leadership-101222151032-phpapp01.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 68

le. ADe. Rs. HIP styles Presented By. PALLAVI THACKER DEEP SHREE 1

2 2/9/2018

3 2/9/2018

4 2/9/2018 CONTENTS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Leadership – introduction Leadership Theories Leadership Styles Leadership development at all levels Shifting focus. . From individual leadership to team leadership Prominent leadership styles in India

5

6 WHY LEADERSHIP ØA successful enterprise is not only the one which maximizes its profits, but also the one which maximizes the interests of various work groups which comes into its contact. Ø Effective leaders play a significant role in: -need satisfaction of the organization, -need satisfaction of its work force and -need satisfaction of the society.

7 LEADERSHIP THEORIES There are three main theories that attempt to explain Leadership. § Personality Trait Theories § Behavior theories § Contingency Theories
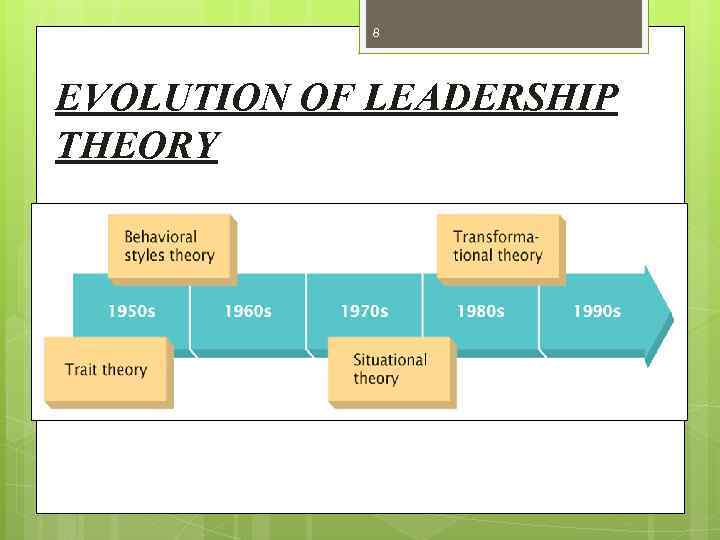
8 EVOLUTION OF LEADERSHIP THEORY

9 2/9/2018 TRAIT THEORY Ø Earlier researchers believed that there were certain unique characteristics in people that made them leaders. According to them , a person must possess certain unique personality traits that are essential for effective leadership.

10 BEHAVIORAL THEORIES Ø The behavioral theorists concentrated on the unique behavioral aspects found in leaders that enabled them to attain effective leadership. Following are the four main behavior theories of leadership 1. The Ohio State studies 2. Universities of Michigan studies 3. The Managerial Grid 4. University of Iowa Studies

11 2/9/2018 THE OHIO STATE STUDIES Ø In 1945 researchers from various fields conducted studies on leadership at Ohio State university. Ø The research was based on a questionnaire called ‘Leader Behavior Description Questionnaire’. Ø They narrowed down to two independent dimensions along which an individual’s leadership behavior could be studied. 1. Initiating Structure 2. Consideration

12 2/9/2018 University of Michigan Studies As a result of these studies, the following dimensions of leadership were observed: 1. Employee-oriented dimension 2. Production-oriented dimension Researchers concluded that leaders with an inclination towards employee oriented dimension resulted in higher job satisfaction and greater productivity.
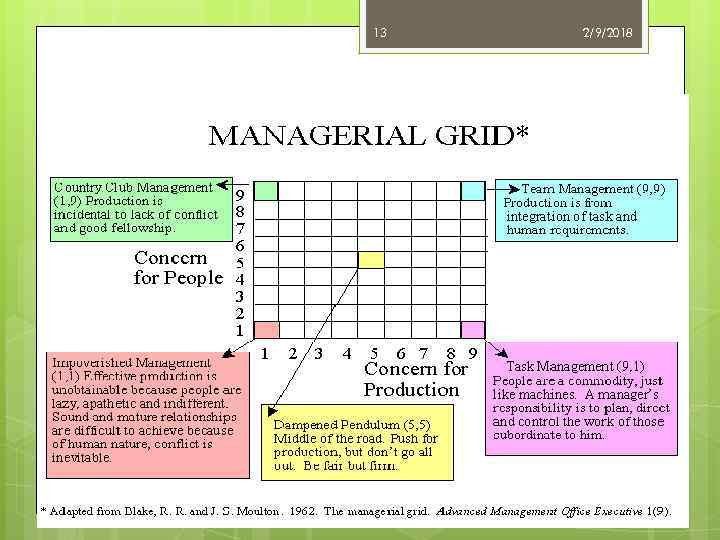
13 2/9/2018

