0ae1ffcbbb1e90fd64db42e14c43847b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Lean Manufacturing & Just-in-Time "The most dangerous kind of waste is the waste we do not recognize. " Shigeo Shingo
Lean Manufacturing & Just-in-Time "The most dangerous kind of waste is the waste we do not recognize. " Shigeo Shingo
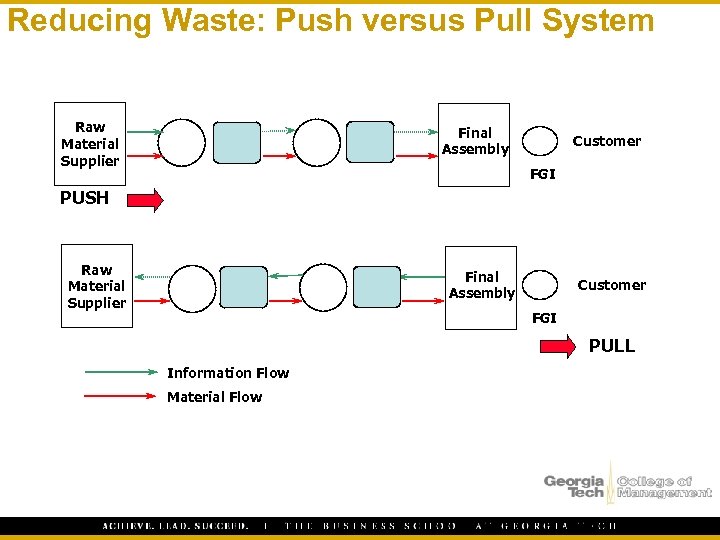 Reducing Waste: Push versus Pull System Raw Material Supplier Final Assembly Customer FGI PUSH Raw Material Supplier Final Assembly Customer FGI PULL Information Flow Material Flow
Reducing Waste: Push versus Pull System Raw Material Supplier Final Assembly Customer FGI PUSH Raw Material Supplier Final Assembly Customer FGI PULL Information Flow Material Flow
 Push System § Every worker maximizes own output, making as many products as possible § Pros and cons: § Focuses on keeping individual operators and workstations busy rather than efficient use of materials § Volumes of defective work may be produced § Throughput time will increase as work-in-process increases (Little’s Law) § Line bottlenecks and inventories of unfinished products will occur § Hard to respond to special orders and order changes due to long throughput time
Push System § Every worker maximizes own output, making as many products as possible § Pros and cons: § Focuses on keeping individual operators and workstations busy rather than efficient use of materials § Volumes of defective work may be produced § Throughput time will increase as work-in-process increases (Little’s Law) § Line bottlenecks and inventories of unfinished products will occur § Hard to respond to special orders and order changes due to long throughput time
 Pull System § Production line is controlled by the last operation, Kanban cards control WIP § Pros and cons § Controls maximum WIP and eliminates WIP accumulating at bottlenecks § Keeps materials busy, not operators. Operators work only when there is a signal to produce. § If a problem arises, there is no slack in the system § Throughput time and WIP are decreased, faster reaction to defects and less opportunity to create defects
Pull System § Production line is controlled by the last operation, Kanban cards control WIP § Pros and cons § Controls maximum WIP and eliminates WIP accumulating at bottlenecks § Keeps materials busy, not operators. Operators work only when there is a signal to produce. § If a problem arises, there is no slack in the system § Throughput time and WIP are decreased, faster reaction to defects and less opportunity to create defects
