62dae75763c8354d8284078f12ced9d9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66

Learning Based Web Query Processing Yanlei Diao Computer Science Department Hong Kong U. of Science & Technology April 12, 2000 Introduction

Outline Background v Learning Based Web Query Processing v FACT: A Prototype System v Preliminary System Evaluation v Conclusions v Demonstration Outline April 12, 2000 2

Searching the Web Want to find a piece of information on the Web? Huge Size Heterogeneity Lack of Structure Diversified User Bases Ever. Changing Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 3

Search Engines v Maintain indices, keyword input, match input keywords with indices, return relevant documents. v Problems w Large hit lists with low precision. Users find relevant documents by browsing. w URLs but not the required information are returned. Users read the pages for the required information. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 4

Web Information Retrieval v IR: Vector-space model, search and browse capabilities v Web IR: Web navigation, indexing, query languages, query-document matching, output ranking, user relevance feedback v Recent Improvement: Hierarchical classification, better presentation of results, hypertext study, metasearching. . . Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 5
Web IR for Query Processing Problems w A list of URLs or documents is returned. Users browse a lot to find information. w It asks users for precise query requirements, which is hard for casual users. w It lacks a well-defined underlying model. Vectorspace model does not convey as much as Hypertext. Large hit lists with low precision, rely on input queries Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 6

Intelligent Agents The agents learn user profiles/models from their search behaviors and employ the knowledge to predict URLs of interest to the user. v Some rely on search engines and heuristics to find targets of a specific type: e. g. papers or homepages v Some help users in an interactive mode: They learn while users are browsing. v Some adaptive agents work autonomously: They use heuristics, recommend pages of interest and take user feedback to improve. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 7

Agents for Query Processing Problems w Recommending pages of interest, but not information of interest to the user w Using vector-space model or converting HTML to text documents w Requiring a prior knowledge, such as user profiles, or using heuristics for a particular domain Not well suited for ad hoc queries Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 8

Database Approaches v The Web is a directed graph: nodes are Web pages and edges are hyperlinks between pages. v Query languages: 1 st generation combines content -based and structure-based queries. 2 nd generation accesses structure of Web objects and creates complex objects. v Wrappers and mediators: they present an integrated view of the resources. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 9

DB Approaches for Query Processing Problems w Wrapper generation is only feasible for a number of sites in a domain. The Web is growing very fast! w Web query languages require knowledge of the Web sites (content and linkage) and the language syntax. They are hard to use. Not scalable, good for Web site management but not queries on the entire Web. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 10

Our Goal A Web query processing system for any Web users that v processes ad hoc queries on HTML pages v automatically extracts succinct and precise query results ( a result may take the form of a table, a list or a paragraph). Learn the knowledge for query processing from the User! Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 11

Proposed Approach An approach with learning capabilities: v Keyword input (probably not precise) v Search engines return a URL list v During browsing, learns from users w to navigate through the web pages w to identify the required information on a web page v Processes the rest URLs automatically v Returns succinct and precise results Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 12

Unique Features v Returning succinct and precise results, i. e. segments of pages; v No a prior knowledge or preprocessing, suited for ad hoc queries; v exploiting page formatting and linkage information simultaneously, good use of rich information conveyed by HTML. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 13
Benefits from Learning Bridging the gap between keyword input and real query requirements v Capable of navigating in the neighborhoods of documents returned by search engines v Automating the processing of all possibly relevant documents in one query v Almost imperceptible to users, user-friendly v Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 14

Outline Background Learning Based Web Query Processing v FACT: A Prototype System v Preliminary System Evaluation v Conclusions v Demonstration Outline April 12, 2000 15
Modeling a Web Page v v Segment: a group of tag delimited elements, unit in query processing, e. g. paragraph, table, list, nested (atomic segments to the document), Segment Tree Attributes of a segment w content: text in the scope of the segment w description: summary of the content v Hyperlink: represented as segments to be comparable w content: URL w description: anchor text w associated with the parent segment Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 16
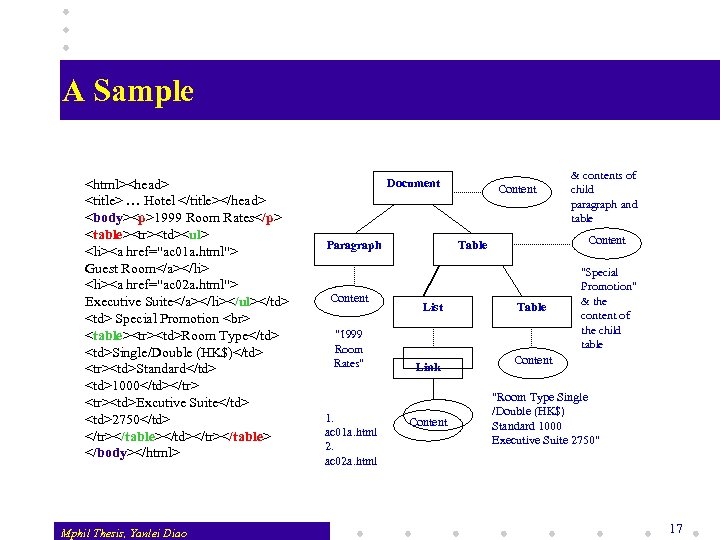
A Sample <html><head> <title> … Hotel </title></head> <body><p>1999 Room Rates</p> <table><tr><td><ul> <li><a href="ac 01 a. html"> Guest Room</a></li> <li><a href="ac 02 a. html"> Executive Suite</a></li></ul></td> <td> Special Promotion <table><tr><td>Room Type</td> <td>Single/Double (HK$)</td> <tr><td>Standard</td> <td>1000</td></tr> <tr><td>Excutive Suite</td> <td>2750</td> </tr></table></td></tr></table> </body></html> Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao Document Paragraph Content "1999 Room Rates" 1. ac 01 a. html 2. ac 02 a. html Content Table List Link Content & contents of child paragraph and table Table "Special Promotion" & the content of the child table Content "Room Type Single /Double (HK$) Standard 1000 Executive Suite 2750" 17
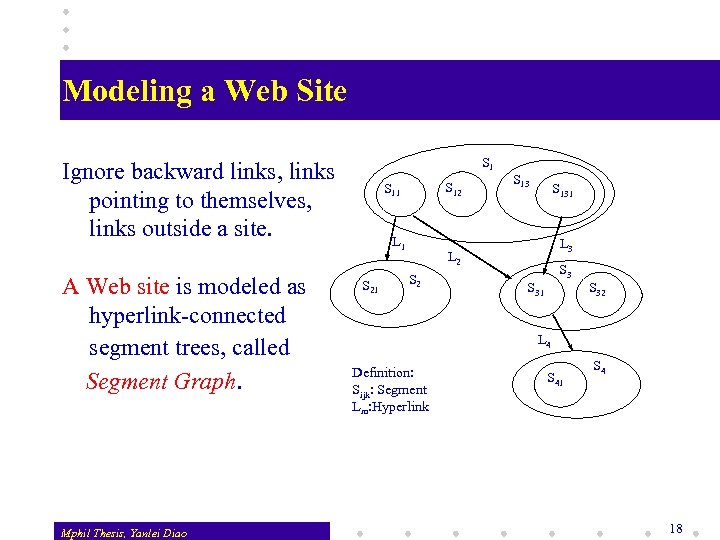
Modeling a Web Site S 1 Ignore backward links, links pointing to themselves, links outside a site. A Web site is modeled as hyperlink-connected segment trees, called Segment Graph. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao S 12 S 11 L 1 S 21 S 131 L 3 L 2 S 3 S 31 S 32 L 4 Definition: Sijk: Segment Lm: Hyperlink S 41 S 4 18

