 Laser Cooling & Atom Lasers Seth A. M. Aubin Dept. of Physics College of William and Mary November 13, 2010 Laser. Fest 2010, Small Hall Open House
Laser Cooling & Atom Lasers Seth A. M. Aubin Dept. of Physics College of William and Mary November 13, 2010 Laser. Fest 2010, Small Hall Open House
 Outline Ø What’s special about LASER light? Ø Laser cooling & Ultracold Matter. Ø Atom Lasers
Outline Ø What’s special about LASER light? Ø Laser cooling & Ultracold Matter. Ø Atom Lasers
 What’s special about LASER light?
What’s special about LASER light?
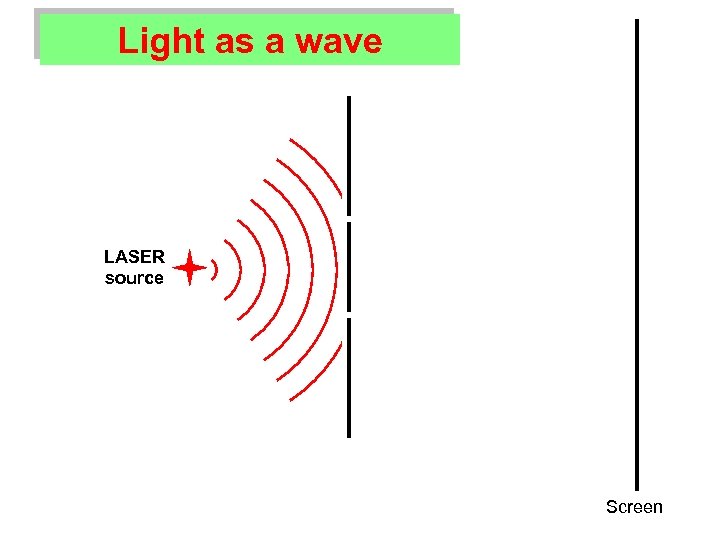
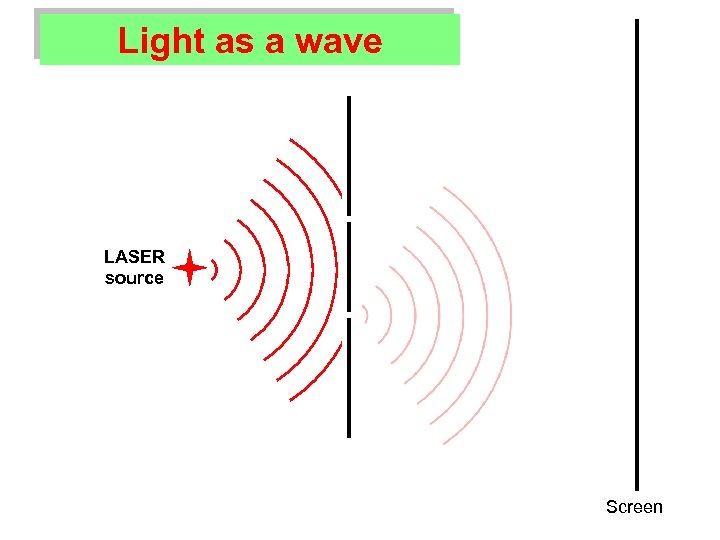
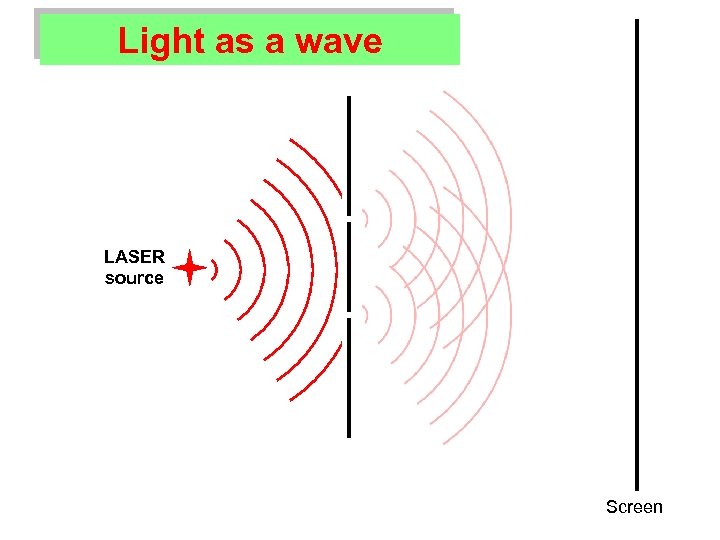
 What’s special about LASER light? Ø Light consists of waves.