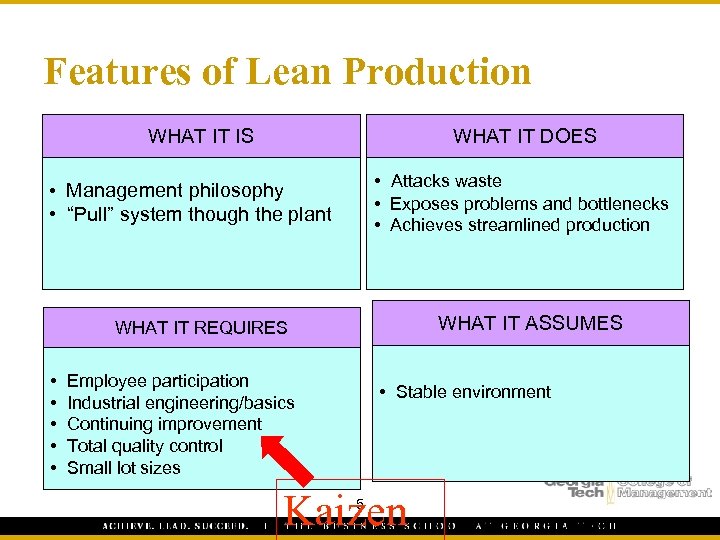 Features of Lean Production WHAT IT IS WHAT IT DOES • Attacks waste • Management philosophy • “Pull” system though the plant • Exposes problems and bottlenecks • Achieves streamlined production WHAT IT ASSUMES WHAT IT REQUIRES • Employee participation • • • Stable environment Industrial engineering/basics Continuing improvement Total quality control Small lot sizes Kaizen 5
Features of Lean Production WHAT IT IS WHAT IT DOES • Attacks waste • Management philosophy • “Pull” system though the plant • Exposes problems and bottlenecks • Achieves streamlined production WHAT IT ASSUMES WHAT IT REQUIRES • Employee participation • • • Stable environment Industrial engineering/basics Continuing improvement Total quality control Small lot sizes Kaizen 5
 A Little History! § Ford: Design for manufacturing § Start with an article that suits and then study to find some way of eliminating the entirely useless parts. This applies to everything— a shoe, a dress, a house, a piece of machinery, a railroad, a steamship, an airplane. As we cut out useless parts and simplify necessary ones, we also cut down the cost of making. . But also it is to be remembered that all the parts are designed so that they can be most easily made. "
A Little History! § Ford: Design for manufacturing § Start with an article that suits and then study to find some way of eliminating the entirely useless parts. This applies to everything— a shoe, a dress, a house, a piece of machinery, a railroad, a steamship, an airplane. As we cut out useless parts and simplify necessary ones, we also cut down the cost of making. . But also it is to be remembered that all the parts are designed so that they can be most easily made. "
 A Little History! § Ohno – put ideas into practice systematically § “When bombarded with questions from our group on what inspired his thinking, Ohno just laughed and said he learned it all from Henry Ford's book. "
A Little History! § Ohno – put ideas into practice systematically § “When bombarded with questions from our group on what inspired his thinking, Ohno just laughed and said he learned it all from Henry Ford's book. "
 TPS: Toyota Production System § A system that continually searches for and eliminates waste throughout the value chain. § Views every enterprise activity as an operation and applies its waste reduction concepts to each activity from Customers to the Board of Directors to Support Staff to Production Plants to Suppliers.
TPS: Toyota Production System § A system that continually searches for and eliminates waste throughout the value chain. § Views every enterprise activity as an operation and applies its waste reduction concepts to each activity from Customers to the Board of Directors to Support Staff to Production Plants to Suppliers.
