e7c29741d1dd8f21992ec6ea1078af2a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release

Overview • What is Lean Six Sigma? • What can Lean Six Sigma do? • How to get started Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 2
Paths to Cost Reduction • • Cut services Reduce labor (lay-off) Contract work out Eliminate product features • Remove roadblocks so your employees can produce • Assign resources to bottlenecks • Maximize internal capabilities • Focus on what the customer wants to buy Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 3
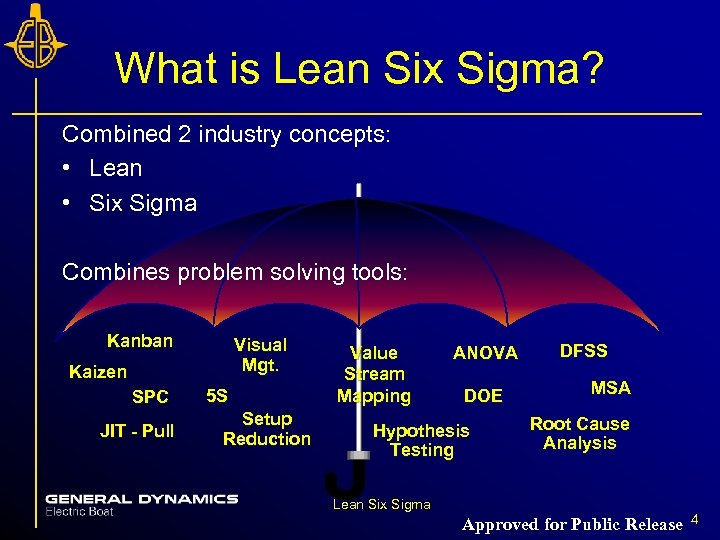
What is Lean Six Sigma? Combined 2 industry concepts: • Lean • Six Sigma Combines problem solving tools: Kanban Visual Mgt. Kaizen SPC JIT - Pull 5 S Setup Reduction Value Stream Mapping ANOVA DOE Hypothesis Testing DFSS MSA Root Cause Analysis Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 4

Lean • Focus on what is of VALUE to the customer • Separate non-value added from value added – Map the actions required to produce (value stream) – Eliminate activities that do not move the product closer to its final form • Make the remaining value added activities flow smoothly • Produce only what customers need (pull) • Continuous improvement Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 5

Which is the better airline ticket? Traveling to Groton, CT Ticket A • $500 round trip • 6 hours • 3 layovers • Arriving in NYC Ticket B • $650 round trip • 3 hours • 1 layover • Arriving in Groton/New London What does value mean to you? Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 6

Lean Philosophy Value – More to value than just cost – “Defined by the ultimate customer” – Womack • Voice of the Customer (VOC) – Expressed in terms of • A specific product • A function or capability – Questions • What does the customer want to buy? • What would they pay extra for? Focus on what is of VALUE to the customer Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 7

Types of Activities Value-Added – Brings product closer to it’s final form – Changes the form, fit or function – An activity the customer is willing to pay for Non-Value-Added – Does not contribute to bringing the product to it’s final form – Doesn’t improve the form, fit, or function of the product or service on the first pass through the process. – An activity the customer is not willing to pay for – Waste Separate non value added from value added Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 8