What’s special about LASER light? Ø Light consists of waves.
 What’s special about LASER light? Ø Light consists of waves. Ø In a LASER: All the light waves are the same. All the light waves are in sync.
What’s special about LASER light? Ø Light consists of waves. Ø In a LASER: All the light waves are the same. All the light waves are in sync.
 What’s special about LASER light? Ø Light consists of waves. Ø In a LASER: All the light waves are the same. All the light waves are in sync.
What’s special about LASER light? Ø Light consists of waves. Ø In a LASER: All the light waves are the same. All the light waves are in sync.
 Light as a wave LASER source Screen
Light as a wave LASER source Screen
 Light as a wave LASER source Screen
Light as a wave LASER source Screen
 Light as a wave LASER source Screen
Light as a wave LASER source Screen
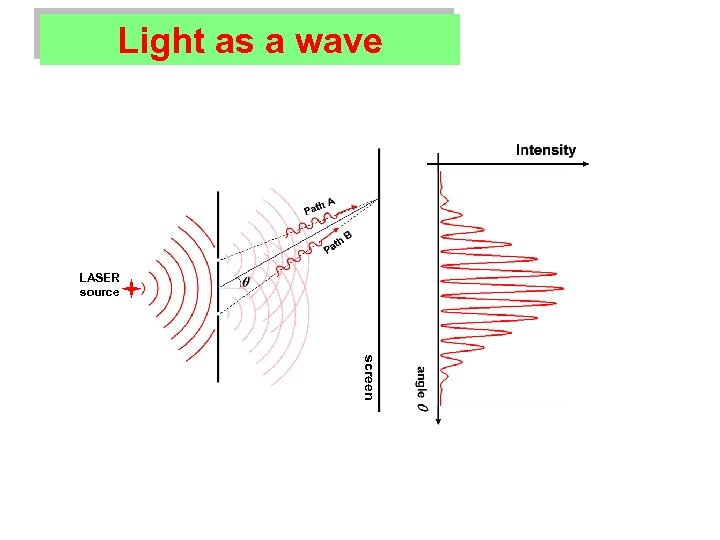 Light as a wave LASER source screen