Knowledge for the Locating Task The locating task is to find a segment in the Segment Graph of a site as the query result. 1) Exhaustive search simplifies it, but is impractical. 2) Navigation in the graph should terminate if a segment answers the query well enough or conclusion of irrelevancy can be drawn. A decision of following a link or choosing a segment should be made on each page. Segments and links on a page should be comparable! Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 19

Two Types of Knowledge A link conveys description of the pointed page while a queried segment contains both description and the result itself. Segments and links on a page are not comparable by content! Two types of knowledge are needed! v One only concerns descriptive information and helps find the navigational path. v The other checks if a segment meets query requirements on both descriptive information and the result. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 20

Navigation Knowledge concerns descriptive information and helps find the navigational path v a set of (term, weight) pairs w Term: a selected word f the description of segments and links on the navigational path w Weight: indicating the importance of the term in leading to the queried segment v Learning April 12, 2000 21
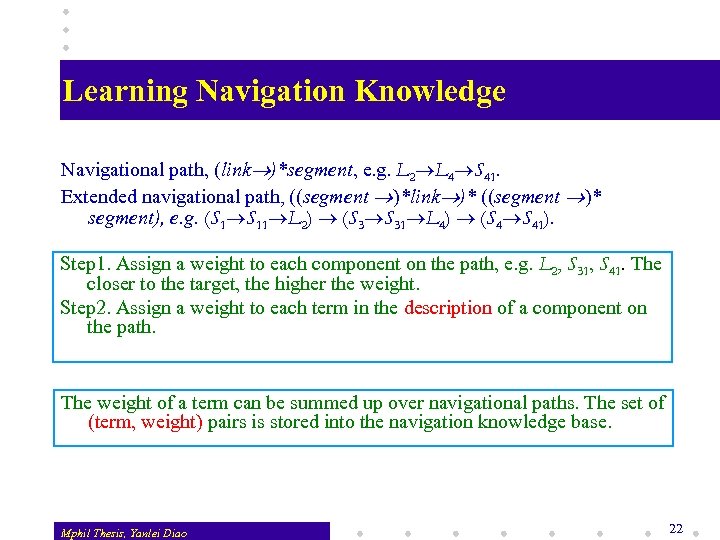
Learning Navigation Knowledge Navigational path, (link )*segment, e. g. L 2 L 4 S 41. Extended navigational path, ((segment )*link )* ((segment )* segment), e. g. (S 1 S 11 L 2) (S 3 S 31 L 4) (S 4 S 41). Step 1. Assign a weight to each component on the path, e. g. L 2, S 31, S 41. The closer to the target, the higher the weight. Step 2. Assign a weight to each term in the description of a component on the path. The weight of a term can be summed up over navigational paths. The set of (term, weight) pairs is stored into the navigation knowledge base. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 22
Classification knowledge Checks if a segment meets query requirements on both descriptive information and the result. v Cast in the Bayesian learning framework. v v Set of triples: (feature, NP, NN) w Feature: word, integer, real, symbol, …, date, time, email address, …, contained in a segment w NP: #occurrences of the feature in positive samples w NN: #occurrences of the feature in negative samples Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 23
Learning Classification knowledge The queried segment is a positive sample. All other segments on the same page are negative samples. The content of each segment is parsed into a set of features, either simple and complex types. Count NP and NN accumulatively for each feature over all samples. Store all triples (feature, NP, NN) into the classification knowledge base. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 24