8 Types of Waste UNDER-UTILIZED SKILLS Steps are wasteful, people are valuable Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 9
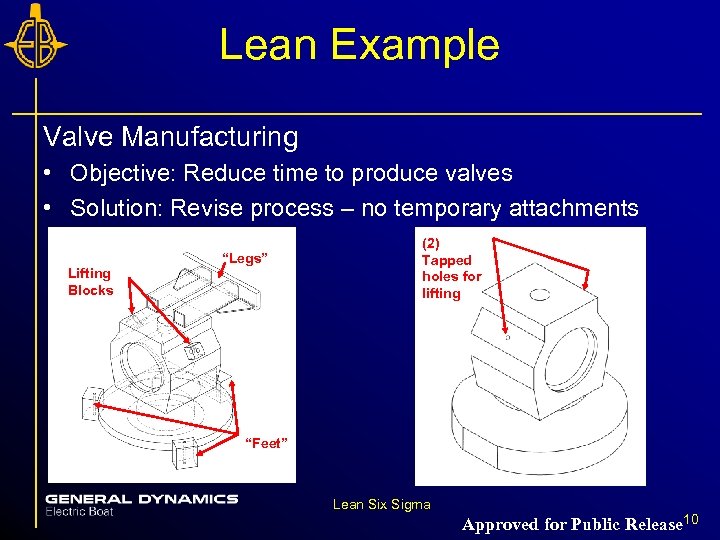
Lean Example Valve Manufacturing • Objective: Reduce time to produce valves • Solution: Revise process – no temporary attachments Lifting Blocks “Legs” (2) Tapped holes for lifting “Feet” Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 10
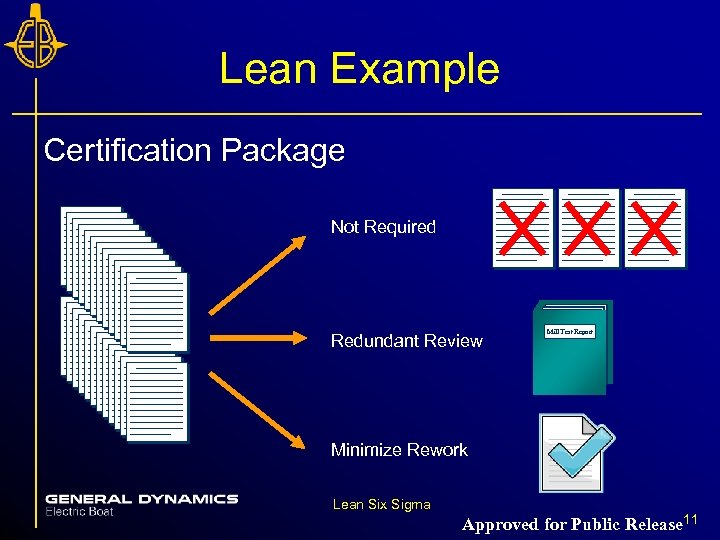
Lean Example Certification Package Not Required Redundant Review Mill Test Report Minimize Rework Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 11
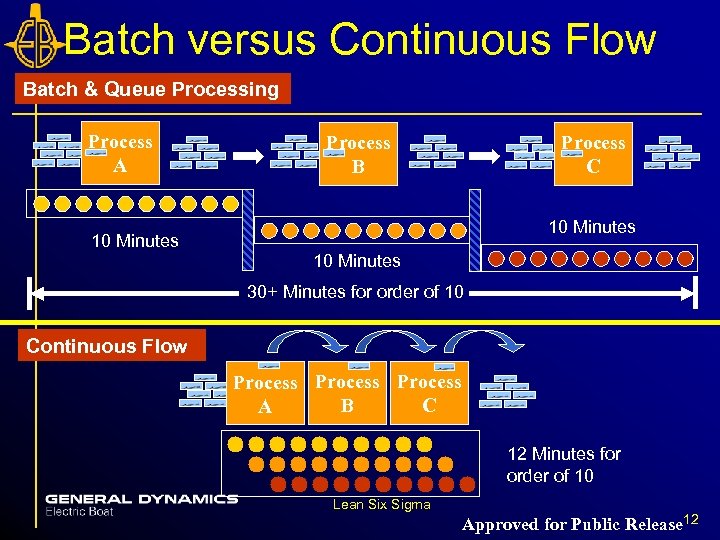
Batch versus Continuous Flow Batch & Queue Processing Process A Process C Process B 10 Minutes 30+ Minutes for order of 10 Continuous Flow Process C B A 12 Minutes for order of 10 Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 12