Light as a wave LASER source screen
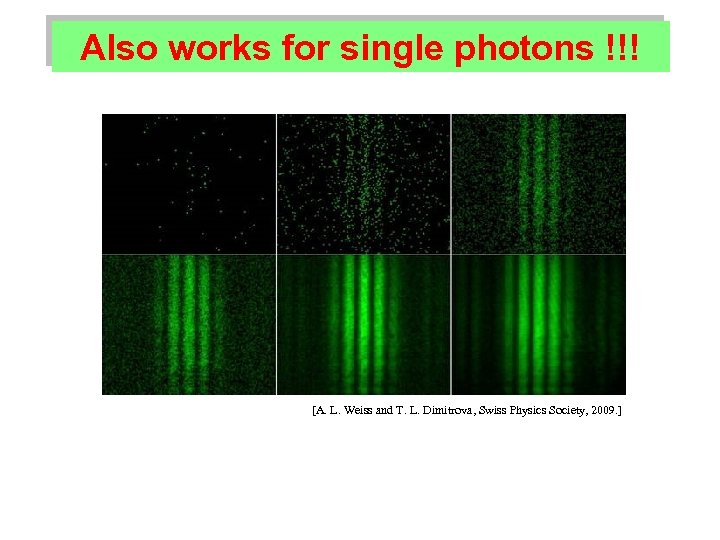 Also works for single photons !!! [A. L. Weiss and T. L. Dimitrova, Swiss Physics Society, 2009. ]
Also works for single photons !!! [A. L. Weiss and T. L. Dimitrova, Swiss Physics Society, 2009. ]
 … Perhaps, Matter is a
… Perhaps, Matter is a
 Laser light is COLD Thermal Physics: COLDER = more order HOTTER = less order
Laser light is COLD Thermal Physics: COLDER = more order HOTTER = less order
 Laser light is COLD Thermal Physics: COLDER = more order HOTTER = less order
Laser light is COLD Thermal Physics: COLDER = more order HOTTER = less order
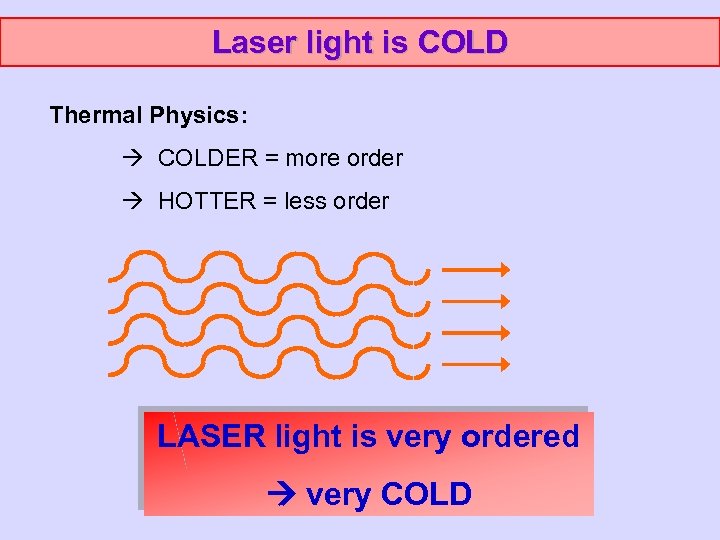 Laser light is COLD Thermal Physics: COLDER = more order HOTTER = less order LASER light is very ordered very COLD
Laser light is COLD Thermal Physics: COLDER = more order HOTTER = less order LASER light is very ordered very COLD