14 2/9/2018 University of Iowa Studies Ø Studies explored three leadership styles to find which was the most effective 1. Autocratic style 2. Democratic style 3. Laissez-faire Ø The results seemed to indicate that the democratic style contributed to both good quantity and quality of work

15 2/9/2018 Contingency Theories Ø According to the contingency approach of leadership, a single leadership style is not applicable to all situations. Ø Below are the 3 contingency models of leadership styles. 1. Tannenbaum and Schmidt’s leadership continuum 2. Fiedler’s Contingency Model 3. Hersey and Blanchard’s situational theory 4. Path Goal Theory

16 2/9/2018 Fiedler’s Contingency Theory Ø The Fiedler contingency model is a leadership theory of industrial and organizational psychology developed by Fred Fiedler Ø Fiedler's model assumes that group performance depends on: Leadership style, described in terms of task motivation and relationship motivation.

17 2/9/2018 Ø Situational favourableness, determined by three factors: 1. Leader-member relations 2. Task structure 3. Position power or the leader’s position

18 2/9/2018 Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational theory Ø In contrast to Fiedler’s contingency leadership model and its underlying assumption that leadership style is hard to change, the Hersey. Blanchard situational leadership model suggests that successful leaders do adjust their styles. Ø The situational leadership model views leaders as varying their emphasis on task and relationship behaviours to best deal with different levels of follower maturity.
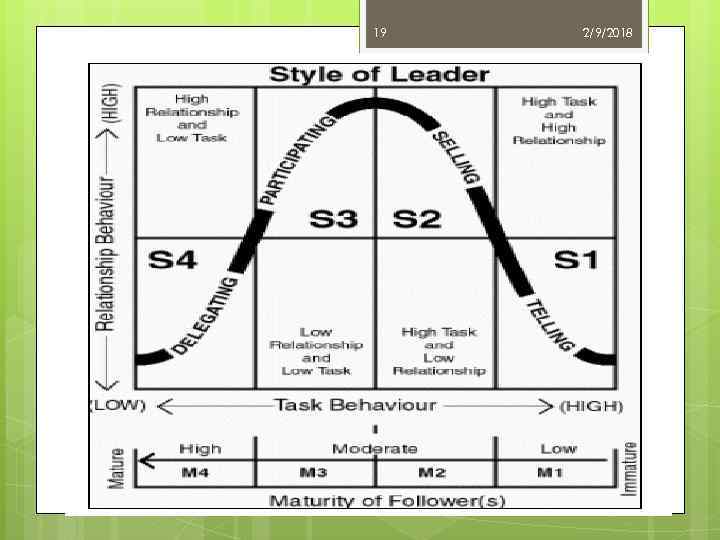
19 2/9/2018

20 2/9/2018 Ø The two-by-two matrix shown in the figure indicates that four leadership styles are possible. Telling Style — giving specific task directions and closely supervising work; this is a high-task, low-relationship style. Selling Style —explaining task directions in a supportive and persuasive way; this is a high-task, high-relationship style.

21 2/9/2018 Participating Style —emphasizing shared ideas and participative decisions on task directions; this is a low-task, highrelationship style. Delegating Style —allowing the group to take responsibility for task decisions; this is a low -task, low-relationship style.

22 2/9/2018 PATH GOAL THEORY Ø This theory was developed by Robert House. Ø Here the leader provides the necessary support and guidance to his followers and help them achieve organizational goals. Ø Leader defines the individual(or groups) goals and help them achieve them.

