c34346ebf860afda160ebef5adac0c64.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 LC Muon Detector Studies Overview (mostly recent prototype hardware development plans) Fermilab A. Bross, B. Choudhary, G. Fisk, K. Krempetz, A. Para, O. Prokovief, R. Stefanski University of California at Davis M. Tripathi, B. Holbrook, J. Lizarazo, Y. Bansal Northern Illinois University G. Blazey, A. Dychkant, D. Hedin, D. Chakraborty, G. Lima, A. Maciel, C. Milstene University of Notre Dame M. Mc. Kenna, M. Vigneault, B. Baumbaugh, M. Wayne State University P. Karchin, A. Gutierrez, R. Medipalli July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 1
LC Muon Detector Studies Overview (mostly recent prototype hardware development plans) Fermilab A. Bross, B. Choudhary, G. Fisk, K. Krempetz, A. Para, O. Prokovief, R. Stefanski University of California at Davis M. Tripathi, B. Holbrook, J. Lizarazo, Y. Bansal Northern Illinois University G. Blazey, A. Dychkant, D. Hedin, D. Chakraborty, G. Lima, A. Maciel, C. Milstene University of Notre Dame M. Mc. Kenna, M. Vigneault, B. Baumbaugh, M. Wayne State University P. Karchin, A. Gutierrez, R. Medipalli July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 1
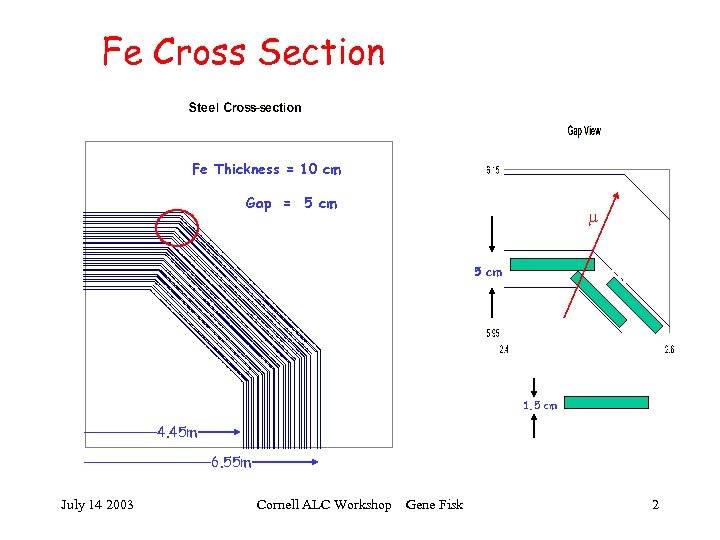 Fe Cross Section Fe Thickness = 10 cm Gap = 5 cm m Steel Cross Section 5 cm 1. 5 cm 4. 45 m 6. 55 m July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 2
Fe Cross Section Fe Thickness = 10 cm Gap = 5 cm m Steel Cross Section 5 cm 1. 5 cm 4. 45 m 6. 55 m July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 2
 The Big Picture - Orientation • • • Scintillator based muon system aims to do both muon identification via their penetration through the solenoid return yoke (> 1. 4 m Fe) and the measurement of hadronic shower energy that escapes out the back of the Hcal. Our candidate geometry for the detector planes consists of scintillator strips with 1. 2 mm dia. WLS fiber that captures light and pipes it to multi-anode PMTs outside the return yoke Fe. The strips are oriented at 45 o w. r. t. the beam axis to make alternating u and v planes with increasing radius. From measurements that MINOS has done we expect a m. i. p. will give ~ 15 p. e. per hit. The expected hadronic energy resolution DEh/Eh~ 1/√E, but this must be measured. Simulation studies show that muon ID is efficient using this prototype design and that in most cases the muons can be tracked back into Hcal. Over the past year, the universities who have joined the LC muon detector studies, have organized to embark on the development of prototype detector planes. July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 3