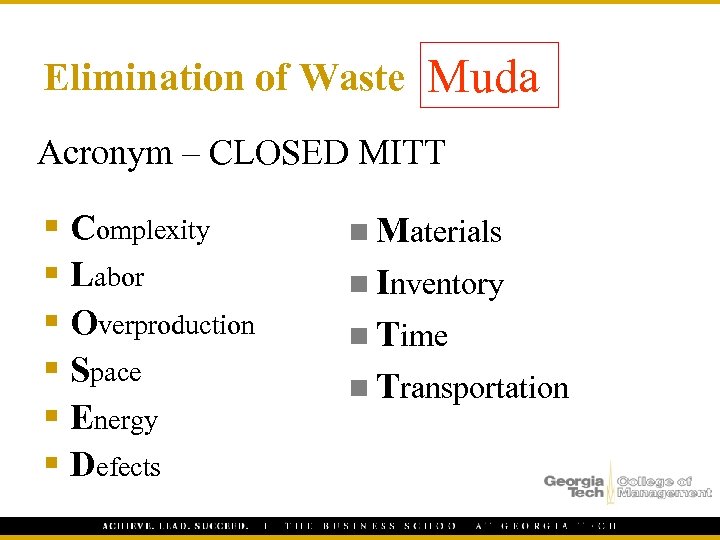 Elimination of Waste Muda Acronym – CLOSED MITT § Complexity § Labor § Overproduction § Space § Energy § Defects n Materials n Inventory n Time n Transportation
Elimination of Waste Muda Acronym – CLOSED MITT § Complexity § Labor § Overproduction § Space § Energy § Defects n Materials n Inventory n Time n Transportation
 Elimination of Waste 1. 5 S 2. Group technology 3. Quality at the source 4. JIT production 5. Kanban production control system 6. Minimized setup times 7. Uniform plant loading 8. Focused factory networks 10
Elimination of Waste 1. 5 S 2. Group technology 3. Quality at the source 4. JIT production 5. Kanban production control system 6. Minimized setup times 7. Uniform plant loading 8. Focused factory networks 10
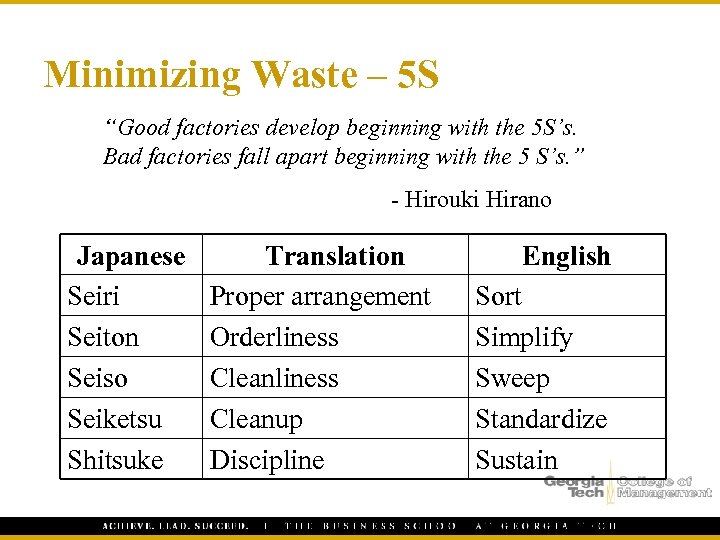 Minimizing Waste – 5 S “Good factories develop beginning with the 5 S’s. Bad factories fall apart beginning with the 5 S’s. ” - Hirouki Hirano Japanese Seiri Seiton Seiso Seiketsu Shitsuke Translation Proper arrangement Orderliness Cleanup Discipline English Sort Simplify Sweep Standardize Sustain
Minimizing Waste – 5 S “Good factories develop beginning with the 5 S’s. Bad factories fall apart beginning with the 5 S’s. ” - Hirouki Hirano Japanese Seiri Seiton Seiso Seiketsu Shitsuke Translation Proper arrangement Orderliness Cleanup Discipline English Sort Simplify Sweep Standardize Sustain
 Minimizing Waste – 5 S § A place for everything and everything in its place § Not just a housekeeping issue § Critical foundation for § § Setup reduction Pull systems Maintenance Inventory management
Minimizing Waste – 5 S § A place for everything and everything in its place § Not just a housekeeping issue § Critical foundation for § § Setup reduction Pull systems Maintenance Inventory management