23 2/9/2018 Robert House suggested 4 types of leadership by this model 1. Directive leadership 2. Supportive leadership 3. Participative leadership 4. Achievement-oriented leadership.

24 LEADERSHIP STYLES Leadership Style is the way in which a leader influences followers. No matter what their traits or skills, leaders carry out their roles in a wide variety of styles.

25 FACTORS AFFECTING LEADERSHIP STYLES Ø Leadership style may be dependent on various factors • Risk - decision making and change initiatives based on degree of risk involved • Type of business – creative business or supply driven?

26 • • • Organisational culture – may be long embedded and difficult to change Nature of the task – needing cooperation? Direction? Structure? How important change is – change for change’s sake?

27 2/9/2018 LEADERSHIP STYLES CONTD…. CLASSIFICATION Ø A. On the basis of giving the REWARDS 1. Positive Leaders 2. Negative Leaders Ø B. On the basis of AUTHORITY 1. Autocratic/Commanding/Bureaucratic leaders 2. Participative Leaders 3. Democratic Leaders 4. Laissez-Faire/Free-Rein/Background Leaders

28 TANNENBAUM AND SCHIMDT’S LEADERSHIP CONTINUUM According to them, there is no best leadership style that a leader can adopt; rather, she/he chooses one amongst the seven leader behaviors, depending upon three important factors. 1) The leader 2) The follower 3) The situation 2/9/2018

29 2/9/2018

30 2/9/2018 OBSERVATION It has been observed that even in case of two extreme styles of leadership, some degree of freedom is enjoyed by subordinates, (howsoever little it may be) at extreme left corner and the managers also exercise some authority at the extreme right corner of the leadership continuum.

A. On the basis of giving the REWARDS 31 Ø Leaders can adopt a leadership style depending upon the rewards that they offer to motivate their followers to perform the desired work.

32 1. POSITIVE LEADERSHIP Ø Motivates through financial and/or non financial rewards Ø Results in -higher morale of workers -increased job satisfaction -higher contribution to organizational productivity and goals

33 2/9/2018 2. NEGATIVE LEADERSHIP Ø Use of penalties and punishments as means of motivation Ø Gets the desired performance from the followers at the cost of their morale and satisfaction Ø Such leaders may appropriately be termed as bosses

34 2/9/2018 B. On the basis of Authority Ø Another classification of the leadership styles can be made on the basis of power.

35 Autocratic Leaders Ø Make decisions and issue orders and instructions. Ø Normally follow the negative leadership styles. Ø The threat of punishment and penalties make the workers obey their orders. Ø May also offer rewards(positive motivation) to their followers for their good performance. In such cases the leaders are termed as BENEVOLENT AUTOCRATIC LEADERS.

36 2/9/2018 ADVANTAGESØ Quick decision-making due to centralized authority Ø Less competent and less skilled employees can also be hired Ø Can prove to be successful in short-run

37 DISADVANTAGESØ Usually no job satisfaction Ø Inhibits the innovative power of the workers Ø Negative impact on organizational productivity due to frustration and dissatisfaction amongst the followers

38 WHEN IS AUTOCRATIC STYLE EFFECTIVE? 1. Short term projects with a highly technical, complex or risky element. 2. Work environments where spans of control are wide and hence the manager has little time to devote to each employee. 3. Industries where employees need to perform lowskilled, monotonous and repetitive tasks and generally have low levels of motivation.

39 4. Projects where the work performed needs to be completed to exact specifications and/or with a tight deadline. 5. Companies that suffer from a high employee turnover, i. e. where time and resources devoted to leadership development would be largely wasted.

40 Participative Leaders Ø These leaders do not centralize the decision making authority with them; rather they decentralize it to their followers Ø Though the ultimate responsibility continues to vest with the leaders, they take all decisions in consultation with their followers Ø The followers thus develop a sense of involvement and contribute positively towards the group goals.