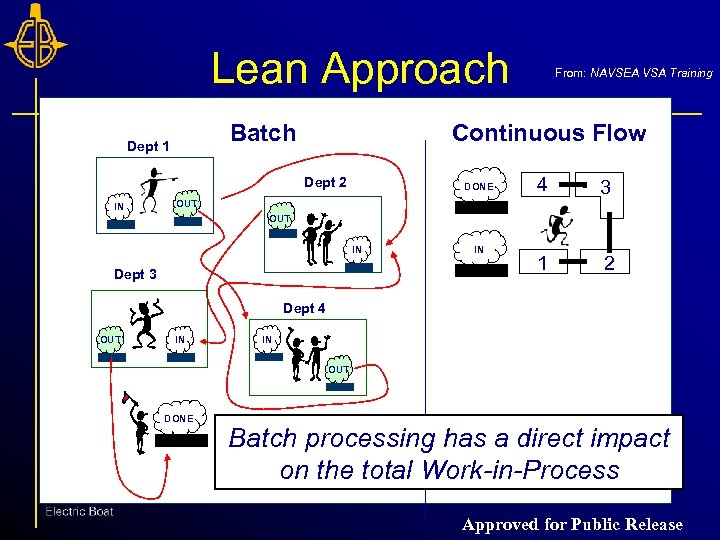
Lean Approach Batch Dept 1 Continuous Flow Dept 2 IN From: NAVSEA VSA Training DONE 4 3 1 2 OUT IN Dept 3 IN Dept 4 OUT IN IN OUT DONE Batch processing has a direct impact on the total Work-in-Process Approved for Public Release
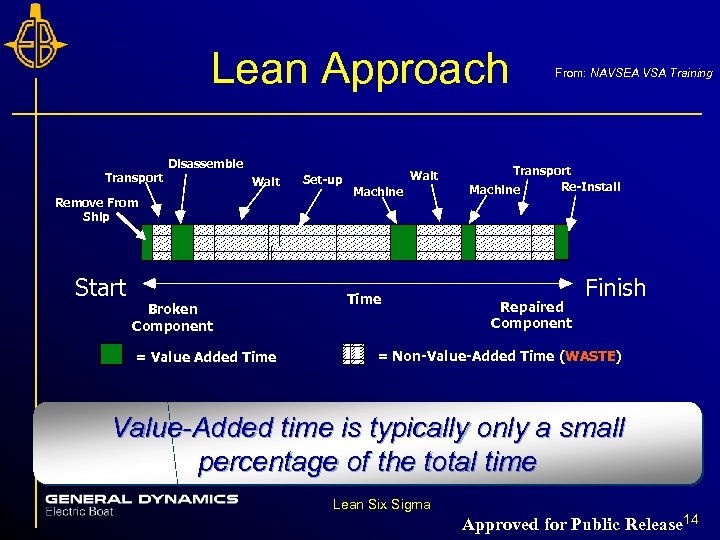
Lean Approach Transport Disassemble Wait Remove From Ship Start Broken Component = Value Added Time Set-up Wait Machine Time From: NAVSEA VSA Training Transport Re-Install Machine Repaired Component Finish = Non-Value-Added Time (WASTE) Value-Added time is typically only a small percentage of the total time Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 14