Query Processing Using Learned Knowledge v v After a Web page is retrieved, the segment graph is built For each segment and link, a score is computed by applying the navigation knowledge (Apply. Navigation). Segments/links are sorted on the score w If a link has the highest score, the system navigates through the link w If a segment has the highest score, all segments on the page are checked to see if there is a queried segment The process is repeated until either a segment is found or conclusion can be made that the site does not contain queried information. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 25
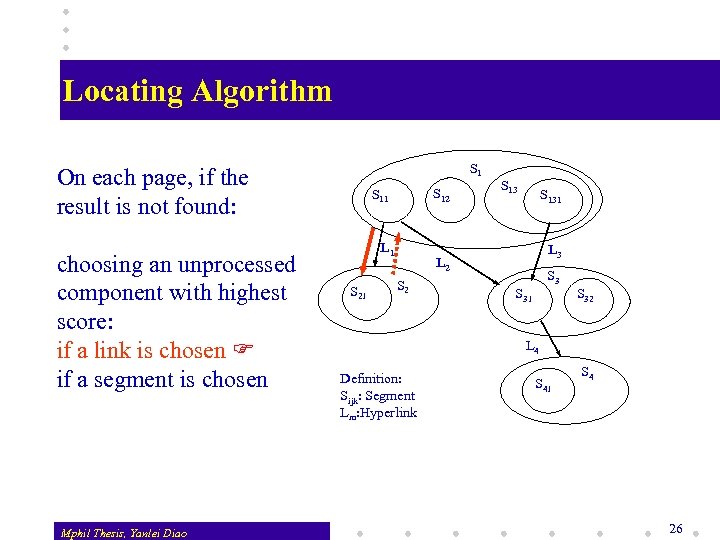
Locating Algorithm S 1 On each page, if the result is not found: choosing an unprocessed component with highest score: if a link is chosen if a segment is chosen Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao S 12 S 11 L 1 S 21 S 131 L 3 L 2 S 3 S 31 S 32 L 4 Definition: Sijk: Segment Lm: Hyperlink S 41 S 4 26
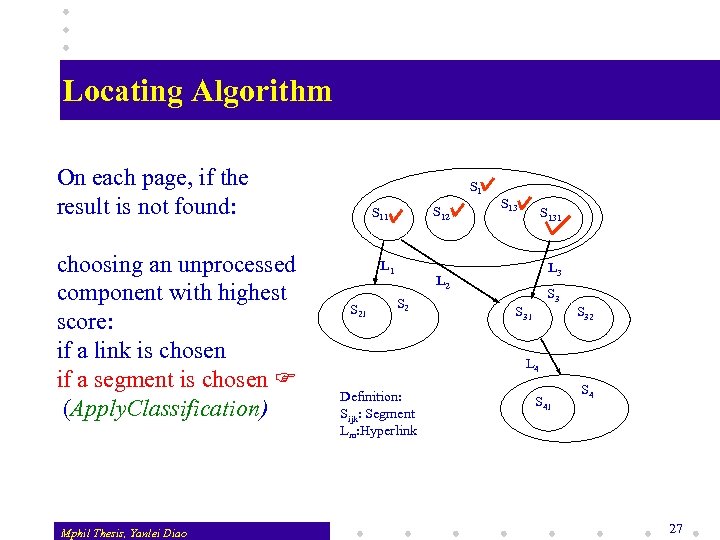
Locating Algorithm On each page, if the result is not found: choosing an unprocessed component with highest score: if a link is chosen if a segment is chosen (Apply. Classification) Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao S 12 S 11 L 1 S 21 S 131 L 3 L 2 S 3 S 31 S 32 L 4 Definition: Sijk: Segment Lm: Hyperlink S 41 S 4 27