The Big Picture - Orientation • • • Scintillator based muon system aims to do both muon identification via their penetration through the solenoid return yoke (> 1. 4 m Fe) and the measurement of hadronic shower energy that escapes out the back of the Hcal. Our candidate geometry for the detector planes consists of scintillator strips with 1. 2 mm dia. WLS fiber that captures light and pipes it to multi-anode PMTs outside the return yoke Fe. The strips are oriented at 45 o w. r. t. the beam axis to make alternating u and v planes with increasing radius. From measurements that MINOS has done we expect a m. i. p. will give ~ 15 p. e. per hit. The expected hadronic energy resolution DEh/Eh~ 1/√E, but this must be measured. Simulation studies show that muon ID is efficient using this prototype design and that in most cases the muons can be tracked back into Hcal. Over the past year, the universities who have joined the LC muon detector studies, have organized to embark on the development of prototype detector planes. July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 3
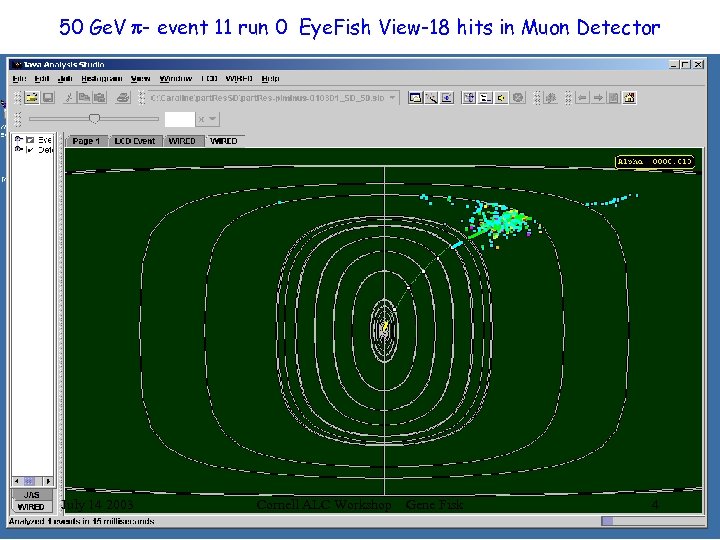 50 Ge. V p- event 11 run 0 Eye. Fish View-18 hits in Muon Detector July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 4
50 Ge. V p- event 11 run 0 Eye. Fish View-18 hits in Muon Detector July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 4
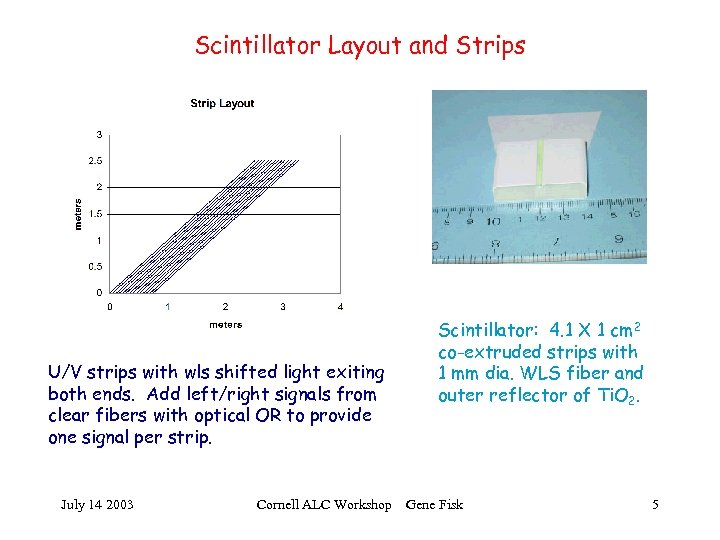 Scintillator Layout and Strips U/V strips with wls shifted light exiting both ends. Add left/right signals from clear fibers with optical OR to provide one signal per strip. July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Scintillator: 4. 1 X 1 cm 2 co-extruded strips with 1 mm dia. WLS fiber and outer reflector of Ti. O 2. Gene Fisk 5
Scintillator Layout and Strips U/V strips with wls shifted light exiting both ends. Add left/right signals from clear fibers with optical OR to provide one signal per strip. July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Scintillator: 4. 1 X 1 cm 2 co-extruded strips with 1 mm dia. WLS fiber and outer reflector of Ti. O 2. Gene Fisk 5
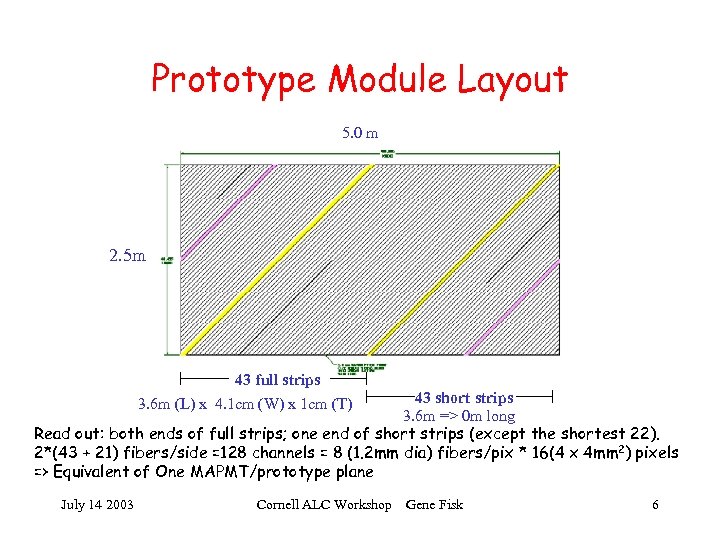 Prototype Module Layout 5. 0 m 2. 5 m 43 full strips 3. 6 m (L) x 4. 1 cm (W) x 1 cm (T) 43 short strips 3. 6 m => 0 m long Read out: both ends of full strips; one end of short strips (except the shortest 22). 2*(43 + 21) fibers/side =128 channels = 8 (1. 2 mm dia) fibers/pix * 16(4 x 4 mm 2) pixels => Equivalent of One MAPMT/prototype plane July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 6
