Latin America. General characteristic Lecture 9 Plan: General






























31794-latin_america.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Latin America. General characteristic Lecture 9
Latin America. General characteristic Lecture 9
 Plan: General information
Plan: General information
 Latin America 8 million square miles 16% of the earth’s surface Historical roots: Spain and Portugal Spanish and Portuguese based on Latin: Latin America
Latin America 8 million square miles 16% of the earth’s surface Historical roots: Spain and Portugal Spanish and Portuguese based on Latin: Latin America
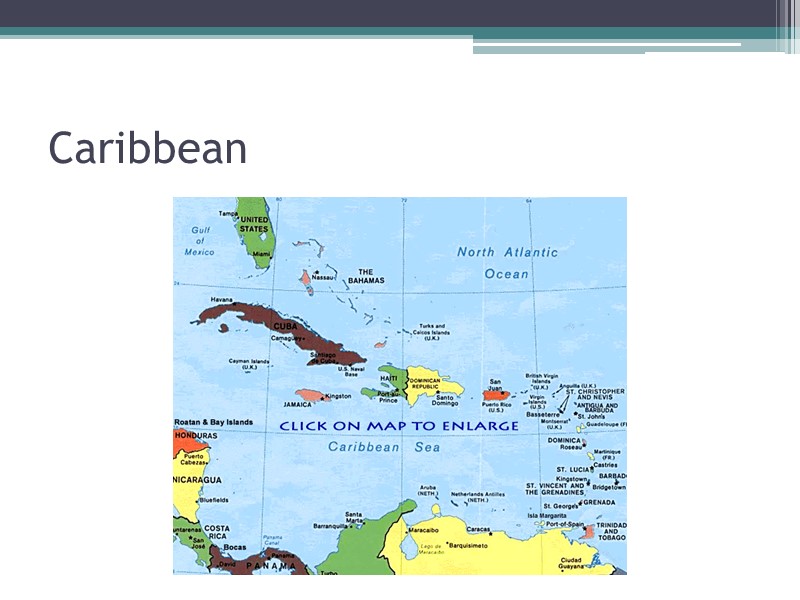
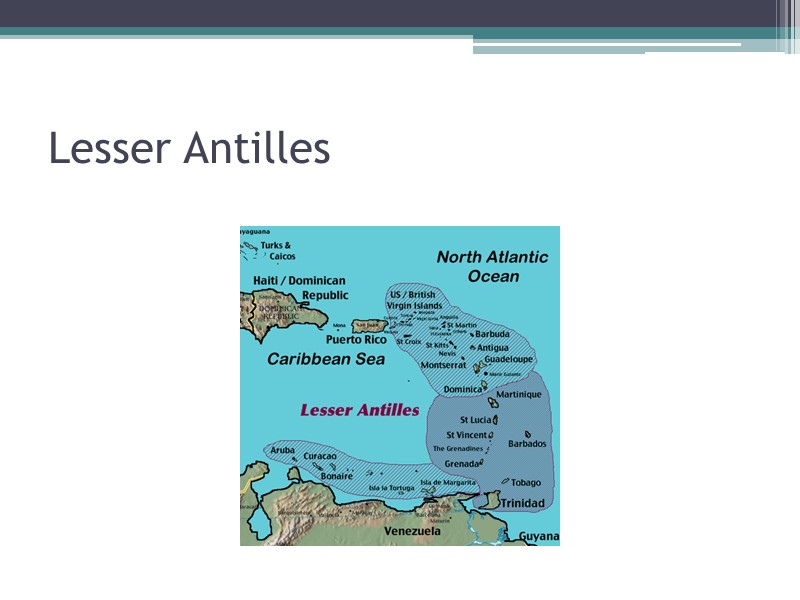
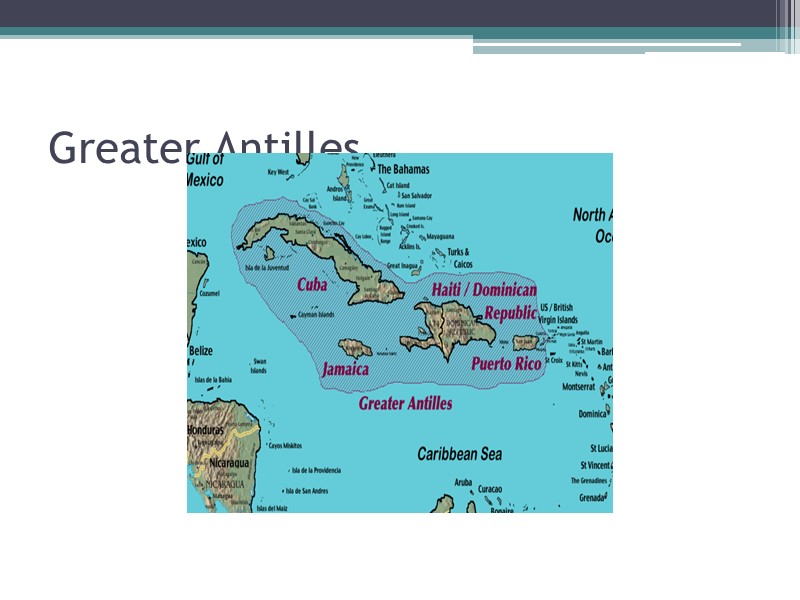
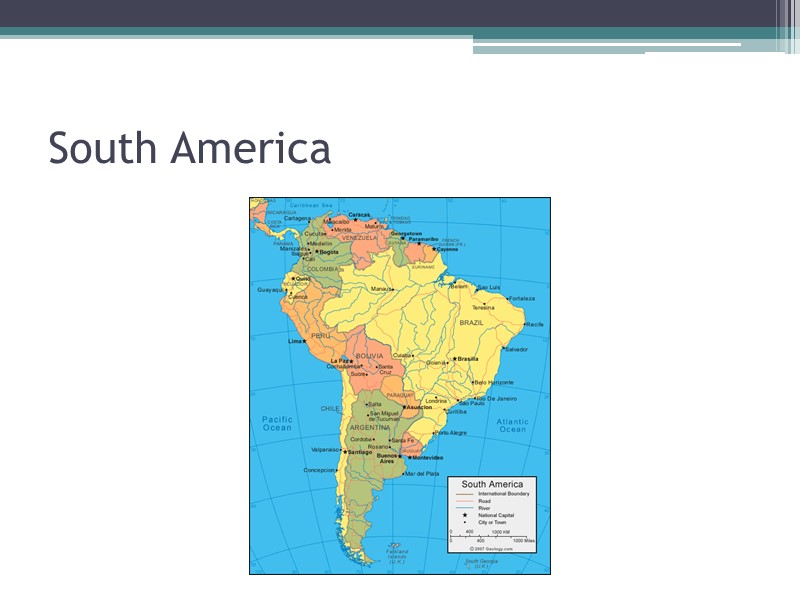
 3 distinct areas of Latin America Middle America Mexico Central America Caribbean a. Bahamas: Bahamas and Turks and Caicos b. Greater Antilles (Cuba, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic) c. Lesser Antilles South America
3 distinct areas of Latin America Middle America Mexico Central America Caribbean a. Bahamas: Bahamas and Turks and Caicos b. Greater Antilles (Cuba, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic) c. Lesser Antilles South America