Applying Learned Knowledge v Application of Navigation Knowledge: w extracts terms in the description of a link/segment w reads the weights of the terms and assigns a score to the link/segment by a certain function (max currently) w sorts all links and segments by their scores v Application of Classification Knowledge: w computes the confidence C to classify a segment as the queried result w chooses the segment on a page with the largest C. If the largest C is over a threshold, returns the segment Locating April 12, 2000 28
forward Hotel 1 3 Hotel 2 User browses it! Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao done 29
User clicks here! Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 30
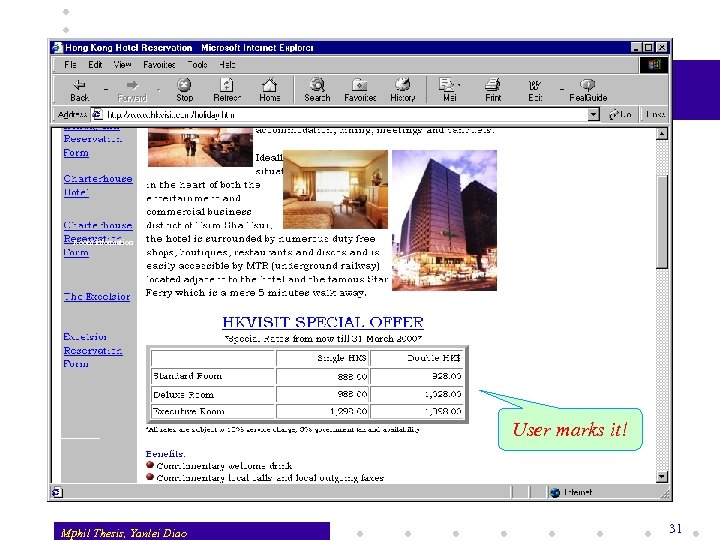
Room information User marks it! Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 31
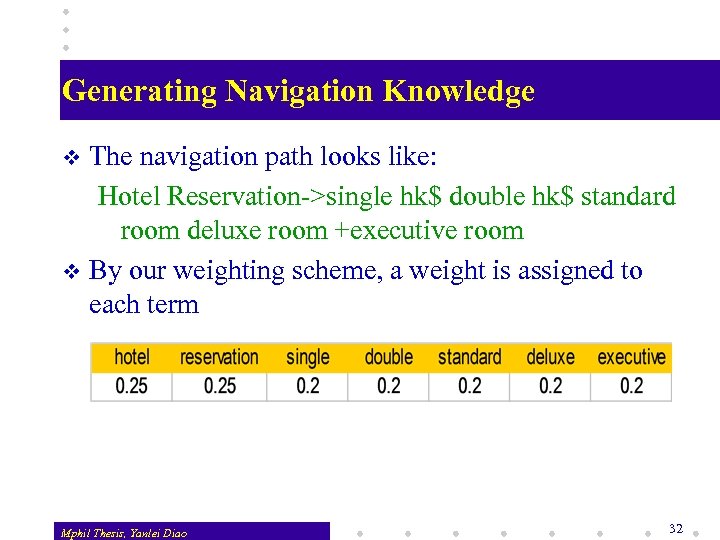
Generating Navigation Knowledge The navigation path looks like: Hotel Reservation->single hk$ double hk$ standard room deluxe room +executive room v By our weighting scheme, a weight is assigned to each term v Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 32
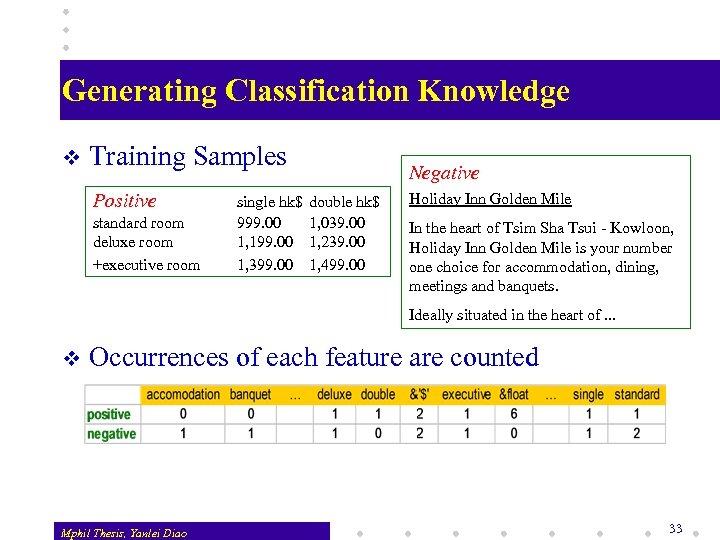
Generating Classification Knowledge v Training Samples Positive standard room deluxe room +executive room single hk$ 999. 00 1, 199. 00 1, 399. 00 Negative double hk$ 1, 039. 00 1, 239. 00 1, 499. 00 Holiday Inn Golden Mile In the heart of Tsim Sha Tsui - Kowloon, Holiday Inn Golden Mile is your number one choice for accommodation, dining, meetings and banquets. Ideally situated in the heart of. . . v Occurrences of each feature are counted Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 33
back Fact starts here! Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 34
Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 35