Approved for Public Release Lean Approach From: NAVSEA VSA Training Total Lead-time = 48 days Lead-time Value added time = 315 secs !!!! Overtype with Section Title Lean Six Sigma Date / Reference / Classification 15
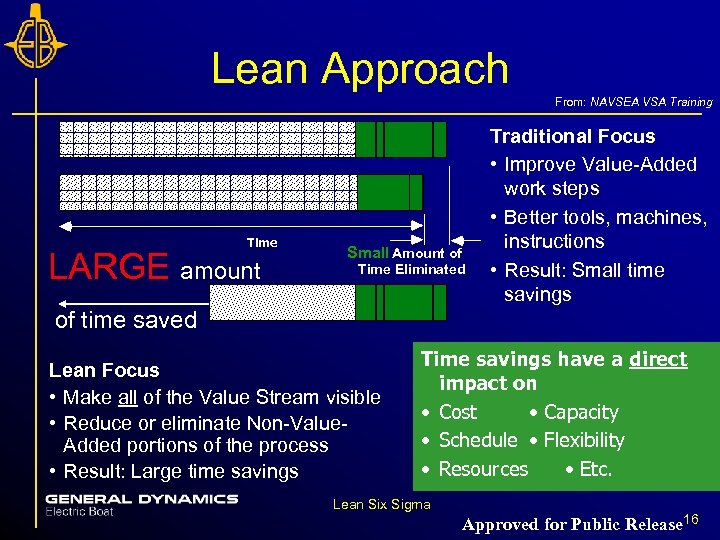
Lean Approach From: NAVSEA VSA Training Time LARGE amount Small Amount of Time Eliminated Traditional Focus • Improve Value-Added work steps • Better tools, machines, instructions • Result: Small time savings of time saved Lean Focus • Make all of the Value Stream visible • Reduce or eliminate Non-Value. Added portions of the process • Result: Large time savings Time savings have a direct impact on • Cost • Capacity • Schedule • Flexibility • Resources • Etc. Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 16