Prototype Module Layout 5. 0 m 2. 5 m 43 full strips 3. 6 m (L) x 4. 1 cm (W) x 1 cm (T) 43 short strips 3. 6 m => 0 m long Read out: both ends of full strips; one end of short strips (except the shortest 22). 2*(43 + 21) fibers/side =128 channels = 8 (1. 2 mm dia) fibers/pix * 16(4 x 4 mm 2) pixels => Equivalent of One MAPMT/prototype plane July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 6
 How many prototype planes & strips? • Each plane is the equivalent of 86 strips that are 3. 6 m long. Each strip has a mass of 1. 52 kg or 3. 3 lbs. • The weight of a plane (86 strips) is 131 kg or 288 lbs. Order 15% extra scintillator – 100 strips per plane or 330 lbs (152 kg). • 3 u & 3 v to over-constrain a straight line = 6 planes + one spare to use for resolving multi-hit ambiguities. => 7 planes. • Total scintillator is 2, 341 lbs (1. 17 T) or 700 strips or 1. 064 Tonnes. • Scintillator Cost - MINOS paid ~ $10/kg or $10 K/tonne. Assume a 50% add’l cost for a small order: $16 K July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 7
How many prototype planes & strips? • Each plane is the equivalent of 86 strips that are 3. 6 m long. Each strip has a mass of 1. 52 kg or 3. 3 lbs. • The weight of a plane (86 strips) is 131 kg or 288 lbs. Order 15% extra scintillator – 100 strips per plane or 330 lbs (152 kg). • 3 u & 3 v to over-constrain a straight line = 6 planes + one spare to use for resolving multi-hit ambiguities. => 7 planes. • Total scintillator is 2, 341 lbs (1. 17 T) or 700 strips or 1. 064 Tonnes. • Scintillator Cost - MINOS paid ~ $10/kg or $10 K/tonne. Assume a 50% add’l cost for a small order: $16 K July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 7
 MINOS Hamamatsu H 6568 Multi-anode PM 16 anodes ea. 4 x 4 mm 2 July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 8
MINOS Hamamatsu H 6568 Multi-anode PM 16 anodes ea. 4 x 4 mm 2 July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 8
 MINOS – MAPMT with fiber guide July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 9
MINOS – MAPMT with fiber guide July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 9
 Fiber quantities and costs • WLS Fiber Buy enough to instrument every strip: 100 strips*3. 6 m/strip = 360 m times 8 planes (one to learn on). => 2. 88 km Kuraray quote of $3. 29 m => $9, 475 plus shipping & duty so add $1, 500, which brings the total to: $11 K WLS • Clear Fiber From engineering drawing: Short near strips: 21*3. 6 m = 76 m Full strips: 43*(3. 6 m +1. 3 m) = 211 m Short far strips: 21*3. 3 m = 69 m Total 356 m => 390 m times 8 planes 3, 120 m Clear cost = 3. 12 km*$3. 11 K/km = $9. 7 K +$1. 5 K = $11. 2 K Clear July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 10