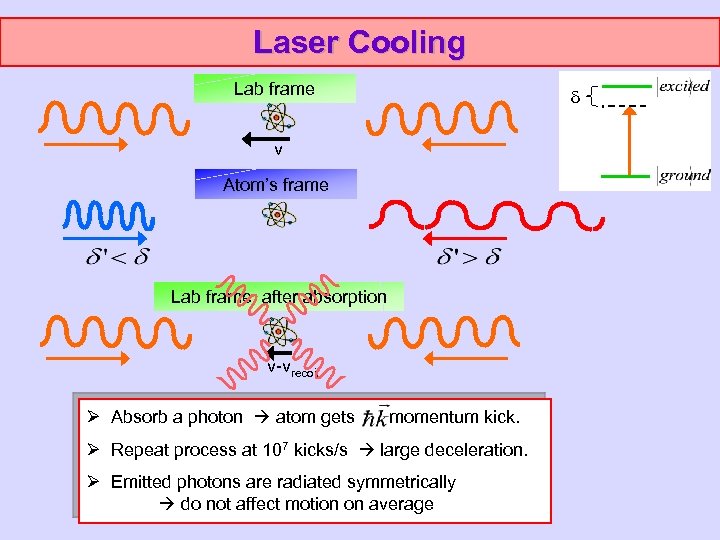 Laser Cooling Lab frame v Atom’s frame Lab frame, after absorption v-vrecoil Ø Absorb a photon atom gets momentum kick. Ø Repeat process at 107 kicks/s large deceleration. Ø Emitted photons are radiated symmetrically do not affect motion on average
Laser Cooling Lab frame v Atom’s frame Lab frame, after absorption v-vrecoil Ø Absorb a photon atom gets momentum kick. Ø Repeat process at 107 kicks/s large deceleration. Ø Emitted photons are radiated symmetrically do not affect motion on average
 Magneto-Optical Trap (MOT)
Magneto-Optical Trap (MOT)
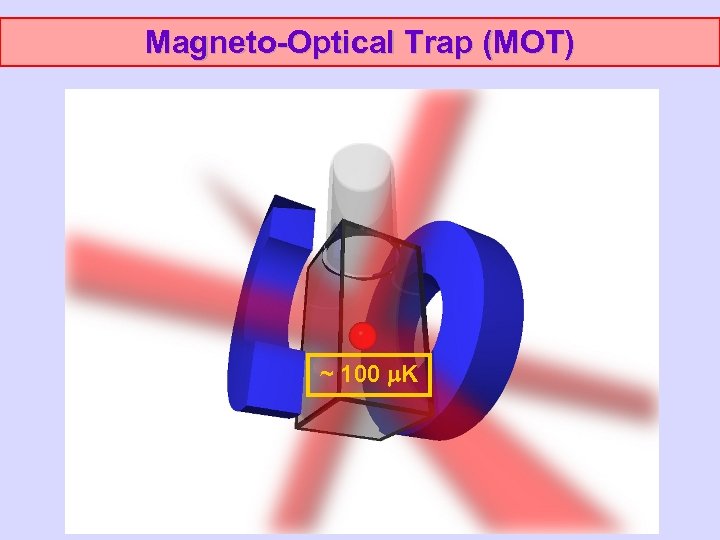 Magneto-Optical Trap (MOT) ~ 100 K
Magneto-Optical Trap (MOT) ~ 100 K
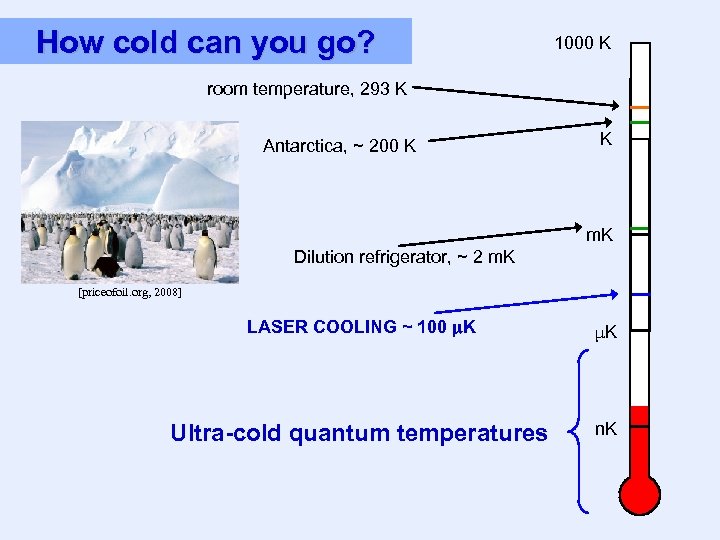 How cold can you go? 1000 K room temperature, 293 K Antarctica, ~ 200 K K m. K Dilution refrigerator, ~ 2 m. K [priceofoil. org, 2008] LASER COOLING ~ 100 K μK Ultra-cold quantum temperatures n. K