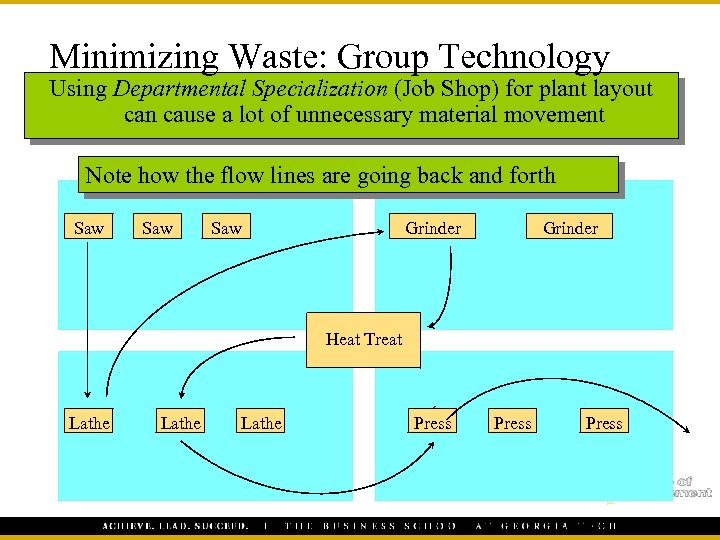 Minimizing Waste: Group Technology Using Departmental Specialization (Job Shop) for plant layout can cause a lot of unnecessary material movement Note how the flow lines are going back and forth Saw Saw Grinder Heat Treat Lathe Press
Minimizing Waste: Group Technology Using Departmental Specialization (Job Shop) for plant layout can cause a lot of unnecessary material movement Note how the flow lines are going back and forth Saw Saw Grinder Heat Treat Lathe Press
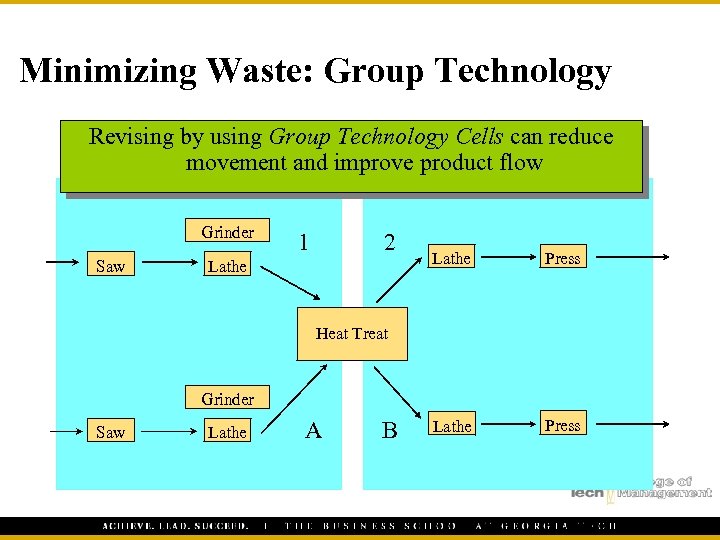 Minimizing Waste: Group Technology Revising by using Group Technology Cells can reduce movement and improve product flow Grinder Saw 1 2 Lathe Press Heat Treat Grinder Saw Lathe A B
Minimizing Waste: Group Technology Revising by using Group Technology Cells can reduce movement and improve product flow Grinder Saw 1 2 Lathe Press Heat Treat Grinder Saw Lathe A B
 Minimizing Waste: JIT § § § Only produce what’s needed The opposite of “Just In Case” philosophy Ideal lot size is one Minimize transit time Frequent small deliveries ? ? ? Pro’s Con’s • Minimal inventory • Requires discipline • Less space • Requires good problem solving • More visual • Suppliers or warehouses must be close • Easier to spot quality issues • Requires high quality
Minimizing Waste: JIT § § § Only produce what’s needed The opposite of “Just In Case” philosophy Ideal lot size is one Minimize transit time Frequent small deliveries ? ? ? Pro’s Con’s • Minimal inventory • Requires discipline • Less space • Requires good problem solving • More visual • Suppliers or warehouses must be close • Easier to spot quality issues • Requires high quality