 Map Activity Place countries found on page 186 to 189 on the attached maps
Map Activity Place countries found on page 186 to 189 on the attached maps
 Caribbean
Caribbean
 Lesser Antilles
Lesser Antilles
 Greater Antilles
Greater Antilles
 South America
South America
 Mountains Run the length from North America to South America Sierra Nevada in Mexico Sierra Madre: Occidental (Pacific Coast) “Western” Sierra Madre: Oriental: (Gulf Coast) “Eastern” Sierra Madre: del Sur: “Of the South” Andes Mountains in South America Formed by colliding tectonic plates (Cocos and Nazca) collide with North and South American Plates: Ring of Fire in the Pacific
Mountains Run the length from North America to South America Sierra Nevada in Mexico Sierra Madre: Occidental (Pacific Coast) “Western” Sierra Madre: Oriental: (Gulf Coast) “Eastern” Sierra Madre: del Sur: “Of the South” Andes Mountains in South America Formed by colliding tectonic plates (Cocos and Nazca) collide with North and South American Plates: Ring of Fire in the Pacific
 Sierra Madre (Occidental)
Sierra Madre (Occidental)
 Mountains as sanctuaries Places of human settlement Escape the heat from lowland climates Rich natural resources (water, volcanic soil, timber and minerals) Isolated peoples from one another Blocked trade and movement
Mountains as sanctuaries Places of human settlement Escape the heat from lowland climates Rich natural resources (water, volcanic soil, timber and minerals) Isolated peoples from one another Blocked trade and movement
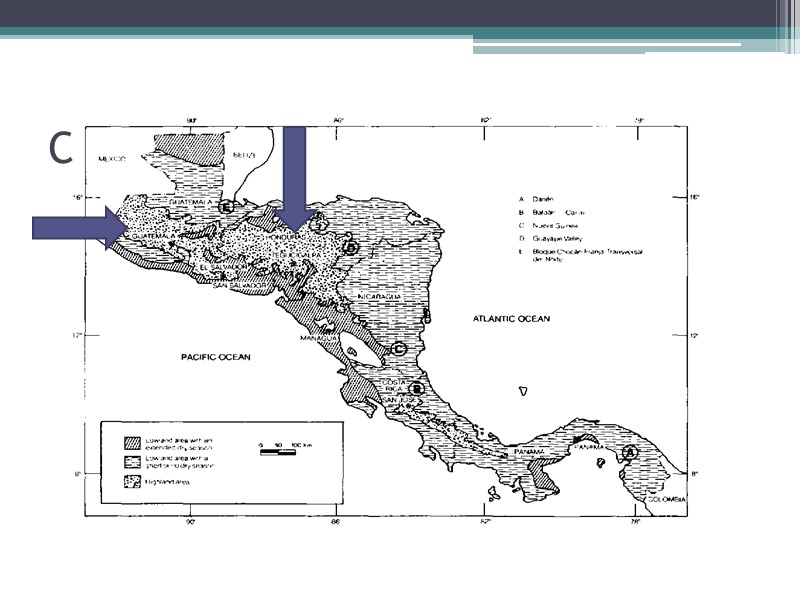
 Additional Areas Mexican Plateau: fertile land area between the Sierra Madres in Mexico Central Highlands: volcanic mountains in Central America
Additional Areas Mexican Plateau: fertile land area between the Sierra Madres in Mexico Central Highlands: volcanic mountains in Central America
 Mexican Plateau
Mexican Plateau
 Central Highlands
Central Highlands
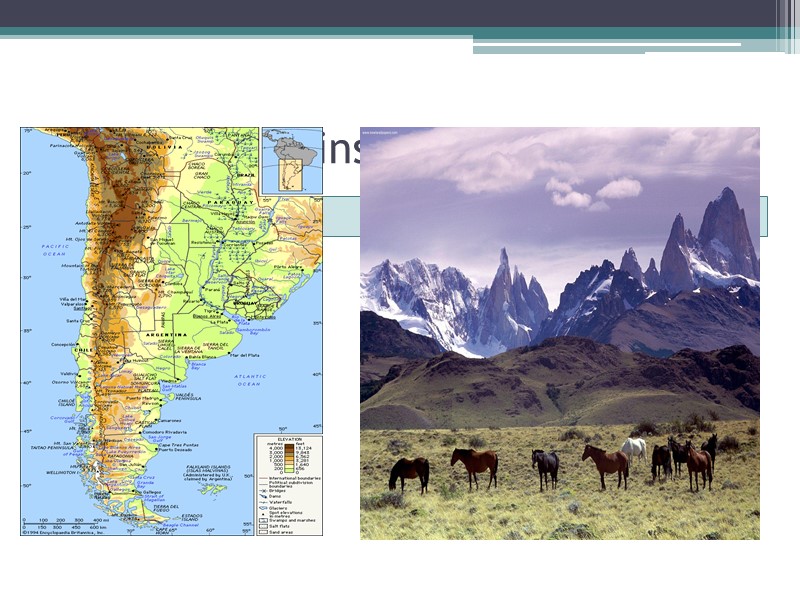
 Andes Mountains Western edge of South America World’s longest mountain chain cordilleras: extensive chain of mountains that run parallel to one another. From the Spanish word cordilla, or cord.
Andes Mountains Western edge of South America World’s longest mountain chain cordilleras: extensive chain of mountains that run parallel to one another. From the Spanish word cordilla, or cord.
