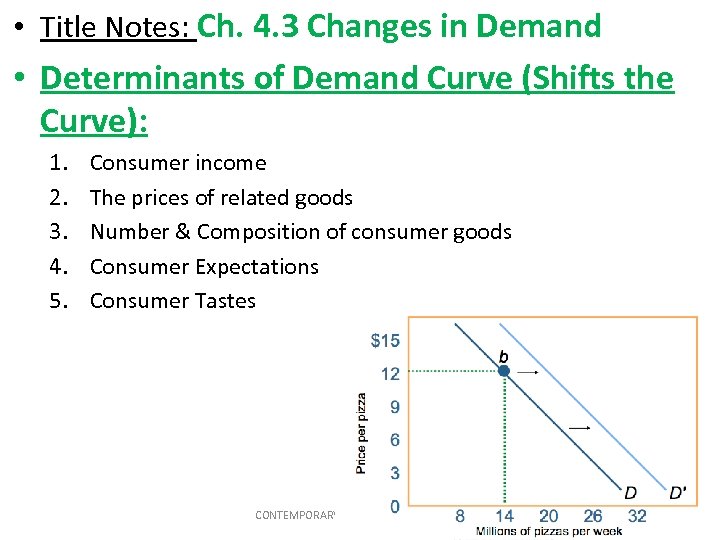
• Title Notes: Ch. 4. 3 Changes in Demand • Determinants of Demand Curve (Shifts the Curve): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Consumer income The prices of related goods Number & Composition of consumer goods Consumer Expectations Consumer Tastes CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 2

• Increase of demand= rightward shift – Consumers more willing & able • 1. Changes in consumer income – Normal goods: • Consumption increases as income increases – Inferior goods: • Consumption increases as income decreases • Less quality goods – Ex. Frozen food, used car, used clothes, etc. 3

• 2. The prices of related goods – Substitutes • Increase/decrease of prices of substitutes shifts curve. – Ex. Costco Pizza—Caeser’s Pizza – Ex. Pizza--Tacos – Complements • Increase/decrease of price of complements shifts curve with it. • Ex. Pizza & Soda—Chips & Salsa CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 4

Check for Understanding 1. Consumption of Normal Goods increases when……. . 2. What are examples of inferior goods? 3. Inferior goods are purchased when……. 4. What is a substitute for Wing Stop? – Perfect or imperfect substitute? 5. What are two different goods that complement each other? CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 5
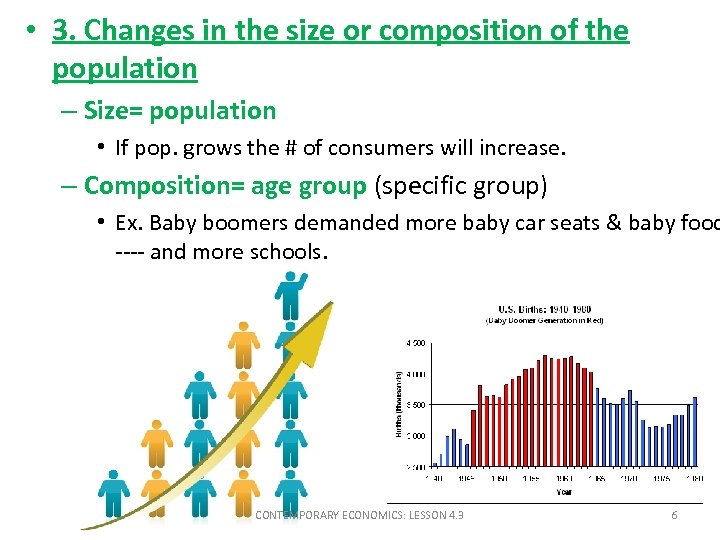
• 3. Changes in the size or composition of the population – Size= population • If pop. grows the # of consumers will increase. – Composition= age group (specific group) • Ex. Baby boomers demanded more baby car seats & baby food ---- and more schools. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 6

• 4. Changes in consumer expectations – Future Income • Ex. Work bonus, you spend more now because you expect more money later. – Future price • Ex. If Price for houses is expected to increase, then consumers will buy now (will shift the demand curve) • 5. Changes in consumer tastes – Likes & Interests: • food, music, clothing, reading, movies, TV shows – indeed, all consumer choices – are influenced by consumer tastes. • After economists have ruled other determinants, they attribute shift of curve to consumer tastes. 7
Check for Understanding 1. What are TWO expectations consumers have that shift the demand curve? ? 2. What are examples of consumers tastes? CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 8
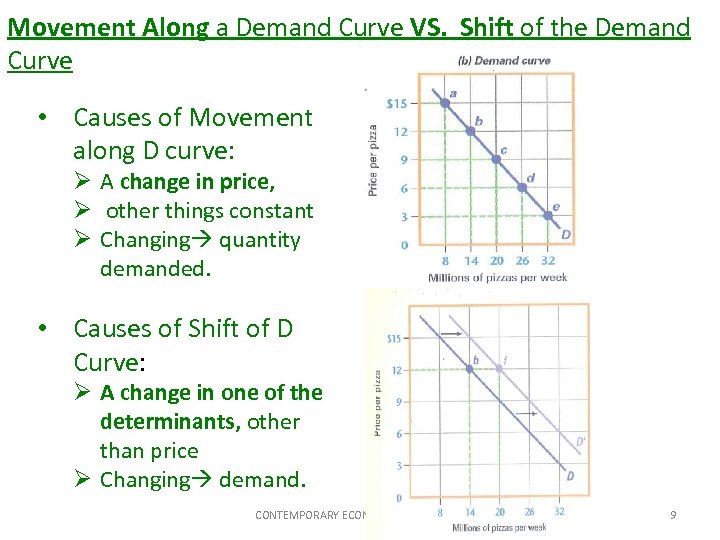
Movement Along a Demand Curve VS. Shift of the Demand Curve • Causes of Movement along D curve: Ø A change in price, Ø other things constant Ø Changing quantity demanded. • Causes of Shift of D Curve: Ø A change in one of the determinants, other than price Ø Changing demand. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 9

Checking for Understanding What are 5 determinants of demand, and how do changes in each shift the demand curve? The 5 determinants are Consumer income – a rise in income causes an outward (increase) shift of the DC The price of related goods – a rise in this causes an outward (increase) shift of the DC Number of consumers in the market – a rise in this causes an outward (increase) shift of the DC Consumer expectations - a rise in this causes an inward (decrease) shift of the DC Consumer tastes - a rise in this causes an inward (decrease) shift of the DC CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 3. 3 10
Check for Understanding 1. Curve moves along the demand curve when……. – Changing……. 2. Curve shifts the demand curve when…. . – Changing…… CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 11
Extensions of Demand Analysis • Role of time in demand – The cost of consumption has two components: • the money price of the good and (price of good) • the time price of the good (value of a good that works faster & more convenient) • The cost of waiting in line – The opportunity cost is not doing something else. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 12

Checkpoint: pg. 123 What’s the difference between the money price of the good and its time price? 1. Money price is how much a good costs. 2. Time price is the monetary value you place on having a good that works faster or is more convenient. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 3. 3 13

Exit Slip • Identify one of the determinants of demand that has applied to you. Describe the situation. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 14

Quiz Time!!!! • Quiz: • When you finish work on Vocabulary! • Work on vocabulary INDEPENDENTLY! – NO TALKING – Headphones allowed • Ch. 4 Vocabulary OR • Ch. 5 Vocabulary CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS: LESSON 4. 3 15
6894a9520ee53e9b1345b5e93eae45e9.ppt