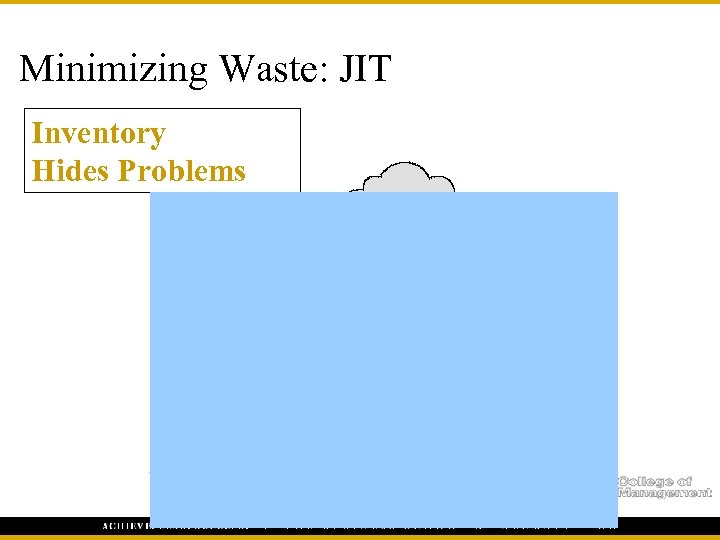 Minimizing Waste: JIT Inventory Hides Problems Machine downtime Scrap Work in process queues (banks) Paperwork backlog Vendor delinquencies Change orders Engineering design redundancies Inspection backlogs 16 Design backlogs Decision backlogs
Minimizing Waste: JIT Inventory Hides Problems Machine downtime Scrap Work in process queues (banks) Paperwork backlog Vendor delinquencies Change orders Engineering design redundancies Inspection backlogs 16 Design backlogs Decision backlogs
 Minimizing Waste – Quality at the Source § “Do it right the first time” § Call for help Andon and correct it vs. § Immediately stop the process passing it on to inspection or repair
Minimizing Waste – Quality at the Source § “Do it right the first time” § Call for help Andon and correct it vs. § Immediately stop the process passing it on to inspection or repair
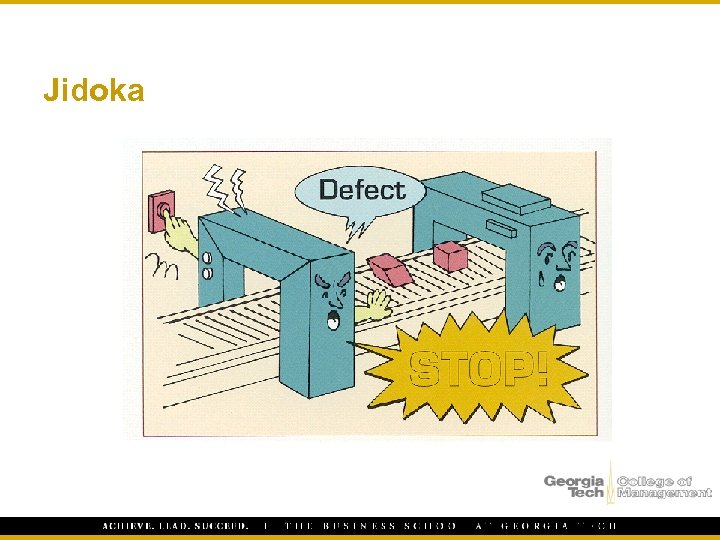 Jidoka
Jidoka
 Minimizing Waste – Kanban Signaling device to control flow of material • Cards • Empty containers • Lights • Colored golf balls • Etc
Minimizing Waste – Kanban Signaling device to control flow of material • Cards • Empty containers • Lights • Colored golf balls • Etc
 Minimizing Waste – Setup Times § Long setup times drive: § Long production runs § Large lots § Long lead times § JIT requires small lots and minimum kanbans § Setup reduction § Focused efforts § Problem solving § Flexible equipment
Minimizing Waste – Setup Times § Long setup times drive: § Long production runs § Large lots § Long lead times § JIT requires small lots and minimum kanbans § Setup reduction § Focused efforts § Problem solving § Flexible equipment
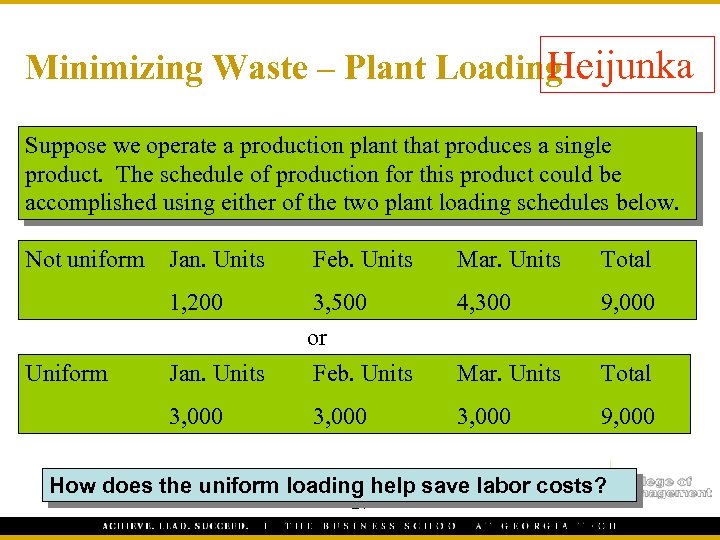 H Minimizing Waste – Plant Loading eijunka Suppose we operate a production plant that produces a single product. The schedule of production for this product could be accomplished using either of the two plant loading schedules below. Not uniform Feb. Units Mar. Units Total 1, 200 4, 300 9, 000 Jan. Units 3, 500 or Feb. Units Mar. Units Total 3, 000 Uniform Jan. Units 3, 000 9, 000 How does the uniform loading help save labor costs? 21