Continuous Flow Traditional Thinking: Batch Production—like a meandering stream with many stagnant pools, waterfalls, and eddies Doubling production rate means doubling resources Continuous Flow Thinking: Pipeline with fast-flowing product – no stops, piles, or back-ups Doubling production rate means halving the time waiting “’Flow’ production was an even more valuable innovation of Henry Ford’s than his better-known ‘mass’ production model. ” Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 17

How Does Lean Solve Problems? • Focuses on what is of VALUE to the customer – Understand customer expectations and requirements – In terms of the what the product provides, not just the product itself • Eliminates activities that do not move the product closer to it’s final form – Reduces the 8 types of waste • Creates continuous flow Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 18

Six Sigma Philosophy • Reduce variation • Y=f(X) • Making decisions based on data Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 19
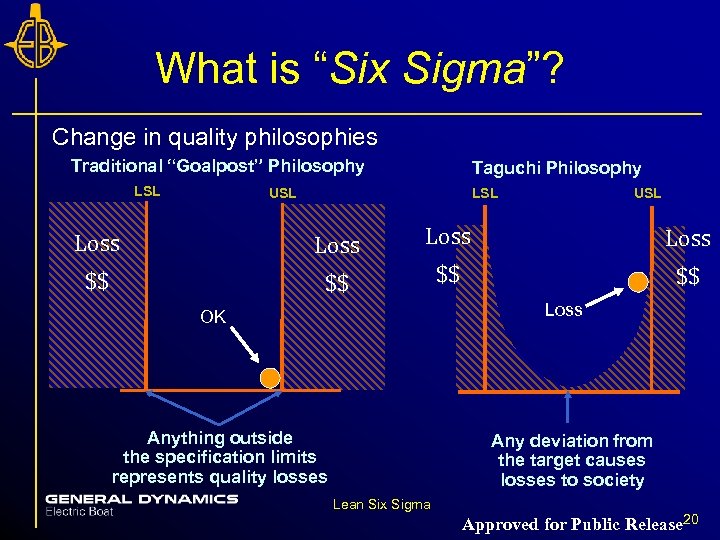
What is “Six Sigma”? Change in quality philosophies Traditional “Goalpost” Philosophy LSL Taguchi Philosophy LSL USL Loss $$ $$ $$ Loss OK Anything outside the specification limits represents quality losses Any deviation from the target causes losses to society Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 20
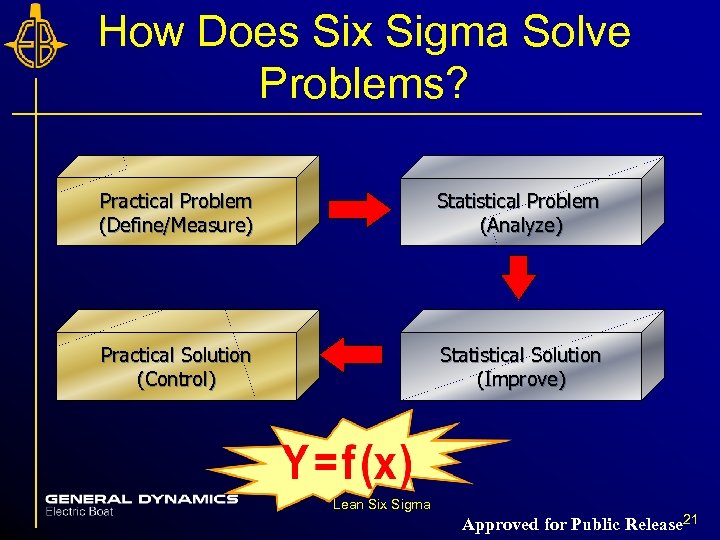
How Does Six Sigma Solve Problems? Practical Problem (Define/Measure) Statistical Problem (Analyze) Practical Solution (Control) Statistical Solution (Improve) Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 21
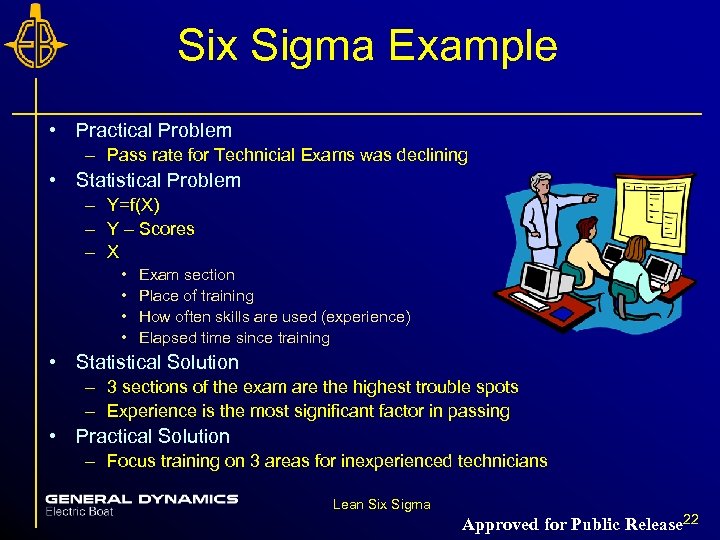
Six Sigma Example • Practical Problem – Pass rate for Technicial Exams was declining • Statistical Problem – Y=f(X) – Y – Scores – X • • Exam section Place of training How often skills are used (experience) Elapsed time since training • Statistical Solution – 3 sections of the exam are the highest trouble spots – Experience is the most significant factor in passing • Practical Solution – Focus training on 3 areas for inexperienced technicians Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 22
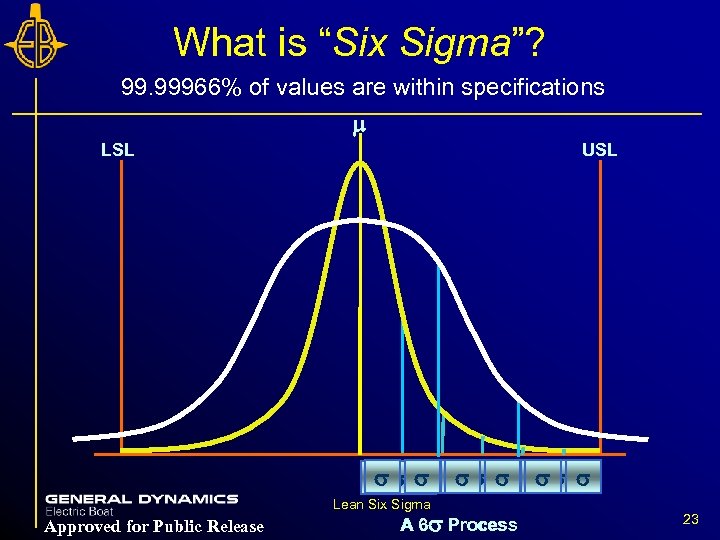
What is “Six Sigma”? 99. 99966% of values are within specifications m LSL USL ss s Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release ss s A 6 s Process 3 ss s 23