41 ADVANTAGES Ø Psychological involvement Ø Motivation Ø Responsibility Ø Increase in power Ø Increase in followers’ job satisfaction and cooperation with management Ø Reduction in employees’ turnover and absenteeism Ø Improved communication

42 LIMITATIONSØMismatch between the desired and actual participation ØLengthy and ‘boring’ decision making ØLike the other styles, the participative style is not always appropriate. It is most successful when used with highly skilled or experienced employees or when implementing operational changes or resolving individual or group problems.

43 DEMOCRATIC LEADERS Ø Democratic Leadership is the leadership style that promotes the sharing of responsibility, the exercise of delegation and continual consultation. Ø It is a step further than the participative leadership Ø The decisions are made in groups through group discussions, by the formation of various committes. It is also called as ‘group dynamics’ approach to participation

44 ADVANTAGES Ø Positive work environment Ø Successful initiatives Ø Creative thinking Ø Reduction of office politics Ø Reduced employee turnover Ø Overall development of the subordinates

45 LIMITATIONS Ø Delay in decision making Ø Suggestions given by subordinates may sometimes be better than what leaders could have thought of. Leaders , in such cases, may not feel happy inviting suggestions Ø Employees may not always be willing to participate Ø Suggestions which are not acceptable to the entire group may invite resistance from some of the group members

46 When Are The Democratic And Participative Leadership Style Effective? 1. 2. Democratic/ participative leadership is applied to an extent in the manufacturing industry, to allow employees to give their ideas on how processes can become leaner and more efficient. Democratic / participative leadership is effective in professionals organizations where the emphasis is clearly on training professional & leadership development.

47 Ø 3. Non profit organizations also tremendously benefit from drawing upon the creative energies of all their staff to bring about cost cutting techniques or fund raising ideas. Ø 4. As previously mentioned, creative industries such as advertising and television enjoy a lot of benefits from the free flow of ideas that democratic / participative leadership brings.

48 2/9/2018 LAISSEZ-FAIRE or FREE-REIN LEADERS Ø This French phrase means “leave it be” and is used to describe a leader who leaves his/her colleagues to get on with their work. The style is largely a "hands off" view that tends to minimize the amount of direction and face time required. Ø The leaders remain indifferent to the group activities. Ø Role of a leader is of a on-looker who plays a minor role in affecting the group-goals.

49 ADVANTAGES Ø Increases morale of employees and they strive for higher job satisfaction as they hold the responsibility for framing and achieving their group-goals. Ø The employees’ satisfaction is exploited to the fullest possible extent. Ø The subordinates train their own group members and motivate them to work. The results are likely to be more productive.

50 DISADVANTAGES Ø It makes employees feel insecure at the unavailability of a leader. Ø The leader cannot provide regular feedback to let employees know how well they are doing. Ø Leaders are unable to thank employees for their good work. Ø The leader doesn’t understand his or her responsibilities and is hoping the employees can cover for him or her.

51 When is The Laissez Faire Style Effective Ø Employees are highly skilled, experienced, and educated. Ø Employees have pride in their work and the drive to do it successfully on their own. Ø Outside experts, such as staff specialists or consultants are being used Ø Employees are trustworthy.

52 Other leadership styles 1. Transformational /Visionary Leadership. These leaders stimulate and inspire(transform) followers to achieve extraordinary outcomes 2. Transactional Leadership. These leaders believe that people are motivated by reward or punishment. 3. Charismatic / Pace-setting leadership. Enthusiastic, self confident leaders whose personalities and actions influence people to behave in certain ways

53 2/9/2018 4. Team Leadership-A team leader is someone (or in certain cases there may be multiple team leaders) who provides guidance, instruction, direction, leadership to a group of other individuals (the team) for the purpose of achieving a key result or group of aligned results. 5. Servant Leadership- In servant leadership, the leader is not officially intended to act as a leader. He is just an informal leader who takes one step forward on behalf of his team members. He takes decisions collectively by consulting with his colleagues.