H Minimizing Waste – Plant Loading eijunka Suppose we operate a production plant that produces a single product. The schedule of production for this product could be accomplished using either of the two plant loading schedules below. Not uniform Feb. Units Mar. Units Total 1, 200 4, 300 9, 000 Jan. Units 3, 500 or Feb. Units Mar. Units Total 3, 000 Uniform Jan. Units 3, 000 9, 000 How does the uniform loading help save labor costs? 21
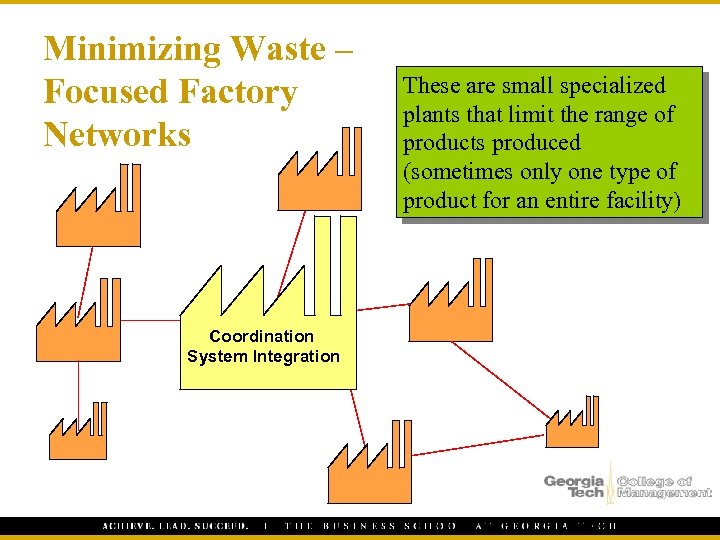 Minimizing Waste – Focused Factory Networks Coordination System Integration These are small specialized plants that limit the range of products produced (sometimes only one type of product for an entire facility)
Minimizing Waste – Focused Factory Networks Coordination System Integration These are small specialized plants that limit the range of products produced (sometimes only one type of product for an entire facility)
 TPS – Respect for People § Level payrolls § Cooperative employee unions § Subcontractor networks Keiretsu § Bottom-up management style § Quality circles (Small Group Problem Solving)
TPS – Respect for People § Level payrolls § Cooperative employee unions § Subcontractor networks Keiretsu § Bottom-up management style § Quality circles (Small Group Problem Solving)
 TPS – 4 Rules 1. All work shall be highly specified as to content, sequence, timing, and outcome 2. Every customer-supplier connection must be direct, and there must be an unambiguous yes-or-no way to send requests and receive responses 3. The pathway for every product and service must be simple and direct 4. Any improvement must be made in accordance with the scientific method, under the guidance of a teacher, at the lowest possible level in the organization