 Andes Mountains
Andes Mountains
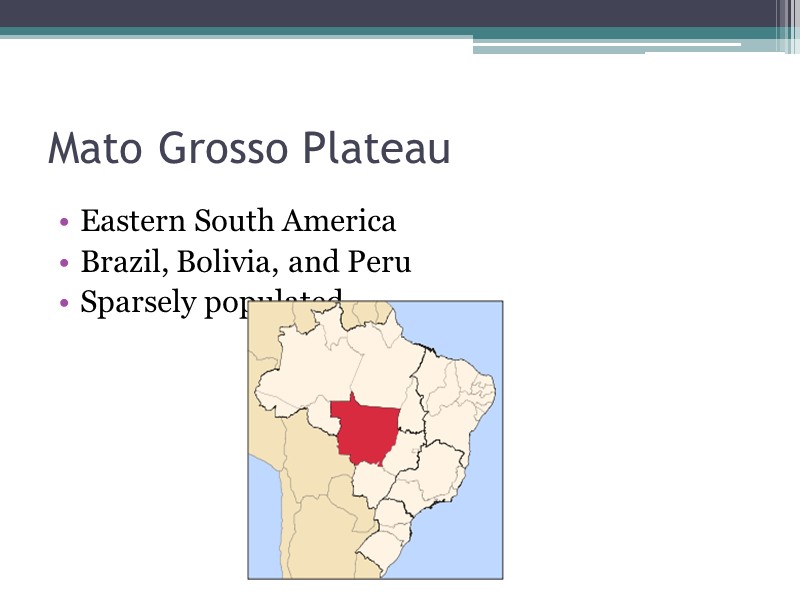
 Mato Grosso Plateau Eastern South America Brazil, Bolivia, and Peru Sparsely populated
Mato Grosso Plateau Eastern South America Brazil, Bolivia, and Peru Sparsely populated
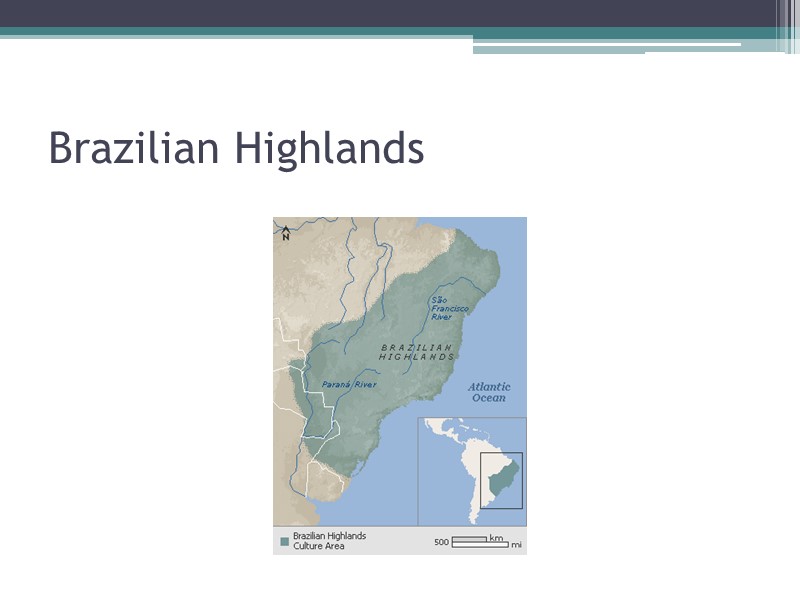
 Brazilian Highlands
Brazilian Highlands
 Brazilian Highlands
Brazilian Highlands
 Lowlands and Coastal Plains Brazil: Atlantic Coast: major area of settlement Vast Grasslands: Ilanos: Columbia Pampas: Argentina and Uruguay Provide grazing area for cattle and produces wheat and corn Llaneros (cowhands) in the Llanos Gauchos: (cowhands) in the Pampas
Lowlands and Coastal Plains Brazil: Atlantic Coast: major area of settlement Vast Grasslands: Ilanos: Columbia Pampas: Argentina and Uruguay Provide grazing area for cattle and produces wheat and corn Llaneros (cowhands) in the Llanos Gauchos: (cowhands) in the Pampas
 Brazilian Coastal Plain
Brazilian Coastal Plain
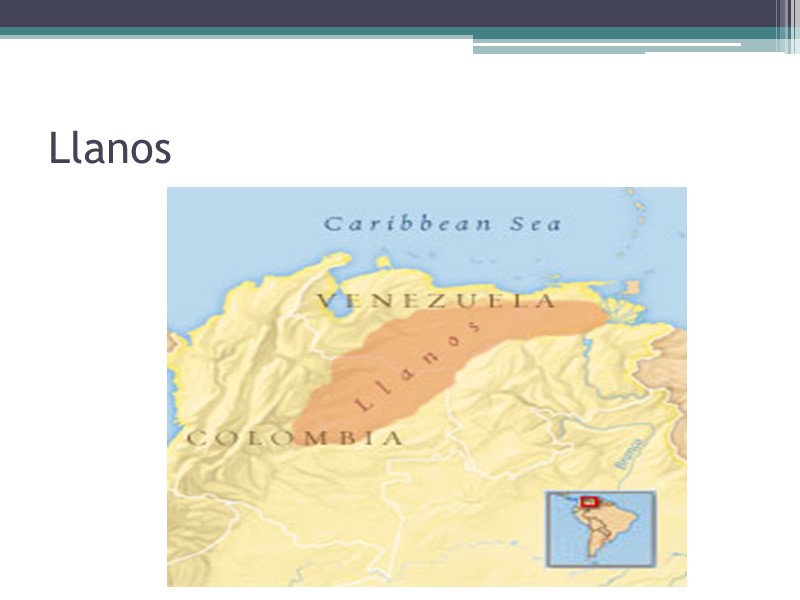
 Llanos
Llanos
 Pampas
Pampas
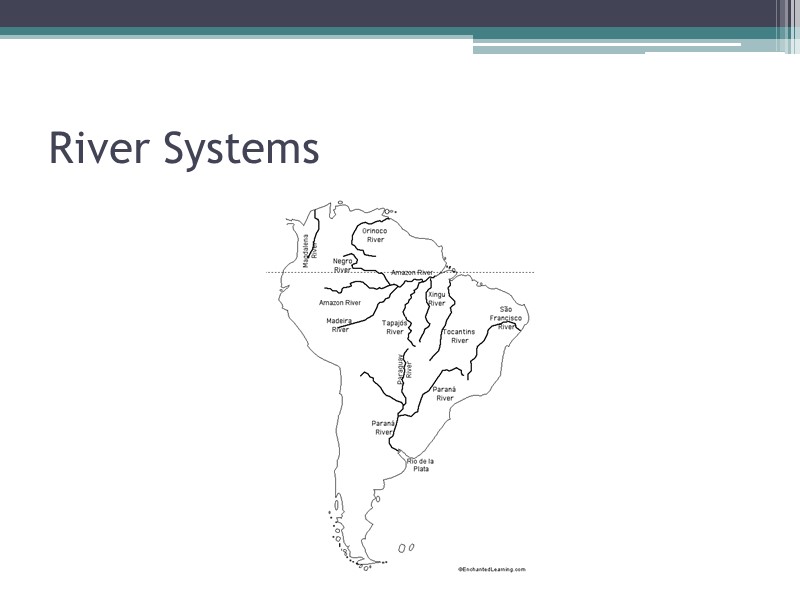
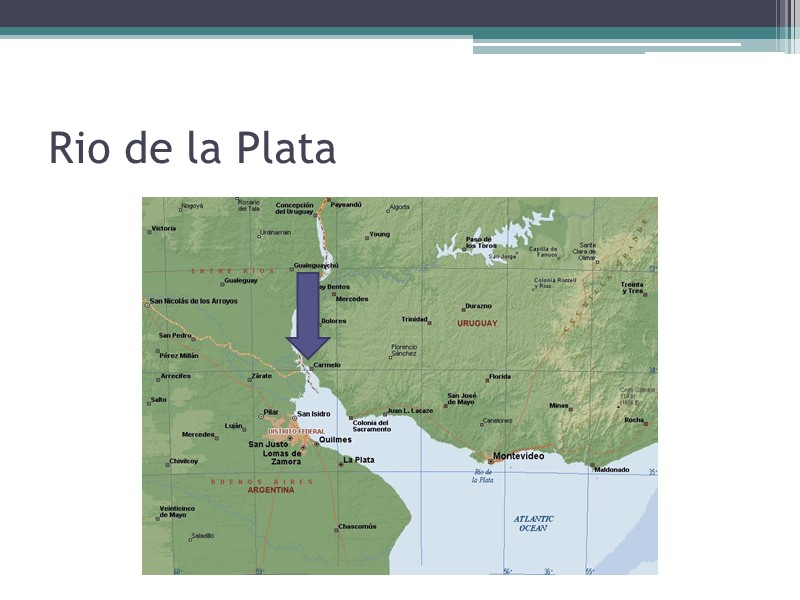