Fiber quantities and costs • WLS Fiber Buy enough to instrument every strip: 100 strips*3. 6 m/strip = 360 m times 8 planes (one to learn on). => 2. 88 km Kuraray quote of $3. 29 m => $9, 475 plus shipping & duty so add $1, 500, which brings the total to: $11 K WLS • Clear Fiber From engineering drawing: Short near strips: 21*3. 6 m = 76 m Full strips: 43*(3. 6 m +1. 3 m) = 211 m Short far strips: 21*3. 3 m = 69 m Total 356 m => 390 m times 8 planes 3, 120 m Clear cost = 3. 12 km*$3. 11 K/km = $9. 7 K +$1. 5 K = $11. 2 K Clear July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 10
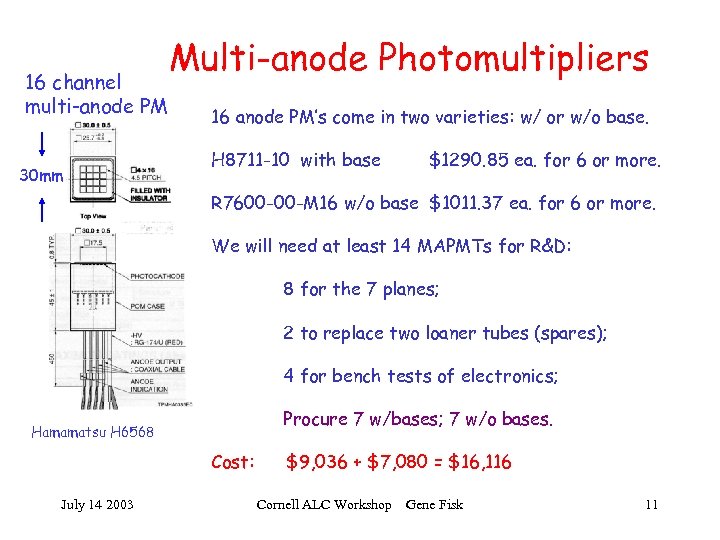 16 channel multi-anode PM 30 mm Multi-anode Photomultipliers 16 anode PM’s come in two varieties: w/ or w/o base. H 8711 -10 with base $1290. 85 ea. for 6 or more. R 7600 -00 -M 16 w/o base $1011. 37 ea. for 6 or more. We will need at least 14 MAPMTs for R&D: 8 for the 7 planes; 2 to replace two loaner tubes (spares); 4 for bench tests of electronics; Procure 7 w/bases; 7 w/o bases. Hamamatsu H 6568 Cost: July 14 2003 $9, 036 + $7, 080 = $16, 116 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 11
16 channel multi-anode PM 30 mm Multi-anode Photomultipliers 16 anode PM’s come in two varieties: w/ or w/o base. H 8711 -10 with base $1290. 85 ea. for 6 or more. R 7600 -00 -M 16 w/o base $1011. 37 ea. for 6 or more. We will need at least 14 MAPMTs for R&D: 8 for the 7 planes; 2 to replace two loaner tubes (spares); 4 for bench tests of electronics; Procure 7 w/bases; 7 w/o bases. Hamamatsu H 6568 Cost: July 14 2003 $9, 036 + $7, 080 = $16, 116 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 11
 Other R&D Items Al skins: (top and bottom) 150 lbs. @ $3/lb => $450/plane; 8 * 450 = $3, 600 Epoxy: $1000 Routing, connectors & clear wave guides: Mitch Wayne – Notre Dame Calibration Scheme/Hardware: Paul Karchin – Wayne State FE & readout electronics: Mani Tripathi – UC Davis & Paul Karchin – Wayne State Cables, PS, Crates, Trigger, DAQ: Mani Tripathi – UC Davis Testing: QC for scintillator/fiber – Fermilab, NIU & ND Cosmic Ray & Source tests at Fermilab – All Beam Tests – Not yet planned July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 12