How cold can you go? 1000 K room temperature, 293 K Antarctica, ~ 200 K K m. K Dilution refrigerator, ~ 2 m. K [priceofoil. org, 2008] LASER COOLING ~ 100 K μK Ultra-cold quantum temperatures n. K
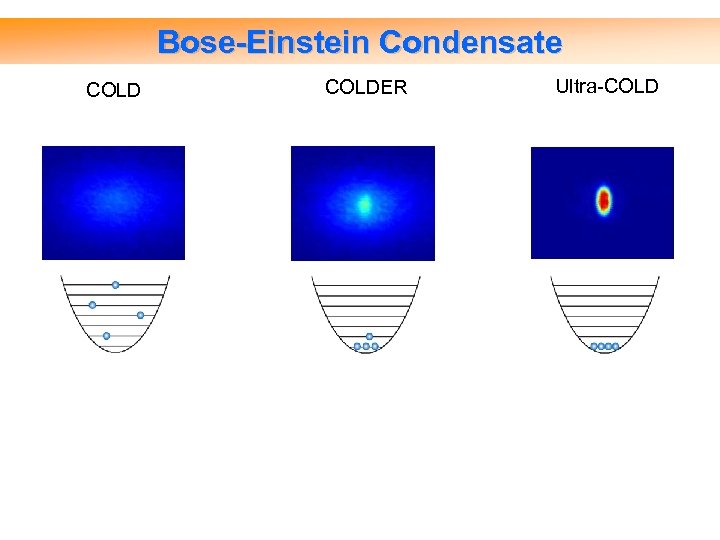 Bose-Einstein Condensate COLDER Ultra-COLD
Bose-Einstein Condensate COLDER Ultra-COLD
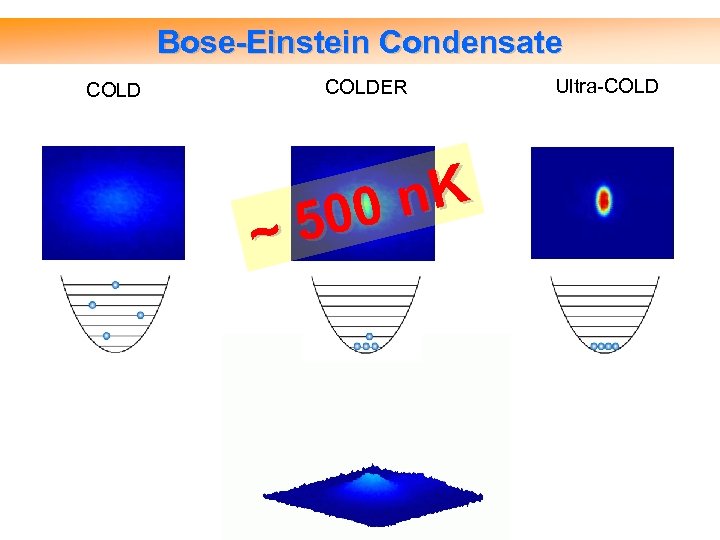 Bose-Einstein Condensate COLDER COLD ~ n. K 00 5 Ultra-COLD
Bose-Einstein Condensate COLDER COLD ~ n. K 00 5 Ultra-COLD
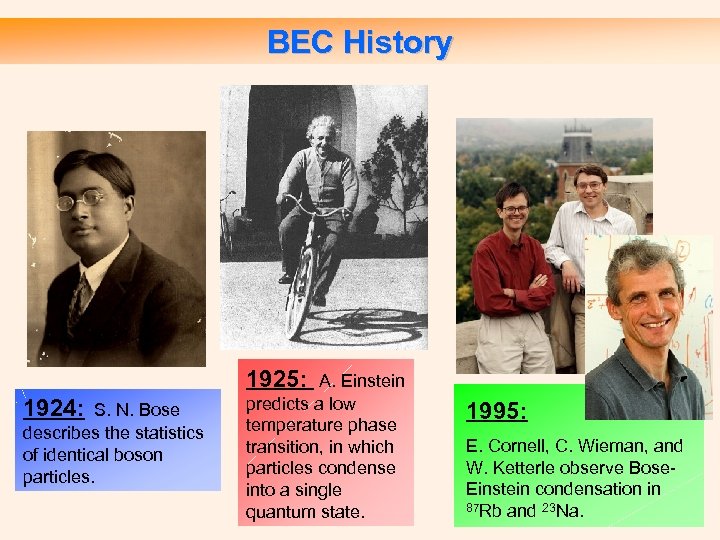 BEC History 1925: 1924: S. N. Bose describes the statistics of identical boson particles. A. Einstein predicts a low temperature phase transition, in which particles condense into a single quantum state. 1995: E. Cornell, C. Wieman, and W. Ketterle observe Bose. Einstein condensation in 87 Rb and 23 Na.