Is “Six Sigma” Overkill? 99. 99966% (6 s) 99% (≈3. 8 s) • 20, 000 lost articles of mail per hour • 15 minutes of unsafe drinking water each day • 5, 000 incorrect surgical operations per week • 2 short or long landings at most major airports each day • 11 hours of no electricity per month • 7 lost articles of mail per hour • 1 minute of unsafe drinking water per 7 months • 1. 7 incorrect surgical operations per week • 1 short or long landing every 5 years • 1 hour of no electricity every 34 years Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 24

Pipe Welding Quality Reduce concave & convex defects in pipe butt welds Experimented on the effects of: • Purge pressure • Starting point • Weld segment overlap • Intersegment temperature • Welder technique Convex Concave Identified key factors to control and ones that had no effect Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 25
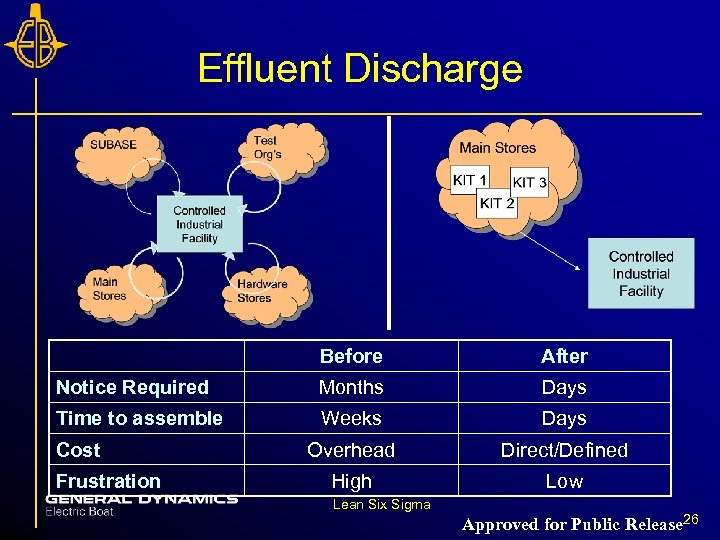
Effluent Discharge Before After Notice Required Months Days Time to assemble Weeks Days Overhead Direct/Defined High Low Cost Frustration Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 26
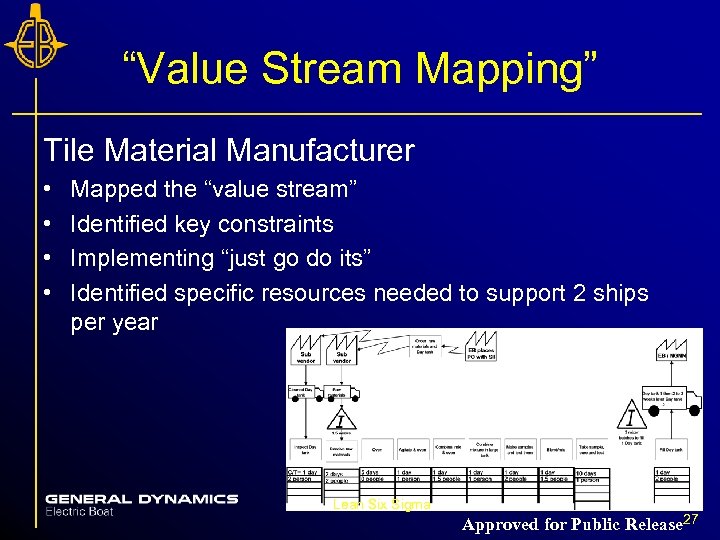
“Value Stream Mapping” Tile Material Manufacturer • • Mapped the “value stream” Identified key constraints Implementing “just go do its” Identified specific resources needed to support 2 ships per year Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 27
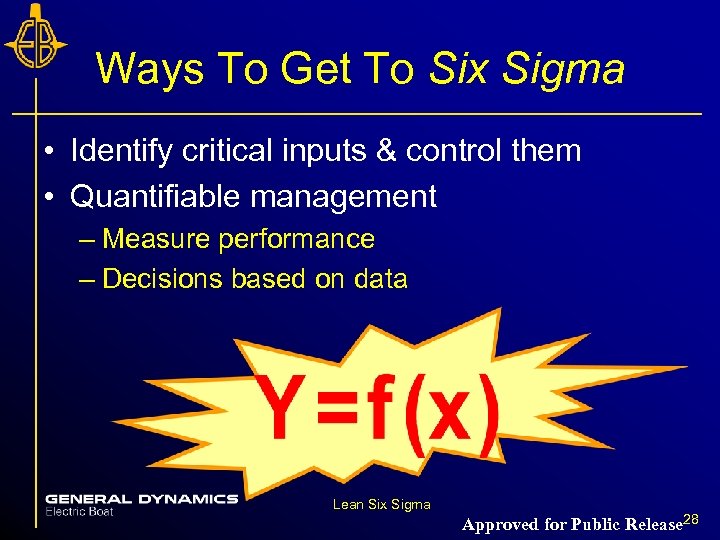
Ways To Get To Six Sigma • Identify critical inputs & control them • Quantifiable management – Measure performance – Decisions based on data Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 28

Ways To Get To Six Sigma Control Methods Best • Type 1 Corrective Action – Countermeasure • Type 2 Corrective Action – Flag • SPC/SPM – Empowered Operators • Type 3 Corrective Action – Inspection • SPC/SPM – Operators Not Empowered • Standard Operating Procedure • Warning Signal – Used to Detect Defects • SPC/SPM - Wallpaper Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 29

“But we aren’t mass production” Look for repetition: • Valve manufacturing • Certification package review • Pipe welding • Effluent discharge Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 30

“But we aren’t mass production” • Product Families – Different products that follow the same steps • Processes – Repetitive tasks • For a product • For a service • For just normal day to day activities – “If it’s not the first time, then there is a process. ” Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 31