 Water Systems Rivers Rio Grande: borders Mexico and United States Amazon: longest river in Western Hemisphere Parana, Paraguay, and Uruguay Rivers form the second largest river system in Latin America Important sources of hydroelectric power: electricity generated from the energy of water Estuary: an area where the tide meets a river current (Rio de la Plata: river of Silver) Buenos Aires and Montevideo lie along the Rio de la Plata
Water Systems Rivers Rio Grande: borders Mexico and United States Amazon: longest river in Western Hemisphere Parana, Paraguay, and Uruguay Rivers form the second largest river system in Latin America Important sources of hydroelectric power: electricity generated from the energy of water Estuary: an area where the tide meets a river current (Rio de la Plata: river of Silver) Buenos Aires and Montevideo lie along the Rio de la Plata
 River Systems
River Systems
 Rio de la Plata
Rio de la Plata
 Lake Titicaca: World’s highest lake
Lake Titicaca: World’s highest lake
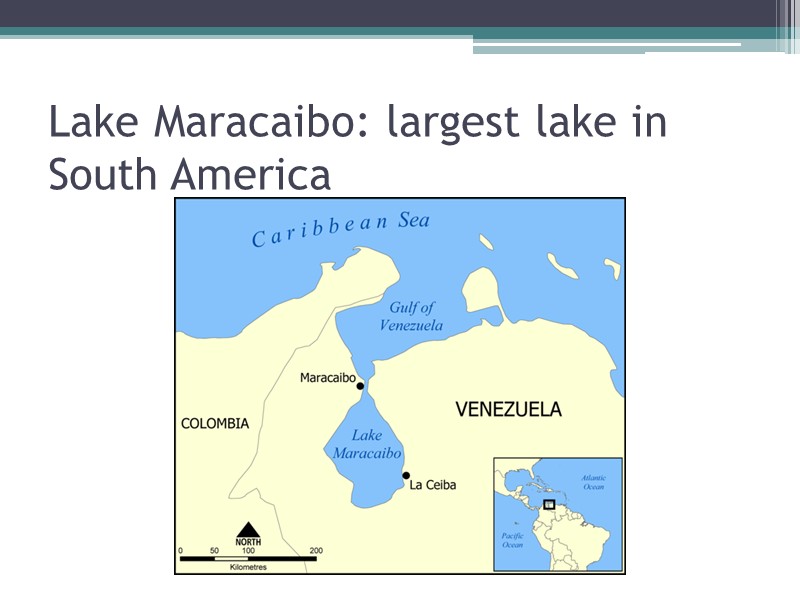
 Lake Maracaibo: largest lake in South America
Lake Maracaibo: largest lake in South America
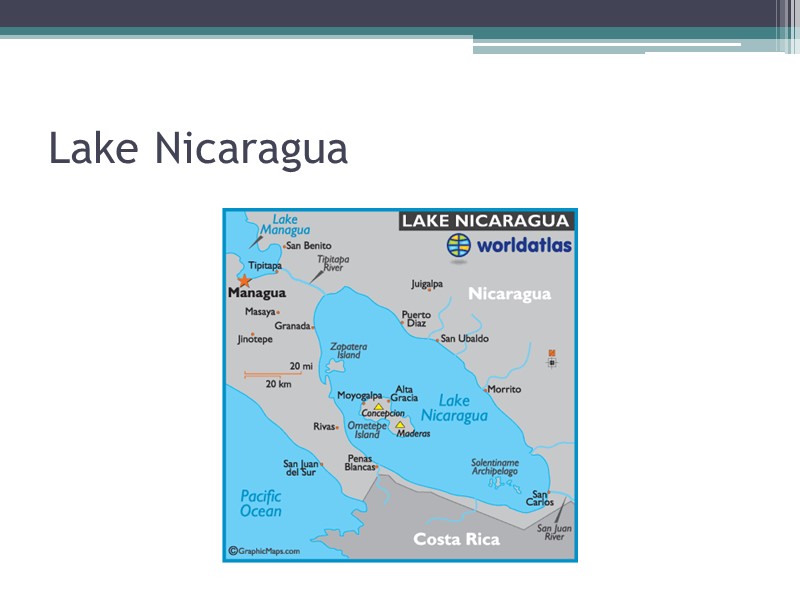
 Lake Nicaragua
Lake Nicaragua