TPS – 4 Rules 1. All work shall be highly specified as to content, sequence, timing, and outcome 2. Every customer-supplier connection must be direct, and there must be an unambiguous yes-or-no way to send requests and receive responses 3. The pathway for every product and service must be simple and direct 4. Any improvement must be made in accordance with the scientific method, under the guidance of a teacher, at the lowest possible level in the organization
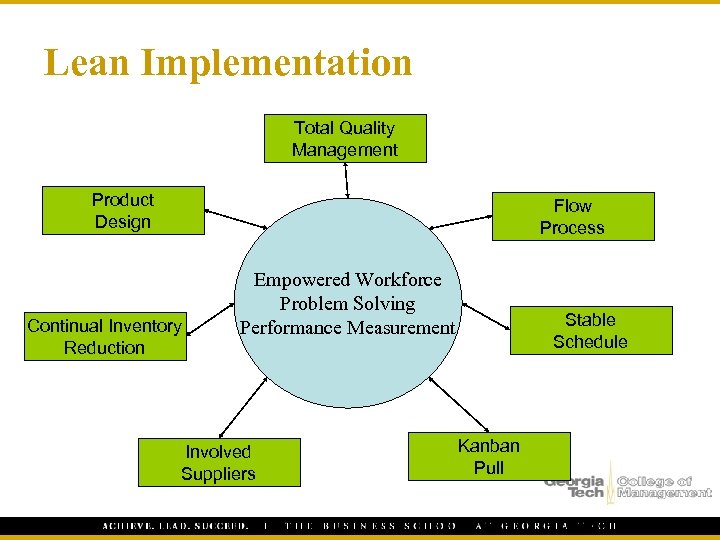 Lean Implementation Total Quality Management Product Design Flow Process Continual Inventory Reduction Empowered Workforce Problem Solving Performance Measurement Involved Suppliers Stable Schedule Kanban Pull
Lean Implementation Total Quality Management Product Design Flow Process Continual Inventory Reduction Empowered Workforce Problem Solving Performance Measurement Involved Suppliers Stable Schedule Kanban Pull
 Summary and Conclusions… § Lean Production is the set of activities that achieves quality production at minimum cost and inventory § The flow of material is pulled through the process by downstream operations § Lean originated with the Toyota Production System and its two philosophies – elimination of waste, and respect for people § CLOSED MITT forms of waste
Summary and Conclusions… § Lean Production is the set of activities that achieves quality production at minimum cost and inventory § The flow of material is pulled through the process by downstream operations § Lean originated with the Toyota Production System and its two philosophies – elimination of waste, and respect for people § CLOSED MITT forms of waste