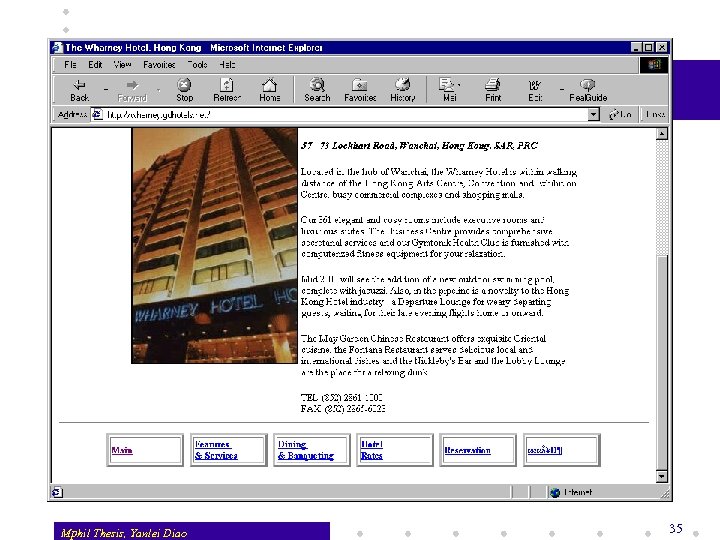
Applying Navigation Knowledge The page contains Links Paragraph 57 - 73 Lockhart Road, Wanchai, Hong Kong, SAR, PRC Main Paragraph Features & Services Located in the hub of Wanchai, the Wharney Hotel is within walking distance of the Hong Kong Arts Centre, Convention and Exhibition Centre, busy commercial complexes and shopping malls. Dining and Banqueting . . . Paragraph Reservation TEL: (852) 2861 -1000 FAX: (852) 2865 -6023 Hotel Rates. . . Navigation knowledge shows Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 36
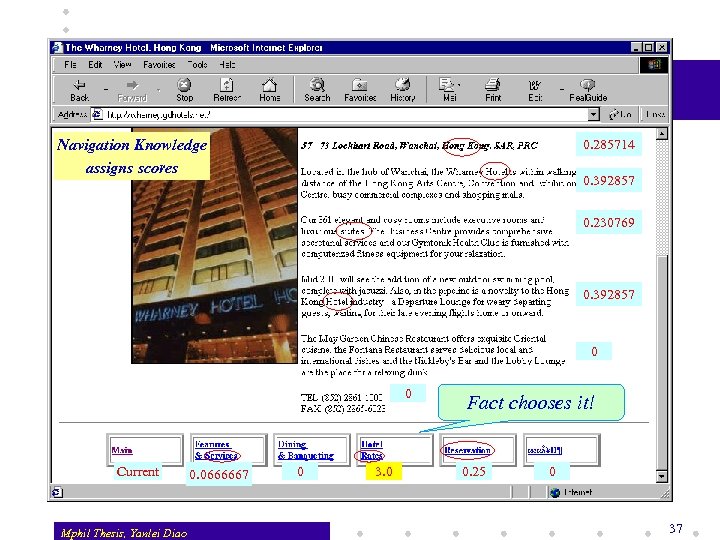
Navigation Knowledge assigns scores 0. 285714 0. 392857 0. 230769 0. 392857 0 0 Current Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 0. 0666667 0 3. 0 Fact chooses it! 0. 25 0 37
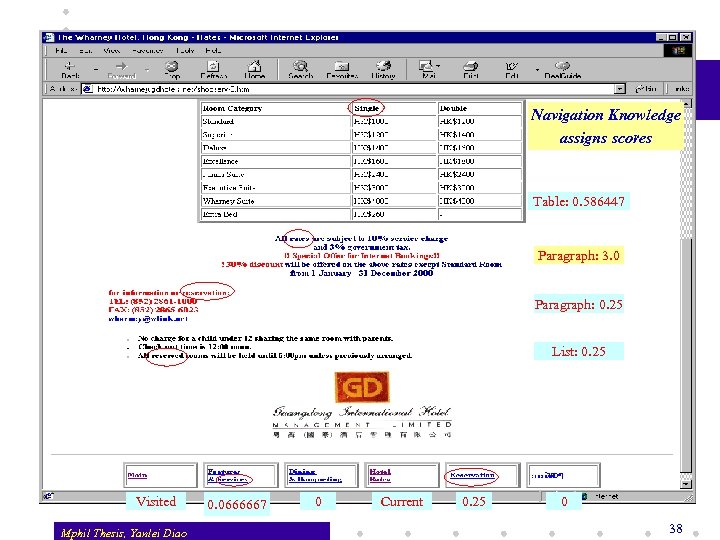
Navigation Knowledge assigns scores Table: 0. 586447 Paragraph: 3. 0 Paragraph: 0. 25 List: 0. 25 Visited Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 0. 0666667 0 Current 0. 25 0 38
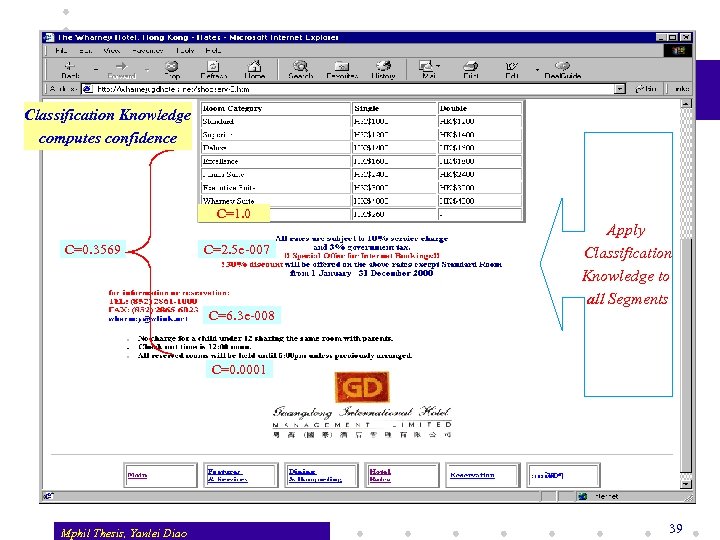
Classification Knowledge computes confidence C=1. 0 C=0. 3569 C=2. 5 e-007 C=6. 3 e-008 Apply Classification Knowledge to all Segments C=0. 0001 Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 39
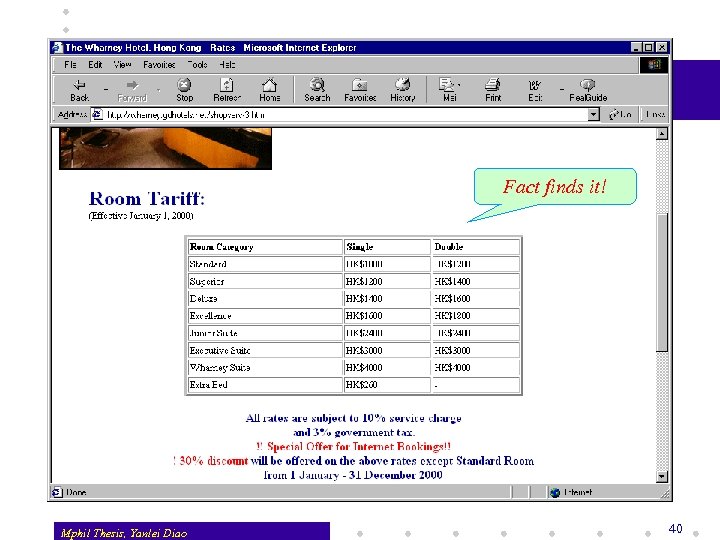
Fact finds it! Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 40

Outline Background v Learning Based Web Query Processing FACT: A Prototype System v Preliminary System Evaluation v Conclusions v Demonstration v Outline April 12, 2000 41