 Natural Resources of Latin America Minerals (gold and silver) Forests Farmland Water Oil Natural gas
Natural Resources of Latin America Minerals (gold and silver) Forests Farmland Water Oil Natural gas
 Climate and Vegetation Rain forests Arid deserts Grassy plains Sandy beaches
Climate and Vegetation Rain forests Arid deserts Grassy plains Sandy beaches
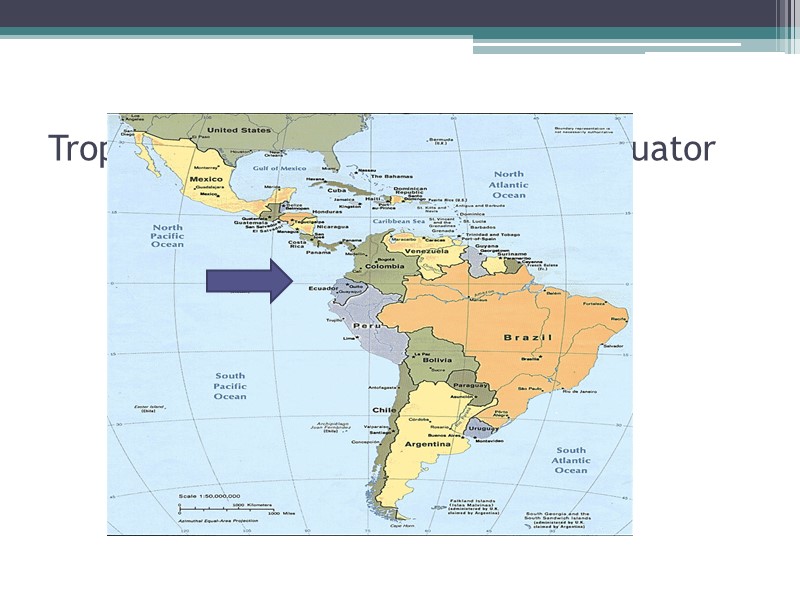
 Tropical Climate: arrow indicates equator
Tropical Climate: arrow indicates equator
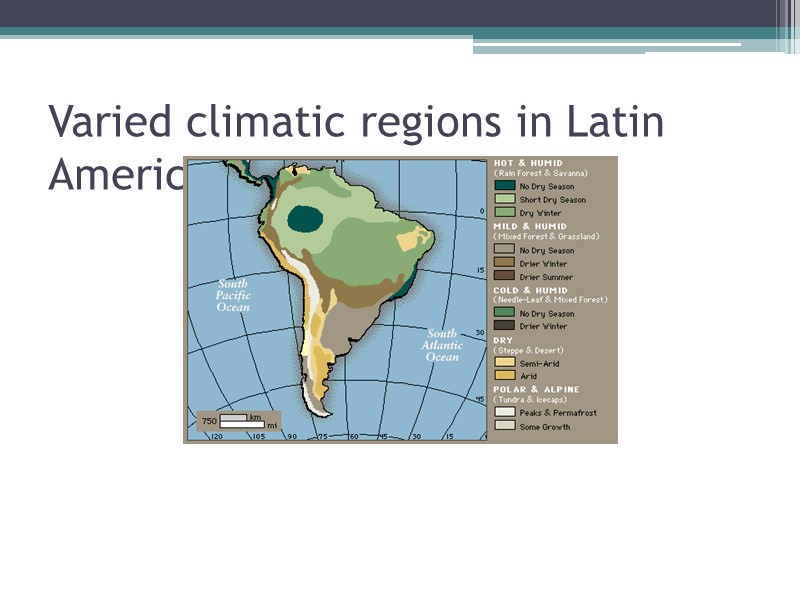
 Varied climatic regions in Latin America
Varied climatic regions in Latin America
 Tropical Region Southern Mexico Eastern Central America Some Caribbean islands Parts of South America Hot Temperatures Abundant rainfall
Tropical Region Southern Mexico Eastern Central America Some Caribbean islands Parts of South America Hot Temperatures Abundant rainfall
 Tropical Rainforest Trees form dense canopies (trees that cover and block out sunlight to the trees below them) Covers 1/3 of South America World’s wettest tropical plain 80-120 inches of rain per year