Supplier Lean Outreach Approved for Public Release
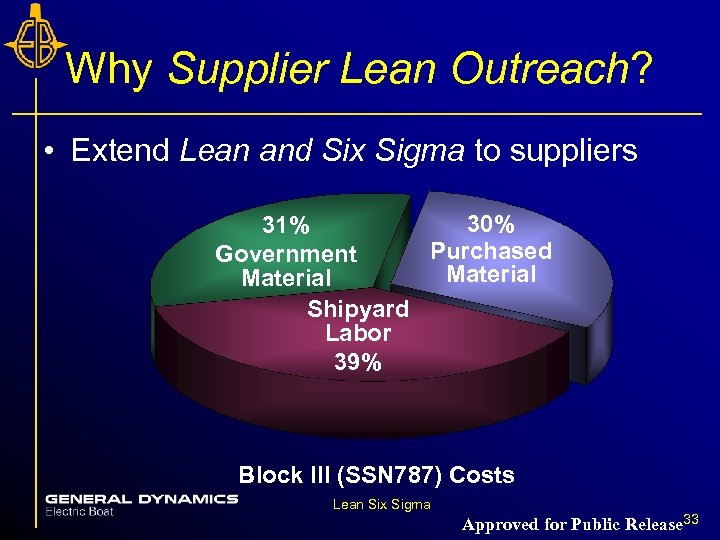
Why Supplier Lean Outreach? • Extend Lean and Six Sigma to suppliers 30% 31% Purchased Government Material Shipyard Labor 39% Block III (SSN 787) Costs Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 33

Goal Conduct joint process improvement projects with VIRGINIA Class vendors to reduce defects, and cycle time via the application of Lean Six Sigma tools and techniques. • Create a win-win between supplier and EB – Tangible improvement – Benefits both companies • Funded for 2 projects/year Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 34

Methodology 1. Voice of the Customer – All customers not just purchasing 2. Kick-off with Vendor – Identify problems, issues, roadblocks 3. Value Stream Analysis & Development of Improvement Plan 4. Improvement Plan Execution and Follow-on Onsites Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 35

How To Get Started “We all tend to concentrate on taking corrective actions that we know how to take, not necessarily concentrating on the problems we should correct and the actions needed to correct (them). ” - Eliyahu Goldratt Approved for Public Release

How To Get Started Involve the employees • Examine the detailed process with them • Empower them to make process changes to: – Eliminate non-value-added steps – Keep adding value continuously without interruptions • Ask the right questions – What can we do to save time? – Not: What can we do to save money? • Get to the root causes – 5 -Whys, etc. Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 37
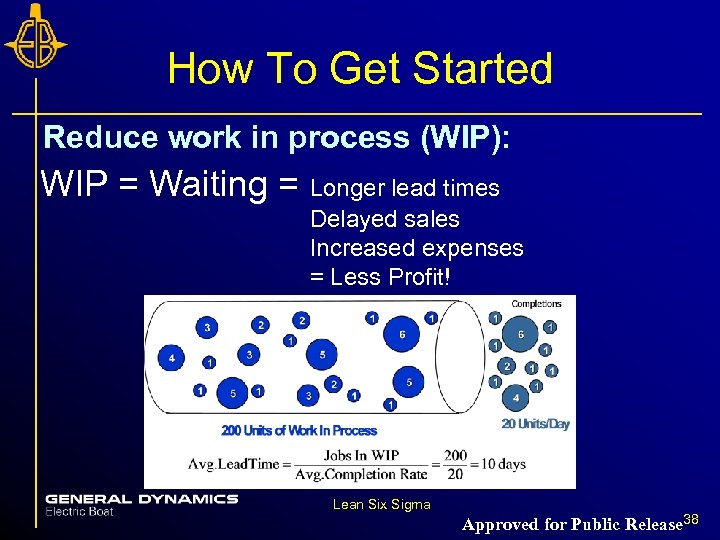
How To Get Started Reduce work in process (WIP): WIP = Waiting = Longer lead times Delayed sales Increased expenses = Less Profit! Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 38

How To Get Started Books to read: • Lean Thinking. Womack & Jones • Lean Six Sigma: Combining Six Sigma Quality With Lean Speed. M. L. George • Theory of Constraints. Goldratt • The Goal. Goldratt Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 39

How To Get Started Communicate with Electric Boat • Things you are doing • Ask for clarification on our needs – Voice of the Customer Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 40

Wrap - Up • What is Lean Six Sigma? • What can Lean Six Sigma do? • How to get started Lean Six Sigma Approved for Public Release 41
e7c29741d1dd8f21992ec6ea1078af2a.ppt