A Query Processing System A learning based query processing system: v User Interface: accepts user queries, presents query results, a browser capable of capturing user actions v Query Analyzer: analyzes and transforms user queries v Session Controller: coordinates learning and locating v v Learner: generates knowledge from captured user actions Locator: applies knowledge and locates query results Retriever & Parser: retrieves pages and parses to trees v Knowledge Base: stores learned knowledge v System April 12, 2000 42
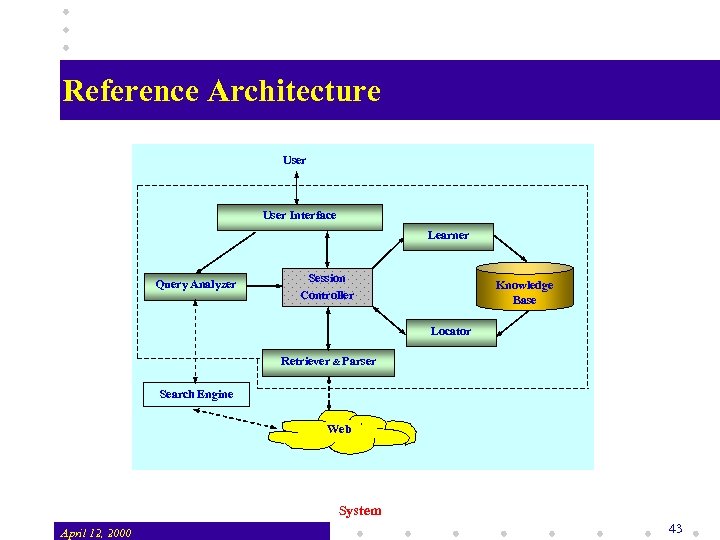
Reference Architecture User Interface Learner Query Analyzer Session Controller Knowledge Base Locator Retriever & Parser Search Engine Web System April 12, 2000 43

A Query Session Learning Process Scripts Browser User Actions URLs Session Controller Result Buffer Query results Learner Training Segment Strategy Graph Knowledge Base Checking Query Result Presenter Locator Locating Process System April 12, 2000 44

Training Strategies v v v Sequential w First n sites: user browses and system learns w Next N-n sites: system processes Random w Randomly choose n sites: user browses and system learns w the system processes the rest Interleaved w First n 0 sites, user browses and system learns w Next n - n 0 site, system makes decision. For incorrect ones, user browses and system re-learns w Next N-n sites: system processes Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 45

Outline Background v Learning Based Web Query Processing v FACT: A Prototype System Preliminary System Evaluation v Conclusions v Demonstration v Outline April 12, 2000 46

System Evaluation System Capabilities v Performance v w Effectiveness: precision, recall, correctness w Efficiency: in a site, how many pages the system visits to find a result or to recognize the irrelevancy w Training efficiency: how many training samples are needed v Key Issues w Effectiveness of the knowledge w Effectiveness of training strategies v Tests on A Range of Queries Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 47
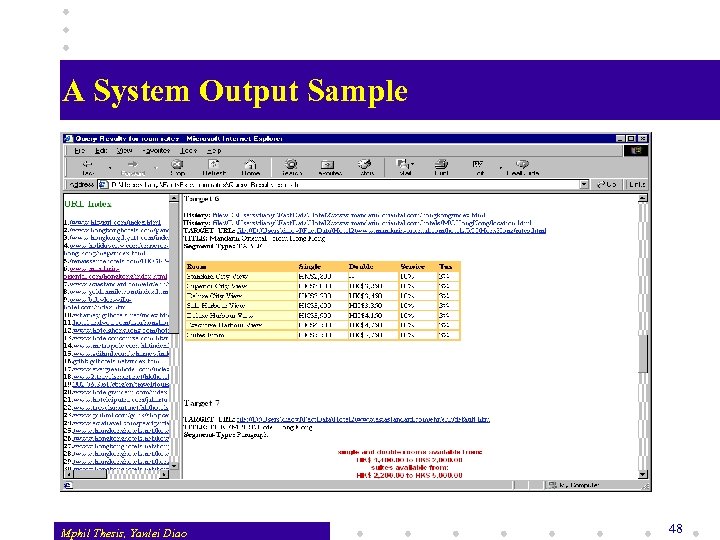
A System Output Sample Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 48

System Capabilities v The system returns segments of the Web pages v The segments may not contain any input keyword but meet the requirement of room rates. The system learned the query requirement from the user! v Segments can be from pages whose URLs are not directly returned by Yahoo!. The system learned how to follow the hyperlinks to the queried segment! Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 49
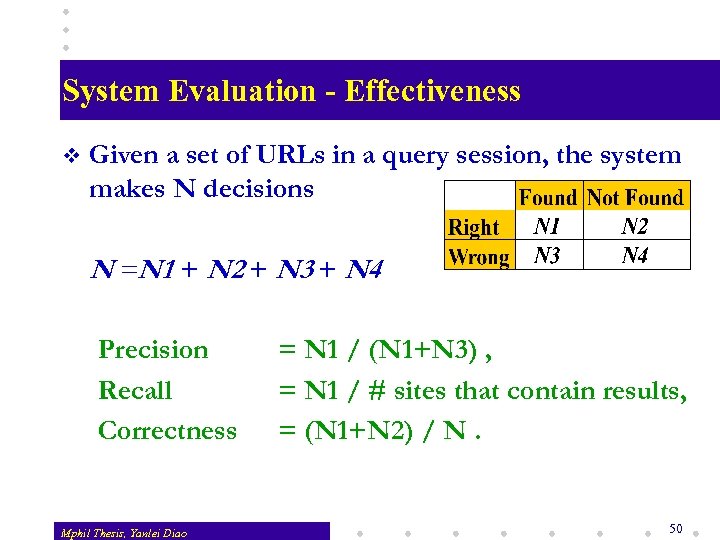
System Evaluation - Effectiveness v Given a set of URLs in a query session, the system makes N decisions N =N 1 + N 2 + N 3 + N 4 Precision Recall Correctness Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao = N 1 / (N 1+N 3) , = N 1 / # sites that contain results, = (N 1+N 2) / N. 50