Tropical Rainforest Trees form dense canopies (trees that cover and block out sunlight to the trees below them) Covers 1/3 of South America World’s wettest tropical plain 80-120 inches of rain per year
 The Rain Forest
The Rain Forest
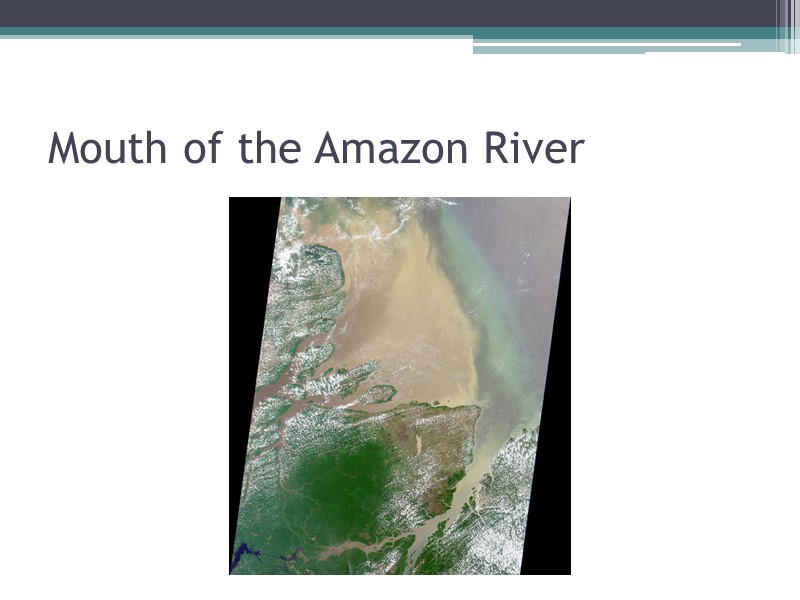
 Mouth of the Amazon River
Mouth of the Amazon River
 Tropical Savannah Coast of southwestern Mexico Most Caribbean islands North-central South America Illanos of Columbia and Venezuela Characteristics Hot temperatures Abundant rainfall Extended dry season
Tropical Savannah Coast of southwestern Mexico Most Caribbean islands North-central South America Illanos of Columbia and Venezuela Characteristics Hot temperatures Abundant rainfall Extended dry season
 Tropical Savannah: Llanos
Tropical Savannah: Llanos
 Humid Subtropics Southeastern South America (Rio de Janeiro to Argentina and Uruguay) Winters (Short and Mild) Summers (Long, hot and humid) Pampas
Humid Subtropics Southeastern South America (Rio de Janeiro to Argentina and Uruguay) Winters (Short and Mild) Summers (Long, hot and humid) Pampas
 Pampas
Pampas
 Gauchos
Gauchos
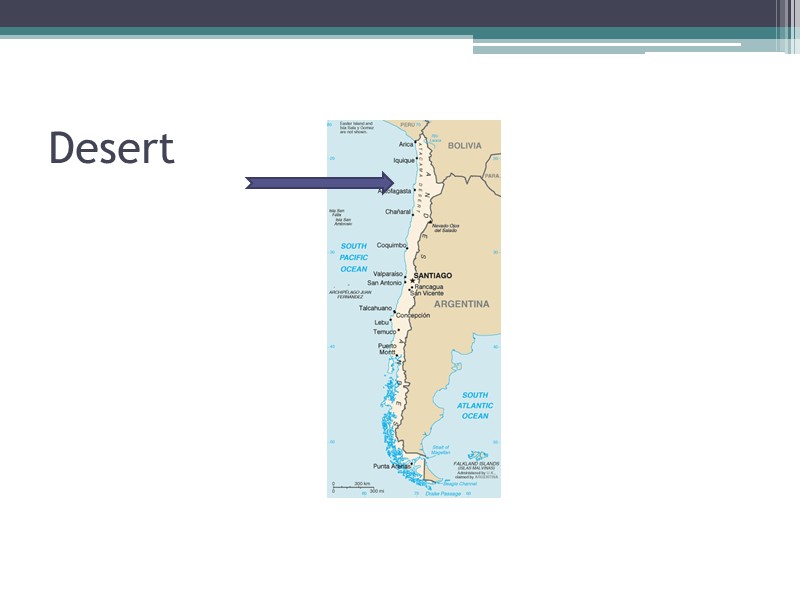