Other R&D Items Al skins: (top and bottom) 150 lbs. @ $3/lb => $450/plane; 8 * 450 = $3, 600 Epoxy: $1000 Routing, connectors & clear wave guides: Mitch Wayne – Notre Dame Calibration Scheme/Hardware: Paul Karchin – Wayne State FE & readout electronics: Mani Tripathi – UC Davis & Paul Karchin – Wayne State Cables, PS, Crates, Trigger, DAQ: Mani Tripathi – UC Davis Testing: QC for scintillator/fiber – Fermilab, NIU & ND Cosmic Ray & Source tests at Fermilab – All Beam Tests – Not yet planned July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 12
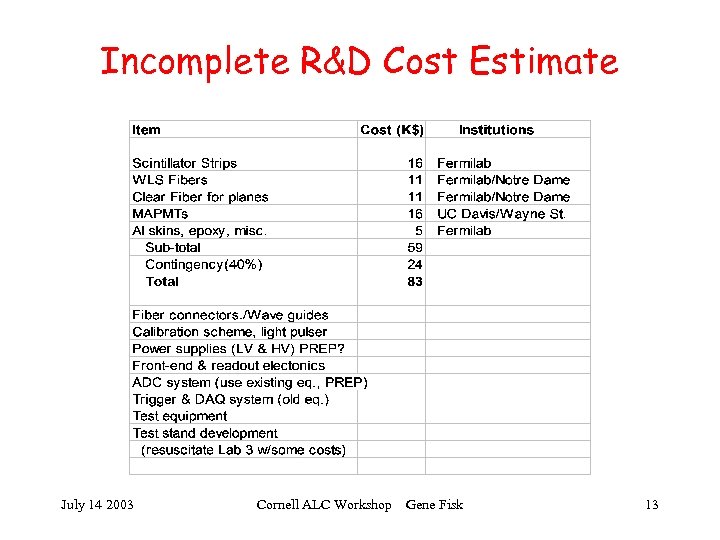 Incomplete R&D Cost Estimate July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 13
Incomplete R&D Cost Estimate July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 13
 Outlook • We will order scintillator strips and fiber after appropriate review of our R&D prototype design. • There is effort on most R&D topics, but not all; e. g. multiplexing scheme needs study. With the scintillator extrusion machine in Lab 5 at Fermilab, there a number of questions that could be investigated, some of which require event simulation studies, e. g. optimal strip width. • We are making slow, but positive progress. Pace is largely dictated by money and manpower. Manpower needs to increase significantly for more rapid progress. University collaborators would do more with increased funding which, we hear, is, or will happen. Muon detector studies are at an interesting point, both with regard to software, such as muon identification, and hardware, such as prototype detector development. • July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 14
Outlook • We will order scintillator strips and fiber after appropriate review of our R&D prototype design. • There is effort on most R&D topics, but not all; e. g. multiplexing scheme needs study. With the scintillator extrusion machine in Lab 5 at Fermilab, there a number of questions that could be investigated, some of which require event simulation studies, e. g. optimal strip width. • We are making slow, but positive progress. Pace is largely dictated by money and manpower. Manpower needs to increase significantly for more rapid progress. University collaborators would do more with increased funding which, we hear, is, or will happen. Muon detector studies are at an interesting point, both with regard to software, such as muon identification, and hardware, such as prototype detector development. • July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 14
 July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 15
July 14 2003 Cornell ALC Workshop Gene Fisk 15