54 6. Strategic Leadership- Strategic leadership basically means using strategy in the management of workers. The main strategy usually employed in a strategic style of leadership is to motivate workers to take the initiative to improve their productive input into the company. 2/9/2018

55 2/9/2018 7. Cross-cultural Leadership. Not all individuals working in an organization come from same culture. Thus it becomes necessary for a leader to lead every member in a way so that they feel comfortable. 8. Coaching/ Affiliative Leadershipleader adopts a focused approach and coaches the team members thus minimizing the risk of possible deviations from predetermined goals and create a harmonious environment.

56 2/9/2018 9. Crisis Leadershipgood at reacting to current circumstances, and driven by necessity, 10. Negotiative leadership this leader has a personal interest in her/his decisions and leader uses incentives to entice her/his followers to do certain things 11. Task-nurturant leadershipterm coined by J. B. P. Sinha T. N. Leadership =concern for task + nurturant orientation in Indian organisations, it is found to be effective

57 Varying leadership styles While the proper leadership style depends on the situation , there are other factors that also influence which leadership style to use. 1. The leader’s personal background. 2. The followers 3. The organization

58 A good leader uses all these styles, depending on what forces are involved between the followers, the leader, and the situation. Some examples include: Ø Using an authoritarian style on a new employee who is just learning the job. This will work best when the employee is of type X Ø Using a participative style with a team of workers who know their job. The leader knows the problem, but does not have all the information. The employees know their jobs and want to become part of the team.

59 Ø Using a delegative style with a worker who knows more about the job than the leader. Leader cannot do everything! The employees need to take ownership of their job. Also, the situation might call for the leader to be at other places, doing other things.

60 Forces that influence the style to be used include: Ø How much time is available. Ø Are relationships based on respect and trust or on disrespect? Ø Who has the information - leader, employees, or both? Ø How well the employees are trained and how well they know the task. Ø Internal conflicts. Ø Type of task. Is it structured, unstructured, complicated, or simple?

61 2/9/2018 LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT at ALL levels Ø Successful Ø Profitable organizations need leaders at all levels. organizations deliberately and systematically develop people to be real leaders, to be people with their own points of view, who motivate others to action. They use every opportunity to promote and encourage leadership at all levels within the organization, and their top leaders are personally committed to developing other leaders.

62 Ø Leadership at all levels is the most important and possibly the least understood asset of any organization. ENGAGE LEADERSHIP AT ALL LEVELS Ø Leadership is the most critical factor for successful change. Ø Front-line advocacy is essential to most successful changes.

63 Ways to Increase the Effectiveness of Leadership at All Levels ü Leading & Developing Others ü Developing Capability & Capacity ü Integrity ü Ethics ü Handling Cultural Diversity

64 SHIFTING FOCUS. . INDIVIDUAL LEADERSHIP TO TEAM LEADERSHIP Ø "Talents win games. Team work wins championships" – Michael Jordan Ø In life we succeed as individuals but we do much more when we work as a team. Indeed, one shall chase a thousand two shall put 10, 000 to flight. With this, imagine what three will do, or what about four, five and so on. .

65 Ø Teams involve more people, thus affording more resources, ideas and energy than any one individual possesses. Ø Teams provide multiple perspectives on how to meet a need or reach a goal Ø Teams share the credit for victories and blame for losses. This fosters genuine humility and strong bonds.

66 Ø Change is much more rapid today; the world is more dynamic, making it harder to maintain the static state in which one person stays at the head of affairs. Also, if you add complexity, it is much harder for any one person to know what to do and, therefore, to provide the group with direction.

67 PROMINENT LEADERSHIP STYLES IN INDIA. . Ø Leadership styles in organizations vary from country to country, as well as from region to region. Ø In India, generally, two leadership styles are more prominent. . 1) Task-nurturant leadership 2) Exploitative-benevolent (Autocraticbenevolent) leadership

68 It is possible to fool yourself. Ø It is possible to fool the people you work for. Ø It is more difficult to fool the people you work with. Ø But it is almost impossible to fool the people who work under you! Ø Thank You!
leadership-101222151032-phpapp01.pptx