 Desert and Steppe Areas Northern Mexico Coastal Peru and Chile SE Argentina Atacama Desert: no rainfall Steppe: Northern Mexico and NE Brazil and Scentral S. America receive little rainfall. Steppe Climate: hot summers, cool winters, and light rainfall
Desert and Steppe Areas Northern Mexico Coastal Peru and Chile SE Argentina Atacama Desert: no rainfall Steppe: Northern Mexico and NE Brazil and Scentral S. America receive little rainfall. Steppe Climate: hot summers, cool winters, and light rainfall
 Desert
Desert
 Atacama Desert (Chile)
Atacama Desert (Chile)
 Elevation and Climate Vertical climate zones Tierra Caliente: sea level to 2,500 ft 68 degrees to 91 degrees Average rainfall Bananas, sugar, rice, and cacao. Tierra Templada: 2,500 feet to 6,500 feet 60 and 72 degrees Coffee and corn are grown Tierra Fria 6,500 to 10,000 feet Frost is common during winter months Potatoes and barley
Elevation and Climate Vertical climate zones Tierra Caliente: sea level to 2,500 ft 68 degrees to 91 degrees Average rainfall Bananas, sugar, rice, and cacao. Tierra Templada: 2,500 feet to 6,500 feet 60 and 72 degrees Coffee and corn are grown Tierra Fria 6,500 to 10,000 feet Frost is common during winter months Potatoes and barley