System Evaluation - Efficiency v How efficiently the system finds a queried segment in a site? Levelof a Queried Segment thelength theshortest = of path to find it Absolute Path length = # Visited pages, Relative Path Length = # Visited pages / Level of the Queried Segment. Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 51
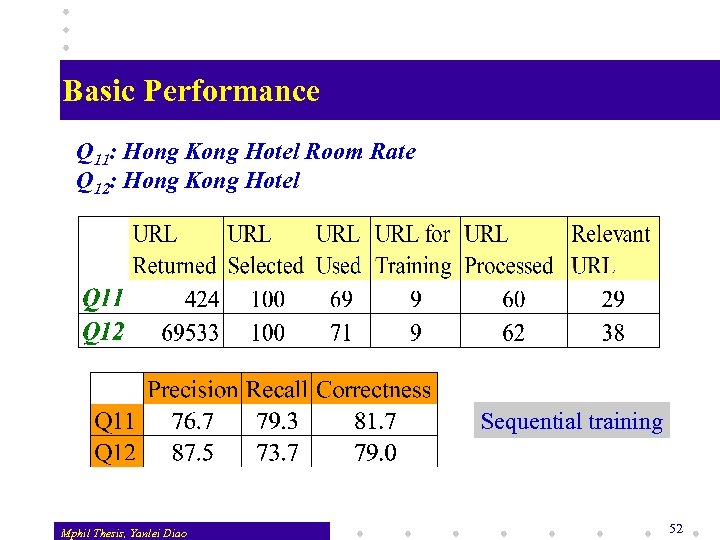
Basic Performance Q 11: Hong Kong Hotel Room Rate Q 12: Hong Kong Hotel Sequential training Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 52
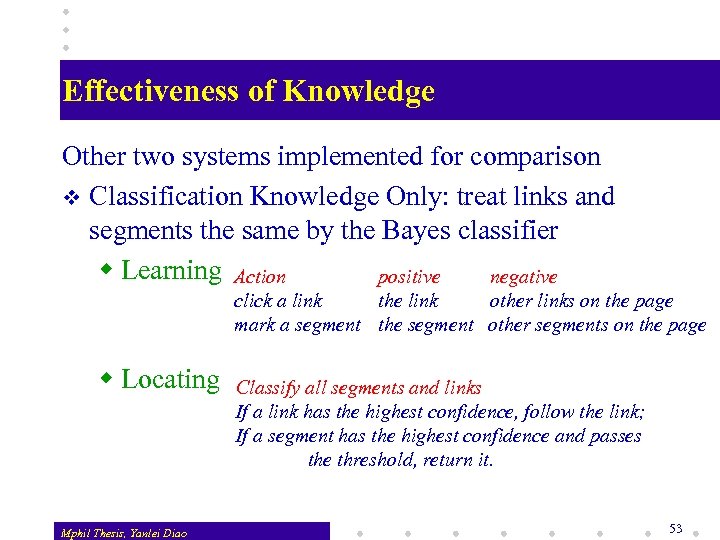
Effectiveness of Knowledge Other two systems implemented for comparison v Classification Knowledge Only: treat links and segments the same by the Bayes classifier w Learning Action positive negative click a link the link other links on the page mark a segment the segment other segments on the page w Locating Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao Classify all segments and links If a link has the highest confidence, follow the link; If a segment has the highest confidence and passes the threshold, return it. 53

Effectiveness of Knowledge v Navigation Knowledge Only: only checks the descriptive information of links and segments w Learning Navigational path Navigation Knowledge w Locating Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao Assigns scores to all links and segments using navigation knowledge If a link has the highest score, follow the link; If a segment has the highest score, return it. 54
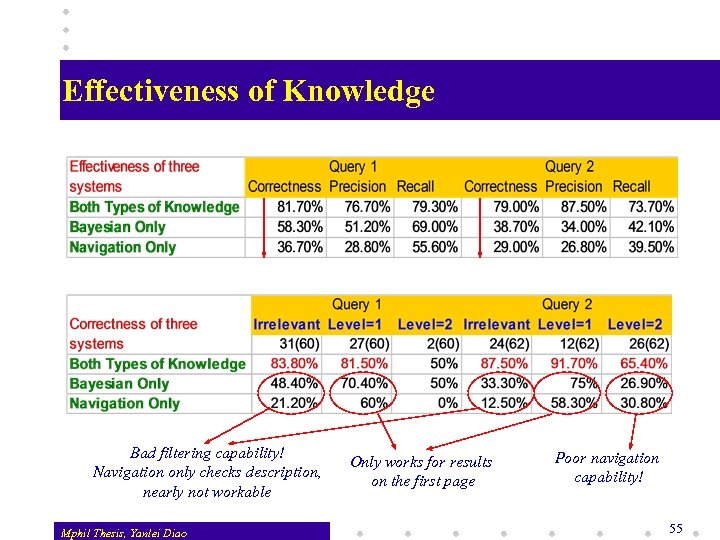
Effectiveness of Knowledge Bad filtering capability! Navigation only checks description, nearly not workable Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao Only works for results on the first page Poor navigation capability! 55
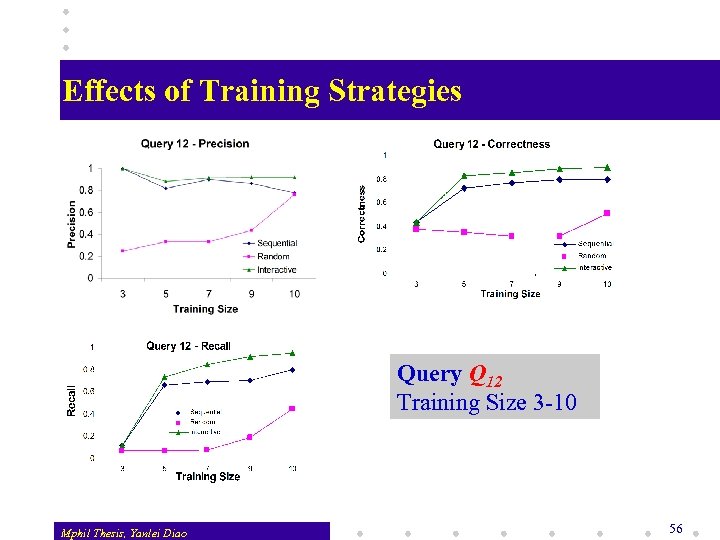
Effects of Training Strategies Query Q 12 Training Size 3 -10 Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 56