BEC History 1925: 1924: S. N. Bose describes the statistics of identical boson particles. A. Einstein predicts a low temperature phase transition, in which particles condense into a single quantum state. 1995: E. Cornell, C. Wieman, and W. Ketterle observe Bose. Einstein condensation in 87 Rb and 23 Na.
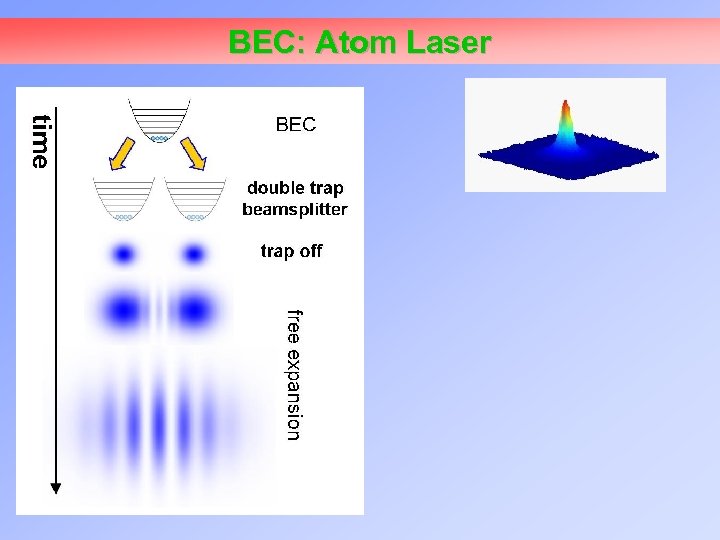 BEC: Atom Laser
BEC: Atom Laser
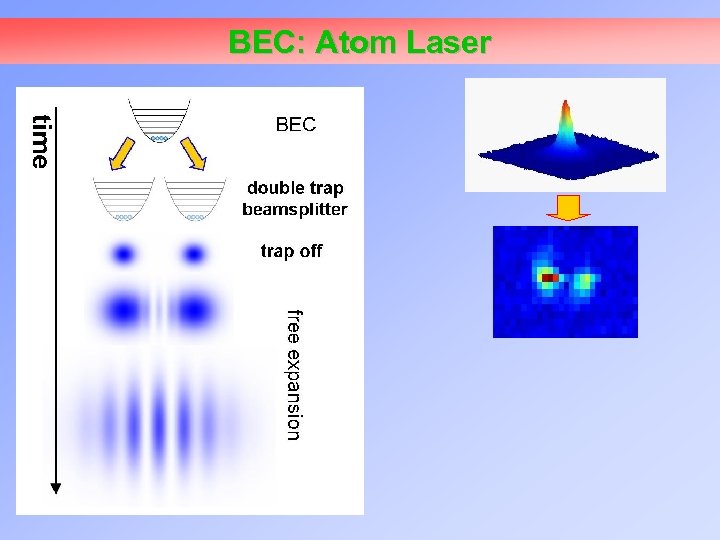 BEC: Atom Laser
BEC: Atom Laser
![BEC: Atom Laser [data from Thywissen group, U. of Toronto] BEC: Atom Laser [data from Thywissen group, U. of Toronto]](https://present5.com/presentation/5b793bba815ee7d66fc0392cf9219043/image-27.jpg) BEC: Atom Laser [data from Thywissen group, U. of Toronto]
BEC: Atom Laser [data from Thywissen group, U. of Toronto]