Effects of Training Strategies Random training performs badly, low in recall v As the training size increases, interleaved training outperforms sequential training v Best accuracy reaches or exceeds 90% in all metrics when the interleaved training strategy is used v Enlarging the training size for random and sequential training is not effective v Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 57
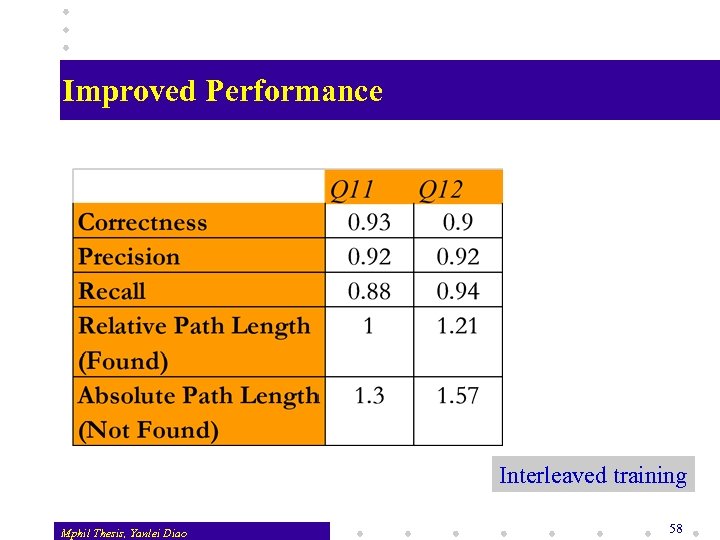
Improved Performance Interleaved training Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 58

A Range of Queries Hotel room rates: targets at prices, easy to identify v Admission requirements on graduate student: includes v items such as degree, GPA, GRE, etc. that are not easy to specify in keywords but easy to show by marking v Data Mining Researcher: concept, subjective, evidence including research interests, projects, professional activity, etc Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 59
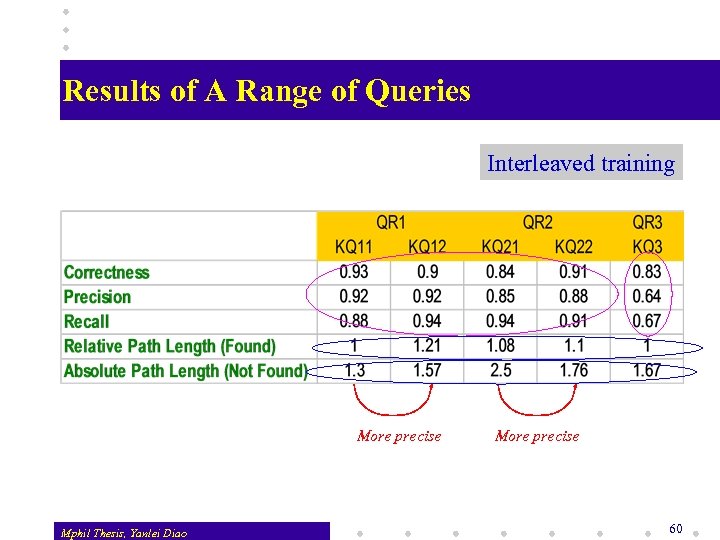
Results of A Range of Queries Interleaved training More precise Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao More precise 60
Performance for the Queries v Effectiveness w first 4 queries: accuracy is 80% to above 90% w the last query: still capable of filtering out irrelevant sites v Efficiency w relative path length to locate a queried segment is close to 1 w absolute path length to conclude irrelevancy is no more than 2. 5 pages. v The performance is not affected much by how precise the keyword query is. The system learns query requirements Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 61

Outline Background v Learning Based Web Query Processing v FACT: A Prototype System v Preliminary System Evaluation Conclusions v Demonstration v Outline April 12, 2000 62

Conclusions Proposed and implemented learning based Web query processing with the following features w Returning succinct results: segments of pages; w No a prior knowledge or preprocessing, suited for ad hoc queries; w exploiting page formatting and linkage information simultaneously. v The preliminary results are promising v Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 63
Future Work Better segmentation for HTML documents v Better knowledge, key factor that affects system performance w other weighting schemes for navigation knowledge w other implementation of classification knowledge v More system evaluation v Dynamic web pages v Future Work April 12, 2000 64

Outline Background v Learning Based Web Query Processing v FACT: A Prototype System v Preliminary System Evaluation v Conclusions Demonstration v Outline April 12, 2000 65

Demonstration Mphil Thesis, Yanlei Diao 66
62dae75763c8354d8284078f12ced9d9.ppt